Salome (opera): Difference between revisions
m better picture |
m Undid revision 603524473 by Meister und Margarita (talk): restore hatnote & navigation box which implements italic title. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{about|the opera by Richard Strauss|the opera by Antoine Mariotte|Salomé (Mariotte)}} |
|||
[[File:Theo-Zasche Strauss-Richard.jpg | thumb | Richard Strauss]] |
|||
{{Richard Strauss operas}} |
|||
'''''Salome''''', Op. 54, is an [[opera]] in one act by [[Richard Strauss]] to a German [[libretto]] by the composer, based on [[Hedwig Lachmann]]'s German translation of the French play ''[[Salome (play)|Salomé]]'' by [[Oscar Wilde]]. Strauss dedicated the opera to his friend [[Edgar Speyer|Sir Edgar Speyer]].<ref name="dedication">{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.boosey.com/includes/imgview.asp?img=/images/print/Music/M060026010%5Fmus%2Ejpg |
|||
|accessdate=13 December 2008 |
|||
|title = ''Salome'' |
|||
|publisher=[[Boosey & Hawkes]] |
|||
|quote= Dedication: Meinem Freunde Sir Edgar Speyer |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
The opera is famous (at the time of its premiere, infamous) for its "[[Dance of the Seven Veils]]". It is now better known for the more shocking final scene (often a concert-piece for [[dramatic soprano]]s), where Salome declares her love to – and kisses – the severed head of [[John the Baptist]]. |
The opera is famous (at the time of its premiere, infamous) for its "[[Dance of the Seven Veils]]". It is now better known for the more shocking final scene (often a concert-piece for [[dramatic soprano]]s), where Salome declares her love to – and kisses – the severed head of [[John the Baptist]]. |
||
| Line 15: | Line 23: | ||
[[Gustav Mahler]] could not gain the consent of the Vienna censor to have it performed, therefore it was not given at the [[Vienna State Opera]] until 1918. The Austrian premiere was given at the [[Graz Opera]] in 1906 under the composer, with [[Arnold Schoenberg]], [[Giacomo Puccini]], [[Alban Berg]], and Gustav Mahler in the audience. |
[[Gustav Mahler]] could not gain the consent of the Vienna censor to have it performed, therefore it was not given at the [[Vienna State Opera]] until 1918. The Austrian premiere was given at the [[Graz Opera]] in 1906 under the composer, with [[Arnold Schoenberg]], [[Giacomo Puccini]], [[Alban Berg]], and Gustav Mahler in the audience. |
||
''Salome'' was banned in London by the [[Lord Chamberlain]]'s office until 1907. When it was given its premiere performance at [[Royal Opera House|Covent Garden]] in London under [[Thomas Beecham]] on 8 December 1910,<ref name="Holden" /> it was modified, much to Beecham's annoyance and later amusement. In |
''Salome'' was banned in London by the [[Lord Chamberlain]]'s office until 1907. When it was given its premiere performance at [[Royal Opera House|Covent Garden]] in London under [[Thomas Beecham]] on 8 December 1910,<ref name="Holden" /> it was modified, much to Beecham's annoyance and later amusement. In New York, the premiere took place on 22 January 1907 after which, under pressure from wealthy patrons, "further performances were cancelled."<ref name="Holden" /> These patrons entreated the visiting [[Edward Elgar]] to lead the objections to the work, but he refused point-blank, stating that Strauss was "the greatest genius of the age".<ref>Liner notes to the recording of ''Salome'' with [[Birgit Nilsson]] and the [[Vienna Philharmonic]] under [[Georg Solti]]. Decca Records, 19XX</ref> |
||
Today, ''Salome'' is a well-established part of the operatic repertoire; there are numerous recordings. |
Today, ''Salome'' is a well-established part of the operatic repertoire; there are numerous recordings. |
||
Revision as of 04:48, 10 April 2014
Template:Richard Strauss operas Salome, Op. 54, is an opera in one act by Richard Strauss to a German libretto by the composer, based on Hedwig Lachmann's German translation of the French play Salomé by Oscar Wilde. Strauss dedicated the opera to his friend Sir Edgar Speyer.[1]
The opera is famous (at the time of its premiere, infamous) for its "Dance of the Seven Veils". It is now better known for the more shocking final scene (often a concert-piece for dramatic sopranos), where Salome declares her love to – and kisses – the severed head of John the Baptist.
Composition history
Oscar Wilde originally wrote his Salomé in French. Strauss saw the play in Lachmann's version and immediately set to work on an opera. The play's formal structure was well-suited to musical adaptation. Wilde himself described Salomé as containing "refrains whose recurring motifs [Wilde's emphasis] make it so like a piece of music and bind it together as a ballad".[2]
Strauss composed the opera in German, and that is the version that has become widely known. It has a long history, however, of being presented also in French, which was the language in which perhaps the world's most famous proponent of the role, Mary Garden, sang the opera in New York, Chicago, Milwaukee, Paris, and other cities. Soprano Marjorie Lawrence sang the role in both French (for Paris) and German (for the Metropolitan Opera, New York) in the 1930s. In 1930, Strauss made an alternate version in French, the language of the original Oscar Wilde play. This version is less known today, although it was revived in Lyon in 1990,[3] performances of which were recorded by Kent Nagano with Karen Huffstodt in the title role and José van Dam as Jochanaan.[4] In 2011, the French version was staged by Liège Opera, starring June Anderson.
Performance history
The combination of the Christian biblical theme, the erotic and the murderous, which so attracted Wilde to the tale, shocked opera audiences from its first appearance. Some of the original performers were very reluctant to handle the material as written and the Salome, Marie Wittich, "refused to perform the 'Dance of the Seven Veils'", thus creating a situation where a dancer stood in for her.[3]
It was first performed at the Hofoper in Dresden on 9 December 1905, and within two years, it had been given in 50 other opera houses.[3]
Gustav Mahler could not gain the consent of the Vienna censor to have it performed, therefore it was not given at the Vienna State Opera until 1918. The Austrian premiere was given at the Graz Opera in 1906 under the composer, with Arnold Schoenberg, Giacomo Puccini, Alban Berg, and Gustav Mahler in the audience.
Salome was banned in London by the Lord Chamberlain's office until 1907. When it was given its premiere performance at Covent Garden in London under Thomas Beecham on 8 December 1910,[3] it was modified, much to Beecham's annoyance and later amusement. In New York, the premiere took place on 22 January 1907 after which, under pressure from wealthy patrons, "further performances were cancelled."[3] These patrons entreated the visiting Edward Elgar to lead the objections to the work, but he refused point-blank, stating that Strauss was "the greatest genius of the age".[5]
Today, Salome is a well-established part of the operatic repertoire; there are numerous recordings.
Roles
| Role | Voice type | Premiere cast, 9 December 1905 Conductor: Ernst von Schuch |
|---|---|---|
| Herodes, Tetrarch of Judaea and Perea | tenor | Karel Burian |
| Herodias, his wife (and sister-in-law) | mezzo-soprano | de |
| Salome, his stepdaughter (and niece) | soprano | Marie Wittich |
| Jochanaan (John the Baptist) | baritone | Karl Perron |
| Narraboth, Captain of the Guard | tenor | Rudolf Ferdinand Jäger |
| The Page of Herodias | contralto | de |
| First Jew | tenor | Hans Rüdiger |
| Second Jew | tenor | Hans Saville |
| Third Jew | tenor | Georg Grosch |
| Fourth Jew | tenor | Anton Erl |
| Fifth Jew | bass | Léon Rains |
| First Nazarene | bass | Theodor Kruis |
| Second Nazarene | tenor | Friedrich Plaschke |
| First soldier | bass | Franz Nebuschka |
| Second soldier | bass | Hans Erwin (Hans Erwin Hey) |
| A Cappadocian | bass | Ernst Wachter |
| A slave | soprano/tenor | Maria Keldorfer |
| Royal guests (Egyptians and Romans), and entourage, servants, soldiers (all silent) | ||
Synopsis

A great terrace in the Palace of Herod, set above the banqueting hall. Some soldiers are leaning over the balcony. To the right there is a gigantic staircase, to the left, at the back, an old cistern surrounded by a wall of green bronze. The moon is shining very brightly.
Narraboth gazes from a terrace in Herod's palace into the banquet hall at the beautiful Princess Salome; he is in love with her, and apotheosizes her, much to the disgusted fearfulness of the Page of Herodias. The voice of the Prophet Jochanaan is heard from his prison in the palace cistern; Herod fears him and has ordered that no one should contact him, including Jerusalem's High Priest.
Tired of the feast and its guests, Salome flees to the terrace. When she hears Jochanaan cursing her mother (Herodias), Salome's curiosity is piqued. The palace guards will not honor her petulant orders to fetch Jochanaan for her, so she teasingly works on Narraboth to bring Jochanaan before her. Despite the orders he has received from Herod, Narraboth finally gives in after she promises to smile at him.
Jochanaan emerges from the cistern and shouts prophecies regarding Herod and Herodias that no one understands, except Salome when the Prophet refers to her mother. Upon seeing Jochanaan, Salome is filled with an overwhelming desire for him, praising his white skin and asking to touch it, but he rejects her. She then praises his black hair, again asking to touch it, but is rejected once more. She finally begs for a kiss from Jochanaan's lips, and Narraboth, who cannot bear to hear this, kills himself. As Jochanaan is returned to the well, he preaches salvation through the Messiah.
Herod enters, followed by his wife and court. He slips in Narraboth's blood and starts hallucinating. He hears the beating of wings. Despite Herodias' objections, Herod stares lustfully at Salome, who rejects him. Jochanaan harasses Herodias from the well, calling her incestuous marriage to Herod sinful. She demands that Herod silence him. Herod refuses, and she mocks his fear. Five Jews argue concerning the nature of God. Two Nazarenes tell of Christ's miracles; at one point they bring up the raising of Jairus' daughter from the dead, which Herod finds frightening.
Herod asks for Salome to eat with him, drink with him; indolently, she twice refuses, saying she is not hungry or thirsty. Herod then begs Salome to dance for him, Tanz für mich, Salome, though her mother objects. He promises to reward her with her heart's desire – even if it were one half of his kingdom.
After Salome inquires into his promise, and he swears to honor it, she prepares for the "Dance of the Seven Veils". This dance, very oriental in orchestration, has her slowly removing her seven veils, until she lies naked at his feet. Salome then demands the head of the prophet on a silver platter. Her mother cackles in pleasure. Herod tries to dissuade her with offers of jewels, peacocks, and the sacred veil of the Temple. Salome remains firm in her demand for Jochanaan's head, forcing Herod to concede to her demands. After a desperate monologue by Salome, the head of the prophet is brought up out of the well and presented to Salome as she requested.
Salome declares her love to the severed head, finally kissing the prophet's lips passionately. Disgusted, the terrified and superstitious Herod then orders his soldiers to kill Salome.
Instrumentation
Strauss scored Salome for the following large orchestra:
- Woodwinds: piccolo, 3 flutes, 2 oboes, English horn, heckelphone, E-flat clarinet, 2 clarinets in B-flat, 2 clarinets in A, bass clarinet, 3 bassoons, contrabassoon
- Brass: 6 horns in F, 4 trumpets, 4 trombones, tuba
- Percussion (8–9 players): 5 timpani, snare drum, bass drum, cymbals, triangle, tam-tam, tambourine, castanets, glockenspiel, xylophone
- Keyboards: celesta, harmonium (offstage), organ (offstage)
- Strings: 2 harps, 16 violins I, 16 violins II, 10–12 violas, 10 violoncellos, 8 double basses
Music
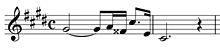

The music of Salome includes a system of leitmotifs, or short melodies with symbolic meanings. Some are clearly associated with people such as Salome and Jochanaan (John the Baptist). Others are more abstract in meaning.[6] Strauss's use of leitmotifs is complex, with both symbolism and musical form subject to ambiguity and transformation. Some leitmotifs, especially those associated with Herod, change frequently in form and symbolic meaning, making it futile to pin them down to a specific meaning.[6] Strauss provided names for some of the leitmotifs, but not consistently, and other people have assigned a variety of names. These names often illustrate the ambiguity of certain leitmotifs. For example, Gilman's labels tend to be abstract (such as "Yearning", "Anger", and "Fear"), while Roese more concrete (he called Gilman's "Fear" leitmotif "Herod's Scale"). Regarding the important leitmotif associated with Jochanaan, which has two parts, Gilman called the first part "Jochanaan" and the second part "Prophecy", while Roese labels them the other way around. Labels for the leitmotifs are common, but there is no final authority. Derrick Puffett cautions against reading too much into any such labels.[6] In addition to the leitmotifs, there are many symbolic uses of musical color in the opera's music. For example, a tambourine sounds every time a reference to Salome's dance is made.[6]
The harmony of Salome makes use of extended tonality, chromaticism, a wide range of keys, unusual modulations, tonal ambiguity, and polytonality. Some of the major characters have keys associated with them, such as Salome and Jochanaan, as do some of the major psychological themes, such as desire and death.
Strauss wrote the opera's libretto, in the process cutting almost half of Wilde's play, stripping it down and emphasizing its basic dramatic structure. The structural form of Strauss's libretto is highly patterned, notably in the use of symmetry and the hierarchical grouping of events, passages, and sections in threes. Examples of three-part structure include Salome's attempt to seduce Narraboth, in order to get him to let her see Jochanaan. She tries to seduce him three times, and he capitulates on the third. When Jochanaan is brought before Salome he issues three prophecies, after which Salome professes love for Jochanaan three times—love of his skin, his hair, and his lips, the last of which results in Jochanaan cursing her. In the following scene Herod three times asks Salome to be with him—to drink, eat, and sit with him. She refuses each time. Later Herod asks her to dance for him, again three times. Twice she refuses, but the third time Herod swears to give her whatever she wants in return and she accepts. After she dances and says she wants Jochanaan's head on a platter, Herod, not wanting to execute the Prophet, makes three offers—an emerald, peacocks, and finally, desperately, the Veil of the Sanctuary of the Holy of Holies. Salome rejects all three offers, each time more stridently insisting on Jochanaan's head. Three-part groupings occur elsewhere on both larger and smaller levels.[2]

In the final scene of the opera, after Salome kisses Jochanaan's severed head, the music builds to a dramatic climax, which ends with a cadence involving a very dissonant unorthodox chord at measure 360 in the score. This single chord has been widely commented on. It has been called "the most sickening chord in all opera", an "epoch-making dissonance with which Strauss takes Salome...to the depth of degradation", and "the quintessence of Decadence: here is ecstasy falling in upon itself, crumbling into the abyss".[7] The chord is often described as polytonal, with a low A7 (a dominant seventh chord) merged with a higher F-sharp major chord. It forms part of a cadence in the key of C-sharp major and is approached and resolved from C–sharp major chords. Not only is the chord shockingly dissonant, especially in its musical context and rich orchestration, it has broader significance due in part to Strauss's careful use of keys and leitmotifs to symbolize the opera's characters, emotions such as desire, lust, revulsion, and horror, as well as doom and death. A great deal has been written about this single chord and its function within the large-scale formal structure of the entire opera.[8]
The thematic material of Strauss's Salome has been explored in detail by Mary Bronach Callaghan in her doctoral dissertation on the opera.[9] It discusses Strauss's compositional method, examines the sketchbooks in which Salome came into being, and places the opera in its historical and cultural context by providing the reactions of many of Strauss's contemporaries to the thematic material and harmonies in the form of newspaper reviews, diary entries and letters.
The role of Salome
This section possibly contains original research. (October 2011) |
The vocal demands of the Salome role are the same as those of an Isolde, Brünnhilde, or Turandot, in that, ideally, the role requires the volume, stamina, and power of a true dramatic soprano. The common theme of these four roles is the difficulty in casting an ideal soprano that has a truly dramatic voice as well as being able to register as a young woman.
Nevertheless, Maria Cebotari, Ljuba Welitsch, Birgit Nilsson, Leonie Rysanek, Éva Marton, Radmila Bakočević, Montserrat Caballé, Anja Silja, Phyllis Curtin, Karan Armstrong, Nancy Shade, Dame Gwyneth Jones, Catherine Malfitano, Hildegard Behrens, Maria Ewing, Teresa Stratas, and Karita Mattila are among the most memorable who have tackled the role in the last half-century. Each of these singers has brought her own interpretation to the title character. Perhaps the most famous recording of the opera is Sir Georg Solti's Decca recording with Birgit Nilsson as Salome.
In addition to the vocal and physical demands, the role also calls for the agility and gracefulness of a prima ballerina when performing the opera's famous "Dance of the Seven Veils". Finding one individual with all of these qualities is extremely daunting. Due to the complexity of the role's demands, some of its performers have had a purely vocal focus by opting to leave the dancing to stand-ins who are professional dancers. Others have opted to combine the two and perform the dance themselves, which is closer to Strauss's intentions. In either case, at the end of the "Dance of the Seven Veils", some sopranos (or their stand-ins) wear a body stocking under the veils, while others (notably Malfitano, Mattila and Ewing) have appeared nude at the conclusion of the dance.
As for the required vocal range of the title role, it is an extraordinary case: The highest note is the high B5, not irregular for a soprano or mezzo-soprano to sing, while the lowest note is a low G♭3, in the contralto range and officially below the standard range for a mezzo-soprano. Considering this range, which is similar to many mezzo roles (such as Carmen and Amneris), one might assume that a high soprano is not essential to the piece, but it is; most of the relatively low sopranos who attempted this role found themselves straining their voices throughout the opera, and having reached the closing scene (the most important part of the opera for the title role) were very fatigued. This role is the classic example of the difference between tessitura and absolute vocal range: While mezzos can perform a high note (like Carmen), or even temporarily sustain a high tessitura, it is impossible for a singer to spend such a long time (with the needed strength and breath-control) in the second octave above the middle C unless she is a high soprano. Moreover, the low G♭ occurs twice in the opera, and in both cases it is in pianissimo—more of a theatrical effect than music—and can be growled instead of sung. The other low notes required are no lower than low A♮, and they are also quiet.
Transcriptions
The English composer Kaikhosru Shapurji Sorabji wrote in 1947 a piano transcription of the closing scene of the opera, called, "Schluß-Szene aus Salome von Richard Strauss—Konzertmäßige Übertragung für Klavier zu zwei Händen" ("Final Scene from Salome by Richard Strauss – Concert Transcription arranged for Piano, two hands").
Recordings
See also
References
Notes
- ^ "Salome". Boosey & Hawkes. Retrieved 13 December 2008.
Dedication: Meinem Freunde Sir Edgar Speyer
- ^ a b Carpenter, Tethys (1989). "6. Tonal and dramatic structure". In Derrick Puffett (ed.). Richard Strauss, Salome. Cambridge University Press. pp. 92–93. ISBN 978-0-521-35970-2. Retrieved 29 September 2011.
- ^ a b c d e Holden, p. 889
- ^ Recordings of the opera on operadis-opera-discography.org.uk
- ^ Liner notes to the recording of Salome with Birgit Nilsson and the Vienna Philharmonic under Georg Solti. Decca Records, 19XX
- ^ a b c d Tethys Carpenter, Craig Ayrey; et al. (1989). Derrick Puffett (ed.). Richard Strauss, Salome. Cambridge University Press. pp. 63, 68–69, 82. ISBN 978-0-521-35970-2.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Ayrey, Craig (1989). "7. Salome's final monologue". In Derrick Puffett (ed.). Richard Strauss, Salome. Cambridge University Press. pp. 123–130. ISBN 978-0-521-35970-2. Retrieved 29 September 2011.
- ^ See Puffett (1989), chapters 6 and 7.
- ^ "Richard Strauss's 'Geheimnisvolle Musik': unveiling the meaning of Salome", PhD dissertation (548 pages) by Mary Bronach Callaghan, 28 November 2003, Queen's University Belfast
Sources
- Amadeus Almanac, accessed 26 August 2008
- Del Mar, Norman (1962). Richard Strauss. London: Barrie & Jenkins. ISBN 0-214-15735-0.
- Gilman, Lawrence (1907). Strauss' Salome: A Guide to the Opera, with Musical Illustrations. J. Lane.
- Holden, Amanda (ed.), The New Penguin Opera Guide, New York: Penguin Putnam, 2001. ISBN 0-14-029312-4
External links
- Salome, German libretto
- Free scores by Salome at the International Music Score Library Project (IMSLP)
