Palm cockatoo
| Palm cockatoo | |
|---|---|

| |
| Palm cockatoo in Lockhart River, Queensland | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Psittaciformes |
| Family: | Cacatuidae |
| Genus: | Probosciger Kuhl, 1820 |
| Species: | P. aterrimus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Probosciger aterrimus (Gmelin, JF, 1788)
| |
| Subspecies | |
|
P. a. aterrimus [Gmelin 1788] | |
| |
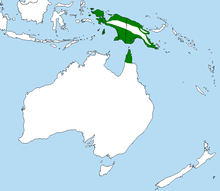
| Australian palm cockatoo range (in green) | |
The palm cockatoo (Probosciger aterrimus), also known as the goliath cockatoo or great black cockatoo, is a large, smoky-grey/black parrot of the cockatoo family native to New Guinea, the Aru Islands and the Cape York Peninsula in Queensland, Australia.[3][4] It has a crest of long feathers atop its head, with a very large and strong, sharply-hooked black beak (with which it can easily open nuts and seeds), and prominent bright-red cheek patches.[5]
Taxonomy
[edit]The palm cockatoo was formally described in 1788 by naturalist Johann Friedrich Gmelin in his revised and expanded edition of Carl Linnaeus's Systema Naturae, in which he classified the bird with other parrots in the genus Psittacus and coined the binomial name Psittacus aterrimus.[6] Gmelin based his description on the "black cockatoo" that had been described and illustrated in 1764 by English naturalist George Edwards.[7] Joan Gideon Loten had provided Edwards with a drawing of the bird by the Sri Lankan artist Pieter Cornelis de Bevere;[8] the original drawing by de Bere is in the collection of the Natural History Museum, London.[9]
The palm cockatoo is, now, the only species within the genus Probosciger that was introduced by Heinrich Kuhl in 1820.[10][3] The generic name combines the Latin proboscis (meaning "snout") with -ger (meaning "carrying"); the specific epithet aterrimus is Modern Latin, meaning "very black".[11] The accepted type locality is Aru Islands,[12][13] rather than "northern Australia".[14]
The palm cockatoo is a member of the white cockatoo subfamily Cacatuinae.[15] Earlier, limited genetic studies found it to be the earliest offshoot from ancestors of what have become the cockatoo family.[16] [disputed (for: conflict with sources cited above) – discuss]
"Palm cockatoo" was designated the official common name for the species by the International Ornithological Committee (IOC).[3] The bird was also referred to as the "Goliath aratoo" in Wood's Natural History (1862). It is sometimes given the misnomer "black macaw" in aviculture, despite the fact that macaws are New World parrots and are unrelated to the palm cockatoo (other than both birds belonging to the Psittaciformes order). Confusingly, this name was also used by early naturalists as well as Brazilian tribes to refer to the dark blue hyacinth macaw (Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus).[citation needed]
Four subspecies are recognised.[3]
- P. a. stenolophus (van Oort, 1911) – Yapen (Geelvink Bay islands, northwest New Guinea) and north, east New Guinea
- P. a. goliath (Kuhl, 1820) – Raja Ampat Islands (northwest of New Guinea), Bird's Head Peninsula (northwest New Guinea) and west, central, southeast New Guinea
- P. a. aterrimus (Gmelin, JF, 1788) – Aru Islands (southwest of New Guinea)
- P. a. macgillivrayi (Mathews, 1912) – south New Guinea and north Cape York Peninsula, northeast Queensland (northeast Australia)
A 2007 genetic study found little support for the above division into subspecies.[17]
Description
[edit]The palm cockatoo is 55 to 60 cm (22 to 24 in) in length and weighs 910–1,200 g (2.01–2.65 lb).[18] It may be the largest cockatoo species and largest parrot in Australia, although large races of yellow-tailed black cockatoos and sulphur-crested cockatoos broadly overlap in size. It is a distinctive bird with a large crest and has one of the largest bills of any parrot (only the hyacinth macaw's is larger). This powerful bill enables palm cockatoos not only to eat very hard nuts and seeds, but also enables males to break off thick (about 1 in (2.5 cm)) sticks from live trees to use for a drumming display.[19] The male has a larger beak than the female.[18] The beak is unusual, as the lower and upper mandibles do not meet for much of its length, allowing the tongue to hold a nut against the top mandible while the lower mandible works to open it. The palm cockatoo also has a distinctive red cheek patch that changes colour when the bird is alarmed or excited.
The races P. a. goliath and P. a. stenolophus are larger than the nominate subspecies. The race stenolophus also has narrower crest feathers.[13]
Vocalisation
[edit]
The vocalizations of palm cockatoos are similar to those of most wild parrots, but they have also been shown to produce a variety of additional syllables in display and exchange with neighbouring individuals. These additional syllables are mainly produced by males and are often combined to form long, complex sequences. In a population in the Iron Range, 30 different syllables were distinguished.[20] The palm cockatoos from the east have different call types from the ones from other areas, due to their long term isolation.[21]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]The palm cockatoo is found in rainforests and woodlands of New Guinea and Cape York Peninsula, Queensland, Australia. It can still be found near Sorong, West Papua, Indonesia, where it is sometimes seen in trees along the roads.[22]
Behaviour and ecology
[edit]It has a unique territorial display where the bird (typically the male) drums with a large (i.e. up to 2.5 cm diameter, 15 cm long) stick or seed pod against a dead bough or tree, creating a loud noise that can be heard up to 100 m away.[23] After drumming, the male occasionally strips the drum tool into small pieces to line the nest.[24] Although this drumming behaviour was discovered over three decades ago (in 1984 by G.A. Wood), the reason why palm cockatoos drum is still a mystery. One reason could be that females can assess the durability of the nesting hollow by the resonance of the drumming. Another possibility could be that males drum to mark their territory against other males.[citation needed] The palm cockatoo is an unusual bird, being an ancient species and one of the few bird species known to use tools.[22]
Flocking
[edit]This species normally does not appear in large numbers. They are not known to flock feed like many of the cockatoo species. Usually only one to six individuals are observed feeding together at one time. As with other large birds, both parents care for young, so seeing a breeding pair is not unusual. If these birds do congregate, it will usually happen in open woodland just after sunrise or along the rainforest edge before returning to individual roosts for the night.[25]
Breeding
[edit]Palm cockatoos only lay one egg every second year and have one of the lowest breeding success rates reported for any species of parrot.[26] Offsetting this is their very long lifespan. A male commenced breeding at 29 in Taronga Zoo in Sydney, and a female at the London Zoo was 40 when she laid her first egg in 1966. Breeding takes place inside tree hollows that look like standing pipes. Fires play an important role in the destruction and creation of nest hollows. Fires allow the colonisation of microorganisms and termites, which enter the tree and start hollowing out the inside. Cyclones are important in the final stage of nest hollow development.
Anecdotal evidence indicates a palm cockatoo reaching 80 or 90 years of age in an Australian zoo,[26] although the oldest confirmed individual was aged 56 in London Zoo in 2000.[27] Although longevity of captive birds is known, the lifespan of palm cockatoos that live in the wild is still unknown.
Food and feeding
[edit]The palm cockatoo often feeds during the early hours of the day, on a diet consisting mostly of wild pandanus palm fruits and kanari tree nuts. They have also been seen eating fruits of Darwin stringy bark and the nonda tree, as well as seeds from the cocky apple tree, beach almond and black bean tree.[25]
Drumming
[edit]A 2023 study by Professor Robert Heinsohn from the Australian National University, has found that palm cockatoos fashion individual musical tools, in the form of wood and seed pods, to drum on trees to mark their territories and attract potential mates. These musical tools are used by the cockatoos to drum out highly personal rhythms and the tools are often highly decorated. [28]
Conservation and status
[edit]
The palm cockatoo is still relatively common in Cape York, where it is nonetheless threatened by habitat destruction (particularly due to bauxite mining around Weipa) and altered fire regimens in the region. Palm cockatoos are also hunted traditionally in New Guinea. The species is currently listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.[1] It is listed on Appendix I of CITES. In Australia, palm cockatoos were relisted from Near Threatened to Vulnerable on 31 October 2015 (EPBC Act List of Threatened Fauna).
Aviculture
[edit]This species is in high demand for the pet trade due to its unusual appearance. In early captive situations, pet owners would either feed dog kibble or generic bird seed mixture, while zoos would give them "monkey biscuits". As their nutritional needs became more apparent over the years, owners have shifted to specially formulated "manufactured diet" pellets along with a wide variety of treats like peanuts, pecans, Brazil nuts, pine nuts, sunflower seeds, oranges, apples, grapes, pomegranate, bananas, sweet potatoes, carrots, beets, broccoli, and kale. Many zoos still give them monkey biscuits to broaden their diet.[29]
References
[edit]- ^ a b BirdLife International (2023). "Probosciger aterrimus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2023: e.T22684723A221314898. Retrieved 12 December 2023.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ a b c d Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (January 2023). "Parrots, cockatoos". IOC World Bird List Version 13.1. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 20 February 2023.
- ^ "Species profile—Probosciger aterrimus macgillivrayi (palm cockatoo)". Species information. Queensland Government. Retrieved 4 April 2024.
- ^ Thane K. Pratt; Bruce M. Beehler (2015). Birds of New Guinea: Second Edition. Princeton University Press. p. 122. ISBN 9780691095639.
- ^ Gmelin, Johann Friedrich (1788). Systema naturae per regna tria naturae : secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis (in Latin). Vol. 1, Part 1 (13th ed.). Lipsiae [Leipzig]: Georg. Emanuel. Beer. p. 330.
- ^ Edwards, George (1764). Gleanings of Natural History, Exhibiting Figures of Quadrupeds, Birds, Insects, Plants &c. Vol. 3. London: Printed for the author. p. 229; Plate 316.
- ^ Ferguson, Donald; Anthonisz, R.G. (1907). "Joan Gideon Loten, F.R.S., the naturalist Governor of Ceylon (1752-57), and the Ceylonese artist de Bevere". Journal of the Ceylon Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society. 19 (58): 217–271. JSTOR 45385020.
- ^ "Collection of 154 coloured drawings of Birds, Mammals, Insects and Plants, painted from the life for J. G. Loten, Dutch Governor of Ceylon, 1752-1757 / by P. C.de Bevere, in Ceylon and the Malay Archipelago, 1754-1757". Natural History Museum, London. Retrieved 20 February 2023.
- ^ Kuhl, Heinrich (1820). "Conspectus Psittacorum". Verhandlungen der Kaiserlichen Leopoldinisch-Carolinische Academie der Naturforscher (in Latin). 10: 1–104 [12].
- ^ Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 317, 58. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ Schodde, Richard (1997). Aves (Columbidae to Coraciidae) in Zoological Catalogue of Australia. Vol. 37, Part 2. Collingwood, Victoria, Australia: Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO). pp. 73–74. ISBN 0-643-06037-5.
- ^ a b Rowley, I. (1997). "Family Cacatuidae (Cockatoos)". In del Hoyo, J.; Elliott, A.; Sargatal, J. (eds.). Handbook of the Birds of the World. Vol. 4: Sandgrouse to Cuckoos. Barcelona, Spain: Lynx Edicions. pp. 246–279 [271]. ISBN 978-84-87334-22-1.
- ^ Peters, James Lee, ed. (1937). Check-List of Birds of the World. Vol. 3. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. p. 171.
- ^ Nicole E. White; Matthew J. Phillips; M. Thomas P. Gilbert; Alonzo Alfaro-Núñez; Eske Willerslev; Peter R. Mawson; Peter B.S. Spencer; Michael Bunce (2011). "The evolutionary history of cockatoos (Aves: Psittaciformes: Cacatuidae)". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 59 (3): 615–622. Bibcode:2011MolPE..59..615W. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2011.03.011. PMID 21419232.
- ^ Brown DM, Toft CA (1999). "Molecular systematics and biogeography of the cockatoos (Psittaciformes: Cacatuidae)". Auk. 116 (1): 141–57. doi:10.2307/4089461. ISSN 0004-8038. JSTOR 4089461.
- ^ Murphy, S.A.; Double, M.C.; Legge, S.M. (2007). "The phylogeography of palm cockatoos, Probosciger aterrimus, in the dynamic Australo-Papuan region". Journal of Biogeography. 34 (9): 1534–1545. Bibcode:2007JBiog..34.1534M. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2699.2007.01706.x. S2CID 84643092.
- ^ a b Forshaw, Joseph M. (2006). Parrots of the World; an Identification Guide. Illustrated by Frank Knight. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-09251-5.
- ^ (Wood 1984)
- ^ Zdenek, C.N.; Heinsohn, R.; Langmore, N.E. (2015). "Vocal complexity in the palm cockatoo (Probosciger aterrimus)". Bioacoustics. 24 (3): 253–257. Bibcode:2015Bioac..24..253Z. doi:10.1080/09524622.2015.1070281. S2CID 55370532.
- ^ Keighley, M.V.; Langmore, N.E.; Zdenek, C.N.; Heinsohn, R. (2017). "Geographic variation in the vocalizations of Australian palm cockatoos (Probosciger aterrimus)". Bioacoustics. 26 (1): 91–108. Bibcode:2017Bioac..26...91K. doi:10.1080/09524622.2016.1201778. S2CID 88696300.
- ^ a b Indonesian Parrot Project Archived 29 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Australian Geographic Archived 2 February 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Heinsohn, Robert; Zdenek, Christina N.; Cunningham, Ross B.; Endler, John A.; Langmore, Naomi E. (1 June 2017). "Tool-assisted rhythmic drumming in palm cockatoos shares key elements of human instrumental music". Science Advances. 3 (6): e1602399. Bibcode:2017SciA....3E2399H. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1602399. ISSN 2375-2548. PMC 5489270. PMID 28782005.
- ^ a b Parrot Tag: Palm Cockatoo Archived 5 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Murphy S, Legge S, Heinsohn R (2003). "The breeding biology of palm cockatoos (Probosciger aterrimus): a case of a slow life history". Journal of Zoology. 261 (4): 327–39. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.475.7031. doi:10.1017/S0952836903004175.
- ^ Brouwer K, Jones M, King C, Schifter H (2000). "Longevity records for Psittaciformes in captivity". International Zoo Yearbook. 37: 299–316. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1090.2000.tb00735.x.
- ^ Sexton-McGrath, Kristy (13 September 2023). "Australian National University researchers find 'master sculptor' in drumming palm cockatoo". Australlian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC).
- ^ "Nutritional Requirements of Adult Palm Cockatoos" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 June 2013. Retrieved 14 July 2012.
Further reading
[edit]- Murphy, S.A.; Legge, S.M. (2007). "The gradual loss and episodic creation of Palm Cockatoo (Probosciger aterrimus) nest-trees in a fire- and cyclone-prone habitat". Emu. 107 (1): 1–6. Bibcode:2007EmuAO.107....1M. doi:10.1071/mu06012. S2CID 84507278.
External links
[edit]- Explore Species: Palm Cockatoo at eBird (Cornell Lab of Ornithology)

