Waste management: Difference between revisions
Carchuleta (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Carchuleta (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[Image:Bin.JPG|right|thumb|A blue wheelie bin in [[Berkshire]], [[England]]]] |
[[Image:Bin.JPG|right|thumb|A blue wheelie bin in [[Berkshire]], [[England]]]] |
||
[[File:Kathmandu-Müllabfuhr.jpg|thumb|Waste management in Kathmandu (Nepal)]] |
[[File:Kathmandu-Müllabfuhr.jpg|thumb|Waste management in Kathmandu (Nepal)]] |
||
'''Waste management''' is the [[waste collection|collection]], [[transport]], [[waste treatment|processing]], [[recycling]] or disposal, and monitoring of [[waste]] materials.<ref name = "Waste Management FAQ">{{cite |
'''Waste management''' is the [[waste collection|collection]], [[transport]], [[waste treatment|processing]], [[recycling]] or disposal, and monitoring of [[waste]] materials.<ref name = "Waste Management FAQ">{{cite. '''If you see this is a trash can that has litter.'''web|url=http://www.wanless.com.au/what_is_waste_management.html |title=What is Waste Management?|date=2009}}</ref> The term usually relates to materials produced by human activity, and is generally undertaken to reduce their effect on [[health]], the [[Environment (biophysical)|environment]] or [[aesthetics]]. Waste management is also carried out to recover [[natural resource|resources]] from it. Waste management can involve [[solid]], [[liquid]], [[gas]]eous or [[radioactive]] substances, with different methods and fields of expertise for each. |
||
Waste management practices differ for [[developed nation|developed]] and [[developing nation]]s, for [[urban area|urban]] and [[rural area]]s, and for [[residential area|residential]] and [[industry|industrial]] producers. Management for non-[[hazardous]] residential and institutional waste in metropolitan areas is usually the responsibility of [[local government]] authorities, while management for non-hazardous commercial and industrial waste is usually the responsibility of the generator. |
Waste management practices differ for [[developed nation|developed]] and [[developing nation]]s, for [[urban area|urban]] and [[rural area]]s, and for [[residential area|residential]] and [[industry|industrial]] producers. Management for non-[[hazardous]] residential and institutional waste in metropolitan areas is usually the responsibility of [[local government]] authorities, while management for non-hazardous commercial and industrial waste is usually the responsibility of the generator. |
||
Revision as of 16:42, 25 February 2010
Look at all the pictures of litter. This tells you all about litter and how much litter is in the United States. Lets read and see.


Waste management is the collection, transport, processing, recycling or disposal, and monitoring of waste materials.[1] The term usually relates to materials produced by human activity, and is generally undertaken to reduce their effect on health, the environment or aesthetics. Waste management is also carried out to recover resources from it. Waste management can involve solid, liquid, gaseous or radioactive substances, with different methods and fields of expertise for each.
Waste management practices differ for developed and developing nations, for urban and rural areas, and for residential and industrial producers. Management for non-hazardous residential and institutional waste in metropolitan areas is usually the responsibility of local government authorities, while management for non-hazardous commercial and industrial waste is usually the responsibility of the generator.
Methods
Methods of disposal
Plasma Gasification
Plasma is a highly ionized or electrically charged gas. An example in nature is lightning, capable of producing temperatures exceeding 12,600 °F (6,980 °C). A gasifier vessel utilizes proprietary plasma torches operating at +10,000 °F (5,540 °C) (the surface temperature of the Sun) in order to create a gasification zone of up to 3,000 °F (1,650 °C) to convert solid or liquid wastes into a syngas. When municipal solid waste is subjected to this intense heat within the vessel, the waste’s molecular bonds break down into elemental components. The process results in elemental destruction of waste and hazardous materials.[2]
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, the U.S. generated 250 million tons of waste in 2008 alone, and this number continues to rise. About 54% of this trash (135,000,000 short tons (122,000,000 t)) ends up in landfills and is consuming land at a rate of nearly 3,500 acres (1,400 ha) per year. In fact, landfilling is currently the number one method of waste disposal in the US. Some states no longer have capacity at permitted landfills and export their waste to other states. Plasma gasification offers states new opportunities for waste disposal, and more importantly for renewable power generation in an environmentally sustainable manner.[3]
Landfill

Disposing of waste in a landfill involves burying the waste, and this remains a common practice in most countries. Landfills were often established in abandoned or unused quarries, mining voids or borrow pits. A properly-designed and well-managed landfill can be a hygienic and relatively inexpensive method of disposing of waste materials. Older, poorly-designed or poorly-managed landfills can create a number of adverse environmental impacts such as wind-blown litter, attraction of vermin, and generation of liquid leachate. Another common byproduct of landfills is gas (mostly composed of methane and carbon dioxide), which is produced as organic waste breaks down anaerobically. This gas can create odor problems, kill surface vegetation, and is a greenhouse gas.

Design characteristics of a modern landfill include methods to contain leachate such as clay or plastic lining material. Deposited waste is normally compacted to increase its density and stability, and covered to prevent attracting vermin (such as mice or rats). Many landfills also have landfill gas extraction systems installed to extract the landfill gas. Gas is pumped out of the landfill using perforated pipes and flared off or burnt in a gas engine to generate electricity.
Incineration

Incineration is a disposal method that involves combustion of waste material. Incineration and other high temperature waste treatment systems are sometimes described as "thermal treatment". Incinerators convert waste materials into heat, gas, steam, and ash.
Incineration is carried out both on a small scale by individuals and on a large scale by industry. It is used to dispose of solid, liquid and gaseous waste. It is recognized as a practical method of disposing of certain hazardous waste materials (such as biological medical waste). Incineration is a controversial method of waste disposal, due to issues such as emission of gaseous pollutants.
Incineration is common in countries such as Japan where land is more scarce, as these facilities generally do not require as much area as landfills. Waste-to-energy (WtE) or energy-from-waste (EfW) are broad terms for facilities that burn waste in a furnace or boiler to generate heat, steam and/or electricity. Combustion in an incinerator is not always perfect and there have been concerns about micro-pollutants in gaseous emissions from incinerator stacks. Particular concern has focused on some very persistent organics such as dioxins which may be created within the incinerator and which may have serious environmental consequences in the area immediately around the incinerator. On the other hand this method produces heat that can be used as energy.
Recycling methods
PVC, LDPE, PP, and PS (see resin identification code) are also recyclable, although these are not commonly collected. These items are usually composed of a single type of material, making them relatively easy to recycle into new products. The recycling of complex products (such as computers and electronic equipment) is more difficult, due to the additional dismantling and separation required.
Sustainability
Waste Management is a key player in maintaining a business’s ISO14001 accreditations. Companies are encouraged to improve their environmental efficiencies each year. One way to do this is by improving a company’s waste management with a new recycling service. (such as recycling: glass, food waste, paper and cardboard, plastic bottles etc)
Biological reprocessing

Waste materials that are organic in nature, such as plant material, food scraps, and paper products, can be recycled using biological composting and digestion processes to decompose the organic matter. The resulting organic material is then recycled as mulch or compost for agricultural or landscaping purposes. In addition, waste gas from the process (such as methane) can be captured and used for generating electricity. The intention of biological processing in waste management is to control and accelerate the natural process of decomposition of organic matter.
There are a large variety of composting and digestion methods and technologies varying in complexity from simple home compost heaps, to industrial-scale enclosed-vessel digestion of mixed domestic waste (see Mechanical biological treatment). Methods of biological decomposition are differentiated as being aerobic or anaerobic methods, though hybrids of the two methods also exist.
An example of waste management through composting is the Green Bin Program in Toronto, Canada, where household organic waste (such as kitchen scraps and plant cuttings) are collected in a dedicated container and then composted.
Energy recovery
The energy content of waste products can be harnessed directly by using them as a direct combustion fuel, or indirectly by processing them into another type of fuel. Recycling through thermal treatment ranges from using waste as a fuel source for cooking or heating, to fuel for boilers to generate steam and electricity in a turbine. Pyrolysis and gasification are two related forms of thermal treatment where waste materials are heated to high temperatures with limited oxygen availability. The process usually occurs in a sealed vessel under high pressure. Pyrolysis of solid waste converts the material into solid, liquid and gas products. The liquid and gas can be burnt to produce energy or refined into other products. The solid residue (char) can be further refined into products such as activated carbon. Gasification and advanced Plasma arc gasification are used to convert organic materials directly into a synthetic gas (syngas) composed of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. The gas is then burnt to produce electricity and steam.
Avoidance and reduction methods
An important method of waste management is the prevention of waste material being created, also known as waste reduction. Methods of avoidance include reuse of second-hand products, repairing broken items instead of buying new, designing products to be refillable or reusable (such as cotton instead of plastic shopping bags), encouraging consumers to avoid using disposable products (such as disposable cutlery), removing any food/liquid remains from cans, packaging, ... [4] and designing products that use less material to achieve the same purpose (for example, lightweighting of beverage cans).
Waste handling and transport

Waste collection methods vary widely between different countries and regions. Domestic waste collection services are often provided by local government authorities, or by private industry. Some areas, especially those in less developed countries, do not have a formal waste-collection system. Examples of waste handling systems include:
- In Australia, curbside collection is the method of disposal of waste. Every urban domestic household is provided with three bins: one for recyclables, another for general waste and another for garden materials - this bin is provided by the municipality if requested. Also, many households have compost bins; but this is not provided by the municipality. To encourage recycling, municipalities provide large recycle bins, which are larger than general waste bins. Municipal, commercial and industrial, construction and demolition waste is dumped at landfills and some is recycled. Household waste is segregated: recyclables sorted and made into new products, and general waste is dumped in landfill areas. According to the ABS, the recycling rate is high and is 'increasing, with 99% of households reporting that they had recycled or reused some of their waste within the past year (2003 survey), up from 85% in 1992'. This suggests that Australians are in favour of reduced or no landfilling and the recycling of waste. Of the total waste produced in 2002–03, '30% of municipal waste, 45% of commercial and industrial waste and 57% of construction and demolition waste' was recycled. Energy is produced from waste as well: some landfill gas is captured for fuel or electricity generation. Households and industries are not charged for the volume of waste they produce.
- In Europe and a few other places around the world, a few communities use a proprietary collection system known as Envac, which conveys refuse via underground conduits using a vacuum system. Other vacuum-based solutions include the MetroTaifun single-line and ring-line systems.
- In Canadian urban centres curbside collection is the most common method of disposal, whereby the city collects waste and/or recyclables and/or organics on a scheduled basis. In rural areas people often dispose of their waste by hauling it to a transfer station. Waste collected is then transported to a regional landfill.
- In Taipei, the city government charges its households and industries for the volume of rubbish they produce. Waste will only be collected by the city council if waste is disposed in government issued rubbish bags. This policy has successfully reduced the amount of waste the city produces and increased the recycling rate.
- In Israel, the Arrow Ecology company has developed the ArrowBio system, which takes trash directly from collection trucks and separates organic and inorganic materials through gravitational settling, screening, and hydro-mechanical shredding. The system is capable of sorting huge volumes of solid waste, salvaging recyclables, and turning the rest into biogas and rich agricultural compost. The system is used in California, Australia, Greece, Mexico, the United Kingdom and in Israel. For example, an ArrowBio plant that has been operational at the Hiriya landfill site since December 2003 serves the Tel Aviv area, and processes up to 150 tons of garbage a day.[5]
Technologies
Traditionally the waste Management industry has been slow to adopt new technologies such as RFID tags, GPS and integrated software packages which enable better quality data to be collected without the use of estimation or manual data entry.
- Technologies like RFID tags are now being used to collect data on presentation rates for curb-side pick-ups which is useful when examining the usage of recycling bins or similar.
- Benefits of GPS tracking is particularly evident when considering the efficiency of ad hoc pick-ups (like skip bins or dumpsters) where the collection is done on a consumer request basis.
- Integrated software packages are useful in aggregating this data for use in optimisation of operations for waste collection operations.
- Rear vision cameras are commonly used for OH&S reasons and video recording devices are becoming more widely used, particularly concerning residential services and contaminations of the waste stream.
Waste management concepts
There are a number of concepts about waste management which vary in their usage between countries or regions. Some of the most general, widely-used concepts include:
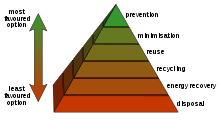
- Waste hierarchy - The waste hierarchy refers to the "3 Rs" reduce, reuse and recycle, which classify waste management strategies according to their desirability in terms of waste minimization. The waste hierarchy remains the cornerstone of most waste minimization strategies. The aim of the waste hierarchy is to extract the maximum practical benefits from products and to generate the minimum amount of waste.
- Extended producer responsibility - Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is a strategy designed to promote the integration of all costs associated with products throughout their life cycle (including end-of-life disposal costs) into the market price of the product. Extended producer responsibility is meant to impose accountability over the entire lifecycle of products and packaging introduced to the market. This means that firms which manufacture, import and/or sell products are required to be responsible for the products after their useful life as well as during manufacture.
- Polluter pays principle - the Polluter Pays Principle is a principle where the polluting party pays for the impact caused to the environment. With respect to waste management, this generally refers to the requirement for a waste generator to pay for appropriate disposal of the waste.
Education and awareness
Education and awareness in the area of waste and waste management is increasingly important from a global perspective of resource management. The Talloires Declaration is a declaration for sustainability concerned about the unprecedented scale and speed of environmental pollution and degradation, and the depletion of natural resources. Local, regional, and global air pollution; accumulation and distribution of toxic wastes; destruction and depletion of forests, soil, and water; depletion of the ozone layer and emission of "green house" gases threaten the survival of humans and thousands of other living species, the integrity of the earth and its biodiversity, the security of nations, and the heritage of future generations. Several universities have implemented the Talloires Declaration by establishing environmental management and waste management programs, e.g. the waste management university project. University and vocational education are promoted by various organizations, e.g. WAMITAB and Chartered Institution of Wastes Management. Many supermarkets encourage customers to use their reverse vending machines to deposit used purchased containers and receive a refund from the recycling fees. Brands that manufacture such machines include Tomra and Envipco.
See also
- Biomedical waste
- Recycling
- Environmental waste controls
- Food waste in the United Kingdom
- History of waste management
- Industrial symbiosis
- List of waste management acronyms
References
Notes
External links
- Waste = Food Documentary - A documentary on the Cradle to Cradle design concept of Michael Braungart and William McDonough.
- Envirowise UK Portal
- "American dumpster: Builders deep-six too much material"
- Analysis of existing methods for refuse processing
- Clean Pyrolysis an alternative approach from Intervate
- What is Waste Management?
- Gasoline from Vinegar | MIT Technology Review
- Timeline of Waste Management
