Vepsians
 Flag of Vepsians[1] | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 4,877 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| 4,534 (2021)[2] | |
| 281 (2001)[3] | |
| 54 (2011)[4] | |
| 8 (2009)[5] | |
| Languages | |
| Vepsian and Russian | |
| Religion | |
| Eastern Orthodoxy majority | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Other Baltic Finns Especially Karelians and Finns | |
Veps, or Vepsians (Veps: vepsläižed), are a Baltic Finnic people who speak the Veps language, which belongs to the Finnic branch of the Uralic languages.
According to the 2002 Russian census, there were 8,240 Veps in Russia. Of the 281 Veps in Ukraine, 11 spoke Vepsian according to the 2001 Ukrainian census.
The self-designations of these people in various dialects are vepslaine, bepslaane and (in northern dialects, southwest of Lake Onega) lüdinik and lüdilaine. Almost all Vepsians are fluent in Russian. The younger generation, in general, does not speak Vepsian; however, many have an understanding of the language.[6]
Geography
[edit]
In modern times, they live in the area between Lake Ladoga, Lake Onega and Lake Beloye – in the Russian Republic of Karelia in the former Veps National Volost, in Leningrad Oblast along the Oyat River in the Podporozhsky and Lodeynopolsky Districts and further south in the Tikhvinsky and Boksitogorsky Districts, and in Vologda Oblast in the Vytegorsky and Babayevsky Districts.[7]
History
[edit]Prehistory
[edit]Archeological and linguistic studies suggest that Vepsians lived in the valleys of the Sheksna, the Suda, and the Syas rivers, developing, according to Kalevi Wiik, from the proto-Vepsian Kargopol culture to the east of Lake Onega. They probably also lived in East Karelia and on the northern coast of Lake Onega. It is possible that the earliest mention of the Veps dates to the sixth century CE, when the Gothic historian Jordanes mentioned a people called Vasina broncas, which may have indicated the Vepsians.[8] One of the eastern routes on which the Vikings went through their area, and the bjarm people mentioned by the Vikings as inhabiting the coast of the White Sea may have referred to the Veps.[9] Evidence from tombs proves that they had contact with Staraya Ladoga, Finland and Meryans, other Volga Finnic tribes and later with the Principality of Novgorod and other Russian states. Later Vepsians also inhabited the western and eastern shores of Onega.
Historical period
[edit]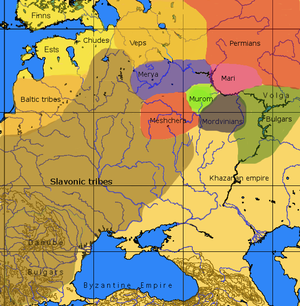
In early Kievan Rus' chronicles, they are called "Весь" (Ves’); in some Arabic sources, they are called Wisu. It is assumed that Bjarmians were at least partly Vepsians. From the 12th century, their history is connected with first the Principality of Novgorod and then Muscovy. Russian settlement reached the Onega Veps in the 14th or 15th century.[10] Eastern Vepsians in the Kargopol area merged linguistically with the Russians before the 20th century.
The existence of the Vepsian people was not widely known until the mid-19th century. Despite its close relationship to the Karelian and the Finnish languages, the Vepsian language was thus one of the last Uralic languages to be recognized as one.
Vepsians numbered 25,607 in 1897. Some 7,300 of them inhabited East Karelia. In the beginning of the 20th century there were some signs of national awakening among Vepsians. Early Soviet nationality politics supported this progress, and 24 administrative units with the status of national village soviets were formed. The alphabet and the written language were developed. Teachers started to instruct in Vepsian in some elementary schools. The Soviet authorities started to oppress the Vepsian culture in 1937. All national activities were stopped and the national districts were abolished. When Finland invaded East Karelia in the Continuation War, some Vepsians joined the so-called Kindred Battalion of the Finnish Army. These troops were relinquished to the Soviet Union after the war.[10][11][12]
In the postwar period, many Veps moved from their historic villages to larger cities. In 1983, on the initiative of national academics, an inquiry was carried out which showed that there were nearly 13,000 Veps in the Soviet Union, 5,600 of whom lived in Karelia, 4,000 in the Leningrad region and just under a 1,000 in the Vologda region.[10] The new Vepsian primer Abekirj and other elementary school books were published in Petrozavodsk in 1991. Kodima, a newspaper in Vepsian, has been published since 1993. The Vepsian rural community was formed in East Karelia in 1994, encompassing 8,200 square kilometers of land and 3,373 inhabitants, 42% of them Vepsian. The authorities of the Republic of Karelia granted some budgetary autonomy to the Vepsian community in 1996. The language was taught as a subject in two schools, in Shyoltozero and Rybreka. However, the cultural revival slowed in the second half of the 1990s and the federal authorities abolished the autonomy in 2006. Nowadays the younger generation in general does not speak the language.[12]
Demographics
[edit]Since 1926, The Vepsian population has been significantly declining likely due to multiple factors such as Stalin's mass forced deportation and assimilation within the Soviet Union.[13] However, it could also be attributed to other factors such as immigration after the Collapse of the Soviet Union or Russia's aging population.[14] As of 2021, 4,534 people identified as Vepsian. However, 16.5 million people refused to declare an ethnicity in the census, leading some to doubt the legitimacy of the most recent census, and whether the population counts of Ethnic minorities in Russia were accurate.[15]
| Population | Change (%) | |
| 1897 | 25,607 | 0% |
| 1926 | 32,800 | +28% |
| 1937 | 29,500 | -10% |
| 1939 | 31,500 | +6.7% |
| 1959 | 16,400 | -47.9% |
| 1970 | 8,000 | -51.2% |
| 1979 | 8,000 | 0% |
| 1989 | 12,501 | +56.2% |
| 2002 | 8,240 | -34% |
| 2010 | 5,936 | -27.9% |
| 2021 | 4,534 | -23.6% |
Genetics
[edit]
Vepsians cluster with Karelians and Finns.[17][18] They share most of their autosomal ancestry with Europeans, but about 12% of their ancestry is Nganasan-like.[17][16] This Siberian-related component is linked to the spread of Uralic languages. Like other Baltic Finnic peoples, Vepsians have a high Steppe-related admixture.[17]
Vepsians share more IBD (identity-by-descent) segments with several Uralic-speaking populations, including geographically distant ones like the Mansis and the Nganasans, than with Russians or other non-Uralic groups near to them. This is consistent with the idea that the Uralic-speaking peoples share some common roots. They have significant IBD segment sharing with the Turkic-speaking Dolgans from Siberia, too.[17]
The most common maternal haplogroups among Vepsians include H (57.6%) and U5 (16.8%), showing similarity with other Baltic Finnic groups. 56.4% of Vepsian men have the haplogroup N, which is of East Eurasian origin and commonly found among Uralic-speaking populations. 38.5% belong to the subclade N1a1a (M178) and 17.9% have the subclade N-P43. The second most common Y-DNA haplogroup among the Veps is R1a (35.9%).[17]
Notable Vepsians
[edit]- Nikolay Abramov – Vepsian-language poet, translator and writer
- Ivan Golunov —Russian investigative journalist and anti-corruption reporter[19]
- Raisa Lardot (born 1938) — Veps-born Finnish writer
- Anna Lisitsyna (1922-1942) — Soviet partisan, Hero of the Soviet Union
- Ryurik Lonin (1930-2009) — collector of Veps folklore and writer
- Alexander Svirsky (1448-1533) — Eastern Orthodox saint

Republic of Karelia, northwestern Russia.
Further reading
[edit]- Kurs, Ott (March 2001). "The Vepsians: An administratively divided nationality". Nationalities Papers. 29 (1): 69–83. doi:10.1080/00905990120036385. S2CID 153956031.
References
[edit]- ^ Paškov, Aleksandr (1994). Karjalan vaakunat ja liput. Petroskoi: KAREKO. p. 327-330. ISBN 5-88129-010-0.
- ^ Russian census 2010 Archived October 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Ukrainian census 2001". Ukrcensus.gov.au. Retrieved 24 October 2017.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Population by Ethnic Nationality, Mother Tongue, Citizenship, Sex, Age Group and Place of Residence, 31 December 2011". Pub.stat.ee. Retrieved 24 October 2017.
- ^ "Население по национальности и родному языку" [Population by nationality and mother language] (PDF). Перепись населения Республики Беларусь 2009 года (in Russian). Нацыянальны статыстычны камітэт Рэспублікі Беларусь. 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Russian Veps: We talk to the Finns without an interpreter".
- ^ "L'extinction d'un peuple finno-ougrien: les Vepses". Regard-est.com. Retrieved 24 October 2017.
- ^ Toivo Vuorela 1960, Suomensukuiset kansat, p. 103
- ^ Saressalo 2005, Vepsa Maa, Kansa, Kulttuuri, p. 13
- ^ a b c "The Red Book of the Peoples of the Russian Empire". Eki.ee. Retrieved 24 October 2017.
- ^ Ott Kurs (1994). "Vepsians: the easternmost Baltic-Finnic people". Terra. 107: 127–135.
- ^ a b Ott Kurs (2001). "The Vepsians: An administratively divided nationality". Nationalities Papers. 29: 69–83. doi:10.1080/00905990120036385. S2CID 153956031.
- ^ "VEPSES". www.suri.ee. Retrieved 2024-04-02.
- ^ "Russia Population (2024) - Worldometer". www.worldometers.info. Retrieved 2024-04-02.
- ^ Coalson, Robert (2023-02-05). "Russia's 2021 Census Results Raise Red Flags Among Experts And Ethnic-Minority Activists". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Retrieved 2024-04-02.
- ^ a b Jeong, Choongwon; Balanovsky, Oleg; Lukianova, Elena; Kahbatkyzy, Nurzhibek; Flegontov, Pavel; Zaporozhchenko, Valery; Immel, Alexander; Wang, Chuan-Chao; Ixan, Olzhas; Khussainova, Elmira; Bekmanov, Bakhytzhan; Zaibert, Victor; Lavryashina, Maria; Pocheshkhova, Elvira; Yusupov, Yuldash (2019). "The genetic history of admixture across inner Eurasia". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 3 (6): 966–976. Bibcode:2019NatEE...3..966J. doi:10.1038/s41559-019-0878-2. ISSN 2397-334X. PMC 6542712. PMID 31036896.
- ^ a b c d e Tambets, Kristiina; Yunusbayev, Bayazit; Hudjashov, Georgi; Ilumäe, Anne-Mai; Rootsi, Siiri; Honkola, Terhi; Vesakoski, Outi; Atkinson, Quentin; Skoglund, Pontus; Kushniarevich, Alena; Litvinov, Sergey; Reidla, Maere; Metspalu, Ene; Saag, Lehti; Rantanen, Timo (2018). "Genes reveal traces of common recent demographic history for most of the Uralic-speaking populations". Genome Biology. 19 (1): 139. doi:10.1186/s13059-018-1522-1. ISSN 1474-760X. PMC 6151024. PMID 30241495.
- ^ Rodríguez-Varela, Ricardo; Moore, Kristjan H.S.; Ebenesersdóttir, S. Sunna; Kilinc, Gulsah Merve; Kjellström, Anna; Papmehl-Dufay, Ludvig; Alfsdotter, Clara; Berglund, Birgitta; Alrawi, Loey; Kashuba, Natalija; Sobrado, Verónica; Lagerholm, Vendela Kempe; Gilbert, Edmund; Cavalleri, Gianpiero L.; Hovig, Eivind (2023). "The genetic history of Scandinavia from the Roman Iron Age to the present". Cell. 186 (1): 32–46.e19. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.11.024. hdl:10810/60423.
- ^ Журналист Иван Голунов стал обладателем зайца в Карелии и признался, что он вепс
