tert-Butyl chloride
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Chloro-2-methylpropane | |||
| Other names
1,1-dimethylethyl chloride
1-chloro-1,1-dimethylethane chlorotrimethylmethane trimethylchloromethane t-butyl chloride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.334 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1127 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H9Cl | |||
| Molar mass | 92.57 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.851 g/ml | ||
| Melting point | −26 °C (−15 °F; 247 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 51 °C (124 °F; 324 K) | ||
| Sparingly soluble in water, miscible with alcohol and ether | |||
| Vapor pressure | 34.9 kPa (20 °C) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Danger | |||
| H225 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P280, P303+P361+P353, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −9 °C (16 °F; 264 K) (open cup) −23 °C (closed cup) | ||
| 540 °C (1,004 °F; 813 K) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkyl halides
|
tert-Butyl bromide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
tert-Butyl chloride is the organochloride with the formula (CH3)3CCl. It is a colorless, flammable liquid. It is sparingly soluble in water, with a tendency to undergo hydrolysis to the corresponding tert-butyl alcohol. It is produced industrially as a precursor to other organic compounds.[1]
Synthesis
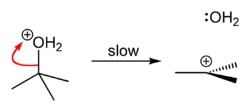
[edit]tert-Butyl chloride is produced by the reaction of tert-butyl alcohol with hydrogen chloride.[1] In the laboratory, concentrated hydrochloric acid is used. The conversion entails a SN1 reaction as shown below.[2]
| Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 |
 |
 |

|
| The acid protonates the alcohol, forming a good leaving group (water). | Water leaves the protonated t-BuOH, forming a relatively stable tertiary carbocation. | The chloride ion attacks the carbocation, forming t-BuCl. |
The overall reaction, therefore, is:
- (CH3)3COH + HCl → (CH3)3CCl + H2O
Because tert-butanol is a tertiary alcohol, the relative stability of the tert-butyl carbocation in the step 2 allows the SN1 mechanism to be followed, whereas a primary alcohol would follow an SN2 mechanism.
Reactions
[edit]When tert-butyl chloride is dissolved in water, it undergoes a hydrolysis to tert-butyl alcohol. When dissolved in alcohols, the corresponding t-butyl ethers are produced.
Uses
[edit]tert-Butyl chloride is used to prepare the antioxidant tert-butylphenol and the fragrance neohexyl chloride.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c M. Rossberg et al. "Chlorinated Hydrocarbons" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_233.pub2
- ^ James F. Norris and Alanson W. Olmsted "tert-Butyl Chloride" Org. Synth. 1928, volume 8, pp. 50. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.008.0050