Ponzo illusion
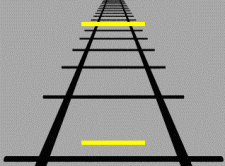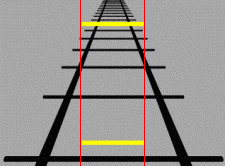
The Ponzo illusion is a geometrical-optical illusion that takes its name from the Italian psychologist Mario Ponzo (1882–1960). Ponzo never claimed to have discovered it, and it is indeed present in earlier work. Much confusion is present about this including many references to a paper that Ponzo published in 1911 on the Aristotle illusion. This is a tactile effect and it has nothing at all to do with what we now call the Ponzo illusion.[1][2] The illusion can be demonstrated by drawing two identical lines across a pair of converging lines, similar to railway tracks, but the effect works also at different orientations.
One of the explanations for the Ponzo illusion is the "perspective hypothesis", which says that the perspective feature in the figure is produced by the converging lines ordinarily associated with distance; the two oblique lines appear to converge toward the horizon or a vanishing point. We interpret the upper line as though it were further away, so we see it as longer. A further object would have to be longer than a nearer one for both to produce retinal images of the same size.
Another explanation is the "framing-effects hypothesis", which says that the difference in the separation or gap of the horizontal lines from the framing converging lines may determine, or at least contribute to the magnitude of the distortion.
The Ponzo illusion is one possible explanation of the Moon illusion, as suggested by Ponzo in 1912.[3] Objects appearing "far away" (because they are "on" the horizon) appears larger than objects "overhead".[4] However, some have argued[5] that explaining one perception ("appears far away") in terms of another ("appears bigger") is problematic scientifically, and there are probably complex internal processes behind these illusions.
The Ponzo illusion also occurs in touch and with an auditory-to-visual sensory-substitution device. However, prior visual experience seems mandatory to perceive it as demonstrated by the fact that congenitally blind subjects are not sensitive to it.
The Ponzo illusion has been used to demonstrate a dissociation between vision-for-perception and vision-for-action . Thus, the scaling of grasping movements directed towards objects embedded within a Ponzo illusion is not subject to the size illusion.[6] In other words, the opening between the index finger and thumb is scaled to the real not the apparent size of the target object as the grasping hand approaches it.
Cross-cultural differences in susceptibility to the Ponzo illusion have been noted, with non-Western and rural people showing less susceptibility.[7] Other recent research suggests that an individual's receptivity to this illusion, as well as the Ebbinghaus illusion, may be inversely correlated with the size of the individual's primary visual cortex.[8]
References
[edit]- ^ Ponzo, M. (1911). "Intorno ad alcune illusioni nel campo delle sensazioni tattili sull'illusione di Aristotele e fenomeni analoghi". Archives Italiennes de Biologie.
- ^ Bertamini M, Wade N (2023). "Mario Ponzo (1928) on Perception of Numerosity: A Translation and Commentary". Perception. 52 (8): 545–575. doi:10.1177/03010066231176744. hdl:11577/3495721.
- ^ Ponzo, M. (1912). "Rapports entre quelques illusions visuelles de contraste angulaire et l'appréciation de grandeur des astres à l'horizon". Archives Italiennes de Biologie.
- ^ "Why does the Sun appear larger on the horizon than overhead?". Astronomy Department at Cornell University. Retrieved 2012-10-02.
- ^ Kaufman, L; Vassiliades, V; Noble, R; Alexander, R; Kaufman, J; Edlund, S (2007). "Perceptual distance and the moon illusion". Spatial Vision. 20 (1): 155–175. doi:10.1163/156856807779369698. PMID 17357720. S2CID 11812239.
- ^ Ganel T, Tanzer M, Goodale MA (2008). "A double dissociation between action and perception in the context of visual illusions: opposite effects of real and illusory size". Psychol. Sci. 19 (3): 221–5. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02071.x. PMID 18315792. S2CID 15679825.
- ^ Shiraev, E.; D. (2007). Cross-Cultural Psychology (3rd ed.). Pearson Education, Inc. p. 110.
- ^ D Samuel Schwarzkopf, Chen Song & Geraint Rees (January 2011). "The surface area of human V1 predicts the subjective experience of object size". Nature Neuroscience. 14 (1): 28–30. doi:10.1038/nn.2706. PMC 3012031. PMID 21131954.
Further reading
[edit]- Renier L, De Volder AG (2005). "Cognitive and brain mechanisms in sensory substitution of vision: a contribution to the study of human perception". Journal of Integrative Neuroscience. 4 (4): 489–503. doi:10.1142/S0219635205000999. PMID 16385643.
- Renier L, Laloyaux C, Collignon O, Tranduy D, Vanlierde A, Bruyer R, De Volder AG (2005). "The Ponzo illusion using auditory substitution of vision in sighted and early blind subjects". Perception. 34 (7): 857–867. doi:10.1068/p5219. PMID 16124271. S2CID 17265107. Archived from the original on 2006-10-26. Retrieved 2006-12-21.
