Paracetamol: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m Added UserMeds social entry for Paracetamol/Acetaminophen |
||
| Line 246: | Line 246: | ||
*[http://www.fda.gov/downloads/ForConsumers/ConsumerUpdates/UCM172664.pdf FDA: Consumer Update "Acetaminophen and Liver Injury: Q and A for Consumers" (PDF)] |
*[http://www.fda.gov/downloads/ForConsumers/ConsumerUpdates/UCM172664.pdf FDA: Consumer Update "Acetaminophen and Liver Injury: Q and A for Consumers" (PDF)] |
||
* [http://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/dpdirect.jsp?name=Acetaminophen U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal – Paracetamol] |
* [http://druginfo.nlm.nih.gov/drugportal/dpdirect.jsp?name=Acetaminophen U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal – Paracetamol] |
||
* [http://www.usermeds.com/drugs/38-ACETAMINOPHEN UserMeds Acetaminophen Social Entry] |
|||
{{Analgesics}} |
{{Analgesics}} |
||
Revision as of 12:45, 24 April 2011
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, rectal, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~100% |
| Metabolism | 90 to 95% Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 1–4 h |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.870 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H9NO2 |
| Molar mass | 151.17 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.263 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 169 °C (336 °F) [2][3] |
| Solubility in water | 12.78[4] mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Paracetamol (INN) (Template:Pron-en, /ˌpærəˈsɛtəmɒl/) or acetaminophen (/əˌsiːtəˈmɪnɵfɨn/ ) (USAN) is a widely used over-the-counter analgesic (pain reliever) and antipyretic (fever reducer). It is commonly used for the relief of headaches, other minor aches and pains, and is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu remedies. In combination with opioid analgesics, paracetamol can also be used in the management of more severe pain such as post surgical pain and providing palliative care in advanced cancer patients.[5] The onset of analgesia is approximately 11 minutes after oral administration of paracetamol,[6] and its half-life is 1–4 hours.
While generally safe for use at recommended doses (1,000 mg per single dose and up to 4,000 mg per day for adults, up to 2,000 mg per day if drinking alcohol),[7] acute overdoses of paracetamol can cause potentially fatal liver damage and, in rare individuals, a normal dose can do the same; the risk is heightened by alcohol consumption. Paracetamol toxicity is the foremost cause of acute liver failure in the Western world, and accounts for most drug overdoses in the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand.[8][9][10][11]
It is the active metabolite of phenacetin, once popular as an analgesic and antipyretic in its own right, but unlike phenacetin and its combinations, paracetamol is not considered to be carcinogenic at therapeutic doses.[12] The words acetaminophen (used in the United States, Canada, Japan, South-Korea, Hong Kong, and Iran[13]) and paracetamol (used elsewhere) both come from chemical names for the compound: para-acetylaminophenol and para-acetylaminophenol. In some contexts, it is simply abbreviated as APAP, for acetyl-para-aminophenol.
Medical uses
Fever
Paracetamol is approved for reducing fever in people of all ages.[14] The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that paracetamol only be used to treat fever in children if their temperature is greater than 38.5 °C (101.3 °F).[15] The efficacy of paracetamol by itself in children with fevers has been questioned[16] with it being less effective than ibuprofen.[17]
Pain
Paracetamol is used for the relief of and pains associated with many parts of the body. It has analgesic properties comparable to those of aspirin, while its anti-inflammatory effects are weaker. It is better tolerated than aspirin in patients in whom excessive gastric acid secretion or prolongation of bleeding time may be a concern. Available without a prescription, it has in recent years increasingly become a common household drug.[18]
Paracetamol can relieve pain in mild arthritis but has no effect on the underlying inflammation, redness, and swelling of the joint. It is as effective as the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen in relieving the pain of osteoarthritis of the knee.
Paracetamol has relatively little anti-inflammatory activity, unlike other common analgesics such as the NSAIDs aspirin and ibuprofen.
Regarding comparative efficacy, studies show conflicting results when compared to NSAIDs. A randomized controlled trial of chronic pain from osteoarthritis in adults found similar benefit from paracetamol and ibuprofen.[19][20]
The efficacy of paracetamol when used in a combination form with weak opioids (such as codeine) has been questioned by recent data studies; the small amount of data available have made reaching a conclusion hard. Combination drugs of paracetamol and strong opioids like morphine have been shown to reduce the amount of opioid used and improve analgesic effect.[21]
A randomized controlled trial of acute musculoskeletal pain in children found that the standard over-the-counter dose of ibuprofen gives greater relief of pain than the standard dose of paracetamol.[22][unreliable source?]
Adverse effects
In recommended doses, paracetamol does not irritate the lining of the stomach, affect blood coagulation as much as NSAIDs, or affect function of the kidneys.[citation needed] However, some studies have shown that high dose-usage (greater than 2,000 mg per day) does increase the risk of upper gastrointestinal complications such as stomach bleeding.[23] The researchers found that heavy use of aspirin or paracetamol – defined as 300 grams a year (1 g per day on average) – was linked to a condition known as small, indented and calcified kidneys.[24] Until 2010 paracetamol was believed to be safe in pregnancy (as it does not affect the closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus as other NSAIDs can.[25]) However, in a study published in October 2010 it has been linked to infertility in the posterior adult life of the unborn.[26] Like NSAIDs and unlike opioid analgesics, paracetamol has not been found to cause euphoria or alter mood although recent research show some evidence that paracetamol can ease psychological pain.[27] Unlike aspirin, it is safe for children, as paracetamol is not associated with a risk of Reye's syndrome in children with viral illnesses.[28] In 2008, the largest study to date on the long-term side-effects of paracetamol in children was published in The Lancet. Conducted on over 200,000 children in 31 countries, the study found that the use of paracetamol for fever in the first year of life was associated with an increase in the incidence of asthmatic symptoms at 6–7 years, and that paracetamol use, both in the first year of life and in children aged 6–7 years, was associated with an increased incidence of rhinoconjunctivitis and eczema.[29] The authors acknowledged that their "findings might have been due to confounding by indication", i.e., that the association may not be causal but rather due to the disease being treated with paracetamol, and emphasized that further research is needed. Furthermore a number of editorials, comments, correspondence, and their replies have been published in The Lancet concerning the methodology and conclusions of this study.[30][31][32][33][34][35][36] The UK regulatory body the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency, also reviewed this research and published a number of concerns over data interpretation, and offer the following advice for healthcare professionals, parents, and care-givers: "The results of this new study do not necessitate any change to the current guidance for use in children. Paracetamol remains a safe and appropriate choice of analgesic in children. There is insufficient evidence from this research to change guidance regarding the use of antipyretics in children."[37]
One study published in 2011 found that usage of paracetamol and other "mild painkillers" in Danish women during pregnancy, especially during the second trimester, increases the risk of mild cryptorchidism in male newborns.[38]
Overdose
Paracetamol hepatotoxicity is, by far, the most common cause of acute liver failure in both the United States and the United Kingdom.[11][39] Paracetamol overdose results in more calls to poison control centers in the US than overdose of any other pharmacological substance.[40] Signs and symptoms of paracetamol toxicity may initially be absent or vague. Untreated overdose can lead to liver failure and death within days. Treatment is aimed at removing the paracetamol from the body and replacing glutathione. Activated charcoal can be used to decrease absorption of paracetamol if the patient presents for treatment soon after the overdose. While the antidote, acetylcysteine, (also called N-acetylcysteine or NAC) acts as a precursor for glutathione, helping the body regenerate enough to prevent damage to the liver, a liver transplant is often required if damage to the liver becomes severe.[8]
There are tablets available (brandname in the UK Paradote) that combine paracetamol with an antidote (methionine), to protect the liver in case of an overdose.
In June 2009, a U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advisory committee recommended that new restrictions should be placed on paracetamol usage in the United States to help protect people from the potential toxic effects. The maximum dosage to be consumed at any given time would be decreased from 1000 mg to 650 mg, while combinations of paracetamol and narcotic analgesics would be prohibited. Committee members were particularly concerned by the fact that the present maximum dosages of paracetamol had been shown to produce alterations in hepatic function.[41] On January 13, 2011, the FDA asked manufacturers of prescription combination products containing paracetamol to limit the amount of paracetamol to no more than 325 mg per tablet or capsule and began requiring manufacturers to update the labels of these products to warn of the potential risk for severe liver damage.[42][43][44][45] Manufacturers will have three years to limit the amount of acetaminophen in their prescription drug products to 325 mg per dosage unit.[43][45] The FDA also is requiring manufacturers to update labels of all prescription combination acetaminophen products to warn of the potential risk for severe liver injury.[42][43][45]
Classification
Paracetamol is part of the class of drugs known as "aniline analgesics"; it is the only such drug still in use today.[46] It is classified as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) by some sources,[47] and not as an NSAID by others,[48] while most sources implicitly distinguish them, for example by mentioning both NSAIDs and paracetamol in the same sentence.[49][50] Paracetamol has few anti-inflammatory effects in comparison to NSAIDs. However, aspirin, paracetamol and other NSAIDs all act by the same mechanism (inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis) and all show varying levels of analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and antiplatelet actions.[51]
Mechanism of action


The main mechanism of action of paracetamol is considered to be the inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX), and recent findings suggest that it is highly selective for COX-2.[52] While it has analgesic and antipyretic properties comparable to those of aspirin or other NSAIDs, its peripheral anti-inflammatory activity is usually limited by several factors, one of which is high level of peroxides present in inflammatory lesions. However, in some circumstances, even peripheral anti-inflammatory activity comparable to other NSAIDs can be observed.
Because of its selectivity for COX-2 it does not significantly inhibit the production of the pro-clotting thromboxanes.[52]
The COX family of enzymes are responsible for the metabolism of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2, an unstable molecule that is, in turn, converted to numerous other pro-inflammatory compounds. Classical anti-inflammatories such as the NSAIDs block this step. Only when appropriately oxidized is the COX enzyme highly active.[53][54]
Paracetamol reduces the oxidized form of the COX enzyme, preventing it from forming pro-inflammatory chemicals.[55][56] This leads to a reduced amount of Prostaglandin E2 in the CNS, thus lowering the hypothalamic set-point in the thermoregulatory centre.
Paracetamol also modulates the endogenous cannabinoid system.[57] Paracetamol is metabolized to AM404, a compound with several actions; what is most important is that it inhibits the uptake of the endogenous cannabinoid/vanilloid anandamide by neurons. Anandamide uptake would result in the activation of the main pain receptor (nociceptor) of the body, the TRPV1 (older name: vanilloid receptor). Furthermore, AM404 inhibits sodium channels, as do the anesthetics lidocaine and procaine.[58] Either of these actions by themselves has been shown to reduce pain, and are a possible mechanism for paracetamol. However, it has been demonstrated that, after blocking cannabinoid receptors with synthetic antagonists, paracetamol's analgesic effects are prevented, suggesting its pain-relieving action involves activation of the endogenous cannabinoid system.[59]
The exact mechanisms how COX is inhibited in various circumstances is still subject of discussion. Because of differences in the activity of paracetamol, aspirin, and other NSAIDs, it has been postulated that further COX variants may exist. A recently discovered COX-1 splice variant termed COX-3 was considered to explain some of the knowledge gap but newer findings do not support the hypothesis that it plays any significant role in the functioning of paracetamol.[52]
Aspirin is known to inhibit the cyclooxygenase (COX) family of enzymes and, because paracetamol's action is partially similar to aspirin's,[clarification needed] much research has focused on whether paracetamol also inhibits COX. It is now clear that paracetamol acts via at least two pathways.[46][55][60][61]
One theory holds that paracetamol works by inhibiting the COX-3 isoform of the COX family of enzymes. When expressed in dogs, this enzyme shares a strong similarity to the other COX enzymes, produces pro-inflammatory chemicals, and is selectively inhibited by paracetamol.[62] However, some research has suggested that, in humans and mice, the COX-3 enzyme is without inflammatory action.[60] Another possibility is that paracetamol blocks cyclooxygenase (as in aspirin), but that is in an inflammatory environment where the concentration of peroxides is high, and the high oxidation state of paracetamol prevents its actions. This would mean that paracetamol has no direct effect at the site of inflammation, but instead acts in the CNS where the environment is not oxidative, to reduce temperature, etc.[62] The exact mechanism by which paracetamol is believed to affect COX-3 is disputed.
Structure and reactivity

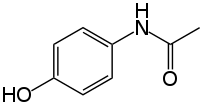
Paracetamol consists of a benzene ring core, substituted by one hydroxyl group and the nitrogen atom of an amide group in the para (1,4) pattern.[63] The amide group is acetamide (ethanamide). It is an extensively conjugated system, as the lone pair on the hydroxyl oxygen, the benzene pi cloud, the nitrogen lone pair, the p orbital on the carbonyl carbon, and the lone pair on the carbonyl oxygen are all conjugated. The presence of two activating groups also make the benzene ring highly reactive toward electrophilic aromatic substitution. As the substituents are ortho,para-directing and para with respect to each other, all positions on the ring are more or less equally activated. The conjugation also greatly reduces the basicity of the oxygens and the nitrogen, while making the hydroxyl acidic through delocalisation of charge developed on the phenoxide anion.
Synthesis
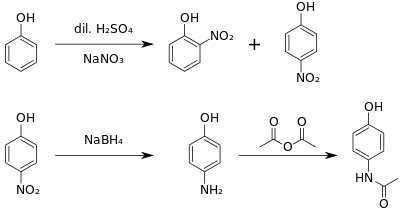
Industrial preparation of paracetamol usually proceeds from nitrobenzene.[64] In the laboratory, paracetamol is easily prepared by nitrating phenol with sodium nitrate, separating the desired p-nitrophenol from the ortho- byproduct, and reducing the nitro group with sodium borohydride. The resultant p-aminophenol is then acetylated with acetic anhydride.[65] In this reaction, phenol is strongly activating, thus the reaction requires only mild conditions (cf. the nitration of benzene):
Reactions
p-Aminophenol may be obtained by the amide hydrolysis of paracetamol. p-Aminophenol prepared this way, and related to the commercially available Metol, has been used as a developer in photography by hobbyists.[66] This reaction is also used to determine paracetamol in urine samples: After hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid, p-aminophenol reacts in ammonia solution with a phenol derivate e.g. salicylic acid to form an indophenol dye under oxidization by air.[67]
Metabolism

Paracetamol is metabolised primarily in the liver, into non-toxic products. Three metabolic pathways are notable:
- Glucuronidation is believed to account for 40% to two-thirds of the metabolism of paracetamol.[68]
- Sulfation (sulfate conjugation) may account for 20–40%.[68]
- N-hydroxylation and rearrangement, then GSH conjugation, accounts for less than 15%. The hepatic cytochrome P450 enzyme system metabolizes paracetamol, forming a minor yet significant alkylating metabolite known as NAPQI (N-acetyl-p-benzo-quinone imine).[69] NAPQI is then irreversibly conjugated with the sulfhydryl groups of glutathione.[69]
All three pathways yield final products that are inactive, non-toxic, and eventually excreted by the kidneys. In the third pathway, however, the intermediate product NAPQI is toxic. NAPQI is primarily responsible for the toxic effects of paracetamol; this constitutes an example of toxication.
Production of NAPQI is due primarily to two isoenzymes of cytochrome P450: CYP2E1 and CYP1A2. The P450 gene is highly polymorphic, however, and individual differences in paracetamol toxicity are believed to be due to a third isoenzyme, CYP2D6. Genetic polymorphisms in CYP2D6 may contribute to significantly different rates of production of NAPQI. Furthermore, individuals can be classified as "extensive", "ultrarapid", and "poor" metabolizers (producers of NAPQI), depending on their levels of CYP2D6 expression. Although CYP2D6 metabolises paracetamol into NAPQI to a lesser extent than other P450 enzymes, its activity may contribute to paracetamol toxicity in extensive and ultrarapid metabolisers, and when paracetamol is taken at very large doses.[70] At usual doses, NAPQI is quickly detoxified by conjugation.[69] Following overdose, and possibly also in extensive and ultrarapid metabolizers, this detoxification pathway becomes saturated, and, as a consequence, NAPQI accumulates.
History

Acetanilide was the first aniline derivative serendipitously found to possess analgesic as well as antipyretic properties, and was quickly introduced into medical practice under the name of Antifebrin by A. Cahn and P. Hepp in 1886.[71] But its unacceptable toxic effects, the most alarming being cyanosis due to methemoglobinemia, prompted the search for less toxic aniline derivatives.[46] Harmon Northrop Morse had already synthesized paracetamol at Johns Hopkins University via the reduction of p-nitrophenol with tin in glacial acetic acid in 1877,[72][73] but it was not until 1887 that clinical pharmacologist Joseph von Mering tried paracetamol on patients.[46] In 1893, von Mering published a paper reporting on the clinical results of paracetamol with phenacetin, another aniline derivative.[74] Von Mering claimed that, unlike phenacetin, paracetamol had a slight tendency to produce methemoglobinemia. Paracetamol was then quickly discarded in favor of phenacetin. The sales of phenacetin established Bayer as a leading pharmaceutical company.[75] Overshadowed in part by aspirin, introduced into medicine by Heinrich Dreser in 1899, phenacetin was popular for many decades, particularly in widely advertised over-the-counter "headache mixtures," usually containing phenacetin, an aminopyrine derivative of aspirin, caffeine, and sometimes a barbiturate.[46]
Von Mering's claims remained essentially unchallenged for half a century, until two teams of researchers from the United States analyzed the metabolism of acetanilide and paracetamol.[75] In 1947 David Lester and Leon Greenberg found strong evidence that paracetamol was a major metabolite of acetanilide in human blood, and in a subsequent study they reported that large doses of paracetamol given to albino rats did not cause methemoglobinemia.[76] In three papers published in the September 1948 issue of the Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, Bernard Brodie, Julius Axelrod and Frederick Flinn confirmed using more specific methods that paracetamol was the major metabolite of acetanilide in human blood, and established it was just as efficacious an analgesic as its precursor.[77][78][79] They also suggested that methemoglobinemia is produced in humans mainly by another metabolite, phenylhydroxylamine. A followup paper by Brodie and Axelrod in 1949 established that phenacetin was also metabolized to paracetamol.[80] This led to a "rediscovery" of paracetamol.[46] It has been suggested that contamination of paracetamol with 4-aminophenol, the substance from which it was synthesized by von Mering, may be the cause for his spurious findings.[75]
Paracetamol was first marketed in the United States in 1953 by Sterling-Winthrop Co., which promoted it as preferable to aspirin since it was safe to take for children and people with ulcers.[75] The best known brand today for paracetamol in the United States, Tylenol, was established in 1955 when McNeil Laboratories started selling paracetamol as a pain and fever reliever for children, under the brand name Tylenol Children's Elixir—the word "tylenol" was a contraction of para-acetylaminophenol.[81] In 1956, 500 mg tablets of paracetamol went on sale in the United Kingdom under the trade name Panadol, produced by Frederick Stearns & Co, a subsidiary of Sterling Drug Inc. Panadol was originally available only by prescription, for the relief of pain and fever, and was advertised as being "gentle to the stomach," since other analgesic agents of the time contained aspirin, a known stomach irritant. In 1963, paracetamol was added to the British Pharmacopoeia, and has gained popularity since then as an analgesic agent with few side-effects and little interaction with other pharmaceutical agents.[73] Concerns about paracetamol's safety delayed its widespread acceptance until the 1970s, but in the 1980s paracetamol sales exceeded those of aspirin in many countries, including the United Kingdom. This was accompanied by the commercial demise of phenacetin, blamed as the cause of analgesic nephropathy and hematological toxicity.[46]
The U.S. patent on paracetamol has long expired, and generic versions of the drug are widely available under the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, although certain Tylenol preparations were protected until 2007. U.S. patent 6,126,967 filed September 3, 1998 was granted for "Extended release acetaminophen particles".[82]
Available forms
Paracetamol is available in a tablet, capsule, liquid suspension, suppository, intravenous, and intramuscular form. The common adult dose is 500 mg to 1000 mg. The recommended maximum daily dose, for adults, is 4000 mg. In recommended doses, paracetamol generally is safe for children and infants, as well as for adults,[83] although rare cases of acute liver injury have been linked to amounts lower than 2500 mg per day.[84]
Panadol, which is marketed in Africa, Asia, Europe, Central America, and Australasia, is the most widely available brand of paracetamol, sold in over 80 countries. In North America, paracetamol is sold in generic form (usually labeled as acetaminophen) or under a number of trade names, for instance, Tylenol (McNeil-PPC, Inc.), Anacin-3, Tempra, Datril, and Ofirmev. While there is brand named paracetamol available in the UK (e.g. Panadol), unbranded or generic paracetamol is more commonly sold. Acamol, a brand name for paracetamol produced by Teva Pharmaceutical Industries in Israel, is one of the most widely used drugs in that country. In the Philippines, the largest-selling paracetamol brand is Biogesic, manufactured by the drug giant United Laboratories. Biogesic tablet sales reach nearly a billion units each year in the country alone, not including liquid suspension formats. The brand is also available in most of the ASEAN countries where the drug giant has market presence. In Europe, the most common brands of paracetamol are Efferalgan and Doliprane. In India, the most common brand of paracetamol is Crocin manufactured by Glaxo SmithKline Asia. In Bangladesh the most popular brand is Napa manufactured by Beximco Pharma. In China paracetamol is sold over the counter as Duiyixiananjifenpian (对乙酰氨基酚片).[85] Likewise in Japan it is sold under the name Acetaminophen (アセトアミノフェン). In North Korea the DPRK-Swiss joint venture PyongSu Pharma markets the drug as PyongSu Cetamol.
In some formulations, paracetamol is combined with the opioid codeine, sometimes referred to as co-codamol (BAN). In the United States and Canada, this is marketed under the name of Tylenol #1/2/3/4, which contain 8–10 mg, 15 mg, 30 mg, and 60 mg of codeine, respectively. In the U.S., this combination is available only by prescription, while the lowest-strength preparation is over-the-counter in Canada, and, in other countries, other strengths may be available over the counter. There are generic forms of these combinations as well. In the UK and in many other countries, this combination is marketed under the names of Tylex CD and Panadeine. Other names include Captin, Disprol, Dymadon, Fensum, Hedex, Mexalen, Nofedol, Paralen, Pediapirin, Perfalgan, and Solpadeine. Paracetamol is also combined with other opioids such as dihydrocodeine, referred to as co-dydramol (BAN), oxycodone or hydrocodone, marketed in the U.S. as Percocet and Vicodin, respectively. Another very commonly used analgesic combination includes paracetamol in combination with propoxyphene napsylate, sold under the brand name Darvocet. A combination of paracetamol, codeine, and the calmative doxylamine succinate is marketed as Syndol or Mersyndol. The efficacy of paracetamol/codeine combinations have been questioned by recent research.[21]
Paracetamol is commonly used in multi-ingredient preparations for migraine headache, typically including butalbital and paracetamol with or without caffeine, and sometimes containing codeine.
-
PyongSu Cetamol250 mg tablets (KP)
Veterinary use
Paracetamol is extremely toxic to cats.[86] Cats lack the necessary glucuronyl transferase enzymes to safely break paracetamol down, and minute portions of a tablet may prove fatal.[86] Initial symptoms include vomiting, salivation, and discolouration of the tongue and gums. Unlike an overdose in humans, liver damage is rarely the cause of death; instead, methemoglobin formation and the production of Heinz bodies in red blood cells inhibit oxygen transport by the blood, causing asphyxiation (methemoglobemia and hemolytic anemia).[87] Treatment with N-acetylcysteine,[86] methylene blue or both is sometimes effective after the ingestion of small doses of paracetamol.
Although paracetamol is believed to have no significant anti-inflammatory activity, it has been reported to be as effective as aspirin in the treatment of musculoskeletal pain in dogs.[88] A paracetamol-codeine product (trade name Pardale-V)[89] licensed for use in dogs is available on veterinary prescription in the UK.[89] It should be administered to dogs only on veterinary advice.[89] The main effects of toxicity in dogs is liver damage.[86][90][91][92] N-acetylcysteine treatment is efficacious in dogs when administered within a few hours of paracetamol ingestion.[86][88]
Paracetamol is also lethal to snakes, and has been suggested as a chemical control program for the brown tree snake (Boiga irregularis) in Guam.[93][94]
References
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1021/ci0500132, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1021/ci0500132instead. - ^ "melting point data for paracetamol". Lxsrv7.oru.edu. Retrieved 2011-03-19.
- ^ Granberg RA, Rasmuson AC (1999). "Solubility of paracetamol in pure solvents". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data. 44 (6): 1391–95. doi:10.1021/je990124v.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) (2008). Scotland: National Health Service (NHS). ISBN 978 1 905813 38 4 http://www.sign.ac.uk/pdf/SIGN106.pdf.
{{cite book}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Text "Section 6.1 and 7.1.1" ignored (help) - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1093/bja/aei109, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1093/bja/aei109instead. - ^ Acetaminophen Drugs.com
- ^ a b Daly FF, Fountain JS, Murray L, Graudins A, Buckley NA (2008). "Guidelines for the management of paracetamol poisoning in Australia and New Zealand—explanation and elaboration. A consensus statement from clinical toxicologists consulting to the Australasian poisons information centres". Med J Aust. 188 (5): 296–301. PMID 18312195.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Khashab M, Tector AJ, Kwo PY (2007). "Epidemiology of acute liver failure". Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 9 (1): 66–73. doi:10.1007/s11894-008-0023-x. PMID 17335680.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hawkins LC, Edwards JN, Dargan PI (2007). "Impact of restricting paracetamol pack sizes on paracetamol poisoning in the United Kingdom: a review of the literature". Drug Saf. 30 (6): 465–79. doi:10.2165/00002018-200730060-00002. PMID 17536874.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Larson AM, Polson J, Fontana RJ; et al. (2005). "Acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: results of a United States multicenter, prospective study" (PDF). Hepatology. 42 (6): 1364–72. doi:10.1002/hep.20948. PMID 16317692.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bergman K, Müller L, Teigen SW (1996). "The genotoxicity and carcinogenicity of paracetamol: a regulatory (re)view". Mutat Res. 349 (2): 263–88. doi:10.1016/0027-5107(95)00185-9. PMID 8600357.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bradley, N (1996). "BMJ should use "paracetamol" instead of "acetaminophen" in its index". BMJ. 313 (7058): 689. PMC 2351967. PMID 8811774.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "Acetaminophen". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
- ^ "Baby paracetamol asthma concern". BBC News. September 19, 2008. Retrieved September 19, 2008.
- ^ Meremikwu M, Oyo-Ita A (2002). "Paracetamol for treating fever in children". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2): CD003676. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003676. PMID 12076499.
- ^ Perrott DA, Piira T, Goodenough B, Champion GD (2004). "Efficacy and safety of acetaminophen vs ibuprofen for treating children's pain or fever: a meta-analysis". Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 158 (6): 521–6. doi:10.1001/archpedi.158.6.521. PMID 15184213.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Medication and Drugs". MedicineNet. 1996–2010. Retrieved April 22, 2010.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ^ Bradley JD, Brandt KD, Katz BP, Kalasinski LA, Ryan SI (1991). "Comparison of an antiinflammatory dose of ibuprofen, an analgesic dose of ibuprofen, and acetaminophen in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee". N. Engl. J. Med. 325 (2): 87–91. doi:10.1056/NEJM199107113250203. PMID 2052056.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ doi:10.1111/j.1365-2710.2006.00754.x
- ^ a b Murnion B. "Combination analgesics in adults". Australian Prescriber (33): 113–5. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ Clark E, Plint AC, Correll R, Gaboury I, Passi B (2007). "A randomized, controlled trial of acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and codeine for acute pain relief in children with musculoskeletal trauma". Pediatrics. 119 (3): 460–7. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-1347. PMID 17332198.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ García Rodríguez LA, Hernández-Díaz S (December 15, 2000). "The risk of upper gastrointestinal complications associated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids, acetaminophen, and combinations of these agents". Arthritis Research and Therapy. 3 (2): 98–101. doi:10.1186/ar146. PMC 128885. PMID 11178116.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Painkillers 'cause kidney damage'". BBC News. November 23, 2003. Retrieved March 27, 2010.
- ^ Rudolph AM (1981). "Effects of aspirin and acetaminophen in pregnancy and in the newborn". Arch. Intern. Med. 141 (3 Spec No): 358–63. doi:10.1001/archinte.141.3.358. PMID 7469626.
- ^ Leffers, H; et al. (2010). "Intrauterine exposure to mild analgesics is a risk factor for development of male reproductive disorders in human and rat". Human Reproduction. 25 (1): 235–244. doi:10.1093/humrep/deq382.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ "Analgesic may take the hurt out of feelings..." News U Can Use. Retrieved 2011-03-19.
- ^ Lesko SM, Mitchell AA (1999). "The safety of acetaminophen and ibuprofen among children younger than two years old". Pediatrics. 104 (4): e39. doi:10.1542/peds.104.4.e39. PMID 10506264.
- ^ Beasley, Richard; Clayton, Tadd; Crane, Julian; von Mutius, Erika; Lai, Christopher; Montefort, Stephen; Stewart, Alistair (2008). "Association between paracetamol use in infancy and childhood, and risk of asthma, rhino conjunctivitis, and eczema in children aged 6–7 years: analysis from Phase Three of the ISAAC programme". The Lancet. 372: 1039–1048. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61445-2. Retrieved September 19, 2008.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61414-2, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61414-2instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61417-8, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61417-8instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60032-5, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60032-5instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60030-1, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60030-1instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60029-5, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60029-5instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60028-3, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60028-3instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60031-3, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60031-3instead. - ^ Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency; Commission on Human Medicines (2008). "Paracetamol use in infancy: no strong evidence for asthma link". Drug Safety Update. 2 (4): 9. Retrieved May 1, 2009.
- ^ Kristensen DM, Hass U, Lesné L; et al. (2011). "Intrauterine exposure to mild analgesics is a risk factor for development of male reproductive disorders in human and rat". Hum. Reprod. 26 (1): 235–44. doi:10.1093/humrep/deq323. PMID 21059752.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ryder SD, Beckingham IJ (2001). "ABC of diseases of liver, pancreas, and biliary system. Other causes of parenchymal liver disease". BMJ. 322 (7281): 290–92. doi:10.1136/bmj.322.7281.290. PMC 1119531. PMID 11157536.
- ^ Lee WM (2004). "Acetaminophen and the U.S. Acute Liver Failure Study Group: lowering the risks of hepatic failure" (PDF). Hepatology. 40 (1): 6–9. doi:10.1002/hep.20293. PMID 15239078.
- ^ "FDA May Restrict Acetaminophen". Webmd.com. 2009-07-01. Retrieved 2011-03-19.
- ^ a b "FDA limits acetaminophen in prescription combination products; requires liver toxicity warnings" (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). January 13, 2011. Retrieved January 13, 2011.
- ^ a b c "FDA Drug Safety Communication: Prescription Acetaminophen Products to be Limited to 325 mg Per Dosage Unit; Boxed Warning Will Highlight Potential for Severe Liver Failure". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). January 13, 2011. Retrieved January 13, 2011.
- ^ Matthew Perrone (January 13, 2011). "FDA orders lowering pain reliever in Vicodin". The Boston Globe. Associated Press. Retrieved January 13, 2011.
- ^ a b c Gardiner Harris (January 13, 2011). "F.D.A. Plans New Limits on Prescription Painkillers". The New York Times. Retrieved January 13, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g Bertolini A, Ferrari A, Ottani A, Guerzoni S, Tacchi R, Leone S (2006). "Paracetamol: new vistas of an old drug" (PDF). CNS drug reviews. 12 (3–4): 250–75. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2006.00250.x. PMID 17227290.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Page 310 in: Hillier, Keith; Waller, Derek J.; Renwick, Andrew (2001). Medical pharmacology and therapeutics. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders. ISBN 0-7020-2272-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Acetaminophen. chemicalland21.com. Retrieved January 2011.
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6257, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6257instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 15254653, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=15254653instead. - ^ Byrant, Bronwen; Knights, Katleen; Salerno, Evelyn (2007). Pharmacology for health professionals. Elsevier. p. 270. ISBN 9780729537872.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Attention: This template ({{cite pmid}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by PMID 17884974, please use {{cite journal}} with
|pmid=17884974instead. - ^ Ohki S, Ogino N, Yamamoto S, Hayaishi O (1979). "Prostaglandin hydroperoxidase, an integral part of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthetase from bovine vesicular gland microsomes". J. Biol. Chem. 254 (3): 829–36. PMID 104998.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Harvison PJ, Egan RW, Gale PH, Nelson SD (1986). "Acetaminophen as a cosubstrate and inhibitor of prostaglandin H synthase". Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 197: 739–47. PMID 3094341.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Aronoff DM, Oates JA, Boutaud O (2006). "New insights into the mechanism of action of acetaminophen: Its clinical pharmacologic characteristics reflect its inhibition of the two prostaglandin H2 synthases". Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 79 (1): 9–19. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2005.09.009. PMID 16413237.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Roberts, L.J. II. & Marrow, J.D. "Analgesic-antipyretic and Antiinflammatory Agents and Drugs Employed in the Treatment of Gout" in, "Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics 10th Edition" by Hardman, J.G. & Limbird, L.E. Published by McGraw Hill, 2001, pp.687–731 ISBN 0071354697
- ^ Högestätt ED, Jönsson BA, Ermund A; et al. (2005). "Conversion of acetaminophen to the bioactive N-acylphenolamine AM404 via fatty acid amide hydrolase-dependent arachidonic acid conjugation in the nervous system". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (36): 31405–12. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501489200. PMID 15987694.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Köfalvi A (2008). "Chapter 9: Alternative interacting sites and novel receptors for cannabinoid ligands. In: 'Cannabinoids and the Brain' Springer-Verlag": 131–160. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-74349-3_9.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Ottani A, Leone S, Sandrini M, Ferrari A, Bertolini A (2006). "The analgesic activity of paracetamol is prevented by the blockade of cannabinoid CB1 receptors". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 531 (1–3): 280–1. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.015. PMID 16438952.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Kis B, Snipes JA, Busija DW (2005). "Acetaminophen and the cyclooxygenase-3 puzzle: sorting out facts, fictions, and uncertainties". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 315 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.085431. PMID 15879007.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Graham GG, Scott KF (2005). "Mechanism of action of paracetamol". American journal of therapeutics. 12 (1): 46–55. doi:10.1097/00045391-200501000-00008. PMID 15662292.
- ^ a b Chandrasekharan NV, Dai H, Roos KL; et al. (2002). "COX-3, a cyclooxygenase-1 variant inhibited by acetaminophen and other analgesic/antipyretic drugs: cloning, structure, and expression". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (21): 13926–31. doi:10.1073/pnas.162468699. PMC 129799. PMID 12242329.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bales, JR (May 1, 1985). "Two-dimensional proton nuclear magnetic resonance "maps" of acetaminophen metabolites in human urine". Clinical Chemistry. 31 (5): 757–762. PMID 3987005.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Anthony S. Travis (2007). "Manufacture and uses of the anilines: A vast array of processes and products". In Zvi Rappoport (ed.). The chemistry of Anilines Part 1. Wiley. p. 764. ISBN 978-0-470-87171-3.
- ^ Ellis, Frank (2002). Paracetamol: a curriculum resource. Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 0-85404-375-6.
- ^ Henney, K (1939). Handbook of Photography. Whittlesey House. p. 324.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Novotny PE, Elser RC (1984). "Indophenol method for acetaminophen in serum examined" (PDF). Clin. Chem. 30 (6): 884–6. PMID 6723045.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b Hendrickson, Robert G.; Kenneth E. Bizovi (2006). "Acetaminophen", in Nelson, Lewis H.; Flomenbaum, Neal; Goldfrank, Lewis R. et al. Goldfrank's toxicologic emergencies, p. 525, New York: McGraw-Hill. Retrieved on January 18, 2009 through Google Book Search.
- ^ a b c Borne, Ronald F. "Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs" in Principles of Medicinal Chemistry, Fourth Edition. Eds. Foye, William O.; Lemke, Thomas L.; Williams, David A. Published by Williams & Wilkins, 1995. p. 544–545.
- ^ Dong, H; Haining, RL; Thummel, KE; Rettie, AE; Nelson, SD (2000). "Involvement of human cytochrome P450 2D6 in the bioactivation of acetaminophen" (PDF). Drug Metab Dispos. 28 (12): 1397–400. PMID 11095574.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Cahn, A (1886). "Das Antifebrin, ein neues Fiebermittel". Centralbl. Klin. Med. 7: 561–64.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Morse HN (1878). "Ueber eine neue Darstellungsmethode der Acetylamidophenole". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft (in German). 11 (1): 232–3. doi:10.1002/cber.18780110151.
- ^ a b Milton Silverman, Mia Lydecker, Philip Randolph Lee (1992). Bad Medicine: The Prescription Drug Industry in the Third World. Stanford University Press. pp. 88–90. ISBN 0804716692.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Von Mering J. (1893) Beitrage zur Kenntniss der Antipyretica. Ther Monatsch 7: 577–587.
- ^ a b c d Sneader, Walter (2005). Drug Discovery: A History. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley. p. 439. ISBN 0471899801.
- ^ Lester D, Greenberg LA, Carroll RP (1947). "The metabolic fate of acetanilid and other aniline derivatives: II. Major metabolites of acetanilid appearing in the blood". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 90: 68–75.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Brodie, BB (1948). "The estimation of acetanilide and its metabolic products, aniline, N-acetyl p-aminophenol and p-aminophenol (free and total conjugated) in biological fluids and tissues". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 94 (1): 22–28. PMID 18885610.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Brodie, BB (1948). "The fate of acetanilide in man" (PDF). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 94 (1): 29–38. PMID 18885611.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Flinn, Frederick B (1948). "The effect on the pain threshold of N-acetyl p-aminophenol, a product derived in the body from acetanilide". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 94 (1): 76–77. PMID 18885618.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Brodie BB, Axelrod J (1949). "The fate of acetophenetidin (phenacetin) in man and methods for the estimation of acetophenitidin and its metabolites in biological material". J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 94 (1): 58–67.
- ^ "A Festival of Analgesics." Chemical Heritage Foundation. 2001. Retrieved on August 17, 2007.
- ^ US patent 6126967, "Extended release acetaminophen particles", issued October 03, 2000
- ^ "Acetaminophen." Physicians' Desk Reference, 63rd ed. Montvale, NJ: Thomson PDR; 2009: 1915–1916.
- ^ "Acetaminophen Overdose and Liver Injury — Background and Options for Reducing Injury", Charles Ganley, MD, Gerald Dal Pan, MD, Bob Rappaport, MD, May 22, 2009, Retrieved July 8, 2010.
- ^ "对乙酰氨基酚片说明书" (in Chinese). Beijing: Chinapharm. Retrieved 18 July 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e Richardson, JA (2000). "Management of acetaminophen and ibuprofen toxicoses in dogs and cats" (PDF). J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care. 10 (4): 285–91. doi:10.1111/j.1476-4431.2000.tb00013.x.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Allen AL (2003). "The diagnosis of acetaminophen toxicosis in a cat". Can Vet J. 44 (6): 509–10. PMC 340185. PMID 12839249.
- ^ a b Maddison, Jill E. (2002). Small Animal Clinical Pharmacology. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 260–1. ISBN 0702025739.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c "Pardale-V Oral Tablets". NOAH Compendium of Data Sheets for Animal Medicines. The National Office of Animal Health (NOAH). 11 November 2010. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- ^ Villar D, Buck WB, Gonzalez JM (1998). "Ibuprofen, aspirin and acetaminophen toxicosis and treatment in dogs and cats". Vet Hum Toxicol. 40 (3): 156–62. PMID 9610496.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Meadows, Irina; Gwaltney-Brant, Sharon (2006). "The 10 Most Common Toxicoses in Dogs". Veterinary Medicine: 142–8.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Dunayer, E (2004). "Ibuprofen toxicosis in dogs, cats, and ferrets". Veterinary Medicine: 580–6.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Johnston J, Savarie P, Primus T, Eisemann J, Hurley J, Kohler D (2002). "Risk assessment of an acetaminophen baiting program for chemical control of brown tree snakes on Guam: evaluation of baits, snake residues, and potential primary and secondary hazards". Environ Sci Technol. 36 (17): 3827–33. doi:10.1021/es015873n. PMID 12322757.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Brad Lendon (2010-09-07). "Tylenol-loaded mice dropped from air to control snakes". CNN. Retrieved 2010-09-07.
External links
- Paracetamol at Chemsynthesis
- Paracetamol Information Centre
- The Julius Axelrod Papers
- FDA: Safe Use of Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers/Fever Reducers
- FDA: Consumer Update "Acetaminophen and Liver Injury: Q and A for Consumers" (link)
- FDA: Consumer Update "Acetaminophen and Liver Injury: Q and A for Consumers" (PDF)
- U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal – Paracetamol
- UserMeds Acetaminophen Social Entry
Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA Template:Link FA