N-Phenethyl-4-piperidinone
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(2-Phenylethyl)piperidin-4-one | |
| Other names
1-Phenethylpiperidin-4-one (no longer recommended)
N-Phenylethyl-4-piperidinone N-Phenethyl-4-piperidone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | NPP |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.049.630 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H17NO | |
| Molar mass | 203.28 g/mol |
| Density | 1.057 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 56 to 60 °C (133 to 140 °F; 329 to 333 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302 | |
| P264, P270 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Legal status | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
N-Phenethyl-4-piperidinone (NPP) is a derivative of 4-piperidinone with the molecular formula C13H17NO. It is used as an intermediate in the manufacture of chemicals and pharmaceutical drugs such as fentanyl.
Because of its possible use in the illicit manufacture of fentanyl, the United States Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) placed NPP under control as a List 1 Chemical in 2007. Both domestic sales and domestic importations are thus subject to DEA reporting requirements.[3]
Preparation
[edit]N-Phenethyl-4-piperidinone can be prepared from 4-piperidinone and phenethyl bromide in biphasic conditions with a variety of phase transfer catalysts.[citation needed]
Uses
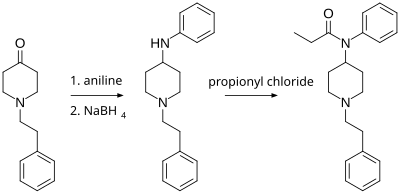
[edit]N-Phenethyl-4-piperidinone is useful in the synthesis of addictive drugs, primarily fentanyl and its analogs. Paul Janssen (founder of Janssen Pharmaceutica) first synthesized fentanyl in 1960 from Benzylfentanyl.[4] The Siegfried method (shown below and published on The Hive) involves reacting N-phenethyl-4-piperidinone with aniline, and then reducing the imine product with sodium borohydride to 4-anilino-N-phenethylpiperidine (ANPP). This product is reacted with propionyl chloride to form fentanyl.
References
[edit]- ^ GHS: PubChem
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-15.
- ^ DEA Chemical Handler's Manual: A Guide to Chemical Control Regulations (2022 ed.). United States Department of Justice Drug Enforcement Administration Office of Diversion Control. May 9, 2014.
- ^ Schulz W. "Fentanyl". List of Top Pharmaceuticals. Chemical & Engineering News.