PDE5 inhibitor
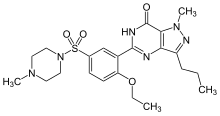
A phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor (PDE5 inhibitor) is a vasodilating drug that works by blocking the degradative action of cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) on cyclic GMP in the smooth muscle cells lining the blood vessels supplying various tissues. These drugs dilate the corpora cavernosa of the penis, facilitating erection with sexual stimulation, and are used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). Sildenafil was the first effective oral treatment available for ED. Because PDE5 is also present in the smooth muscle of the walls of the arterioles within the lungs, two PDE5 inhibitors, sildenafil and tadalafil, are FDA-approved for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. As of 2019, the wider cardiovascular benefits of PDE5 inhibitors are being appreciated.[1]
Medical uses
[edit]Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), vardenafil (Levitra), and avanafil (Stendra) are clinically indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction.[2] Sildenafil and tadalafil are also indicated for the treatment of some subtypes of pulmonary hypertension, while tadalafil is also licensed for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.[1]
PDE5 inhibitors have been used as a second line therapy in severe cases of Raynaud phenomenon when it is related to systemic sclerosis per The European Society for Vascular Medicine guidelines.[3]
Sildenafil, the prototypical PDE5 inhibitor, was originally discovered during the search of a novel treatment for angina. Studies in 2002 explored its potential for increasing neurogenesis after stroke,[4] but clinical evidence for benefit in cerebrovascular diseases is currently lacking.[1]
Contraindications
[edit]PDE5 inhibitors are contraindicated within 24 hours (or 48 hours with tadalafil) of taking alpha-blockers, soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators, or nitrate medications such as isosorbide mononitrate or isosorbide dinitrate.[1] Concurrent use of these medications can lead to life-threatening low blood pressure.[5] PDE5 inhibitors are also contraindicated in patients with previous nonarteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy and hereditary eye diseases.[1]
Despite initial concerns of adverse cardiovascular events in patients prescribed PDE5 inhibitors, several long-term studies have established the safety of the drugs in both healthy patients and patients with cardiovascular risk factors.[1]
Adverse effects
[edit]All PDE5 inhibitors are generally well tolerated.[1] The occurrence of side effects, or adverse drug reactions (ADRs), with PDE5 inhibitors depends on the dose and type of agent.[1] Headache is a very common ADR, occurring in >10% of patients. Other common ADRs include: dizziness, flushing, dyspepsia, nasal congestion or rhinitis.[6] Back pain and muscle aches are also more common in patients taking tadalafil.[1]
In 2007, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced that a warning about possible sudden hearing loss would be added to drug labels of PDE5 inhibitors.[7]
Since 2007 there has been evidence to suggest that PDE5 inhibitors can cause an anterior optic neuropathy,[8] although the absolute risk increase is small.[1]
Finally, there are concerns that PDE5 inhibitors may increase the risk of neonatal mortality in pregnant women, and trials investigating use of the drugs for fetal growth restriction have been suspended.[1]
Drug interactions
[edit]PDE5 inhibitors are primarily metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, particularly CYP3A4. The potential exists for adverse drug interactions with other drugs which inhibit or induce CYP3A4, including HIV protease inhibitors, ketoconazole, and itraconazole,[6] although coadministration has not been linked to changes in the safety or efficacy of either agent.[1] Combination with nitrovasodilators such as nitroglycerin and PETN is contraindicated because potentially life-threatening hypotension may occur.[9] PDE5 inhibitors do not interact synergistically with other antihypertensive drugs.[1]
Examples
[edit]
The PDE5 inhibitor story begins with the work of the British physician and physiologist Henry Hyde Salter who, in 1886, noticed that his asthma symptoms eased after drinking a strong cup of coffee. We now know that this was due to the bronchodilator properties of caffeine, a non-selective, albeit weak, PDE5 inhibitor.[10] In 1986, Pfizer scientists at Sandwich, UK, started preclinical work on the development of a PDE5 inhibitor (later known as sildenafil citrate) for the treatment of angina.
Sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil and avanafil are the main agents marketed globally, although mirodenafil, udenafil, gisadenafil, yonkenafil (tunodafil) and lodenafil are available in some countries.[1] Other agents with weak PDE5 inhibitory properties include fenspiride, MBCQ, zaprinast and icariin.[11]
Although all PDE5 inhibitors share the same mechanism of action, each agent has different pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics which affect how quickly it acts, how long its effects last, and its side effects.[1] Notably, although all PDE5 inhibitors preferentially inhibit PDE5, the degree to which they also inhibit other phosphodiesterases influences their side effect profile.[1] For example, sildenafil also inhibits PDE6 which is present in the retina of the eye; this reaction is thought to be responsible for the temporary visual changes which some patients using sildenafil experience. Similarly tadalafil also inhibits PDE11 which is present in the prostate, although no effects on fertility have been reported.[1] Although agents more selective for PDE5 were in development, these trials have been suspended, likely due to the saturation of the market with the introduction of agents with broad cardiovascular benefits, such as SGLT2 inhibitors and endothelin receptor antagonists.[1]
Nevertheless, PDE5 inhibitors already marketed for erectile dysfunction and pulmonary arterial hypertension are undergoing research in several conditions such as resistant hypertension, myocardial infarction, heart failure, intermittent claudication, Raynaud's phenomenon, chronic kidney disease, and diabetes mellitus due to our greater appreciation of their broad physiological properties.[1]
There are some PDE5 inhibitors, generally not approved by any health regulatory agency, that have been found as undeclared ingredients or adulterants in a variety of supplements which are sold as "natural" or "herbal" sexual enhancement products. Examples are acetildenafil, aildenafil, homosildenafil, nitrosoprodenafil, and sulfoaildenafil, thioquinapiperifil.[citation needed]
Mechanism of action
[edit]Part of the physiological process of vasodilatation involves the release of nitric oxide (NO) by vascular endothelial cells which then diffuses to nearby vascular smooth muscle cells. There, NO activates soluble guanylate cyclase which converts guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), the main effector of the system. For example, in the penis, NO release at high levels from endothelial cells and penile nerves during sexual stimulation leads to relaxation of the smooth vasculature of the corpus cavernosum, causing vasocongestion and a sustained erection.[1]
PDE5 inhibitors prolong the action of cGMP by inhibiting its degradation by the enzyme PDE5, which is found throughout the body. In the penis, PDE5 inhibitors potentiate the effects of cGMP to prolong erections and increase sexual satisfaction.[12] However, PDE5 inhibitors do not cause erections without sexual stimulation.
As well as their haemodynamic effects, PDE5 inhibitors have also been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiproliferative, and metabolic properties in several experiments.[1] However, larger and longer-term studies are needed to establish their effectiveness and safety compared to other medications in other diseases.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u Tzoumas N, Farrah TE, Dhaun N, Webb DJ (November 2019). "Established and emerging therapeutic uses of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors in cardiovascular disease". British Journal of Pharmacology. 177 (24): 5467–5488. doi:10.1111/bph.14920. PMC 7707100. PMID 31721165.
- ^ Kandeel FR. "Treatment of Erectile Dsyfunction in Men with Heart Disease". Male Sexual Dysfunction: Pathophysiology and Treatment. CRC Press, 2013. p. 453.
- ^ Belch, Jill; Carlizza, Anita; Carpentier, Patrick H.; Constans, Joel; Khan, Faisel; Wautrecht, Jean-Claude; Visona, Adriana; Heiss, Christian; Brodeman, Marianne; Pécsvárady, Zsolt; Roztocil, Karel (2017-10-01). "ESVM guidelines – the diagnosis and management of Raynaud's phenomenon". VASA. Zeitschrift für Gefässkrankheiten. 46 (6): 413–423. doi:10.1024/0301-1526/a000661. ISSN 0301-1526. PMID 28895508.
- ^ Zhang R, Wang Y, Zhang L, Zhang Z, Tsang W, Lu M, et al. (November 2002). "Sildenafil (Viagra) induces neurogenesis and promotes functional recovery after stroke in rats". Stroke. 33 (11): 2675–80. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000034399.95249.59. PMID 12411660.
- ^ Webb DJ, Freestone S, Allen MJ, Muirhead GJ (March 1999). "Sildenafil citrate and blood-pressure-lowering drugs: results of drug interaction studies with an organic nitrate and a calcium antagonist". The American Journal of Cardiology. 83 (5A): 21C – 28C. doi:10.1016/S0002-9149(99)00044-2. PMID 10078539.
- ^ a b Rossi S, editor. Australian Medicines Handbook 2006. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook; 2006.[page needed]
- ^ "FDA Announces Revisions to Labels for Cialis, Levitra and Viagra". Food and Drug Administration. 2007-10-18. Retrieved 2011-10-30.
- ^ Rao AR, Thwaini A, Ahmed HU, Shergill IS, Minhas S (July 2007). "The phosphodiesterase inhibitors and non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy: increased vigilance is necessary". BJU International. 100 (1): 3–4. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.06839.x. PMID 17488310. S2CID 43862884.
- ^ Haberfeld H, ed. (2009). Austria-Codex (in German) (2009/2010 ed.). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. ISBN 978-3-85200-196-8.
- ^ Boswell-Smith V, Spina D, Page CP (January 2006). "Phosphodiesterase inhibitors". British Journal of Pharmacology. 147 Suppl 1 (S1): S252-7. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706495. PMC 1760738. PMID 16402111.
- ^ Dell'Agli M, Galli GV, Dal Cero E, Belluti F, Matera R, Zironi E, et al. (September 2008). "Potent inhibition of human phosphodiesterase-5 by icariin derivatives". Journal of Natural Products. 71 (9): 1513–7. doi:10.1021/np800049y. PMID 18778098. S2CID 86637628.
- ^ Goldstein I, Lue TF, Padma-Nathan H, Rosen RC, Steers WD, Wicker PA (May 1998). "Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Sildenafil Study Group". The New England Journal of Medicine. 338 (20): 1397–404. doi:10.1056/NEJM199805143382001. PMID 9580646.
Further reading
[edit]- Uzunov P, Weiss B (September 1972). "Separation of multiple molecular forms of cyclic adenosine-3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase in rat cerebellum by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 284 (1): 220–6. doi:10.1016/0005-2744(72)90060-5. PMID 4342220.
- Weiss, B (1975). "Differential activation and inhibition of the multiple forms of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase". Advances in Cyclic Nucleotide Research. 5: 195–211. PMID 165666.
- Fertel R, Weiss B (July 1976). "Properties and drug responsiveness of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases of rat lung". Molecular Pharmacology. 12 (4): 678–87. PMID 183099.
- Weiss B, Hait WN (1977). "Selective cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents". Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 17: 441–77. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.17.040177.002301. PMID 17360.
- Kanthapillai P, Lasserson T, Walters E (October 2004). "Sildenafil for pulmonary hypertension". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2004 (4): CD003562. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003562.pub2. PMC 6396057. PMID 15495058.
- Rao AR, Thwaini A, Ahmed HU, Shergill IS, Minhas S (July 2007). "The phosphodiesterase inhibitors and non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy: increased vigilance is necessary". BJU International. 100 (1): 3–4. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.06839.x. PMID 17488310. S2CID 43862884.
