Palladium on carbon

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Palladium on carbon, Pd/C, Pd-C
| |
| Identifiers | |
| Properties | |
| Appearance | Black powder |
| Solubility | Aqua regia |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Palladium on carbon, often referred to as Pd/C, is a form of palladium used as a catalyst.[1] The metal is supported on activated carbon to maximize its surface area and activity.
Uses
[edit]Hydrogenation
[edit]Palladium on carbon is used for catalytic hydrogenations in organic synthesis. Examples include reductive amination,[2] carbonyl reduction, nitro compound reduction,[3][4] the reduction of imines and Schiff bases[1] and debenzylation reactions.
Hydrogenolysis
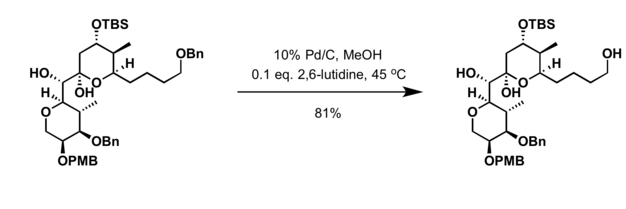
[edit]Palladium on carbon is a common catalyst for hydrogenolysis. Such reactions are helpful in deprotection strategies. Particularly common substrates for hydrogenolysis are benzyl ethers:[5]
Other labile substituents are also susceptible to cleavage by this reagent. [6]
Coupling reactions
[edit]Palladium on carbon is also used for coupling reactions. Examples include the Suzuki reaction and Stille reaction.[7]
Preparation
[edit]A solution of palladium chloride and hydrochloric acid is combined with aqueous suspension of activated carbon. The palladium(II) is then reduced by the addition of formaldehyde.[8] Palladium loading is typically between 5% and 10%. Often the catalyst mixture is stored moist.
See also
[edit]- Palladium black
- Platinum on carbon
- Platinum dioxide
- Rhodium-platinum oxide
- Lindlar catalyst
- Raney nickel
- Urushibara nickel
References
[edit]- ^ a b Nishimura, Shigeo (2001). Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation for Organic Synthesis (1st ed.). New York: Wiley-Interscience. pp. 34–38. ISBN 9780471396987.
- ^ Romanelli, Michael G.; Becker, Ernest I. (1967). "Ethylp-dimethylaminophenylacetate". Organic Syntheses. 47: 69. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.047.0069.
- ^ Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007). March's Advanced Organic Chemistry (6th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 1816. ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1.
- ^ Ram, Siya; Ehrenkaufer, Richard E. (1984). "A general procedure for mild and rapid reduction of aliphatic and aromatic nitro compounds using ammonium formate as a catalytic hydrogen transfer agent". Tetrahedron Letters. 25 (32): 3415–3418. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)91034-2. hdl:2027.42/25034.
- ^ Smith, Amos B.; Zhu, Wenyu; Shirakami, Shohei; Sfouggatakis, Chris; Doughty, Victoria A.; Bennett, Clay S.; Sakamoto, Yasuharu (2003-03-01). "Total Synthesis of (+)-Spongistatin 1. An Effective Second-Generation Construction of an Advanced EF Wittig Salt, Fragment Union, and Final Elaboration". Organic Letters. 5 (5): 761–764. doi:10.1021/ol034037a. ISSN 1523-7060. PMID 12605509.
- ^ Musliner, Walter J.; Gates, Jr, John W. (1971). "Dehydroxylation of Phenols; Hydrogenolysis of Phenolic Ethers: Biphenyl". Organic Syntheses. 51: 82. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.051.0082.
- ^ Liebeskind, Lanny S.; Peña-Cabrera, Eduardo (2000). "Stille couplings catalyzed by palladium-on-carbon with CuI as a co-catalyst: synthesis of 2-(4'-Acetylhenyl)thiophene". Organic Syntheses. 77: 138. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.077.0135.
- ^ Mozingo, Ralph (1946). "Palladium catalysts". Organic Syntheses. 26: 77–82. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.026.0077. PMID 20280763.