Monosodium xenate
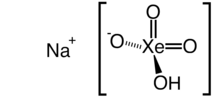
| |||

| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| NaHXeO4 | |||
| Molar mass | 219.29 g/mol | ||
| Properties | |||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Soluble, decomposes in water[1] | |||
| Solubility | insoluble chloroform, methanol, ethanol, and carbon tetrachloride[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
extremely unstable, vigorous oxidizer | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | Non-Flammable | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Monosodium xenate is the sodium salt of xenic acid with formula NaHXeO4. It is a powerful oxidizer, owing to being a highly reactive compound of xenon.[2]
Synthesis
[edit]Monosodium xenate can be made by mixing solutions of xenon trioxide and sodium hydroxide, followed by freezing to liquid nitrogen temperatures, and dehydrating in a vacuum.[1]
Properties
[edit]Monosodium xenate usually exists in the sesquihydrate form, with 1.5 waters of hydration per unit molecule. It is stable up to 160 °C heated in a pure state. However it can explode when subjected to mechanical shock, or lower temperatures when mixed with XeO3.[1] Sodium xenate is slightly toxic with a median lethal dose between 15 and 30 mg/kg of body weight in mice. Xenate leaves the body very quickly. In mice, the level in blood drops by half in twenty seconds due to it being decomposed and exhaled. In the peritoneum the half-life extends to six minutes.[3]
The dialkali xenates XeO42- have not been discovered, as xenate disproportionates in more alkaline conditions, hence it being rare to the find the dialkaline salt Na2XeO4.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e Spittler, T. M.; Jaselskis, Bruno (August 1965). "Preparation and Properties of Monoalkali Xenates". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 87 (15): 3357–3360. doi:10.1021/ja01093a013.
- ^ Peterson, Jeffrey L.; Claassen, Howard H.; Appelman, Evan H. (March 1970). "Vibrational spectra and structures of xenate(VI) and perxenate(VIII) ions in aqueous solution". Inorganic Chemistry. 9 (3): 619–621. doi:10.1021/ic50085a037.
- ^ Finkel, A. J.; Miller, C. E.; Katz, J. J. (April 1968). "Metabolic and Toxicological Effects of Water-Soluble Xenon Compounds Are Studied" (PDF). Atomic Energy Commission USA.



