Rufous-lored tyrannulet
| Rufous-lored tyrannulet | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Tyrannidae |
| Genus: | Phylloscartes |
| Species: | P. flaviventris
|
| Binomial name | |
| Phylloscartes flaviventris (Hartert, 1897)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |

The rufous-lored tyrannulet (Phylloscartes flaviventris) is a Near Threatened species of bird in the family Tyrannidae, the tyrant flycatchers. It is endemic to Venezuela.[1][2]
Taxonomy and systematics
[edit]The rufous-lored tyrannulet was originally described in 1897 as Leptotriccus flaviventris.[3] It was later moved to genus Pogonotriccus and still later to its present Phylloscartes. Some authors called it the "yellow-bellied bristle-tyrant" but it gained its present English name when it was moved to Phylloscartes and the true bristle-tyrants alone were retained in Pogonotriccus. The rufous-lored tyrannulet and the cinnamon-faced tyrannulet (P. parkeri) form a superspecies.[4]
The rufous-lored tyrannulet is monotypic.[2]
Description
[edit]The rufous-lored tyrannulet is about 12 cm (4.7 in) long and weighs about 8 g (0.28 oz). The sexes have the same plumage. Adults have a rufous forehead whose color extends to above the eye and becomes yellow beyond it. Their lores and "moustache" are blackish, they have a rufous arc below the eye, and a black crescent wraps around their yellowish ear coverts. Their crown is pearly gray and the rest of their upperparts are bright olive. Their wings are blackish with bright yellow edges and tips on the flight feathers. Their wing coverts have wide yellow tips that show as two wing bars. Their long slender tail is olive. Their underparts are entirely bright yellow. Both sexes have a brown iris, a long, pointed, black bill, and gray legs and feet.[5][6]
Distribution and habitat
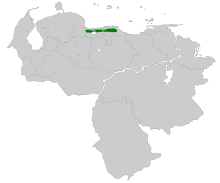
[edit]The rufous-lored tyrannulet has a disjunct distribution within Venezuela. It is found in the mountains of Yaracuy state, in the section of the Coastal Cordillera from western Carabobo east to Aragua and the Capital District, and away from the coast in Miranda and in Guatopo National Park on the Miranda-Guárico border. It inhabits humid to wet montane evergreen forest, mostly in the upper tropical zone but also higher in cloudforest. It primarily is found in the forest interior but often also occurs at its edges. In elevation it ranges from 300 to 1,000 m (1,000 to 3,300 ft) and probably higher.[5][6]
Behavior
[edit]Movement
[edit]The rufous-lored tyrannulet is a year-round resident.[5]
Feeding
[edit]The rufous-lored tyrannulet's diet has not been detailed but is thought to be primarily insects. It forages actively, mostly from the forest's mid-story to its canopy. It typically perches horizontally on a branch, sometimes with its tail slightly cocked up, and makes short sallies to grab or hover-glean prey from leaves and twigs. It also occasionally gleans while perched. It typically forages in pairs or small family groups, and usually as part of a mixed-species feeding flock.[5][6]
Breeding
[edit]Nothing is known about the rufous-lored tyrannulet's breeding biology.[5]
Vocalization
[edit]As of late 2024 xeno-canto had only three recordings of rufous-lored tyrannulet vocalizations and the Cornell Lab of Ornithology's Macaulay Library had only five, with some overlap between the two collections.[5] While foraging the species makes a quick, one to four note, "fussy...high, thin, and jangling teep-teep-teep". It also makes a "sputtery, jangling te'te'skeek!".[6]
Status
[edit]The IUCN originally in 2004 assessed the rufous-lored tyrannulet as being of Least Concern but from February 2024 as Near Threatened. It has a small range; its population size is not known and is believed to be decreasing. "Due to its habitat requirements, the species is threatened by the loss of forests within the range, mainly through logging and conversion for agriculture and livestock pastures. Tree cover loss is however still slow and localised, with large areas of undisturbed habitat remaining."[1] It is considered uncommon to fairly common.[6] It occurs in at least two national parks, but "deforestation has been severe around residential areas, e.g. Caracas, as well as in many other areas".[5]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c BirdLife International (2024). "Rufous-lored Tyrannulet Phylloscartes flaviventris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2024: e.T22699491A247527035. Retrieved 24 December 2024.
- ^ a b Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (August 2024). "Tyrant flycatchers". IOC World Bird List. v 14.2. Retrieved 19 August 2024.
- ^ Hartert, E. (1897). "[A new species of Leptotriccus ...]". Bulletin of the British Ornithologists' Club. 7 (47): v.
- ^ Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, G. Del-Rio, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 18 November 2024. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved 26 November 2024
- ^ a b c d e f g Fitzpatrick, J. W. (2020). Rufous-lored Tyrannulet (Phylloscartes flaviventris), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.rultyr1.01 retrieved December 24, 2024
- ^ a b c d e Hilty, Steven L. (2003). Birds of Venezuela (second ed.). Princeton NJ: Princeton University Press. p. 585.
Further reading
[edit]- Hellmayr, Charles E. (1927). "Pogonotriccus flaviventris (Hartert). Yellow-bellied Bristle-tyrant". Catalogue of Birds of the America and the Adjacent Islands in Field Museum of Natural History. Part V. Tyrannidae. Field Museum of Natural History—Zoology. Vol. 13. Chicago. pp. 348–349.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Traylor, Melvin A. Jr. (1979). "Phylloscartes flaviventris (Hartert)". Check-list of Birds of the World. Vol. 8. Cambridge, MA: Museum of Comparative Zoology. p. 65.


