Contrast effect
A contrast effect is the enhancement or diminishment, relative to normal, of perception, cognition or related performance as a result of successive (immediately previous) or simultaneous exposure to a stimulus of lesser or greater value in the same dimension. (Here, normal perception, cognition or performance is that which would be obtained in the absence of the comparison stimulus—i.e., one based on all previous experience.)
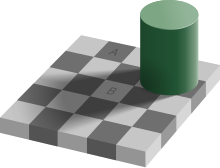
Perception example: A neutral gray target will appear lighter or darker than it does in isolation when immediately preceded by, or simultaneously compared to, respectively, a dark gray or light gray target.
Cognition example: A person will appear more or less attractive than that person does in isolation when immediately preceded by, or simultaneously compared to, respectively, a less or more attractive person.
Performance example: A laboratory rat will work faster, or slower, during a stimulus predicting a given amount of reward when that stimulus and reward are immediately preceded by, or alternated with, respectively, different stimuli associated with either a lesser or greater amount of reward.
Types
[edit]
Simultaneous contrast
[edit]The oldest reference to simultaneous contrast in the scientific literature is by the hand of the 11th century physicist Ibn al-Haytham who describes spots of paint on a white background appearing almost black and conversely paler than their true colour on black:[1]
He also describes that a leaf green paint may appear clearer and younger on dark blue and darker and older on yellow:[1]
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe writes in 1810 that a grey image on a black background appears much brighter than the same on white.[2] And Johannes Peter Müller notes the same in 1838 and also that a strip of grey on a brightly coloured field appears to be tinted ever so slightly in the contrasting colour.[3]
The subject of the impact of the surrounding field on colour perception has been a subject of ongoing research since. It has been found that the size of the surrounding field has an impact,[4] as does the separation between colour and surround,[5] similarity of chromaticity,[6] luminance difference[7] and the structure of the surround.[8][9][10]
There has been some debate over the degree to which simultaneous contrast is a physiological process caused by the connections of neurons in the visual cortex, or whether it is a psychological effect.[11] Both appear to have some effect. A possible source of the effect are neurons in the V4 area that have inhibitory connections to neighboring cells. The most likely evolutionary rationale for this effect is that it enhances edges in the visual field, thus facilitating the recognition of shapes and objects.
Successive contrast
[edit]Successive contrast occurs when the perception of currently viewed stimuli is modulated by previously viewed stimuli.[12][13] In the example below you can use the scrollbar to quickly swap the red and green disks for two orange disks. Staring at the dot in the centre of one of the top two coloured disks and then looking at the dot in the centre of the corresponding lower disk makes the two lower disks briefly appear to have different colours, though in reality their colour is identical.
Metacontrast and paracontrast
[edit]
Metacontrast and paracontrast involve both time and space. When one half of a circle is lit for 10 milliseconds (ms), it is at its maximal intensity. If the other half is displayed at the same time (but 20–50 ms later), there is a mutual inhibition: the left side is darkened by the right half (metacontrast), and the center may be completely obliterated. At the same time, there is a slight darkening of the right side due to the first stimulus (paracontrast).[14][clarification needed]
Domains
[edit]The contrast effect was noted by the 17th century philosopher John Locke, who observed that lukewarm water can feel like hair or feel cold depending on whether the hand touching it was previously in hot or cold water.[15]
In the early 20th century, Wilhelm Wundt identified contrast as a fundamental principle of perception, and since then the effect has been confirmed in many different areas.[15] Contrast effects can shape not only visual qualities like color and brightness, but other kinds of perception, including the perception of weight.[16] Whether a piece of music is perceived as good or bad can depend on whether the music heard before it was unpleasant or pleasant.[17] For the effect to work, the objects being compared need to be similar to each other: a television reporter can seem to shrink when interviewing a tall basketball player, but not when standing next to a tall building. Furthermore, the contrast effect has been argued to apply to foreign policies of states. For example,[18] African countries have increasingly looked to China and India as opposed to the US, the EU and the World Bank because these Asian states have highlighted their lack of "interference" and "conditionality" in exchange for foreign aid and FDI.
See also
[edit]- Assimilation and contrast effects
- Checker shadow illusion
- Chubb illusion
- Less-is-better effect and distinction bias
- Negative (Positive) contrast effect
- List of cognitive biases
References
[edit]- ^ a b أبو علي، الحسن بن الحسن بن الهيثم: 1011–1021, كتاب المناظر, 1 § 6 ¶ 113–114
- ^ Johann Wolfgang von Goethe: Zur Farbenlehre III § 38: ‘Ein graues Bild auf ſchwarzem Grunde erſcheint viel heller, als daſſelbe Bild auf weißem. Stellt man beyde Faͤlle neben einander, ſo kann man ſich kaum uͤberzeugen, daß beyde Bilder aus Einem Topf gefaͤrbt seyen.’
- ^ Johannes Peter Müller: Handbuch der Physiologie des Menschen V § I § III ¶ 3B2: ‘So z. B. erscheint der graue Papierschnitzel leicht röthlich auf grünem Felde, dagegen grünlich auf rothem Felde, mit orangefarbener Nebentinte auf hellblauem Felde, und mit bläulicher Tinte auf orangenem Felde, gelblich auf hellvioletem Felde, violet auf hellgelbem Felde.’
- ^ Joseph C. Stevens: Brightness inhibition re size of surround
- ^ Robert E. Cole & A. Leonard Diamond: Amount of surround and test-inducing separation in simultaneous brightness contrast
- ^ Tadasu Oyama, Muneo Mitsuboshi & Takashi Kamoshita: Wavelength-specific brightness contrast as a function of surround luminance
- ^ María José Luque, Pascual Capilla, Adelina Felipe & José María Artigas: Brightness induction in a chromatic center – achromatic surround configuration
- ^ Michael White: The effect of the nature of the surround on the perceived lightness of grey bars within square-wave test gratings
- ^ Edward Howard Adelson: Perceptual organization and the judgment of brightness
- ^ Iris K. Zemach, & Michael E. Rudd: Effects of surround articulation on lightness depend on the spatial arrangement of the articulated region
- ^ Kingdom, Fred (1997). "Simultaneous Contrast: The Legacies of Hering and Helmholtz". Perception. 26 (6): 673–677. doi:10.1068/p260673. PMID 9474338. S2CID 411796.
- ^ Chevreul, Michel Eugène (1839). De la loi du contraste simultané des couleurs et de l'assortiment des objets colorés – translated into English by Charles Martel as The Principles of Harmony and Contrast of Colors (1854) and by Dan Margulis as On the Law of Simultaneous Contrast of Colors (2020)
- ^ Hermann von Helmholtz: Handbuch der physiologischen Optik section II § 24: ‘Genauer unterscheidet Chevreul die hierher gehörigen Erscheinungen unter dem Namen des simultanen Contrastes von denjenigen, wo zwei Farben nach einander auf derselben Netzhautstelle erscheinen, welche er mit dem Namen des successiven Contrastes belegt.’
- ^ "Eye, human". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2008. Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD.
- ^ a b Kushner, Laura H. (2008). Contrast in judgments of mental health. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-549-91314-6. Retrieved 24 March 2011.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Plous, Scott (1993). The psychology of judgment and decision making. McGraw-Hill. pp. 38–41. ISBN 978-0-07-050477-6. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
- ^ Popper, Arthur N. (30 November 2010). Music Perception. Springer. p. 150. ISBN 978-1-4419-6113-6. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
- ^ Ndzendze, Bhaso. (23 March 2017). "Choosing 'the better evil'? The contrast effect and the relative nature of soft power". Modern Diplomacy. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
