Neodymium(II) chloride
Appearance
(Redirected from Neodymium dichloride)
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Neodymium dichloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NdCl2 | |
| Molar mass | 215.14 g/mol |
| Appearance | Black solid[1] |
| Structure | |
| Orthorhombic | |
| Pnma, No. 62 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Neodymium(II) bromide Neodymium(II) iodide |
Other cations
|
SmCl2, EuCl2, DyCl2, TmCl2, YbCl2, |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Neodymium(II) chloride or neodymium dichloride is a chemical compound of neodymium and chlorine with the formula NdCl2.
Preparation
[edit]Neodymium(II) chloride can be prepared by reducing neodymium(III) chloride with lithium metal/naphthalene or lithium chloride in THF.[2]
Reduction of neodymium(III) chloride with neodymium metal at temperatures above 650 °C also yields neodymium(II) chloride:[3]
- 2 NdCl3 + Nd → 3 NdCl2
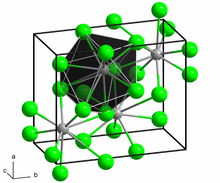
Structure
[edit]Neodymium(II) chloride adopts the PbCl2 (cotunnite) structure. Each Nd2+ ion is coordinated by nine Cl− ions in a tricapped trigonal prismatic arrangement. Seven of the Nd-Cl distances are in the range 2.95-3.14 Å while two are longer at 3.45 Å.[4][5]
References
[edit]- ^ Brauer, Georg; Baudler, Marianne (1975). Handbuch der Präparativen Anorganischen Chemie, Band I. (3rd ed.). Stuttgart: Ferdinand Enke. ISBN 3-432-02328-6.
- ^ Rossmainth, K. (1979-07-01). "Herstellung von Neodym(II)-chlorid in Lösung" [Preparation of neodymium(II) chloride in solution]. Monatshefte für Chemie - Chemical Monthly. 110 (4): 1019–1023. doi:10.1007/BF00906697. S2CID 99130833.
- ^ Gerd Meyer, Lester R. Morss (1991). Synthesis of lanthanide and actinide compounds. Springer. p. 161. ISBN 0-7923-1018-7.
- ^ Meyer, Gerd; Schleid, Thomas (1985). "Zweiwertiges Neodym: NdCl2 und KNd2Cl5". Z. anorg. allg. Chem. 528 (9): 55–60. doi:10.1002/zaac.19855280906.
- ^ "ICSD Entry: 48206". Cambridge Structural Database: Access Structures. Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre. Retrieved 2021-06-06.
