Weak and strong sustainability
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| Part of a series on |
| Ecological economics |
|---|
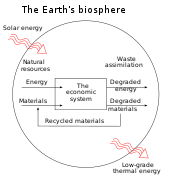 |
Weak and strong sustainability are terms that have emerged from the field of environmental economics and describe opposing approaches to sustainability, specifically in relation to natural resource management and economic development. Weak sustainability argues that natural and human capital are interchangeable, meaning that the use or loss of natural capital can be considered sustainable if the human capital meets or exceeds the value of the natural capital. It assumes that different types of value can be measured and given value in the same way. Strong sustainability argues that natural capital should be maintained or enhanced independently of human-made capital. It considers that certain natural assets are incommensurable and have critical ecological functions that cannot be substituted by human-made alternatives.
For example, according to weak sustainability, replacing a natural forest with a park or agricultural land can be considered sustainable if the recreational or economic value equal the value of the biodiversity lost and further environmental impact caused. According to strong sustainability, cutting down trees in a natural forest and planting new trees elsewhere cannot be considered sustainable, as the value of biodiversity was lost and wider ecological implications cannot truly be measured or offset.
One of the first pieces of work to discuss these ideas was "Blueprint for a Green Economy" by Pearce, Markandya, and Barbier, published in 1989.[1] This work laid the foundations for further discussion on the substitutability of natural capital (e.g., forests, water, and clean air) and human-made capital (e.g., buildings, machinery, and technology), and the implications for long-term ecological and economic health.
Origins and theory
[edit]Capital approach to sustainability and intergenerational equity
[edit]To understand the concept of weak sustainability, it is first necessary to explore the capital approach to sustainability. This is key to the idea of intergenerational equity. This implies that a fair distribution of resources and assets between generations exists. Decision makers, both in theory and practice, need a concept that enables assessment in order to decide if intergenerational equity is achieved. The capital approach lends itself to this task. In this context we must distinguish between the different types of capital. Human capital (e.g. skills, knowledge) and natural capital (e.g. minerals, water) tend to be the most frequently cited examples. Within the concept it is believed that the amount of capital a generation has at its disposal is decisive for its development. A development is then called sustainable when it leaves the capital stock at least unchanged.[2][3]
Sustainable development
[edit]Although related, sustainable development and sustainability are two different concepts. Weak sustainability is an idea based upon the work of Nobel laureate Robert Solow,[4][5][6] and John Hartwick.[7][8][9] which states that 'human capital' can substitute 'natural capital'. The weak sustainability paradigm stems from the 1970s. It began as an extension of the neoclassical theory of economic growth, accounting for non-renewable natural resources as a factor of production.[4][7] However, it only really came into the mainstream in the 1990s as the idea received more political attention as sustainable development discussions evolved in the late 1980s and early 1990s. A key landmark was the Rio Summit in 1992 where the vast majority of nation-states committed themselves to sustainable development. This commitment was demonstrated by the signing of Agenda 21, a global action plan on sustainable development. At its inception, sustainability was interpreted as a requirement to preserve, intact, the environment as we find it today in all its forms. The Brundtland Report, for example, stated that ‘The loss of plant and animal species can greatly limit the options of future generations. The result is that sustainable development requires the conservation of plant and animal species’.
Development of theory
[edit]Wilfred Beckerman[10] posits that the absolutist concept of sustainable development given above is morally repugnant. The largest part of the world's population live in acute poverty. Taking that as well as the acute degradation into account, one could justify using up vast resources in an attempt to preserve certain species from extinction. These species providing no real benefit for society other than a possible value for the knowledge of their continued existence. He argues that such a task would involve using resources that could have instead been devoted to more pressing world concerns. Examples include increasing access to clean drinking water or sanitation in the Third World.
Many environmentalists shifted their attention to the idea of ‘weak’ sustainability.[10] This allows for some natural resources to decrease as long as sufficient compensation is provided by increases in other resources. The result usually was an increase in human capital. This compensation is in the form of sustained human welfare. This is illustrated in a well-regarded definition by David Pearce,[11] the author of numerous works on sustainability. He defines sustainability as implying something about maintaining the level of human welfare (or well-being) so that it may improve, but never declines (or, not more than temporarily). This implies sustainable development will not decrease over time.
Inter-generational equity assumes each following generation has at least as much capital at its disposal as the preceding generation. The idea of leaving capital stock at least unchanged is widely accepted. The question arises, whether or not one form of capital may be substituted by another.[12] This is the focus of the debate between ‘weak’ and ‘strong’ sustainability, and how intergenerational equity is to be achieved.
Strong sustainability argument
[edit]Strong sustainability does not share the notion of inter-changeability; it assumes that economic and environmental capital are complementary but not interchangeable. Since the nineties, there has been an ardent debate on the substitutability between natural and human-made capital. While "Weak Sustainability" supporters mainly believe that these are substitutable, "Strong Sustainability" followers generally contest the possibility of inter-changeability.[13] Strong sustainability accepts there are certain functions that the environment performs that cannot be duplicated by humans or human made capital. The ozone layer is one example of an ecosystem service that is crucial for human existence, forms part of natural capital, but is difficult for humans to duplicate.[14]
Unlike weak sustainability, strong sustainability puts the emphasis on ecological scale over economic gains. This implies that nature has a right to exist and that it has been borrowed and should be passed on from one generation to the next still intact in its original form.
One version of strong sustainability is in defining and respecting hard boundaries and limits in relation to planetary boundaries. This attempts to give incommensurable value to certain environmental changes or actions.[15][16][17]
Weak sustainability in practice
[edit]Weak sustainability has been defined using concepts like human capital and natural capital.[18] Human (or produced) capital incorporates resources such as infrastructure, labour and knowledge. Natural capital covers the stock of environmental assets such as fossil fuels, biodiversity and other ecosystem structures and functions relevant for ecosystem services. In very weak sustainability, the overall stock of man-made capital and natural capital remains constant over time. It is important to note that, unconditional substitution between the various kinds of capital is allowed within weak sustainability. This means that natural resources may decline as long as human capital is increased. Examples include the degradation of the ozone layer, tropical forests and coral reefs if accompanied by benefits to human capital. An example of the benefit to human capital could include increased financial profits.[19] If capital is left constant over time intergenerational equity, and thus Sustainable Development, is achieved.[12] An example of weak sustainability could be mining coal and using it for production of electricity. The natural resource coal, is replaced by a manufactured good which is electricity. The electricity is then in turn used to improve domestic life quality (e.g. cooking, lighting, heating, refrigeration and operating boreholes to supply water in some villages) and for industrial purposes (growing the economy by producing other resources using machines that are electricity operated.)
Case studies of weak sustainability in practice have had both positive and negative results. The concept of weak sustainability still attracts a lot of criticism. Some even suggest that the concept of sustainability is redundant. Other approaches are advocated, including ‘social bequests’, which focus the attention away from neoclassical theory altogether.
A prime example of a weak sustainability is the Government Pension Fund of Norway. Statoil ASA, a state-owned Norwegian oil company invested its surplus profits from petroleum into a pension portfolio to date worth over $1 trillion. The oil, a type of natural capital, was exported in vast quantities by Norway. The resultant fund allows for long-lasting income for the population in exchange for a finite resource, actually increasing the total capital available for Norway above the original levels. This example shows how weak sustainability and substitution can be cleverly applied on a national scale, although it is recognised that its applications are very restricted on a global scale. In this application, Hartwick's rule would state that the pension fund was sufficient capital to offset the depletion of the oil resources.
A less positive case is that of the small Pacific nation of Nauru. A substantial phosphate deposit was found on the island in 1900, and now approximately 80% of the island has been rendered uninhabitable after over 100 years of mining.[20] Concurrent with this extraction, Nauru's inhabitants, over the last few decades of the twentieth century, have enjoyed a high per capita income. Money from the mining of phosphate enabled the establishment of a trust fund, which was estimated to be as much as $1 billion. However, chiefly as a result of the Asian financial crisis, the trust fund was almost entirely wiped out. This ‘development’ of Nauru followed the logic of weak sustainability, and almost led to complete environmental destruction.[21] This case presents a telling argument against weak sustainability, suggesting that a substitution of natural for man-made capital may not be reversible in the long-term.
Role of governance and policy recommendations
[edit]The implementation of weak sustainability in governance can be viewed theoretically and practically through Hartwick's rule.[7] In resource economics, Hartwick's rule defines the amount of investment in human capital that is needed to offset declining stocks of non-renewable resources. Solow[4] showed that, given a degree of substitutability between human capital and natural capital, one way to design a sustainable consumption program for an economy is to accumulate man-made capital. When this accumulation is sufficiently rapid the effect from the shrinking exhaustible resource stock is countered by the services from the increased human capital stock. Hartwick's rule, is often referred to as "invest resource rents", where ‘rent’ is payment to a factor of production (in this case capital) in excess of that needed to keep it in its present use. This requires that a nation invest all rent earned from exhaustible resources currently extracted.
Later, Pearce and Atkinson[22] and Hamilton[23] added to Hartwick's rule, by setting out a theoretical and empirical measure of net investment in human and natural capital (and later human capital) that became known as genuine savings. Genuine savings measures net changes in produced, natural and human capital stocks, valued in monetary terms.
The aim of governance therefore should be to keep genuine savings above or equal to zero. In this sense it is similar to green accounting, which attempts to factor environmental costs into the financial results of operations. A key example of this is the World Bank, who now regularly publishes a comparative and comprehensive set of genuine savings estimates for over 150 countries which is called ‘adjusted savings’.[24]
Criticisms of the strong vs. weak sustainability model
[edit]Martinez-Allier's address[25] concerns over the implications of measuring weak sustainability, after results of work conducted by Pearce & Atkinson in the early 1990s.[22] By their measure, most of the Northern, industrialised countries are deemed sustainable, as is the world economy as a whole. This point of view can be considered to be flawed since the world would (arguably) not be sustainable if all countries have the resource intensity rate and pollution rate of many industrialised countries. Industrialization does not necessarily equate to sustainability.
According to Pearce and Atkinson's calculations, the Japanese economy is one of the most sustainable economies in the world. The reason for this is that its saving rate is so high. This trend still remains today and therefore exceeds depreciation on both natural and man-made capital. Thus, they suggest that it is the gross negligence of factors other than savings in measuring sustainability that makes weak sustainability an inappropriate concept.
The integrative sustainability model has the economy completely located within society and society completely located within the environment. In other words, the economy is a subset of society and society is completely dependent upon the environment. This interdependence means that any sustainability-related issue must be considered holistically.

Other inadequacies of the paradigm include the difficulties in measuring savings rates and the inherent problems in quantifying the many different attributes and functions of the biophysical world in monetary terms.[27] By including all human and biophysical resources under the same heading of ‘capital’, the depleting of fossil fuels, reduction of biodiversity and so forth, are potentially compatible with sustainability. As Gowdy & O'Hara[28] so aptly put it, "As long as the criterion of weak sustainability is met, with savings outstripping capital depletion, there is no conflict between the destruction of species and ecosystems or the depletion of fossil fuels, and the goal of sustainability."
Opposing weak sustainability, strong sustainability supporters contend that we need "a more small-scale decentralized way of life based upon greater self-reliance, so as to create a social and economic system less destructive towards nature." Strong sustainability does not make allowances for the substitution of human, and human made capital for Earth's land, water, and their biodiversity. The products created by mankind cannot replace the natural capital found in ecosystems.[29]
Another critical weakness of the concept is related to environmental resilience. According to Van Den Bergh,[30] resilience can be considered as a global, structural stability concept, based on the idea that multiple, locally stable ecosystems can exist. Sustainability can thus be directly related to resilience. With this in mind, weak sustainability can cause extreme sensitivity to either natural disturbances (such as diseases in agriculture with little crop diversity) or economic disturbances (as outlined in the case study of Nauru above). This high level of sensitivity within regional systems in the face of external factors brings to attention an important inadequacy of weak sustainability.[30]
Rejection of both weak and strong models
[edit]Some critics dismiss the entire concept of sustainability. Beckerman's influential work concludes that weak sustainability is “redundant and illogical”.[10] He holds that sustainability only makes sense in its 'strong' form, but that "requires subscribing to a morally repugnant and totally impracticable objective."[10] He also says that he regrets that so much time has been wasted on the entire concept of sustainable development.
Others[who?] have suggested that a better approach to sustainability would be that of social bequests.[clarification needed] This approach is intended to "free us from a 'zero-sum' game in which our gain is an automatic loss for future generations".[31] The social bequest approach reframes the problem to focus on what we leave to future generations rather than how much; the argument is that when the problem is phrased as ‘how much,' this implies that some amount of a resource should be used, and some amount should be left.[clarification needed] Daniel Bromley[31] uses the example of rainforests to illustrate his argument: If we decide to use 25% of a rainforest and leave the rest, but then the next time we make a decision we start all over again and use 25% of what's left, and so on, eventually there will be no rainforest left. By focusing on bequests of specific rights and opportunities for future generations, we can remove ourselves from the "straightjacket of substitution and marginal tradeoffs of neoclassical theory".[21]
References
[edit]- ^ Pearce, David W.; Markandya, Anil; Barbier, Edward (1989). Blueprint for a green economy. Great Britain. London: Earthscan. ISBN 978-1-85383-066-2.
- ^ Pearce, D.W.; Barbier, E.B.; Markandya, A. (1990). sustainable development: economics and environment in the third world. Hants: Edward Elgar.
- ^ Stern, D.I. (1997). "the capital theory approach to sustainability: a critical appraisal" (PDF). Journal of Economic Issues. 31 (1): 145–73. doi:10.1080/00213624.1997.11505895.
- ^ a b c Solow, R.M. (1974). "Intergenerational equity and exhaustible resources". Review of Economic Studies. 41: 29–46. doi:10.2307/2296370. hdl:1721.1/63764. JSTOR 2296370.
- ^ Solow, R.M. (1986). "On the intergenerational allocation of natural resources". Scandinavian Journal of Economics. 88 (1): 141–9. doi:10.2307/3440280. JSTOR 3440280.
- ^ Solow, R.M. (1993). "An almost practical step towards sustainability". Resources Policy. 16 (3): 162–72. Bibcode:1993RePol..19..162S. doi:10.1016/0301-4207(93)90001-4.
- ^ a b c Hartwick, J.M. (1977). "Intergenerational equity and the investing of rents from exhaustible resources". The American Economic Review. 67 (5): 972–4.
- ^ Hartwick, J.M. (1978a). "Investing returns from depleting renewable resource stocks and intergenerational equity". Economics Letters. 1 (1): 85–8. doi:10.1016/0165-1765(78)90102-7.
- ^ Hartwick, J.M. (1978b). "Substitution among exhaustible resources and intergenerational equity". The Review of Economic Studies. 45 (2): 347–54. doi:10.2307/2297349. JSTOR 2297349.
- ^ a b c d Beckerman, Wilfred (1994). "Sustainable development: is it a useful concept?". Environmental Values. 3 (3): 191–209. doi:10.3197/096327194776679700.
- ^ David Pearce, ed. (1992). Macmillan Dictionary of Modern Economics (4th ed.). London: Macmillan.
- ^ a b Figge, F. (2005). "Capital Substitutability and Weak Sustainability Revisited: The Conditions for Capital Substitution in the Presence of Risk". Environmental Values. 14 (2): 185–201. doi:10.3197/0963271054084966.
- ^ "Division of Bioeconomics - KU Leuven".
- ^ "Sustainability continued". Archived from the original on August 26, 2012. Retrieved May 20, 2013.
- ^ Steffen, Will; Richardson, Katherine; Rockström, Johan; Cornell, Sarah E.; Fetzer, Ingo; Bennett, Elena M.; Biggs, Reinette; Carpenter, Stephen R.; de Vries, Wim; de Wit, Cynthia A.; Folke, Carl; Gerten, Dieter; Heinke, Jens; Mace, Georgina M.; Persson, Linn M. (2015-02-13). "Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet". Science. 347 (6223). doi:10.1126/science.1259855. hdl:1885/13126. ISSN 0036-8075.
- ^ Rockström, Johan; Steffen, Will; Noone, Kevin; Persson, Åsa; Chapin, F. Stuart III; Lambin, Eric; Lenton, Timothy M.; Scheffer, Marten; Folke, Carl; Schellnhuber, Hans Joachim; Nykvist, Björn; de Wit, Cynthia A.; Hughes, Terry; van der Leeuw, Sander; Rodhe, Henning (2009). "Planetary Boundaries: Exploring the Safe Operating Space for Humanity". Ecology and Society. 14 (2). doi:10.5751/ES-03180-140232. hdl:10535/5421. ISSN 1708-3087.
- ^ Ross, Florian (2019-12-15). "Kate Raworth - Doughnut Economics: Seven Ways to Think Like a 21st Century Economist (2017)" (PDF). Regional and Business Studies. 11 (2). doi:10.33568/rbs.2409. ISSN 2061-2311.
- ^ Cabeza-Gutes, M. (1996). "The concept of weak sustainability". Ecological Economics. 17 (3): 147–56. doi:10.1016/s0921-8009(96)80003-6.
- ^ Cart, N. (2001). The Politics of the Environment. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Gowdy, J.M.; McDaniel, C. (1999). "The physical destruction of Nauru: An example of weak sustainability". Land Economics. 75 (2): 33–8. doi:10.2307/3147015. JSTOR 3147015.
- ^ a b Ayres, R.; Van den Bergh, J.; Gowdy, J. (1998). "Viewpoint: weak versus strong sustainability" (PDF). tinbergen.nl.
- ^ a b Pearce, D.W.; Atkinson, G.D. (1993). "Capital theory and the measurement of sustainable development: an indicator of weak sustainability". Ecological Economics. 8 (2): 103–108. doi:10.1016/0921-8009(93)90039-9.
- ^ Hamilton, K (1994). "Green adjustments to GDP". Resources Policy. 20 (3): 125–68. Bibcode:1994RePol..20..155H. doi:10.1016/0301-4207(94)90048-5.
- ^ Dietz, S. & Neumayer, E. Economics and the governance of sustainable development. In Governing sustainability. by Adger, N & Jordan, A. 2009. Cambridge: Cambridge university press.
- ^ Martinez-Alier, J. (1995). "The environment as a luxury or "too poor to be green"?". Ecological Economics. 13: 1–10. doi:10.1016/0921-8009(94)00062-z.
- ^ Scott Cato, M. (2009). Green Economics. London: Earthscan, pp. 36–37. ISBN 978-1-84407-571-3.
- ^ Vatn, A. & Bromley, D. (1994). "Choices without prices without apologies". Journal of Environmental Economics and Management. 26 (2): 125–48. doi:10.1006/jeem.1994.1008.
- ^ Gowdy, J.; O' Hara, S. (1997). "Weak sustainability and viable technologies". Ecological Economics. 22 (3): 239–47. doi:10.1016/s0921-8009(97)00093-1.
- ^ "2ndgreenrevolution".
- ^ a b Van den Bergh, J. (2007). Handbook of Sustainable Development (Atkinson, G., Dietz, S. & Neumayer, E.). Cheltenham: Edward Elgar.
- ^ a b Bromley, D. (1998). "Searching for sustainability: the poverty of spontaneous order". Ecological Economics. 24 (2–3): 231–40. doi:10.1016/s0921-8009(97)00145-6.
Further reading
[edit]Ecological economists writing on the topic of sustainable development:
- Daly, H.E. 1991. Steady state economics (2nd edition). Washington D.C. Island press.
- Daly, Herman E.; Cobb, John B.; Cobb, Clifford W. (1989). For the common good: redirecting the economy toward community, the environment, and a sustainable future. Boston: Beacon Press. ISBN 9780807047026.
Different ways of defining sustainable development:
- Pezzy, J. (1992). "Sustainable development concepts:an economic analysis / World Bank environment paper 2" (PDF). World bank.
- Pezzy, J. (1992). "Sustainability: an interdisciplinary guide" (PDF). Environmental Values. 1 (4): 321–62. doi:10.3197/096327192776680034.
Informative work on the concept of strong sustainability:
- Costanza, R., Norton, B. & Haskell, B.J.1992. Ecosystem health: new goals for environmental management. Washington D.C. : Island press.
- Common, Mick; Perrings, Charles (July 1992). "Towards an ecological economics of sustainability". Ecological Economics. 6 (1): 7–34. doi:10.1016/0921-8009(92)90036-R.
- Turner, R.K. 1992. Speculations on strong and weak sustainability. CSERGE working paper GEC. 92-26.
