Media (communication)
This article is written like a personal reflection, personal essay, or argumentative essay that states a Wikipedia editor's personal feelings or presents an original argument about a topic. (September 2023) |
In communication, media (sing. medium) are the outlets or tools used to store and deliver semantic information or contained subject matter, described as content.[1][2] The term generally refers to components of the mass media communications industry, such as print media (publishing), news media, photography, cinema, broadcasting (radio and television), digital media, and advertising.[3] Each of these different channels requires a specific, thus media-adequate approach, to a successful transmission of content.[4]
The development of early writing and paper enabling longer-distance communication systems such as mail, including in the Persian Empire (Chapar Khaneh and Angarium) and Roman Empire, can be interpreted as early forms of media.[5] Writers such as Howard Rheingold have framed early forms of human communication, such as the Lascaux cave paintings and early writing, as early forms of media.[6] Another framing of the history of media starts with the Chauvet Cave paintings and continues with other ways to carry human communication beyond the short range of voice: smoke signals, trail markers, and sculpture.[7]
In its modern application, the term media is relating to communication channels was first used by Canadian communications theorist Marshall McLuhan, who stated in Counterblast (1954): "The media are not toys; they should not be in the hands of Mother Goose and Peter Pan executives. They can be entrusted only to new artists because they are art forms." By the mid-1960s, the term had spread to general use in North America and the United Kingdom. According to H. L. Mencken, the phrase mass media was used as early as 1923 in the United States.[8][9]
The term medium (the singular form of media) is defined as "one of the means or channels of general communication, information, or entertainment in society, as newspapers, radio, or television."[10]
Regulations
[edit]The role of regulatory authorities (license broadcaster institutions, content providers, platforms) and the resistance to political and commercial interference in the autonomy of the media sector are both considered as significant components of media independence. In order to ensure media independence, regulatory authorities should be placed outside of governments' directives. This can be measured through legislation, agency statutes and rules.[11]
Government regulations
[edit]Licensing
[edit]In the United States, the Radio Act of 1927 established that the radio frequency spectrum was public property. This prohibited private organizations from owning any portion of the spectrum.[12] A broadcast license is typically given to broadcasters by communications regulators, allowing them to broadcast on a certain frequency and typically in a specific geographical location. Licensing is done by regulators in order to manage a broadcasting medium and as a method to prevent the concentration of media ownership.[13]
Licensing has been criticized for an alleged lack of transparency. Regulatory authorities in certain countries have been accused of exhibiting political bias in favor of the government or ruling party, which has resulted in some prospective broadcasters being denied licenses or being threatened with license withdrawal. As a consequence, there has been a decrease in diversity of content and views in certain countries due to actions made against broadcasters by states via their licensing authorities. This can have an impact on competition and may lead to an excessive concentration of power with potential influence on public opinion.[14] Examples include the failure to renew or retain licenses for editorially critical media, reducing the regulator's competences and mandates for action, and a lack of due process in the adoption of regulatory decisions.[15]
Internet regulation
[edit]Governments worldwide have sought to extend regulation to internet companies, whether connectivity providers or application service providers, and whether domestically or foreign-based. The impact on journalistic content can be severe, as internet companies can err too much on the side of caution and take down news reports, including algorithmically, while offering inadequate opportunities for redress to the affected news producers.[11]
Self-regulation
[edit]At the regional level
[edit]In Western Europe, self-regulation provides an alternative to state regulatory authorities. In such contexts, newspapers have historically been free of licensing and regulation, and there has been repeated pressure for them to self-regulate or at least to have in-house ombudsmen. However, it has often been difficult to establish meaningful self-regulatory entities.
In many cases, self-regulations exists in the shadow of state regulation, and is conscious of the possibility of state intervention. In many countries in Central and Eastern Europe, self-regulatory structures seems to be lacking or have not historically been perceived as efficient and effective.[16]
The rise of satellite channels that delivered directly to viewers, or through cable or online systems, renders much larger the sphere of unregulated programing. There are, however, varying efforts to regulate the access of programmers to satellite transponders in parts of the Western Europe, North America, the Arab region and in Asia and the Pacific. The Arab Satellite Broadcasting Charter was an example of efforts to bring formal standards and some regulatory authority to bear on what is transmitted, but it appears to not have been implemented.[17]
International organizations and NGOs
[edit]Self-regulation is expressed as a preferential system by journalists but also as a support for media freedom and development organizations by intergovernmental organizations such as UNESCO and non-governmental organizations. There has been a continued trend of establishing self-regulatory bodies, such as press councils, in conflict and post-conflict situations.[18]
Major internet companies have responded to pressure by governments and the public by elaborating self-regulatory and complaints systems at the individual company level, using principles they have developed under the framework of the Global Network Initiative. The Global Network Initiative has grown to include several large telecom companies alongside internet companies such as Google, Facebook and others, as well as civil society organizations and academics.[19]
The European Commission's 2013 publication, ICT Technology Sector Guide on Implementing the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights, impacts on the presence of independent journalism by defining the limits of what should or should not be carried and prioritized in the most popular digital spaces.[20]
Private sector
[edit]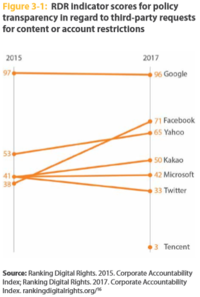

Public pressure on technology giants has motivated the development of new strategies aimed not only at identifying 'fake news', but also at eliminating some of the structural causes of their emergence and proliferation. Facebook has created new buttons for users to report content they believe is false, following previous strategies aimed at countering hate speech and harassment online. These changes reflect broader transformations occurring among tech giants to increase their transparency. As indicated by the Ranking Digital Rights Corporate Accountability Index, most large internet companies have reportedly become relatively more forthcoming in terms of their policies about transparency in regard to third party requests to remove or access content, especially in the case of requests from governments.[21][22] At the same time, however, the study signaled a number of companies that have become more opaque when it comes to disclosing how they enforce their own terms of service, in restricting certain types of content and account.[22] State governments can also use "Fake news" in order to spread propaganda.[23]
Fact-checking and news literacy
[edit]In addition to responding to pressure for more clearly defined self-regulatory mechanisms, and galvanized by the debates over so-called 'fake news', internet companies such as Facebook have launched campaigns to educate users about how to more easily distinguish between 'fake news' and real news sources. Ahead of the United Kingdom national election in 2017, for example, Facebook published a series of advertisements in newspapers with 'Tips for Spotting False News' which suggested 10 things that might signal whether a story is genuine or not.[24] There have also been broader initiatives bringing together a variety of donors and actors to promote fact-checking and news literacy, such as the News Integrity Initiative at the City University of New York's School of Journalism. This 14 million USD investment by groups including the Ford Foundation and Facebook was launched in 2017 so its full impact remains to be seen. It will, however, complement the offerings of other networks such as the International Fact-Checking Network launched by the Poynter Institute in 2015 which seeks to outline the parameters of the field.[25] Instagram has also created a way to potentially expose "fake news" that is posted on the site. After looking into the site, it seemed as more than a place for political memes, but a weaponized platform, instead of the creative space it used to be.[26] Since that, Instagram has started to put warning labels on certain stories or posts if third-party fact checkers believe that false information is being spread.[27] Instagram works with these fact checkers to ensure that no false information is being spread around the site.[28] Instagram started this work in 2019, following Facebook with the idea as they started fact checking in 2016.[28]
Electronic media
[edit]Developments in telecommunications has provided media the ability to conduct long-distance communication via analog and digital media:
- Analog telecommunications include some radio systems, historical telephony systems, and historical television broadcasts.
- Digital telecommunications allow for computer-mediated communication, telegraphy, computer networks, digital radio, digital telephony and digital television.
Modern communication media includes long-distance exchanges between larger numbers of people (many-to-many communication via email, Internet forums, and telecommunications ports). Traditional broadcast media and mass media favor one-to-many communication (television, cinema, radio, newspaper, magazines, and social media).[29][30]
Social Media
[edit]Electronic Media, specifically social media has become one of the top forms of media that people use in the twenty-first century. The percent of people that use social media and social networking outlets rose dramatically from 5% in 2005 to 79% in 2019. Instagram, Twitter, Pinterest, Tiktok, and Facebook are the most commonly used social media platforms. The average time that an individual spends on social media is 2.5 hours a day. This exponential increase of social media has additionally caused a change in which people communicate with others as well as receive information. About 53% use social media to read/watch the news.[31] Many people use the information specifically from social media influencers to understand more about a topic, business, or organization.[32] Social media has now been made part of everyday news production for journalists around the world.[33] Not only does social media provide more connection between readers and journalists, but it also cultivates the participation and community amongst technical communicators and their audiences, clients, and stakeholders.[34]
Gaming
[edit]Online
[edit]The gaming community has grown exponentially, and about 63% have taken to playing with others, whether online or in-person.[35] Players online will communicate through the system of microphone applicability either through the game or a third party application such as Discord. The improvements upon connectivity and software allowed for players online to keep in touch and game instantaneously, disregarding location almost entirely. With online gaming platforms it has been noted that they support diverse social gaming communities allowing players to feel a sense of belonging through the screen.[36]
Age
[edit]Gaming is an activity shared amongst others regardless of age, allowing for a diverse group of players to connect and enjoy their favorite games with. This helps with creating or maintaining relationships: friendships, family, or a significant other.[35]
Ratings and content
[edit]As with most interactive media content, games have ratings to assist in choosing appropriate games regarding younger audiences. This is done by ESRB ratings and consists of the following: E for Everyone, E for Everyone 10+, T for Teen, and M for Mature 17+. Whenever a new game is released, it is reviewed by associations to determine a suitable rating so younger audiences do not consume harmful or inappropriate content.[35] With these ratings it helps the risks and effects of gaming on younger audiences because the exposure of media is believed to influence children's attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors.[37]
Reach
[edit]The usage and consumption of gaming has tremendously increased within the last decade with estimates of around 2.3 billion people from around the world playing digital and online video games.[38] The growth rate for the global market for gaming was expected to grow 6.2% towards 2020. Areas like Latin America had a 20.1% increase, Asia-Pacific - 9.2%, North America - 4.0%, and Europe -11.7%.[39]
Communication
[edit]Studies show that digital and online gaming can be used as a communication method to aid in scientific research and create interaction. The narrative, layout, and gaming features all share a relationship that can deliver meaning and value that make games an innovative communication tool.[40] Research-focused games showed a connection towards a greater usage of dialogue within the science community as players had the opportunity to address issues with a game with themselves and scientists. This helped to push the understanding of how gaming and players can help advance scientific research via communication through games.[41]
vBook
[edit]A vBook is an eBook that is digital first media with embedded video, images, graphs, tables, text, and other useful media.[42]
E-Book
An E-book combines reading and listening media interaction. It is compact and can store a large amount of data which has made them very popular in classrooms.[43]
See also
[edit]- Distributed presence
- Media franchise
- Media manipulation
- Media psychology
- Media and gender
- Press conference
- Attention economy
- Media literacy
References
[edit]- ^ "What is media? definition and meaning". BusinessDictionary.com. Archived from the original on 2017-05-07. Retrieved 2014-10-03.
- ^ Cory Janssen. "What is Communication Media? - Definition from Techopedia". Techopedia.com. Archived from the original on 2017-04-03. Retrieved 2014-10-03.
- ^ Martin Lister; Jon Dovey; Seth Giddings; Iain Grant; Kieran Kelly. New Media: A Critical Introduction (PDF) (2nd ed.). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-03-06. Retrieved 2014-10-03.
- ^ Giessen, H W (2015). "Media-Based Learning Methodology: Stories, Games, and Emotions". In Ally, Mohamed; Khan, Badrul H. (eds.). International Handbook of E-Learning Volume 2: Implementation and Case Studies. Routledge, 43-54.
- ^ Dunston, Bryan (2002). "Postal system". The Chicago School of Media Theory. Archived from the original on 2020-11-04. Retrieved 2019-02-18.
- ^ Livingstone, Sonia M.; Lievrouw, Leah A. (2009). New Media: A Critical Introduction. Taylor & Francis. pp. 52–53. ISBN 9780415431606. Archived from the original on 2023-06-28. Retrieved 2020-10-27.
- ^ Lule, Jack (2012). Globalization and Media: Global Village of Babel. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 33–34. ISBN 9780742568365. Archived from the original on 2023-06-28. Retrieved 2020-10-27.
- ^ Colombo, John Robert (1994). Colombo's All-Time Great Canadian Quotations. Stoddart Publishing. p. 176. ISBN 0-7737-5639-6.
- ^ Group 3. "The Evolution of Media". Evolution of Media. Archived from the original on 2022-02-11. Retrieved 2022-02-11.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "medium". Dictionary.com. Archived from the original on 2016-03-05. Retrieved 2015-08-10.
- ^ a b World Trends in Freedom of Expression and Media Development Global Report 2017/2018 (PDF) (Report). UNESCO. 2018.
- ^ "The law of radio communication / by Stephen Davis". HathiTrust. Retrieved 2024-03-31.
- ^ Nuechterlein, Jonathan; Weiser, Philip J. (2005). Digital Crossroads. Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT Press. p. 235. ISBN 9780262140911.
- ^ Hanretty, Chris (2014). "Media outlets and their moguls: Why concentrated individual or family ownership is bad for editorial independence". European Journal of Communication. 29 (3): 335–350. doi:10.1177/0267323114523150. ISSN 0267-3231. S2CID 53710900. Archived from the original on 2023-01-11. Retrieved 2023-01-11.
- ^ Buckley, Steve, Kreszentia Duer, Toby Mendel, and Sean O. Siochru. 2008. Broadcasting, Voice, and Accountability : A Public Interest Approach to Policy, Law, and Regulation. Washington, DC: World Bank.
- ^ Fengler, Susanne, Tobias Eberwein, Salvador Alsius, Olivier Baisnée, Klaus Bichler, Boguslawa Dobek-Ostrowska, Huub Evers, et al. 2015. How effective is media self-regulation? Results from a comparative survey of European journalists. European Journal of Communication 30 (3): 249–266.
- ^ World Trends in Freedom of Expression and Media Development (PDF) (Report). Paris: UNESCO. 2014.
- ^ Lewis, David (2014). Non-Governmental Organizations, Management and Development. Oxfordshire, England, UK: Routledge. pp. 25, 71, 155.
- ^ "Global Network Initiative Adds Seven Companies in Milestone Expansion of Freedom of Expression and Privacy Initiative" (Press release). Global Network Initiative. March 28, 2017. Archived from the original on Jun 8, 2023.
- ^ Shift and Institute for Human Rights and Business (2013). "ICT Sector Guide on Implementing the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights" (PDF) (Report). European Commission. Archived (PDF) from the original on Dec 4, 2023.
- ^ "Ranking Digital Rights". Corporate Accountability Index. 2015. Archived from the original on 2020-11-10. Retrieved 2018-07-05.
- ^ a b "Ranking Digital Rights". Corporate Accountability Index. 2017. Archived from the original on 2020-12-12. Retrieved 2018-07-05.
- ^ Nadeem, M.A.; Mustafa, G.; Kakar, A. (2021). "Fifth Generation Warfare and its Challenges to Pakistan". Pakistan Journal of International Affairs. 4 (1).
- ^ "Tips to Spot False News | Facebook Help Center | Facebook". www.facebook.com. Archived from the original on 2020-11-12. Retrieved 2018-07-03.
- ^ "International Fact-Checking Network fact-checkers' code of principles". Poynter. Archived from the original on 2020-12-08. Retrieved 2018-07-03.
- ^ Al-Rawi, Ahmed (2021-03-03). "Political Memes and Fake News Discourses on Instagram". Media and Communication. 9 (1): 276–290. doi:10.17645/mac.v9i1.3533. ISSN 2183-2439. S2CID 233468644. Archived from the original on 2022-11-22. Retrieved 2022-11-22.
- ^ "Help Center". help.instagram.com. Archived from the original on 2022-11-22. Retrieved 2022-11-22.
- ^ a b Harrison, Sara. "Instagram Now Fact-Checks, but Who Will Do the Checking?". Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Retrieved 2022-11-22.
- ^ "What is telecommunications? Definition and meaning". Market Business News. Archived from the original on 23 February 2023. Retrieved 7 March 2023.
- ^ "1 to Many, Many to Many and Many to 1 – for PR and Inbound". Imre. 11 January 2018. Archived from the original on 23 February 2023. Retrieved 7 March 2023.
- ^ Ortiz-Ospina, Esteban; Roser, Max (2023-03-20). "The rise of social media". Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 2023-04-09. Retrieved 2023-04-21.
- ^ Enke, Nadja; Borchers, Nils S. (2019-08-08). "Social Media Influencers in Strategic Communication: A Conceptual Framework for Strategic Social Media Influencer Communication". International Journal of Strategic Communication. 13 (4): 261–277. doi:10.1080/1553118X.2019.1620234. ISSN 1553-118X.
- ^ Moon, Young Eun; Lewis, Seth C. (2024-02-06). "Social Media as Commodifier or Homogenizer? Journalists' Social Media Use in Individualistic and Collectivist Cultures and Its Implications for Epistemologies of News Production". Digital Journalism: 1–20. doi:10.1080/21670811.2024.2303988. ISSN 2167-0811.
- ^ Katajisto, Laura (2010-07-29). "Implementing Social Media in Technical Communication". IEEE Xplore.
- ^ a b c "2019 Essential Facts About the Computer and Video Game Industry" (PDF). Entertainment Software Association. 2019. pp. 4–13. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 August 2019. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ^ de Freitas, Sara; Griffiths, Mark (March 2008). "The convergence of gaming practices with other media forms: what potential for learning? A review of the literature". Learning, Media and Technology. 33 (1): 11–20. doi:10.1080/17439880701868796. ISSN 1743-9884.
- ^ Livingstone, Sonia (2016-01-02). "Reframing media effects in terms of children's rights in the digital age". Journal of Children and Media. 10 (1): 4–12. doi:10.1080/17482798.2015.1123164. ISSN 1748-2798.
- ^ Wijman, T. (April 30, 2018). "Mobile Revenues Account for More Than 50% of the Global Games Market as It Reaches $137.9 Billion in 2018". Newzoo.
- ^ McDonald, E (April 20, 2017). "The Global Games Market Will Reach $108.9 Billion in 2017 With Mobile Taking 42%". Newzoo.
- ^ Ouariachi, Olvera-Lobo, Gutierrez-Perez, T., M. D., J. (2017). "Analyzing climate change communication through online games: development and application of validated criteria". Science Communication. 39 (1): 10–44. doi:10.1177/1075547016687998. S2CID 151746669. Archived from the original on 2023-04-21. Retrieved 2023-04-21.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Curtis, V. (2014). "Public engagement through the development of science-based computer games: the Wellcome Trust's "Gamify your PhD" initiative". Science Communication. 36 (3): 379–387. doi:10.1177/1075547013492436. S2CID 53590587. Archived from the original on 2023-04-21. Retrieved 2023-04-21.
- ^ "A vBook (Video Book) is the New Alternative to an eBook".
- ^ Ma, Min-Yuan; Wei, Chun-Chun (2016-11-16). "A comparative study of children's concentration performance on picture books: age, gender, and media forms". Interactive Learning Environments. 24 (8): 1922–1937. doi:10.1080/10494820.2015.1060505. ISSN 1049-4820.
![]() This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY SA 3.0 IGO (license statement/permission). Text taken from World Trends in Freedom of Expression and Media Development Global Report 2017/2018, 202, UNESCO.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY SA 3.0 IGO (license statement/permission). Text taken from World Trends in Freedom of Expression and Media Development Global Report 2017/2018, 202, UNESCO.
Further reading
[edit]- McQuail, Denis (2001) McQuail's Mass Communication Theory (fourth edition), Sage, London, pp. 16–34. MAS
- Biagi, S. (2004). Media Impact. Wadsworth Pub Co, 7th edition.
- Caron, A. H. and Caronia, L. (2007). Moving cultures: mobile communication in everyday life. McGill-Queen's University Press.
