Soleal line
| Soleal line | |
|---|---|
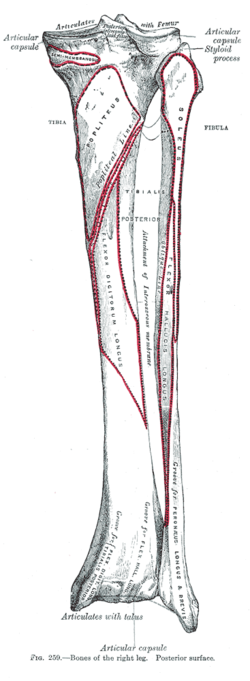 Bones of the right leg. Posterior surface. (Popliteal line visible at top center.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | linea musculi solei |
| TA98 | A02.5.06.015 |
| TA2 | 1417 |
| FMA | 43773 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The soleal line, also known as the popliteal line (in older texts), is a prominent ridge on the posterior surface of the tibia. It is the site of many muscle origins and insertions, such as those of popliteus muscle, soleus muscle, flexor digitorum longus muscle, and tibialis posterior muscle.
Structure
[edit]The soleal line is a prominent ridge on the posterior surface of the tibia. It extends obliquely downward from the back part of the articular facet for the fibula to the medial border, at the junction of its upper and middle thirds.
Development
[edit]The soleal line becomes more prominent between childhood and adulthood.[1] It is rarely seen in children between the ages of 6 and 8.[1]
Function
[edit]The soleal line marks the lower limit of the insertion of the popliteus muscle.[2] It is the attachment of the fascia covering this muscle. It is the origin of part of soleus muscle (along with a triangular area above it),[3] flexor digitorum longus muscle, and tibialis posterior muscle.
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 258 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 258 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b Cunningham, Craig; Scheuer, Louise; Black, Sue (2016-01-01). "Chapter 12 - The Lower Limb". The Lower Limb. Academic Press. pp. 385–472. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-382106-5.00012-8. ISBN 978-0-12-382106-5.
- ^ Chaitow, Leon; DeLany, Judith (2011-01-01). "Chapter 13 - The knee". Clinical Application of Neuromuscular Techniques. Vol. 2 (2nd ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 447–501. doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-06815-7.00013-9. ISBN 978-0-443-06815-7.
- ^ Woo, Eun Jin; Pak, Sunyoung (2013-04-01). "Degenerative joint diseases and enthesopathies in a Joseon Dynasty population from Korea". HOMO. 64 (2). Elsevier: 104–119. doi:10.1016/j.jchb.2013.02.001. ISSN 0018-442X. PMID 23477801 – via ScienceDirect.
External links
[edit]- Description at uams.edu
- Mysorekar V, Nandedkar A (1983). "The soleal line". Anat Rec. 206 (4): 447–51. doi:10.1002/ar.1092060410. PMID 6625203. S2CID 43473407.
