Vaupés Department: Difference between revisions
GrouchoBot (talk | contribs) m robot Adding: yo:Vaupés Department |
|||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
# [[Acaricuara]] |
# [[Acaricuara]] |
||
# [[Villa Fátima]] |
# [[Villa Fátima]] |
||
Mitú : es la capital del departamento de Vaupés, ubicado al oriente del país en la región de la Amazonia. |
|||
Tiene una superficie de 54.135 km2 y limita por el Norte con los departamentos de Guaviare y Guainía, por el Este con Brasil, por el Sur con el río Apoporis que lo separa de los departamentos de Amazonas y Caquetá y por el Oeste con los departamentos de Caquetá y Guaviare. |
|||
Se caracteriza por ser un sector de transición entre las llanuras secas de la Orinoquia, al norte, y la selva húmeda amazónica. Sus temperaturas oscilan entre 25 y 30°C. El Vaupés comparte con el departamento del Guaviare la reserva nacional natural Nukak. |
|||
La belleza de sus paisajes naturales y la riqueza de fauna, y flora, lo hacen un verdadero atractivo turístico. |
|||
Por medio del artículo 309 de la Constitución Política de Colombia de 1991, se elevó la comisaría del Vaupés a la categoría de departamento |
|||
Los principales cultivos son yuca, maíz, plátano y arroz. Se explotan metales preciosos como el oro y la ilmenita. El principal producción artesanal es la cestería. |
|||
El Vaupés carece de vías terrestres para su comunicación y sólo es posible llegar hasta su capital por vías fluvial y aérea. |
|||
Cuenta con aeropuertos en Mitú, Carurú y Pacoa que permiten la conexión con las principales capitales de la región y la capital de la República. |
|||
==Notes== |
==Notes== |
||
Revision as of 19:57, 27 May 2010
Template:Infobox Department of Colombia
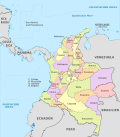
Vaupés is a department of Colombia in the jungle covered Amazonas Region. It is located in the southeast part of the country, bordering Brazil to the east, the department of Amazonas to the south, Caquetá and Guaviare, and Guainía to the north covering a total area of 54,135 km². Its capital is the town of Mitú.
History
During the colonization by the Spanish and first days of the first republic, the territory of Vaupes was part of the Province of Popayán, during the Greater Colombia. After the independence from Spain between 1821 and 1830 became part of the first version of the Boyacá Department. Between 1831 and 1857 the territory became part of the National Territory of Caquetá to later be part of the Sovereign State of Cauca. In 1886 became part of the then recently created Cauca Department.[1]
With the expansion of the rubber industry and the industrial revolution, exploration for rubber reached the area briging colonizers that altered and in some cases extinguished the majority of the indigenous population.
The territory was first made into a territorial division in 1910 and functioned as Commissaries (Comisarias) with the town of Calamar as capital (located in present day Guaviare) but later moved to the town of Mitú to make an "act of presence" near the border with Brasil. In 1963 Guainía segregated from the Vaupes and became a commissary. In 1977, Guaviare followed the same path.
The Department was created after the Colombian Constitution of 1991 which established it as a Department of Colombia on July 4, 1991.[2]
Armed Conflict
In November 1998 an estimate of a 1,000 FARC guerrilla members of the Eastern Bloc of the FARC-EP tried to take over by force the capital town Mitú, against 120 National Police members and one Colombian National Army Battalion. The Colombian Air Force and Army Aviation supported ground forces with air raids. Mitú was left partially destroyed and some 60 policemen and 10 civilians died. In their escape FARC took hostages as human shields including some 40 to 45 members of the Colombian Military.[3]
Economy
The department's main economic activities feature logging and fishing, with much exportation to neighboring Brazil.
Demographics
The vast majority of the population consists of indigenous inhabitants.
Transportation
Because of its location in the Amazon jungle, it has no roads connecting it with the rest of the country or internally from settlement to settlement, and commerce and contact with the outside world is achieved through travel along the main rivers and by means of air travel. Several of the small settlements have airstrips with service to the department's capital, Mitú, and from there with the rest of the country.[4]
Administrative divisions
Because of its small population and vast extension of land, Vaupés only has 3 municipalities. Other sections of the Department were classified as an especial type of Corregimiento, which has certain hybrid functions from a municipality and corregimiento.
Municipalities
Department Corregimientos
Municipal Corregimientos
Mitú : es la capital del departamento de Vaupés, ubicado al oriente del país en la región de la Amazonia. Tiene una superficie de 54.135 km2 y limita por el Norte con los departamentos de Guaviare y Guainía, por el Este con Brasil, por el Sur con el río Apoporis que lo separa de los departamentos de Amazonas y Caquetá y por el Oeste con los departamentos de Caquetá y Guaviare. Se caracteriza por ser un sector de transición entre las llanuras secas de la Orinoquia, al norte, y la selva húmeda amazónica. Sus temperaturas oscilan entre 25 y 30°C. El Vaupés comparte con el departamento del Guaviare la reserva nacional natural Nukak. La belleza de sus paisajes naturales y la riqueza de fauna, y flora, lo hacen un verdadero atractivo turístico. Por medio del artículo 309 de la Constitución Política de Colombia de 1991, se elevó la comisaría del Vaupés a la categoría de departamento Los principales cultivos son yuca, maíz, plátano y arroz. Se explotan metales preciosos como el oro y la ilmenita. El principal producción artesanal es la cestería. El Vaupés carece de vías terrestres para su comunicación y sólo es posible llegar hasta su capital por vías fluvial y aérea. Cuenta con aeropuertos en Mitú, Carurú y Pacoa que permiten la conexión con las principales capitales de la región y la capital de la República.
Notes
- ^ Vaupes - Capitán Paz
- ^ Template:Es icon Vaupes Secretary of Education; History of Vaupes
- ^ INTERNACIONAL | Colombia. La guerrilla causa 70 muertos en la ciudad de Mitú
- ^ Template:Es icon Finagro; Vaupes Department
See also
References
- Template:Es icon national lottery on Vaupes
- Template:Es icon Encolombia.com - Vaupes
- Template:Es icon National Federation of Departments: Vaupes
External links