Hundreds of Cornwall


The hundreds of Cornwall (Cornish: Keverangow Kernow) were administrative divisions or Shires (hundreds) into which Cornwall, the present day administrative county of England, in the United Kingdom, was divided between c. 925 and 1894, when they were replaced with local government districts.
Some of the names of the hundreds ended with the suffix shire as in Pydarshire, East and West Wivelshire and Powdershire which were first recorded as names between 1184 and 1187.[1]
In the Cornish language the word keverang (pl. keverangow) is the equivalent for English "hundred" and the Welsh cantref. The word, in its plural form, appears in place names like Meankeverango (i.e. stone of the hundreds) in 1580 (now The Enys, north of Prussia Cove and marking the southern end of the boundary between the hundreds of Penwith and Kerrier), and Assa Govranckowe 1580, Kyver Ankou c. 1720, also on the Penwith – Kerrier border near Scorrier. It is also found in the singular form at Buscaverran, just south of Crowan churchtown and also on the Penwith-Kerrier border. The hundred of Trigg is mentioned by name during the 7th century, as "Pagus Tricurius", "land of three war hosts".[2]
History
[edit]The division of Wessex into hundreds is thought to date from the reign of King Athelstan, and in the Geld Inquest of 1083, only seven hundreds are found in Cornwall, identified by the names of the chief manors of each: Connerton, Winnianton, Pawton, Tybesta, Stratton, Fawton and Rillaton (corresponding to Penwith, Kerrier, Pydar, Powder, Trigg, West Wivel and East Wivel). At the time of the Domesday Survey of 1086, the internal order of the Cornish manors in the Exeter Domesday Book is in most cases based on the hundreds to which they belonged, although the hundred names are not used.[3][4][5][6]
All of the lordships of the Hundreds of Cornwall belonged, and still belong, to the Duchy of Cornwall, apart from Penwith which belonged to the Arundells of Lanherne. The Arundells sold their lordship to the Hawkins family in 1813 and the Hawkinses went on to sell it to the Paynters in 1832. The Lordship of Penwith came with a great number of rights over the entire hundred. These included: rights to try certain cases of trespass, trespass on the law, debt and detinue, to appoint a jailor for the detention of persons apprehended, to receive high-rent from the lords of the principal manors and to claim the regalia of the navigable rivers and havens, the profits of the royal gold and silver mines, and all wrecks, escheats, deodands, treasure trove, waifs, estrays, goods of felons and droits of admiralty happening within the hundred.[7]

The Lann Pydar[8] joint benefice is a benefice combining those of St Ervan, St Eval, St Mawgan and St Columb Major. It is in Pydar deanery of the Diocese of Truro.
Origin of the hundred names
[edit]The origins of the names have puzzled some earlier writers on the subject: Penwith is certainly the name of Land's End in Cornish (earliest occurrence in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle for 997); Kerrier (sometimes Kirrier) is thought by Thomas to be derived from an obsolete name (ker hyr = long fort) of Castle Pencaire on Tregonning Hill, Breage; Lesnewth denotes a place where a 'new court' has been established (the 'old court' having been at Henlis(-ton): Helstone, formerly Helston-in-Trigg); Powder has no certain derivation: 'pou' means 'territory' in Cornish; Pydar (or Pyder) has been variously explained: perhaps it derives from a Cornish word meaning 'a fourth part'; Stratton was at the time of Domesday an important manor and 200 years earlier it is mentioned as 'Strætneat' (etym. dub.); Trigg is explained in the separate article; East and West (Wivelshire) must have originally had a Cornish name but it is not recorded. The original English name was Twofold-shire, because it was divided into the two parts, East and West. The names East Twofold-shire and West Twofold-shire were then misdivided, giving the name Wivelshire.[9]
List of hundreds in 1841
[edit]
By 1841 Cornwall was composed of ten hundreds as listed below here:
- Penwith (Penwyth)
- Kerrier (Keryer)
- Pydarshire (Pedera)
- Powdershire (Pow Ereder)
- Triggshire (Trigor)
- Lesnewth (Lysnowyth)
- Stratton (Stradneth)
- East Wivelshire (Ryslegh)
- West Wivelshire (Fawy)
- Scilly (Syllan)
Parishes in the ten hundreds
[edit]Penwith
[edit]
- St Buryan, Camborne, Crowan, St Erth, Gulval [alias Lanisly], Gwinear, Gwithian, St Hilary, Illogan, St Ives, St Just in Penwith, Lelant [Uny Lelant], St Levan, Ludgvan, Madron, Morvah, Paul, Perranuthnoe, Phillack, Redruth, Sancreed, Sennen, Towednack, Zennor.
Kerrier
[edit]
- St Anthony-in-Meneage, Breage, Budock, Constantine, Cury, Falmouth, Germoe, St Gluvias, Grade, Gunwalloe [alias Winnington], Gwennap with St Day, Helston, St Keverne, Landewednack, Mabe, Manaccan, St Martin-in-Meneage, Mawgan-in-Meneage, Mawnan, Mullion, Mylor, Perranarworthal, Ruan Major, Ruan Minor, Sithney, St Stithians, Wendron
Pydarshire
[edit]
- St Agnes, St Breock, Colan, St Columb Minor & St Columb Major, Crantock, Cubert, St Enoder, St Ervan, St Eval, St Issey, Lanhydrock, Lanivet, St Mawgan-in-Pydar, St Merryn, St Newlyn East, Padstow, Perranzabuloe, Little Petherick, St Wenn, Withiel
Powdershire
[edit]
- St Allen, St Anthony-in-Roseland, St Austell, St Blazey, St Clement, Cornelly, Creed-with-Grampound, Cuby-with-Tregony, St Dennis, St Erme, St Ewe, Feock, Fowey, Gerrans, Gorran, St Just-in-Roseland, Kea, Kenwyn, Ladock, Lamorran, Lanlivery, Lostwithiel, Luxulyan, Merther, Mevagissey, St Mewan, St Michael Caerhays, St Michael Penkevil, Philleigh, Probus, Roche, Ruan Lanihorne, St Sampson Golant, St Stephen-in-Brannel, Truro St Mary, Tywardreath, Veryan
Triggshire
[edit]
- Bodmin, Blisland, St Breward, Egloshayle, St Endellion, Helland, St Kew, St Mabyn, St Minver, St Teath, Temple, St Tudy
Lesnewth
[edit]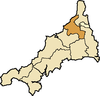
- Advent, Altarnun, St Clether, Davidstow, Forrabury, St Gennys, St Juliot, Lanteglos-by-Camelford, Lesnewth, Michaelstow, Minster, Otterham, Poundstock, Tintagel [with Bossiney], Treneglos, Trevalga, Warbstow.
Stratton
[edit]
- Boyton, Bridgerule, Jacobstow, Kilkhampton, Launcells, Marhamchurch, Morwenstow, Poughill, Stratton, North Tamerton, Week St Mary, Whitstone
East Wivelshire
[edit]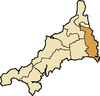
- Antony St Jacob, Botus Fleming, Callington, Calstock, Egloskerry, Landulph, Landrake [with St Erney], Laneast, Launceston St Mary Magdalene, Lawhitton, Lewannick, Lezant, Linkinhorne, Maker, St Mellion, Menheniot, North Hill, Pillaton, Quethiock, Rame, Sheviock, South Hill, South Petherwin, St Germans, St John, St Stephens-with-Newport, Stoke Climsland, St Dominick, St Ive, St Stephen-by-Saltash, St Thomas Apostle-by-Launceston, Torpoint, Tremaine, Tresmeer, Trewen
West Wivelshire
[edit]
- Boconnoc, Braddock, Cardinham, St Cleer, Duloe, St Keyne, Lanreath, Lansallos, Lanteglos by Fowey, Liskeard, St Martin-by-Looe, Morval, St Neot, Pelynt, St Pinnock, Talland, St Veep, Warleggan, St Winnow
Scilly
[edit]Other medieval divisions of Cornwall
[edit]- Brannel – Cornish: Bronel, meaning hilly place
- Meneage – Cornish: Manahek, meaning monastic lands
- Roseland – Cornish: Ros, meaning moor/heath
- Rame Peninsula – Cornish: Ros, meaning moor/heath[10]
References and bibliography
[edit]- ^ Gover, J. E. B. (1946) Research paper at the Courtney Library, Royal Institution of Cornwall, Truro.
- ^ Craig Weatherhill, Article in Cornish World; March 2007
- ^ Henderson, Charles 'A note on the hundreds of Pydar and Powder' in Essays in Cornish History (Oxford University Press, 1935)
- ^ W. G. Hoskins, The Westward Expansion of Wessex (Leicester: Univ. Press, 1960)
- ^ Thomas, Charles, 'Settlement History in Early Cornwall: I; the antiquity of the hundreds' in: Cornish Archaeology vol. 3 (St Ives: Cornwall Archaeological Society, 1964), pp. 70–79
- ^ Thorn, Caroline & Frank, eds., Domesday Book. 10: Cornwall (Chichester: Phillimore, 1979)
- ^ National Archives. Cat 021-ar-6 &c
- ^ "The Benefice of LannPydar". A Church Near You – The Church of England. Archived from the original on 16 August 2022. Retrieved 16 August 2022.
- ^ Thomas, Charles (1964) pp. 70–79)
- ^ Weatherhill, Craig (2009). A Concise Dictionary of Cornish Place-Names. Leac an Anfa, Cathair na Mart: Evertype. ISBN 978-1-904808-22-0.
- Padel, O. J. (1985) Cornish Place-name Elements. Nottingham: English Place-name Society ISBN 0-904889-11-4
