Plesiadapiformes
| Plesiadapiformes | |
|---|---|
| |
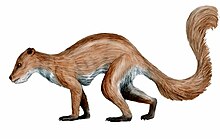
| Plesiadapis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Clade: | Pan-Primates |
| Order: | Plesiadapiformes Simons and Tattersall, 1972 |
| Groups included | |
Plesiadapiformes ("Adapid-like" or "near Adapiformes") is an extinct basal pan-primates group, as sister to the rest of the pan-primates.[4][5][6][7][8] The pan-primates together with the Dermoptera form the Primatomorpha. Purgatorius may not be a primate as an extinct sister to the rest of the Dermoptera[8] or a separate, more basal stem pan-primate branch. Even with Purgatorius removed, the crown primates may even have emerged in this group.

Plesiadapiformes first appear in the fossil record between 65 and 55 million years ago,[9][10] although many were extinct by the beginning of the Eocene. They may be the earliest known mammals to have finger nails in place of claws.[11] In 1990, K.C. Beard attempted to link the Plesiadapiformes with the order Dermoptera. They proposed that paromomyid Phenacolemur had digital proportions of the fossil indicated gliding habits similar to that of colugos.[12]
In the following simplified cladogram, the crown primates are classified as highly derived Plesiadapiformes, possibly as sister of the Plesiadapoidea.[7] The crown primates are cladistically granted here into the Plesiadapiformes, and "Plesiadapiformes" become a junior synonym of the primates. With this tree, the Plesiadapiformes are not literally extinct (in the sense of having no surviving descendants). The crown primates are also called "Euprimates" in this context.
| Euarchontoglires |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Alternatively, in 2018, the Plesiadapiformes were proposed to be more related to Dermoptera, or roughly corresponding to Primatomorpha, with both Dermoptera and the primates emerging within this group.[13][14][15] Also in a 2020 paper, the primates and Dermoptera were jointly considered sister to the plesiadapiform Purgatoriidae, resulting in the following phylogenetic tree.[16]
| Euarchontoglires |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Traditionally, they were regarded as a separate extinct order of Primatomorpha, but it now appears that groups such as the extant primates and/or the Dermoptera have emerged in the group.[citation needed]
Similarly, in 2021 the Purgatoriidae were classified as sister to Dermoptera, while the rest of the Plesiadapiformes appear to be sister to the remaining primates:[8]
| Euarchonta | |
One possible classification table of plesiadapiform families is listed below.[citation needed]
- Plesiadapiformes
- Family Micromomyidae
- Superfamily Paromomyoidea
- Family Paromomyidae
- Family Picromomyidae
- Family Palaechthonidae
- Family Microsyopidae
- Superfamily Plesiadapoidea[17]
- Family Carpolestidae
- Family Chronolestidae
- Family Plesiadapidae
- Family Saxonellidae
References
[edit]- ^ "Plesiadapiformes". paleobiodb.org. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ Scott, Craig S.; Fox, Richard C.; Redman, Cory M. (21 March 2016). "A new species of the basal plesiadapiform Purgatorius (Mammalia, Primates) from the early Paleocene Ravenscrag Formation, Cypress Hills, southwest Saskatchewan, Canada: further taxonomic and dietary diversity in the earliest primates". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 53 (4): 343–354. Bibcode:2016CaJES..53..343S. doi:10.1139/cjes-2015-0238. hdl:1807/71784.
- ^ a b Silcox, Mary T.; Bloch, Jonathan I.; Boyer, Doug M.; Chester, Stephen G. B.; López‐Torres, Sergi (April 2017). "The evolutionary radiation of plesiadapiforms". Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews. 26 (2): 74–94. doi:10.1002/evan.21526. ISSN 1060-1538. PMID 28429568.
- ^ Henke, Winfried; Tattersall, Ian; Hardt, Thorolf (2007). Handbook of Paleoanthropology: Vol I:Principles, Methods and Approaches Vol II:Primate Evolution and Human Origins Vol III:Phylogeny of Hominids. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 839. ISBN 978-3-540-32474-4. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- ^ Boyer, Doug M.; Costeur, Loïc; Lipman, Yaron (2012). "Earliest record of Platychoerops(Primates, Plesiadapidae), a new species from Mouras Quarry, Mont de Berru, France". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 149 (3): 329–346. doi:10.1002/ajpa.22119. ISSN 0002-9483. PMID 22926965. S2CID 37772289.
- ^ Ni, X.; Meng, J.; Beard, K. C.; Gebo, D. L.; Wang, Y.; Li, C. (2009). "A new tarkadectine primate from the Eocene of Inner Mongolia, China: phylogenetic and biogeographic implications". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 277 (1679): 247–256. doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.0173. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 2842661. PMID 19386655.
- ^ a b Silcox, Mary T.; Bloch, Jonathan I.; Boyer, Doug M.; Chester, Stephen G. B.; López‐Torres, Sergi (2017). "The evolutionary radiation of plesiadapiforms". Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews. 26 (2): 74–94. doi:10.1002/evan.21526. ISSN 1520-6505. PMID 28429568.
- ^ a b c Wisniewski, Anna L.; Lloyd, Graeme T.; Slater, Graham J. (25 May 2022). "Extant species fail to estimate ancestral geographical ranges at older nodes in primate phylogeny". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 289 (1975): 20212535. doi:10.1098/rspb.2021.2535. ISSN 0962-8452. PMC 9115010. PMID 35582793.
- ^ Paleontologists discover most primitive primate skeleton - PhysOrg.com
- ^ March 2021, Patrick Pester-Staff Writer 04. "Primate ancestor of all humans likely roamed with the dinosaurs". livescience.com. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ ""Sleep, First Primates, Earthquakes in the Midwest and Profile: Sang-Mook Lee"". NOVA scienceNOW. Season 4. Episode 8. 9 July 2008. 13:04 minutes in. PBS. Transcripts – NOVA scienceNOW: 9 July 2008.
- ^ Beard, K. C. (1990). "Gliding behaviour and palaeoecology of the alleged primate family Paromomyidae (Mammalia, Dermoptera)". Nature. 345 (6273): 340–341. Bibcode:1990Natur.345..340B. doi:10.1038/345340a0. S2CID 4369153.
- ^ Morse, Paul E.; Chester, Stephen G.B.; Boyer, Doug M.; Smith, Thierry; Smith, Richard; Gigase, Paul; Bloch, Jonathan I. (2019). "New fossils, systematics, and biogeography of the oldest known crown primate Teilhardina from the earliest Eocene of Asia, Europe, and North America". Journal of Human Evolution. 128: 103–131. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2018.08.005. PMID 30497682. S2CID 54167483.
- ^ Godinot, Marc (16 April 2017), "Paleocene and Eocene Primates", in Bezanson, Michele; MacKinnon, Katherine C; Riley, Erin; Campbell, Christina J (eds.), The International Encyclopedia of Primatology, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., pp. 1–9, doi:10.1002/9781119179313.wbprim0331, ISBN 9781119179313
- ^ Boyer, Doug M.; Maiolino, Stephanie A.; Holroyd, Patricia A.; Morse, Paul E.; Bloch, Jonathan I. (1 September 2018). "Oldest evidence for grooming claws in euprimates". Journal of Human Evolution. 122: 1–22. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2018.03.010. PMID 29935935.
- ^ Seiffert, Erik R.; Tejedor, Marcelo F.; Fleagle, John G.; Novo, Nelson M.; Cornejo, Fanny M.; Bond, Mariano; de Vries, Dorien; Campbell, Kenneth E. (10 April 2020). "A parapithecid stem anthropoid of African origin in the Paleogene of South America". Science. 368 (6487): 194–197. Bibcode:2020Sci...368..194S. doi:10.1126/science.aba1135. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 32273470. S2CID 215550773.
- ^ "Plesiadapoidea". paleobiodb.org. Retrieved 1 March 2022.





