Shoulder: Difference between revisions
m Reverted unexplained removal of content (HG) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 203: | Line 203: | ||
| pmid =2860095 | doi = 10.1007/s10764-010-9399-1 |
| pmid =2860095 | doi = 10.1007/s10764-010-9399-1 |
||
}}</ref> |
}}</ref> |
||
==Imaging== |
|||
===Variability=== |
|||
'' |
|||
<big>SKIZZEN?! TEXT?! SIEHE ORIGINALFILE!!!</big>'' |
|||
'''Labrum:'''<br /> |
|||
The glenoid labrum is a wedge shaped fibro cartilaginous structure that is fixed at the glenoid border of the scapula and surrounds the glenoid like a wreath. The labrum doubles the joint surface of the glenoid for the humeral head and is also responsible for a certain stability in the antero posterior movements. The following variants from the norm can be mis-interpreted as so-called SLAP lesions.<br /> |
|||
1. The sublabral superior recess<br /> |
|||
2. The sublabral foramen<br /> |
|||
3. The Buford complex<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
And furthermore:<br /> |
|||
4. In 50% of the cases a triangular linear signal increasement can be found at the area of the anterior labrum through hyaline cartilage. This is the most common shape and accounts for 73% in the posterior area and for 45% in the anterior area.<br /> |
|||
5. In 20% of the cases the labrum is rounded.<br /> |
|||
6. In 7% of the cases the labrum is comma-shaped flattened.<br /> |
|||
7. In 15% of the cases the labrum is splitted.<br /> |
|||
8. In 8% of the cases the labrum is notched.<br /> |
|||
9. The labrum has a central signal increasement.<br /> |
|||
10. The labrum has a linear signal increasement.<br /> |
|||
<ref>MR Diagnostics of Glenoid Labrum Changes in Patients with Unstable Shoulder Joints; J. Jerosch</ref> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
'''Superior labrum and biceps tendon:'''<br /> |
|||
'''The sublabral superior recess,'''<br /> |
|||
which is depicted at the 12 o’clock position in the oblique sagittal projection.<br /> |
|||
'''Type 1:''' The labral bicipital complex is entirely fixed at the glenoidal rim, that’s why the glenoid cannot be distinguished arthroscopically from the labrum. Park et al. examined 95 asymptomatic shoulders using MRA and was able to demonstrate a recess in 30%.<ref>MR imaging of variants of the superior labral-bicipital complex and SLAP lesions; Wörtler K.</ref><br /> |
|||
'''Type 2:''' A narrow sulcus between the labrum and the glenoid rim.<br /> |
|||
'''Type 3:''' An extended sulcus between the labrum and the glenoid rim, which allows now an arthroscopical distinction between labrum and glenoidal cartilage.<br /> |
|||
{| |
|||
| [[File:MRI. Anterior sublabral recess..jpg|thumb|MRI. Anterior sublabral recess.]] |
|||
|} |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
'''The sublabral foramen.'''<br /> |
|||
It can be found in around 11% of the cases and should not be confused with a sublabral superior recess. The range of the foramen is large. From only few milimeters up to a complete ablation of the anterosuperior labrum. In contrast to the sublabral superior recess, is the sublabral superior foramen depictable in the oblique sagittal projection positioned antero-superiorly at 2 o’clock. And Inflow of contrast agent can be seen at the axial sequence between labrum and glenoid.<ref>MR imaging of variants of the superior labral-bicipital complex and SLAP lesions; Wörtler K.</ref> It is therefore more anterior of the biceps tendon insertion. It can sometimes be found combined with a sublabral superior recess. The through an intraarticular contrast agent injection enhanced MR imaging, can lead to a false positive interpretation as a labral injury. This variation of the norm is positioned anterosuperiorly. Bankart lesions for example have an anteroinferior localisation.<ref>MR imaging of variants of the superior labral-bicipital complex and SLAP lesions; Wörtler K.</ref> |
|||
'''The Buford complex'''<br /> |
|||
can be found in 1.5% of the population. It consists of a ribbon-like thickening of the medial glenohumeral ligament (GHL) and is further characterized by a lack of anterior superior labrum. The medial GHL inserts just at the area of the antero superior glenoid. A thickened medial GHL can be confused with a displaced labral fragment on the arthroscope. |
|||
{| |
|||
| [[File:MRI. Buford complex..jpg|thumb|File:MRI. Buford complex.]] |
|||
|} |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
<br /> |
|||
==Additional images== |
==Additional images== |
||
Revision as of 20:09, 4 October 2011
| Shoulder | |
|---|---|
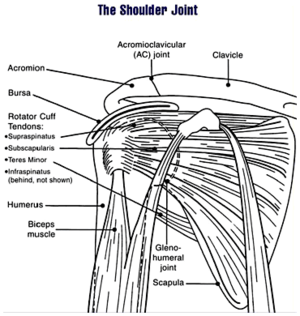 Diagram of the human shoulder joint | |
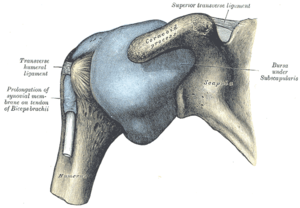 Capsule of shoulder-joint (distended). Anterior aspect. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | articulatio humeri |
| MeSH | D012782 |
| TA98 | A01.1.00.020 |
| TA2 | 139 |
| FMA | 25202 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The major joint of the shoulder is the glenohumeral joint, which "shoulder joint" generally refers to. In human anatomy, the shoulder joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula, the head sitting in the glenoid fossa.[1] The shoulder is the group of structures in the region of the joint.[2]
There are two kinds of cartilage in the joint. The first type is the white cartilage on the ends of the bones (called articular cartilage) which allows the bones to glide and move on each other. When this type of cartilage starts to wear out (a process called arthritis), the joint becomes painful and stiff. The labrum is a second kind of cartilage in the shoulder which is distinctly different from the articular cartilage. This cartilage is more fibrous or rigid than the cartilage on the ends of the ball and socket. Also, this cartilage is also found only around the socket where it is attached.[3]
The shoulder must be mobile enough for the wide range actions of the arms and hands, but also stable enough to allow for actions such as lifting, pushing and pulling. The compromise between mobility and stability results in a large number of shoulder problems not faced by other joints such as the hip.
Human anatomy
Joints
There are three joints of the shoulder: The glenohumeral, acromioclavicular, and the sternoclavicular joints.
Glenohumeral joint
The glenohumeral joint is the main joint of the shoulder and the generic term "shoulder joint" usually refers to it. It is a ball and socket joint that allows the arm to rotate in a circular fashion or to hinge out and up away from the body. It is formed by the articulation between the head of the humerus and the lateral scapula (specifically-the glenoid fossa of the scapula). The "ball" of the joint is the rounded, medial anterior surface of the humerus and the "socket" is formed by the glenoid fossa, the dish-shaped portion of the lateral scapula. The shallowness of the fossa and relatively loose connections between the shoulder and the rest of the body allows the arm to have tremendous mobility, at the expense of being much easier to dislocate than most other joints in the body.Approximately its 4 to 1 disproportion between the large head of the humerus and the shallow glenoid cavity.
The capsule is a soft tissue envelope that encircles the glenohumeral joint and attaches to the scapula, humerus, and head of the biceps. It is lined by a thin, smooth synovial membrane. This capsule is strengthened by the coracohumeral ligament which attaches the coracoid process of the scapula to the greater tubercle of the humerus. There are also three other ligaments attaching the lesser tubercle of the humerus to lateral scapula and are collectively called the glenohumeral ligaments.
There is also a ligament called semicirculare humeri which is a transversal band between the posterior sides of the tuberculum minus and majus of the humerus. This band is one of the most important strengthening ligaments of the joint capsule. The shoulder is a vital joint and critical for movement.
Sternoclavicular joint
The sternoclavicular occurs at the medial end of the clavicle with the manubrium or top most portion of the sternum. The clavicle is triangular and rounded and the manubrium is convex; the two bones articulate. The joint consists of a tight capsule and complete intra-articular disc which ensures stability of the joint. The costoclavicular ligament is the main limitation to movement, therefore, the main stabilizer of the joint. A fibrocartilaginous disc present at the joint increases the range of movement. Sternoclavicular dislocation is rare,[4] however it can be caused by direct trauma.
Movements
The muscles and joints of the shoulder allow it to move through a remarkable range of motion, making it one of the most mobile joints in the human body. The shoulder can abduct, adduct (such as during the shoulder fly), rotate, be raised in front of and behind the torso and move through a full 360° in the sagittal plane. This tremendous range of motion also makes the shoulder extremely unstable, far more prone to dislocation and injury than other joints [5]
The following describes the terms used for different movements of the shoulder: [6]
| Name | Description | Muscles |
|---|---|---|
| Scapular retraction [7] (aka adduction of the scapula) | The scapula is moved posteriorly and medially along the back, moving the arm and shoulder joint posteriorly. Retracting both scapulae gives a sensation of "squeezing the shoulder blades together." | rhomboideus major, minor, and trapezius |
| Scapular protraction[7] (aka abduction of the scapula) | The opposite motion of scapular retraction. The scapula is moved anteriorly and laterally along the back, moving the arm and shoulder joint anteriorly. If both scapulae are protracted, the scapulae are separated and the pectoralis major muscles are squeezed together. | serratus anterior (prime mover), pectoralis minor and major |
| Scapular elevation [8] | The scapula is raised in a shrugging motion. | levator scapulae, the upper fibers of the trapezius |
| Scapular depression [8] | The scapula is lowered from elevation. The scapulae may be depressed so that the angle formed by the neck and shoulders is obtuse, giving the appearance of "slumped" shoulders. | pectoralis minor, lower fibers of the trapezius, subclavius, latissimus dorsi |
| Arm abduction [9] | Arm abduction occurs when the arms are held at the sides, parallel to the length of the torso, and are then raised in the plane of the torso. This movement may be broken down into two parts: True abduction of the arm, which takes the humerus from parallel to the spine to perpendicular; and upward rotation of the scapula, which raises the humerus above the shoulders until it points straight upwards. | True abduction: supraspinatus (first 15 degrees), deltoid; Upward rotation: trapezius, serratus anterior |
| Arm adduction [10] | Arm adduction is the opposite motion of arm abduction. It can be broken down into two parts: downward rotation of the scapula and true adduction of the arm. | Downward rotation: pectoralis minor, pectoralis major, subclavius, latissimus dorsi (same as scapular depression, with pec major replacing lower fibers of trapezius); True Adduction: same as downward rotation with addition of teres major and the lowest fibers of the deltoid |
| Arm flexion [11] | The humerus is rotated out of the plane of the torso so that it points forward (anteriorly). | pectoralis major, coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, anterior fibers of deltoid. |
| Arm extension [11] | The humerus is rotated out of the plane of the torso so that it points backwards (posteriorly) | latissimus dorsi and teres major, long head of triceps, posterior fibers of the deltoid |
| Medial rotation of the arm [12] | Medial rotation of the arm is most easily observed when the elbow is held at a 90-degree angle and the fingers are extended so they are parallel to the ground. Medial rotation occurs when the arm is rotated at the shoulder so that the fingers change from pointing straight forward to pointing across the body. | subscapularis, latissimus dorsi, teres major, pectoralis major, anterior fibers of deltoid |
| Lateral rotation of the arm[12] | The opposite of medial rotation of the arm. | infraspinatus and teres minor, posterior fibers of deltoid |
| Arm circumduction[13] | Movement of the shoulder in a circular motion so that if the elbow and fingers are fully extended the subject draws a circle in the air lateral to the body. In circumduction, the arm is not lifted above parallel to the ground so that "circle" that is drawn is flattened on top. | pectoralis major, subscapularis, coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, supraspinatus, deltoid, latissimus dorsi, teres major and minor, infraspinatus, long head of triceps |
Muscles
Major muscles
The muscles that are responsible for movement in the shoulder attach to the scapula, humerus, and clavicle. The muscles that surround the shoulder form the shoulder cap and underarm.
| Name | Attachment | Function |
| serratus anterior | Originates on the surface of the upper eight ribs at the side of the chest and inserts along the entire anterior length of the medial border of the scapula. | It fixes the scapula into the thoracic wall and aids in rotation and abduction of the shoulders. |
| subclavius | Located inferior to the clavicle, originating on the first rib and inserting (penetrating) on the subclavian groove of the clavicle. | It depresses the lateral clavicle and also acts to stabilize the clavicle. |
| pectoralis minor | Arises from the third, fourth, and fifth ribs, near their cartilage and inserts into the medial border and upper surface of the coracoid process of the scapula. | This muscle aids in respiration, medially rotates the scapula, protracts the scapula, and also draws the scapula inferiorly. |
| sternocleidomastoid | Attaches to the sternum (sterno-), the clavicle (cleido-), and the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull. | Most of its actions flex and rotate the head. In regards to the shoulder, however, it also aids in respiration by elevating the sternoclavicular joint when the head is fixed. |
| levator scapulae | Arises from the transverse processes of the first four cervical vertebrae and inserts into the medial border of the scapula. | It is capable of rotating the scapula downward and elevating the scapula. |
| rhomboid major and rhomboid minor (work together) | They arise from the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae T1 to T5 as well as from the spinous processes of the seventh cervical. They insert on the medial border of the scapula, from about the level of the scapular spine to the scapula's inferior angle. | They are responsible for downward rotation of the scapula with the levator scapulae, as well as adduction of the scapula. |
| trapezius | Arises from the occipital bone, the ligamentum nuchae, the spinous process of the seventh cervical, and the spinous processes of all the thoracic vertebrae, and from the corresponding portion of the supraspinal ligament. It inserts on the lateral clavicle, the acromion process, and into the spine of the scapula. | Different portions of the fibers perform different actions on the scapula: depression, upward rotation, elevation, and adductions. |
| deltoid, anterior fibers | Arises from the anterior border and upper surface of the lateral third of the clavicle. | The anterior fibres are involved in shoulder abduction when the shoulder is externally rotated. The anterior deltoid is weak in strict transverse flexion but assists the pectoralis major during shoulder transverse flexion / shoulder flexion (elbow slightly inferior to shoulders). |
| deltoid, middle fibers | Arises from the lateral margin and upper surface of the acromion. | The middle fibres are involved in shoulder abduction when the shoulder is internally rotated, are involved in shoulder flexion when the shoulder is internally rotated, and are involved in shoulder transverse abduction (shoulder externally rotated) -- but are not utilized significantly during strict transverse extension (shoulder internally rotated). |
| deltoid, posterior fibers | Arises from the lower lip of the posterior border of the spine of the scapula, as far back as the triangular surface at its medial end. | The posterior fibres are strongly involved in transverse extension particularly since the latissimus dorsi muscle is very weak in strict transverse extension. The posterior deltoid is also the primary shoulder hyperextensor. |
Rotator cuff
The rotator cuff is an anatomical term given to the group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the shoulder. It is composed of the tendons and muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor and subscapularis) that hold the head of the humerus (ball) in the glenoid fossa (socket).
Two filmy sac-like structures called bursae permit smooth gliding between bone, muscle, and tendon. They cushion and protect the rotator cuff from the bony arch of the acromion.
Medical problems
Shoulder problems including pain, are one of the more common reasons for physician visits for musculoskeletal symptoms. The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. This instability increases the likelihood of joint injury, often leading to a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well.
Major injuries to the shoulder include rotator cuff tear and bone fractures of one or more of the bones of the shoulder.
Shoulder fractures include:
Evolutionary variation
Tetrapod forelimb are characterised by a high degree of mobility in the shoulder-thorax connection. Lacking of a solid skeletal connection between the shoulder girdle and the vertebral column, the forelimb's attachment to the trunk is instead mainly controlled by serratus lateralis and levator scapulae. Depending on locomotor style, a bone connect the shoulder girdle to the trunk in some animals; the coracoid bone in reptiles and birds, and the clavicle in primates and bats; but cursorial mammals lack this bone. In primates, the shoulder shows characteristics the differs from other mammals, including a well developed clavicle, a dorsally shifted scapula with prominent acromion and spine, and a humerus featuring a straight shaft and a spherical head. [14]
Imaging
Variability
SKIZZEN?! TEXT?! SIEHE ORIGINALFILE!!!
Labrum:
The glenoid labrum is a wedge shaped fibro cartilaginous structure that is fixed at the glenoid border of the scapula and surrounds the glenoid like a wreath. The labrum doubles the joint surface of the glenoid for the humeral head and is also responsible for a certain stability in the antero posterior movements. The following variants from the norm can be mis-interpreted as so-called SLAP lesions.
1. The sublabral superior recess
2. The sublabral foramen
3. The Buford complex
And furthermore:
4. In 50% of the cases a triangular linear signal increasement can be found at the area of the anterior labrum through hyaline cartilage. This is the most common shape and accounts for 73% in the posterior area and for 45% in the anterior area.
5. In 20% of the cases the labrum is rounded.
6. In 7% of the cases the labrum is comma-shaped flattened.
7. In 15% of the cases the labrum is splitted.
8. In 8% of the cases the labrum is notched.
9. The labrum has a central signal increasement.
10. The labrum has a linear signal increasement.
[15]
Superior labrum and biceps tendon:
The sublabral superior recess,
which is depicted at the 12 o’clock position in the oblique sagittal projection.
Type 1: The labral bicipital complex is entirely fixed at the glenoidal rim, that’s why the glenoid cannot be distinguished arthroscopically from the labrum. Park et al. examined 95 asymptomatic shoulders using MRA and was able to demonstrate a recess in 30%.[16]
Type 2: A narrow sulcus between the labrum and the glenoid rim.
Type 3: An extended sulcus between the labrum and the glenoid rim, which allows now an arthroscopical distinction between labrum and glenoidal cartilage.
 |
The sublabral foramen.
It can be found in around 11% of the cases and should not be confused with a sublabral superior recess. The range of the foramen is large. From only few milimeters up to a complete ablation of the anterosuperior labrum. In contrast to the sublabral superior recess, is the sublabral superior foramen depictable in the oblique sagittal projection positioned antero-superiorly at 2 o’clock. And Inflow of contrast agent can be seen at the axial sequence between labrum and glenoid.[17] It is therefore more anterior of the biceps tendon insertion. It can sometimes be found combined with a sublabral superior recess. The through an intraarticular contrast agent injection enhanced MR imaging, can lead to a false positive interpretation as a labral injury. This variation of the norm is positioned anterosuperiorly. Bankart lesions for example have an anteroinferior localisation.[18]
The Buford complex
can be found in 1.5% of the population. It consists of a ribbon-like thickening of the medial glenohumeral ligament (GHL) and is further characterized by a lack of anterior superior labrum. The medial GHL inserts just at the area of the antero superior glenoid. A thickened medial GHL can be confused with a displaced labral fragment on the arthroscope.
 |
Additional images
-
The left shoulder and acromioclavicular joints, and the proper ligaments of the scapula
-
Instrumented shoulder endoprosthesis, with a 9-channel telemetry transmitter to measure six load components in vivo. (cut model)
See also
- Shoulder girdle (Pectoral girdle)
- Glenohumeral joint (Shoulder joint)
- Acromioclavicular joint
- Sternoclavicular joint
- Chip on shoulder
References
- ^ Template:EMedicineDictionary[dead link]
- ^ Template:EMedicineDictionary[dead link]
- ^ "labrum tear Johns Hopkins Orthopaedic Surgery". www.hopkinsortho.org. Retrieved 2010-05-16.
- ^ Cadogan, Mike (2010). "Sternoclavicular Joint Dislocations". Life in the Fast Lane. Retrieved June 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Scientific Keys Volume I, The Key Muscles of Hatha Yoga, Ray Long MD FRCSC, Third Edition, pg. 174
- ^ "Movements of the Upper Limb — Introduction". University of Michigan Medical School. 2002. Retrieved December 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b "Scapular Protraction and Retraction". University of Michigan Medical School. 2002. Retrieved December 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b "Scapular Elevation and Depression". University of Michigan Medical School. 2002. Retrieved December 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Arm Abduction". University of Michigan Medical School. 2002. Retrieved December 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Arm Adduction". University of Michigan Medical School. 2002. Retrieved December 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b "Arm Flexion and Extension". University of Michigan Medical School. 2002. Retrieved December 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ a b "Arm Medial and Lateral Rotation". University of Michigan Medical School. 2002. Retrieved December 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Arm Circumduction". University of Michigan Medical School. 2002. Retrieved December 2010.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Preuschoft, Holger; Hohn, Bianca; Scherf, Heike; Schmidt, Manuela (2010). "Functional Analysis of the Primate Shoulder". Int J Primatol. 31 (2): 301–320. doi:10.1007/s10764-010-9399-1. PMID 2860095.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ MR Diagnostics of Glenoid Labrum Changes in Patients with Unstable Shoulder Joints; J. Jerosch
- ^ MR imaging of variants of the superior labral-bicipital complex and SLAP lesions; Wörtler K.
- ^ MR imaging of variants of the superior labral-bicipital complex and SLAP lesions; Wörtler K.
- ^ MR imaging of variants of the superior labral-bicipital complex and SLAP lesions; Wörtler K.

