Central arteries
| Central arteries | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Source | Circle of Willis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
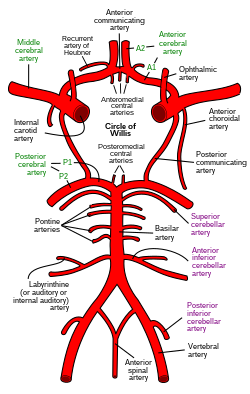
Central arteries (or perforating or ganglionic arteries) of the brain are numerous small arteries branching from the Circle of Willis, and adjacent arteries that often enter the substance of the brain through the anterior and posterior perforated substances. They supply structures of the base of the brain and internal structures of the cerebral hemispheres. They are separated into four principal groups: anteromedial central arteries; anterolateral central arteries (lenticulostriate arteries); posteromedial central arteries (paramedian arteries); and posterolateral central arteries.
Anteromedial central arteries
[edit]Anteromedial central arteries[1] (also anteromedial perforating arteries, or anteromedial ganglionic arteries) are arteries that arise from the anterior cerebral artery and anterior communicating artery, and pass into the substance of the cerebral hemispheres through the (medial portion of) the anterior perforated substance to supply the optic chiasm, (anterior nucleus, preoptic area, and supraoptic nucleus of the) hypothalamus, lamina terminalis, septum pellucidum, (anterior portions of the) columns of fornix, rostrum of corpus callosum, (anterior portion of) putamen, head of caudate nucleus, and cingulate cortex.[2]
Anterolateral central arteries
[edit]The anterolateral central arteries or lenticulostriate arteries[3] (also anterolateral perforating arteries, anterolateral ganglionic arteries, striate arteries, or lateral striate arteries; latin aa. centrales anterolaterales,[4] or aa. lenticulostriatae[4]) are a group of small arteries mostly arising from (the initial M1 part of) the middle cerebral artery that enter the brain through the anterior perforated substance to provide arterial supply to parts of the basal ganglia.[2] They are end arteries.[citation needed]
The name of these arteries is derived from some of the structures they supply, namely the lentiform nucleus and the striatum.[citation needed]
Distribution
[edit]- posterior portion of the striatum
- putamen
- (head of) caudate nucleus
- (lateral portion of) globus pallidus
- (all parts of) internal capsule (anterior limb, genu, and - a portion of - posterior limb)
- claustrum
- external capsule
The distal medial striate artery (Recurrent artery of Heubner) arises either from the middle cerebral artery or anterior cerebral artery, and supplies the rostral/anterior portion of the caudate nucleus and putamen, and the anterior limb and genu of the internal capsule.[2]
Clinical significance
[edit]Blockage of the lenticulostriate arteries causes lacunar strokes. These infarcts are most often due to hyaline arteriosclerosis secondary to hypertension. This can lead to contralateral paresis (muscular weakness) and/or sensory loss of the face and body.
Posteromedial central arteries
[edit]The posteromedial central arteries or paramedian arteries[6] (also posteromedial perforating arteries, or posteromedial ganglionic arteries[2]) are branches of the posterior cerebral artery, and posterior communicating artery. They enter the substance of the brain through the posterior perforated substance. They supply a large portion of the diencephalon as well as some subcortical telencephalic structures.
The thalamoperforating arteries[7] are posteromedial central arteries which supply parts of the thalamus.[2][8][4] According to the Medical Dictionary of the French Academy of Medicine, a single thalamoperforating artery arises from the (pre-communicating (P1) segment of) the posterior cerebral artery, piercing the anterior perforated substance to reach and supply the ventral portion of the thalamus.[8] The Sobotta Anatomy Textbook (2018) distinguishes an anterior thalamoperforating artery which arises from the posterior communicating artery and supplies the rostral portion of the thalamus, and a posterior thalamoperforating artery which supplies multiple thalamic nuclei.[4]
Origin
[edit]PMCAs arise from the proximal (pre-communicating segment (P1)[9] of the posterior cerebral artery (PCA),[2][4][9] and along the entire length of[2] the posterior communicating artery[2][10][5]: 372 (though branches arising from the latter may be considered as a distinct anatomical entity[4]). The PMCAs thus arise at and near the bifurcation of the basilar artery.[5]: 378 The PMCAs are the very first branches of the PCA.[5]: 377
Course
[edit]PMCAs intermingle to form an extensive venous plexus in the interpeduncular fossa[11] before entering the substance of the brain through the posterior perforated substance,[4][11][9] then also passing through the posterior part of the internal capsule along their path.[12]
Distribution
[edit]The PMCAs supply a substantial part of the diencephalon.[4]
The PMCAs are distributed to:[2][4][5]: 380
- globus pallidus
- (lateral wall of) third ventricle,
- (parts of the) thalamus (partially via the thalamoperforating artery)[10]
- subthalamus
- hypothalamus[9]
- mammillary bodies[9][10]
- pituitary gland
- optic chiasm[10] and tracts[10]
- tuber cinereum[10]
- posterior limb of internal capsule[9]
- mesencephalon (midbrain)[5]: 380
Clinical significance
[edit]An embolus passing along a vertebral artery will typically continue into the basilar artery before finally lodging at the bifurcation of the basilar artery, thus bilaterally obstructing the PMCAs (as well as the superior cerebellar artery); such occlusion of the PMCAs will swiftly result in infarction of the reticular formation at the level of the mesencephalon-pons junction (resulting in coma) as well as destruction of the fibers of both oculomotor nerve (CN III) (resulting in divergence of both eyes, and fixed mydriasis).[5]: 377-378
An embolism of a single PMCA at mesencephalic levels may result in a small infarction of the mesencephalon, causing Weber's syndrome.[5]: 378
Uncal herniation can cause compression of the PMCAs, which may result in Duret haemorrhages.[citation needed]
Posterolateral central arteries
[edit]Posterolateral central arteries[13] (also posterolateral perforating arteries, or posterolateral ganglionic arteries) are arteries that arise from the posterior cerebral artery distal to its first - pre-communicating (P1) -segment (i.e. distal to the origin of the posterior communicating artery).[2]
They are distributed to the:[5][2]
- (lateral part of) cerebral peduncle
- tectum
- corpora quadrigemina (i.e. superior and inferior colliculi)
- pineal gland
- (via the thalamogeniculate arteries) (the posterior parts of) thalamus[14]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Anatonomina". terminologia-anatomica.org. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 419. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "Anatonomina". terminologia-anatomica.org. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Waschke, Jens; Böckers, Tobias M.; Paulsen, Friedrich; Arnold, Wolfgang; Bechmann, Ingo, eds. (2018). Sobotta Anatomy Textbook: English Edition with Latin Nomenclature (1st ed.). München: Elsevier. p. 622. ISBN 978-0-7020-6760-0.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Kiernan, John A.; Rajakumar, Nagalingam (2013). Barr's The Human Nervous System: An Anatomical Viewpoint (10th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-1-4511-7327-7.
- ^ "Anatonomina". terminologia-anatomica.org. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- ^ "Anatonomina". terminologia-anatomica.org. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- ^ a b "thalamoperforating artery - Dictionnaire médical de l'Académie de Médecine". www.academie-medecine.fr. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- ^ a b c d e f "posteromedial central arteries of posterior cerebral artery - Dictionnaire médical de l'Académie de Médecine". www.academie-medecine.fr. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- ^ a b c d e f "posteromedial central arteries of posterior communicating artery - Dictionnaire médical de l'Académie de Médecine". www.academie-medecine.fr. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- ^ a b Carpenter, Malcolm B. (1985). Core text of neuroanatomy (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins. p. 409. ISBN 0683014552.
- ^ Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). Elsevier Australia. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ "Anatonomina". terminologia-anatomica.org. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- ^ "Thalamogeniculate artery - Dictionnaire médical de l'Académie de Médecine". www.academie-medecine.fr. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
Further reading
[edit]- Le, Tao and Bhushan, Vikas. First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2017 (p.484). New York: McGraw-Hill Education, 2017.
