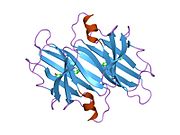
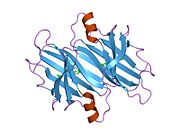
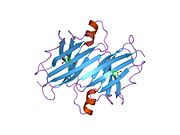
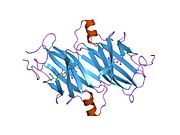
Transthyretin
Transthyretin (TTR or TBPA) is a transport protein in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid that transports the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and retinol to the liver. This is how transthyretin gained its name: transports thyroxine and retinol. The liver secretes TTR into the blood, and the choroid plexus secretes TTR into the cerebrospinal fluid.
TTR was originally called prealbumin[5] (or thyroxine-binding prealbumin) because it migrated faster than albumin on electrophoresis gels. Prealbumin was felt to be a misleading name, it is not a synthetic precursor of albumin. The alternative name TTR was proposed by DeWitt Goodman in 1981.
Transthyretin protein is encoded by the TTR gene located on the 18th chromosome.
Binding affinities
[edit]It functions in concert with two other thyroid hormone-binding proteins in the serum:
| Protein | Binding strength | Plasma concentration |
|---|---|---|
| thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) | highest | lowest |
| transthyretin (TTR or TBPA) | lower | higher |
| albumin | poorest | much higher |
In cerebrospinal fluid TTR is the primary carrier of T4. TTR also acts as a carrier of retinol (vitamin A) through its association with retinol-binding protein (RBP) in the blood and the CSF. Less than 1% of TTR's T4 binding sites are occupied in blood, which is taken advantage of below to prevent TTRs dissociation, misfolding and aggregation which leads to the degeneration of post-mitotic tissue.
Numerous other small molecules are known to bind in the thyroxine binding sites, including many natural products (such as resveratrol), drugs (tafamidis,[6] diflunisal,[7][8][9] and flufenamic acid),[10] and toxicants (PCB[11]).
Structure
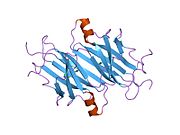
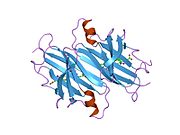
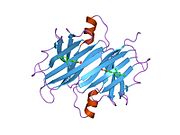
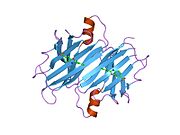
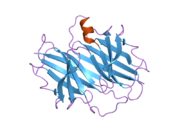
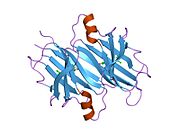
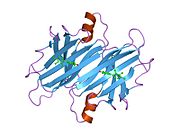
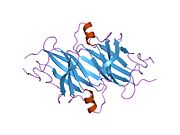
[edit]TTR is a 55kDa homotetramer with a dimer of dimers quaternary structure that is synthesized in the liver, choroid plexus and retinal pigment epithelium for secretion into the bloodstream, cerebrospinal fluid and the eye, respectively. Each monomer is a 127-residue polypeptide rich in beta sheet structure. Association of two monomers via their edge beta-strands forms an extended beta sandwich. Further association of two of these dimers in a face-to-face fashion produces the homotetrameric structure and creates the two thyroxine binding sites per tetramer. This dimer-dimer interface, comprising the two T4 binding sites, is the weaker dimer-dimer interface and is the one that comes apart first in the process of tetramer dissociation.[12]
Role in disease
[edit]TTR misfolding and aggregation is known to be associated with amyloid diseases[13] including wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis,[14] hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis,[15] familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP),[16][17] and familial amyloid cardiomyopathy (FAC).[18]
TTR tetramer dissociation is known to be rate-limiting for amyloid fibril formation.[19][20][21] However, the monomer also must partially denature in order for TTR to be mis-assembly competent, leading to a variety of aggregate structures, including amyloid fibrils.[22]
At least 114 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered.[23] While wild type TTR can dissociate, misfold, and aggregate, leading to SSA (senile systemic amyloidosis), point mutations within TTR are known to destabilize the tetramer composed of mutant and wild-type TTR subunits, facilitating more facile dissociation and/or misfolding and amyloidogenesis.[24] A replacement of valine by methionine at position 30 (TTR V30M) is the mutation most commonly associated with FAP.[25] A position 122 replacement of valine by isoleucine (TTR V122I) is carried by 3.9% of the African-American population, and is the most common cause of FAC.[18] SSA is estimated to affect over 25% of the population over age 80.[14] Severity of disease varies greatly by mutation, with some mutations causing disease in the first or second decade of life, and others being more benign. Deposition of TTR amyloid is generally observed extracellularly, although TTR deposits are also clearly observed within the cardiomyocytes of the heart.
Treatment of familial (hereditary) TTR amyloid disease has historically relied on liver transplantation as a crude form of gene therapy.[26] Because TTR is primarily produced in the liver, replacement of a liver containing a mutant TTR gene with a normal gene is able to reduce the mutant TTR levels in the body to < 5% of pretransplant levels. Certain mutations, however, cause CNS amyloidosis, and due to their production by the choroid plexus, the CNS TTR amyloid diseases do not respond to gene therapy mediated by liver transplantation.
In 2011, the European Medicines Agency approved tafamidis (Vyndaqel) for the amelioration of FAP.[6] Tafamidis kinetically stabilizes the TTR tetramer, preventing tetramer dissociation required for TTR amyloidogenesis and degradation of the autonomic nervous system[27] and/or the peripheral nervous system and/or the heart.[21]
TTR is also thought to have beneficial side effects, by binding to the infamous beta-amyloid protein, thereby preventing beta-amyloid's natural tendency to accumulate into the plaques associated with the early stages of Alzheimer's disease. Preventing plaque formation is thought to enable a cell to rid itself of this otherwise toxic protein form and, thus, help prevent and maybe even treat the disease.[28]
There is now strong genetic[29][30] and pharmacologic data (see European Medicines Agency website for the tafamidis clinical trial results) indicating that the process of amyloid fibril formation leads to the degeneration of post-mitotic tissue causing FAP and likely FAC and SSA. Evidence points to the oligomers generated in the process of amyloidogenicity leading to the observed proteotoxicity.[31][32]
Transthyretin level in cerebrospinal fluid has also been found to be lower in patients with some neurobiological disorders such as schizophrenia.[33] The reduced level of transthyretin in the CSF may indicate a lower thyroxine transport in brains of patients with schizophrenia.
Transthyretin is known to contain a Gla domain, and thus be dependent for production on post-translational modification requiring vitamin K, but the potential link between vitamin k status and thyroid function has not been explored.
Because transthyretin is made in part by the choroid plexus, it can be used as an immunohistochemical marker for choroid plexus papillomas as well as carcinomas.[citation needed]
As of March 2015, there are two ongoing clinical trials undergoing recruitment in the United States and worldwide to evaluate potential treatments for TTR amyloidosis.[34][needs update]
Interactions
[edit]Transthyretin has been shown to interact with perlecan.[35]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000118271 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000061808 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Prealbumin at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ^ a b Razavi H, Palaninathan SK, Powers ET, Wiseman RL, Purkey HE, Mohamedmohaideen NN, Deechongkit S, Chiang KP, Dendle MT, Sacchettini JC, Kelly JW (June 2003). "Benzoxazoles as transthyretin amyloid fibril inhibitors: synthesis, evaluation, and mechanism of action". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 42 (24): 2758–61. doi:10.1002/anie.200351179. PMID 12820260.
- ^ Sekijima Y, Dendle MA, Kelly JW (December 2006). "Orally administered diflunisal stabilizes transthyretin against dissociation required for amyloidogenesis". Amyloid. 13 (4): 236–49. doi:10.1080/13506120600960882. PMID 17107884. S2CID 32736564.
- ^ Adamski-Werner SL, Palaninathan SK, Sacchettini JC, Kelly JW (January 2004). "Diflunisal analogues stabilize the native state of transthyretin. Potent inhibition of amyloidogenesis". J. Med. Chem. 47 (2): 355–74. doi:10.1021/jm030347n. PMID 14711308.
- ^ Vilaro M, Arsequell G, Valencia G, Ballesteros A, Barluenga J, Nieto J, Planas A, Almeida R, Saraiva MJ (2007). "Reengineering TTR amyloid inhibition properties of diflunisal". In Seldin DC, Skinner M, Berk JL, Connors LH (eds.). XIth International Symposium on Amyloidosis. Boca Raton: CRC. pp. 205–207. doi:10.1201/9781420043358.ch69 (inactive 2024-11-12). ISBN 978-1-4200-4281-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ Baures PW, Oza VB, Peterson SA, Kelly JW (July 1999). "Synthesis and evaluation of inhibitors of transthyretin amyloid formation based on the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, flufenamic acid". Bioorg. Med. Chem. 7 (7): 1339–47. doi:10.1016/S0968-0896(99)00066-8. PMID 10465408.
- ^ Purkey HE, Palaninathan SK, Kent KC, Smith C, Safe SH, Sacchettini JC, Kelly JW (December 2004). "Hydroxylated polychlorinated biphenyls selectively bind transthyretin in blood and inhibit amyloidogenesis: rationalizing rodent PCB toxicity". Chem. Biol. 11 (12): 1719–28. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.10.009. PMID 15610856.
- ^ Foss TR, Wiseman RL, Kelly JW (November 2005). "The pathway by which the tetrameric protein transthyretin dissociates". Biochemistry. 44 (47): 15525–33. doi:10.1021/bi051608t. PMID 16300401.
- ^ Zeldenrust SR, Benson MD (2010). "Familial and senile amyloidosis caused by transthyretin". In Ramirez-Alvarado M, Kelly JW, Dobson C (eds.). Protein misfolding diseases: current and emerging principles and therapies. New York: Wiley. pp. 795–815. doi:10.1002/9780470572702.ch36. ISBN 978-0-471-79928-3.
- ^ a b Westermark P, Sletten K, Johansson B, Cornwell GG (April 1990). "Fibril in senile systemic amyloidosis is derived from normal transthyretin". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87 (7): 2843–5. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.2843W. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.7.2843. PMC 53787. PMID 2320592.
- ^ "Familial amyloid polyneuropathy", Wikipedia, 2021-11-02, retrieved 2021-12-05
- ^ Andrade C (September 1952). "A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy; familiar atypical generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of the peripheral nerves". Brain. 75 (3): 408–27. doi:10.1093/brain/75.3.408. PMID 12978172.
- ^ Coelho T (October 1996). "Familial amyloid polyneuropathy: new developments in genetics and treatment". Curr. Opin. Neurol. 9 (5): 355–9. doi:10.1097/00019052-199610000-00007. PMID 8894411. S2CID 43007619.
- ^ a b Jacobson DR, Pastore RD, Yaghoubian R, Kane I, Gallo G, Buck FS, Buxbaum JN (February 1997). "Variant-sequence transthyretin (isoleucine 122) in late-onset cardiac amyloidosis in black Americans". N. Engl. J. Med. 336 (7): 466–73. doi:10.1056/NEJM199702133360703. PMID 9017939.
- ^ Colon W, Kelly JW (September 1992). "Partial denaturation of transthyretin is sufficient for amyloid fibril formation in vitro". Biochemistry. 31 (36): 8654–60. doi:10.1021/bi00151a036. PMID 1390650.
- ^ Lai Z, Colón W, Kelly JW (May 1996). "The acid-mediated denaturation pathway of transthyretin yields a conformational intermediate that can self-assemble into amyloid". Biochemistry. 35 (20): 6470–82. doi:10.1021/bi952501g. PMID 8639594.
- ^ a b Hammarström P, Wiseman RL, Powers ET, Kelly JW (January 2003). "Prevention of transthyretin amyloid disease by changing protein misfolding energetics". Science. 299 (5607): 713–6. Bibcode:2003Sci...299..713H. doi:10.1126/science.1079589. PMID 12560553. S2CID 30829998.
- ^ Jiang X, Smith CS, Petrassi HM, Hammarström P, White JT, Sacchettini JC, Kelly JW (September 2001). "An engineered transthyretin monomer that is nonamyloidogenic, unless it is partially denatured". Biochemistry. 40 (38): 11442–52. doi:10.1021/bi011194d. PMID 11560492.
- ^ Šimčíková D, Heneberg P (December 2019). "Refinement of evolutionary medicine predictions based on clinical evidence for the manifestations of Mendelian diseases". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 18577. Bibcode:2019NatSR...918577S. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-54976-4. PMC 6901466. PMID 31819097.
- ^ Sekijima Y, Wiseman RL, Matteson J, Hammarström P, Miller SR, Sawkar AR, Balch WE, Kelly JW (April 2005). "The biological and chemical basis for tissue-selective amyloid disease". Cell. 121 (1): 73–85. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.018. PMID 15820680. S2CID 12503292.
- ^ Saraiva MJ (1995). "Transthyretin mutations in health and disease". Hum. Mutat. 5 (3): 191–6. doi:10.1002/humu.1380050302. PMID 7599630. S2CID 10124222.
- ^ Holmgren G, Ericzon BG, Groth CG, Steen L, Suhr O, Andersen O, Wallin BG, Seymour A, Richardson S, Hawkins PN (May 1993). "Clinical improvement and amyloid regression after liver transplantation in hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis". Lancet. 341 (8853): 1113–6. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(93)93127-m. PMID 8097803. S2CID 26093858.
- ^ Ando Y, Suhr OB (December 1998). "Autonomic dysfunction in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP)". Amyloid. 5 (4): 288–300. doi:10.3109/13506129809007303. PMID 10036588.
- ^ Li X, Buxbaum JN (2011). "Transthyretin and the brain re-visited: is neuronal synthesis of transthyretin protective in Alzheimer's disease?". Mol Neurodegener. 6 (1): 79. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-6-79. PMC 3267701. PMID 22112803.
- ^ Coelho, T., Carvalho, M., Saraiva, M.J., Alves, I., Almeida, M.R., and Costa, P.P. (1993). A strikingly benign evolution of FAP in an individual found to be a compound heterozygote for two TTR mutations: TTR MET 30 and TTR MET 119. J Rheumatol 20, 179.
- ^ Hammarström P, Schneider F, Kelly JW (September 2001). "Trans-suppression of misfolding in an amyloid disease". Science. 293 (5539): 2459–62. Bibcode:2001Sci...293.2459H. doi:10.1126/science.1062245. PMID 11577236. S2CID 39689656.
- ^ Sousa MM, Cardoso I, Fernandes R, Guimarães A, Saraiva MJ (December 2001). "Deposition of transthyretin in early stages of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: evidence for toxicity of nonfibrillar aggregates". Am. J. Pathol. 159 (6): 1993–2000. doi:10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63050-7. PMC 1850610. PMID 11733349.
- ^ Reixach N, Deechongkit S, Jiang X, Kelly JW, Buxbaum JN (March 2004). "Tissue damage in the amyloidoses: Transthyretin monomers and nonnative oligomers are the major cytotoxic species in tissue culture". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (9): 2817–22. Bibcode:2004PNAS..101.2817R. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400062101. PMC 365703. PMID 14981241.
- ^ Huang JT, Leweke FM, Oxley D, Wang L, Harris N, Koethe D, Gerth CW, Nolden BM, Gross S, Schreiber D, Reed B, Bahn S (November 2006). "Disease biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with first-onset psychosis". PLOS Med. 3 (11): e428. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030428. PMC 1630717. PMID 17090210.
- ^ Clinical trial number NCT01960348 for "APOLLO: The Study of an Investigational Drug, Patisiran (ALN-TTR02), for the Treatment of Transthyretin (TTR)-Mediated Amyloidosis" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ^ Smeland S, Kolset SO, Lyon M, Norum KR, Blomhoff R (September 1997). "Binding of perlecan to transthyretin in vitro". Biochem. J. 326 (3): 829–36. doi:10.1042/bj3260829. PMC 1218739. PMID 9307034.
Further reading
[edit]- Sakaki Y, Yoshioka K, Tanahashi H, Furuya H, Sasaki H (1989). "Human transthyretin (prealbumin) gene and molecular genetics of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy". Mol. Biol. Med. 6 (2): 161–8. PMID 2693890.
- Saraiva MJ (1995). "Transthyretin mutations in health and disease". Hum. Mutat. 5 (3): 191–6. doi:10.1002/humu.1380050302. PMID 7599630. S2CID 10124222.
- Ingenbleek Y, Young V (1994). "Transthyretin (prealbumin) in health and disease: nutritional implications". Annu. Rev. Nutr. 14: 495–533. doi:10.1146/annurev.nu.14.070194.002431. PMID 7946531.
- Hesse A, Altland K, Linke RP, Almeida MR, Saraiva MJ, Steinmetz A, Maisch B (1993). "Cardiac amyloidosis: a review and report of a new transthyretin (prealbumin) variant". Br Heart J. 70 (2): 111–5. doi:10.1136/hrt.70.2.111. PMC 1025267. PMID 8038017.
- Blanco-Jerez CR, Jiménez-Escrig A, Gobernado JM, Lopez-Calvo S, de Blas G, Redondo C, García Villanueva M, Orensanz L (1998). "Transthyretin Tyr77 familial amyloid polyneuropathy: a clinicopathological study of a large kindred". Muscle Nerve. 21 (11): 1478–85. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4598(199811)21:11<1478::AID-MUS17>3.0.CO;2-X. PMID 9771673. S2CID 19532662.