Stefan Branković
Stefan Branković Стефан Бранковић | |
|---|---|
 from the Esphigmenou charter (1429) | |
| Despot of Serbia | |
| Reign | January 19, 1458 – March 21, 1459 |
| Predecessor | Lazar Branković |
| Successor | Stephen Tomašević |
| Born | c. 1417 Belgrade |
| Died | October 9, 1476 Castle Belgrado near Varmo |
| Burial | |
| Spouse | Angelina Arianiti |
| Issue | Đorđe Branković Jovan Branković Marija Branković |
| House | Branković |
| Father | Đurađ Branković |
| Mother | Irene Kantakouzene |
| Religion | Orthodox Christian (Serbian Church) |
Stefan Branković (Serbian Cyrillic: Стефан Бранковић; c. 1417 – 9 October 1476), also known in historiography as Stefan the Blind (Стефан Слепи), was briefly the despot (ruler) of the Serbian Despotate between 1458 and 1459. He was the last ruling member of the Branković dynasty.[1][2][3][4][5]
Family
[edit]Stefan and his relations are named in Dell'Imperadori Constantinopolitani (also known as the "Massarelli manuscript" after the work was found in papers of Angelo Massarelli, the general secretary of the Council of Trent[6]), a manuscript held in the Vatican Library.[7] This manuscript names him a son of Đurađ Branković and Eirene Kantakouzene. D. M. Nicol (1994) questioned his maternity, suggesting Đurađ had a prior marriage to a daughter of John IV of Trebizond. However his theory presented no sources and failed to take into account that John IV was born between 1395 and 1417. He would be unlikely to be a grandparent by the 1410s.[citation needed]
On 11 September 1429, Đurađ made a donation to Esphigmenou Monastery at Mount Athos. The charter for the document names his wife Irene and five children. The Masarelli manuscript also names the same five children of Đurađ and Eirene. Other genealogies mention a sixth child, Todor Branković. He could be a child who died young and thus not listed with his siblings.[citation needed] The oldest sibling listed in the Massarelli document was Grgur Branković. The 1429 document mentions him with the title of Despot. Grgur was appointed governor of territories of southern Serbia associated to the House of Branković.[8] He was reportedly appointed by Murad II of the Ottoman Empire in 1439. In April 1441, Grgur was accused of plotting against Murad and his governorship terminated. He was imprisoned in Amasya and blinded on 8 May 1441.[8] Grgur and his brothers co-signed a charter by which Đurađ confirmed the privileges to the Republic of Ragusa[9] Grgur retired to a monastery under the monastic name "German".[10] According to Fine, Grgur resurfaced in 1458, claiming the succession of the vacant throne of Serbia for himself or his son.[11] The Massarelli manuscript mentioned Grgur as unwed. Later genealogies name his wife as "Jelisaveta". Vuk Grgurević, a son of Grgur, was later a titular Serbian despot (1471–1485). He was possibly an illegitimate.[citation needed]
The Massarelli next names an older sister of Stefan, Mara Branković. She was one of the wives of Murad II.[citation needed] Stefan himself is listed third. His younger sister is listed as Cantacuzina, the Latinized version of their mother's last name. Later genealogies give her name as Katarina. She married Ulrich II of Celje. The last and youngest sibling listed was Lazar Branković, successor to their father.[citation needed]
Reign
[edit]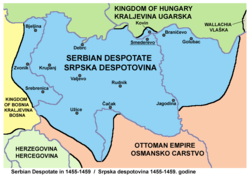
According to Nicol, Stefan had become a citizen of the Republic of Venice. He was blinded alongside his brother Grgur in 1441.[citation needed] Both blind brothers seem to have been omitted from considerations as possible heirs to their father. They could only claim the throne in 1458, since the death of Lazar left them the only male representatives of the Branković.
According to Fine, Stefan secured the throne by co-operating with his sister-in-law Helena Palaiologina, widow of Lazar. She was a daughter of Thomas Palaiologos, Despot of the Morea, and Catherine Zaccaria of the Principality of Achaea. Helena however arranged the marriage of one of her daughters to Stjepan Tomašević, prince of Bosnia. She thus managed to secure the throne for her new son-in-law.[citation needed] Matthias Corvinus of Hungary and Stjepan Tomaš Kotromanić, King of Bosnia and father of Tomašević, dethroned Stefan on April 8, 1459. They enthroned Stjepan Tomašević as his replacement. At the end of 1459 Stefan decided to travel to Albania, where he had relatives.[12] In mid-1460 he travelled to Albania where he married Angelina Arianit Komneni in November 1460. Angelina was the sister of Donika, who married Skanderbeg.[13] Skanderbeg gave to Stefan Branković an unknown estate as apanage.[12] At the beginning of 1461 Stefan Branković went to Italy with Skanderbeg's written recommendation.[12]
He gained (c. 1462) the Castle Belgrado, in the region of Friuli (northern Italy), where he lived with his family, until his death in 1476.[14]
Marriage and children
[edit]
In 1461, Stefan married Albanian princess Angelina Arianiti, daughter of the Arianiti Principality's ruler, Prince Gjergj Arianiti and Princess Maria Muzaka, eldest daughter of Despot Andrea III of Mosacchia. The couple had several children:[3]
- Đorđe (d. 18 January 1516). Titular Despot of Serbia, and noble in the Kingdom of Hungary. Married Isabella del Balzo, daughter of Agilberto, Duke of Nardò. Later retired as a monk under the monastic name "Maxim". Resurfaced as Metropolitan of Ungro-Wallachia from 1508 to 1521. He also held the title of Archbishop of Belgrade.
- Jovan (d. 10 December 1502). Titular Despot of Serbia, and noble in the Kingdom of Hungary. Married Jelena Jakšić. She is mentioned as "Helena, Serbiæ despotissa" in a charted dated to 1502.
- Irene: mentioned third in the Massarelli manuscript. Considered to have died young.
- Marija (died 27 August 1495). Mentioned fourth and last in the Massarelli manuscript. Married Boniface III, Marquess of Montferrat (1424–1494, reign 1483–1494).
Legacy
[edit]He is venerated as a Saint Stefan the Blind by the Serbian Orthodox Church.
Ancestry
[edit]| Ancestors of Stefan Branković | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Spremić 1982, p. 303-311.
- ^ Ćirković 2004, p. 107-108.
- ^ a b Spremić 2004, p. 445-446.
- ^ Fotić 2008a, p. 94.
- ^ Fotić 2008b, p. 518.
- ^ "The Archives: the past & the present", section "The Council of Trent" Archived 2008-10-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Tony Hoskins, "Anglocentric medieval genealogy" Archived 2011-07-16 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Fine 1994.
- ^ Miklosich (1858), p.[page needed]
- ^ Schwennicke 1878, p. 180
- ^ Fine 1994, p. 574.
- ^ a b c Ćirković 1982, p. 375.
- ^ Elsie, Robert (2000). A dictionary of Albanian religion, mythology and folk culture. New York University Press. p. 9. ISBN 0-8147-2214-8.
- ^ Spremić 2004, p. 445.
- ^ Brook, Lindsay L. (1989). "The Problematic Ascent of Eirene Kantakouzene Brankovič". Studies in Genealogy and Family History in Tribute to Charles Evans on the Occasion of His Eightieth Birthday. Salt Lake City, Utah : Association for the Promotion of Scholarship in Genealogy. p. 5.
- ^ Williams, Kelsey Jackson (2006). "A Genealogy of the Grand Komnenoi of Trebizond" (PDF). Foundations. 2 (3): 171–189. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 June 2019.
Sources
[edit]- Bataković, Dušan T., ed. (2005). Histoire du peuple serbe [History of the Serbian people]. Lausanne: L’Age d’Homme.
- Ćirković, Sima (1982). "Српска властела у борби за обнову Деспотовине" [Serbian nobility in the struggle for the restoration of the Despotate]. Историја српског народа [History of the Serbian people]. Vol. 2. Београд: Српска књижевна задруга. pp. 373–389.
- Ćirković, Sima (2004). The Serbs. Malden: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 9781405142915.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp Jr. (1994) [1987]. The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0472082604.
- Fotić, Aleksandar (2008a). "Branković family". Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire. New York: Infobase Publishing. pp. 93–94.
- Fotić, Aleksandar (2008b). "Serbia". Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire. New York: Infobase Publishing. pp. 517–519.
- Ivanović, Miloš (2018). "The Nobility of the Despotate of Serbia between Ottoman Empire and Hungary (1457-1459)". Secular Power and Sacral Authority in Medieval East-Central Europe. Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press. pp. 167–177. ISBN 9789462981669.
- Miklosich, Franz (1858), Monumenta Serbica Spectantia Historiam Serbiae, Bosniae, Ragusii
- Odak, Marina I. (2015). "Ikonografija i simbolika predstava na srpskom srednjovekovnom novcu". Belgrade: Filozofski fakultet.
- Porčić, Nebojša. "Документи Лазара и Стефана Бранковића о подизању поклада деспота Ђурђа." Иницијал. Часопис за средњовековне студије 2 (2014): 215–239.
- Schwennicke, Detlev (1878), Europäische Stammtafeln: Stammtafeln zur Geschichte der Europäischen Staaten, vol. 3, p. 180
- Spremić, Momčilo (1982). "Пропаст средњовековне државе" [The fall of the medieval state]. Историја српског народа [History of the Serbian people]. Vol. 2. Београд: Српска књижевна задруга. pp. 303–313.
- Spremić, Momčilo (2004). "La famille serbe des Branković – considérations généalogiques et héraldiques" (PDF). Зборник радова Византолошког института (in French). 41: 441–452.

