Ideological leanings of United States Supreme Court justices
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Supreme Court of the United States |
|---|
 |
| The Court |
| Current membership |
|
| Lists of justices |
|
| Court functionaries |
The Supreme Court of the United States is the country's highest federal court. The Court has ultimate—and largely discretionary—appellate jurisdiction over all federal courts and state court cases involving issues of U.S. federal law, plus original jurisdiction over a small range of cases.
The nine Supreme Court justices base their decisions on their interpretation of both legal doctrine and the precedential application of laws in the past. In most cases, interpreting the law is relatively clear-cut and the justices decide unanimously; however, in more complicated or controversial cases, the Court is often divided.
In modern discourse, the justices of the Court are often categorized as having conservative, moderate, or liberal philosophies of law and of judicial interpretation. It has long been commonly assumed that justices' votes are a reflection of their judicial decision-making philosophy as well as their ideological leanings, personal attitudes, values, political philosophies, or policy preferences. A growing body of academic research has confirmed this understanding, as scholars have found that the justices largely vote in consonance with their perceived values.[1][2][3] Analysts have used a variety of methods to deduce the specific perspective of each justice.
Partisan balance
[edit]The simplest way to approximate the ideological leanings of Supreme Court justices is by the political party of the president who appointed them. In a 2000 paper, Segal, Timpone, and Howard found that, in their study area (civil liberties and economics cases from 1937 to 1994), presidents appear to be reasonably successful in extending their policy preferences by appointing like-minded justices to the court, though they found that justices appear to deviate over time away from the presidents who appointed them.[4] In 1999, Pinello conducted a meta-analysis of 84 studies of American courts covering 222,789 cases adjudicated since World War II and found that political party affiliation was a dependable indicator of rulings: Democratic judges voted in favor of liberal solutions more often than Republican judges did, especially in federal courts (the U.S. Supreme Court, U.S. Courts of Appeal, and U.S. District Courts).[5]
The graph below, based on data from the Supreme Court Database, shows this partisan split.[6] In all the non-unanimous decisions made by the Supreme Court in the terms from 1937 to 2023 in which there was a specifiable ideological direction, justices appointed by Republican presidents (red bars) generally cast liberal votes much less frequently than justices appointed by Democratic presidents (blue bars). At the top of this graph, the 7 justices, including two chief justices (marked "CJ") and 2 current justices (with solid red bars), who cast the lowest percentage of liberal votes were all appointed by Republican presidents. At the bottom of the graph, the 3 justices, including 1 current justice (with a solid blue bar), who cast the highest percentage of liberal votes were appointed by Democratic presidents. The current justices (those voting in the 2023 term, shown with solid bars) are near the extremes for this period with all the 6 Republican-appointed justices near the top and the 3 Democratic-appointed justices near the bottom.
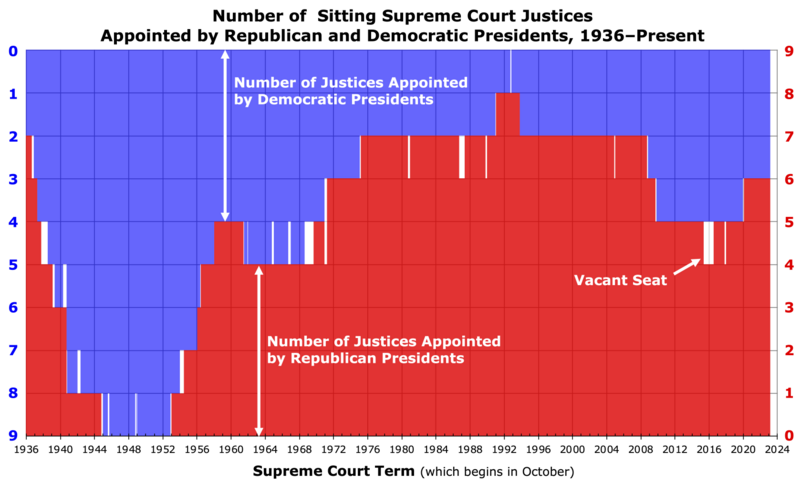
The graph below (using data from List of justices of the Supreme Court of the United States) shows the number of justices sitting in the Supreme Court who were appointed by Democratic or Republican presidents since 1936. In 1936, the Court had 7 justices appointed by Republican presidents and 2 appointed by Democratic presidents. Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt then filled the Supreme Court with 8 appointees in the late 1930s and 40s and promoted Chief Justice Harlan F. Stone, who had originally been appointed to the Court by Republican President Calvin Coolidge. Then Democratic President Harry S. Truman appointed 4 justices. In the 1950s, Republican President Dwight D. Eisenhower appointed 5 justices, reversing the partisan balance.
In the 1960s, Democratic Presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson, appointed 2 justices each, flipping the balance back to a majority of Democratic-appointed justices. This was reversed by Republican President Richard Nixon who appointed 4 justices, followed by Republican Presidents Gerald Ford, Ronald Reagan, and George H.W. Bush appointing a total of 7 more justices. (Democratic President Jimmy Carter was not able to appoint any justices in his single term). In succession, Democratic President Bill Clinton, Republican President George W. Bush, and then Democratic President Barack Obama each appointed 2 justices. Since 2020, with the appointment of 3 justices by Republican President Donald Trump, the Court has 6 justices appointed by Republican presidents. Democratic President Joe Biden appointed 1 justice, but that appointment did not change the partisan balance. As the graph clearly shows, in every term since 1970, the Court majority (consisting of at least 5 of the justices) has been appointed by Republican presidents. Every chief justice since 1953 has also been appointed by Republican presidents.
Devins and Baum point out that "before 2010, the Court never had clear ideological blocs that coincided with party lines." In choosing their appointments, Presidents often focused more on friendship and political connections than on ideology. Republican presidents sometimes appointed liberals and Democratic presidents sometimes appointed conservatives. As a result, "... between 1790 and early 2010 there were only two decisions that the Guide to the U.S. Supreme Court designated as important and that had at least two dissenting votes in which the Justices divided along party lines, about one-half of one percent."[7]: 316 [8] Even in the turbulent 1960s and 1970s, Democratic and Republican elites tended to agree on some major issues, especially concerning civil rights and civil liberties—and so did the justices. But since 1991, ideology has been much more important in choosing justices—all Republican appointees have been committed conservatives and all Democratic appointees have been liberals.[7]: 331–344 As the more moderate Republican justices retired, the court has become more partisan. The Court is now divided sharply along partisan lines with justices appointed by Republican presidents taking increasingly conservative positions and those appointed by Democrats taking moderate liberal positions.[7]: 357 This alignment between the Justices' partisanship and their ideological leanings (known as "partisan sorting") appears to be greater than ever before.[9][6][10][11]
Measuring ideological leanings
[edit]To further discern the justices' ideological leanings, researchers have carefully analyzed the judicial rulings of the Supreme Court—the votes and written opinions of the justices—as well as their upbringing, their political party affiliation, their speeches, their political contributions before appointment, editorials written about them at the time of their Senate confirmation, the political climate in which they are appointed, confirmed, and work, and the political contributions of the law clerks they hire. Bonica and Sen provide an extensive overview of these methods.[12]
From this data, scholars have inferred the ideological leanings of each justice and how the justices are likely to vote on upcoming cases. For example, Segal and Cover found a strong correlation (r=0.80) between justices' perceived ideological perspectives on civil liberties and civil rights issues as attributed to them in elite newspaper editorials written just before their confirmation (their Segal–Cover score) and their later votes in the study period 1953–1988.[13]: 561 [14] Epstein, Walker, and Dixon found they could explain and predict rulings in criminal justice cases (in the study period 1946–1986) using a simple model with four inputs: the political party affiliation of the majority of justices, the political party affiliation of the current president (representing the current political climate), the Supreme Court rulings in criminal justice cases in the previous year, and the percent of criminal cases the Court decides to hear in the current year (how much interest they take in the issue). In this analysis, the political party affiliation of the majority of justices provided about one-fourth of the predictive power.[15] Bonica et al. utilized the ideology of the law clerks hired by federal judges (as estimated by the law clerks' political donations) to estimate the ideology of the judges themselves.[16]
Using statistical analysis of Supreme Court votes, scholars found that an inferred value representing a justice's ideological preference on a simple conservative–liberal scale is sufficient to predict a large number of that justice's votes. For example, Grofman and Brazill performed multidimensional scaling (MDS) using SYSTAT 5.0 of the entire range of cases considered by the Supreme Court, 1953–1991. Analyzing terms with an unchanging membership ("natural courts") and a complete bench of nine members (3,363 cases), they found that a one-dimensional scale provided a satisfactory explanation of votes and that the degree of unidimensionality generally rose over the years, writing: "On average, over the 15 courts, the mean r2 values are 0.86 for a one dimensional metric MDS solution, and 0.97 for a two dimensional metric MDS solution."[17] In 2003, Poole used various statistical measures to show that a unidimensional scale provided a good measure of the Rehnquist Court during the 8-year period 1995–2002.[18]
Ideological leanings over time
[edit]Using increasingly sophisticated statistical analysis, researchers have found that the policy preferences of many justices shift over time.[19][20][21] The ideological leanings of justices and the drift over time can be seen clearly in the research results of two sets of scholars using somewhat different models:
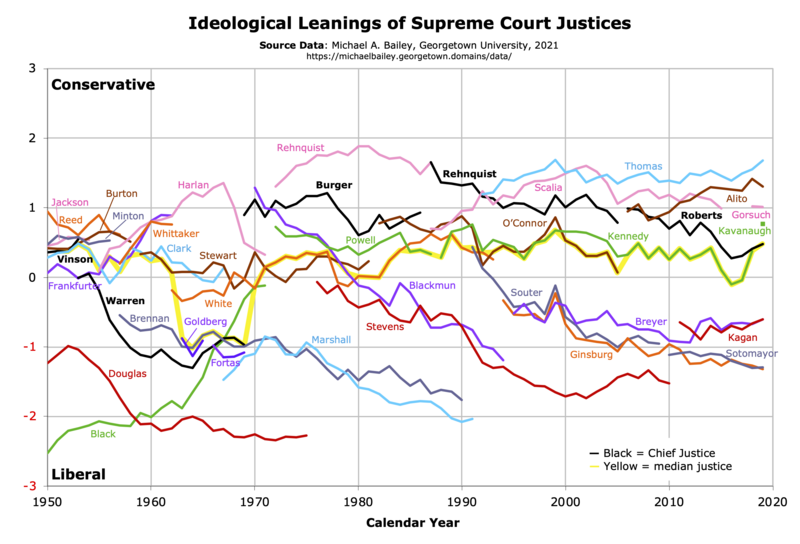
Andrew D. Martin and Kevin M. Quinn have employed Markov chain Monte Carlo methods to fit a Bayesian statistic measurement model[22] of ideal points (policy preferences on a one-dimensional scale) for all the justices based on the votes in every contested Supreme Court case since 1937.[23][24][25][26] The graph below shows the results of their analysis: the ideological leaning of each justice from the term that began in October 1937 to the term that began in October 2022.[27] Note that the scale and zero point are strongly dependent on the particular set of cases chosen to be reviewed by the Court each year; the relative distance between the lines for each justice is most informative. Each unique color represents a particular Supreme Court seat. The black lines represent the leanings of the chief justices. The yellow line represents the estimated location of the median justice—who, as Duncan Black's median voter theorem posits, is often the swing vote in closely divided decisions.[28]
Michael A. Bailey used a slightly different Markov chain Monte Carlo Bayesian method to determine ideological leanings and made significantly different scaling assumptions.[29][30][31] He analyzed cases by calendar year (rather than Supreme Court term) and supplemented the data regarding votes in each Court case with additional information from the majority, concurring, and dissenting opinions in which justices commented on previous cases, as well as with votes made by members of Congress on similar legislation, amicus filings by U.S. solicitors general and members of Congress, and presidential and Congressional positions on Court cases. This additional information gave him a richer dataset and also enabled him to deduce preference values that are more consistent with the DW-Nominate Common Space scores used to evaluate the ideological leanings of members of Congress and presidents.[32] However, he only used votes and cases related to the major topics addressed by the courts in the postwar era: crime, civil rights, free speech, religion, abortion, privacy, and labor unions. He did not include cases addressing federalism, judicial power, economic activity, or federal taxation.[29][33]
The graph below shows the ideological leaning of each justice by calendar year from 1950 to 2019.[34][29] The scale and zero point roughly correspond to DW-Nominate Common Space scores. As in the graph above, each unique color represents a particular Supreme Court seat. The black lines represent the leanings of the chief justices, and the yellow line represents the median justice.
These two graphs differ because of the choices of data sources, data coverage, coding of complicated cases, smoothing parameters, and statistical methods. Each of the lines in these graphs also has a wide band of uncertainty. Because these analyses are based on statistics and probability, it is important not to over-interpret the results.[35][36] Also note that the nature of the cases the Supreme Court chooses to hear and which questions they choose to address may lead the justices to appear more liberal or conservative than they would if they were hearing a different set of cases and chose to answer a different set of questions; the Court accepts only 100–200 of the more than 7,000 cases that it is asked to review each year.[37][38][39] In addition, all cases are valued equally even though some cases are much more important than others.[40][41] Moreover, recent consequential cases decided through the "shadow docket" are not included at all.[42] Still, these graphs offer an indication of the overall ideological orientation of the justices and provide a visualization of changes in the Court's orientation over time.
Ideological shifts since 1937
[edit]In the early 1930s, which is earlier than the data on the Martin–Quinn graph, the "Four Horsemen" (justices James McReynolds, Pierce Butler, George Sutherland, and Willis Van Devanter) mostly opposed the New Deal agenda proposed by President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The liberal "Three Musketeers" (justices Harlan Stone, Benjamin Cardozo, and Louis Brandeis) generally supported the New Deal. Two justices (Chief Justice Charles Evans Hughes and Justice Owen Roberts) normally cast the swing votes.
The Martin–Quinn graph (and underlying data) shows that, by the 1939 term, Roosevelt had moved the Court to a more liberal position by appointing four new justices including strong liberals Hugo Black, William O. Douglas, and Frank Murphy. Led by the increasingly conservative chief justices Harlan F. Stone and Fred M. Vinson, the Court shifted in a more conservative direction through the 1940s and early 1950s.
President Dwight Eisenhower appointed Earl Warren to be chief justice in 1953, and both graphs indicate that the Court then turned in a more liberal direction as Warren himself grew substantially more liberal and especially when he was joined by strong liberal justices William J. Brennan Jr., Arthur Goldberg, Abe Fortas, and Thurgood Marshall, although justices Black and Felix Frankfurter became slightly more conservative over time. In the 1970s, the Court shifted in a more conservative direction when President Richard Nixon appointed Chief Justice Warren Burger and conservative justices Lewis Powell, William Rehnquist, and Harry Blackmun, and more so when President Ronald Reagan elevated Rehnquist to chief justice, although Blackmun became more liberal over time. The Court shifted to an even more conservative orientation when it was joined by strong conservative justices Antonin Scalia (appointed by President Ronald Reagan), Clarence Thomas (appointed by President George H. W. Bush), and Samuel Alito and Chief Justice John Roberts (both whom were appointed by President George W. Bush). During this time, Justice David Souter became more liberal.[43][26][44]
Since 2020, the Roberts Court is more conservative, with six conservative justices that include justices Neil Gorsuch, Brett Kavanaugh, and Amy Coney Barrett (appointed by President Donald Trump). Dissenting in many key cases are justices Sonia Sotomayor and Elena Kagan (appointed by President Barack Obama).[45] In 2022, Justice Stephen Breyer (appointed by President Bill Clinton) retired and was replaced by Ketanji Brown Jackson (appointed by President Joe Biden). Jackson is widely considered to be, like Breyer, an ideological liberal.[46]
The most volatile seat appears to be Seat 10 (light blue lines), which was held by conservative Pierce Butler until 1939, then liberal Frank Murphy until 1949, then moderate-conservative Tom Clark until 1967, then strong liberal Thurgood Marshall until 1991, and then strong conservative Clarence Thomas. The path of Justice Harry Blackmun illustrates the ideological drift shown by many justices.[19] Blackmun (purple line) had a conservative score (Quinn–Martin = 1.459; Bailey = 1.289) in the 1969–70 term, his first on the bench, but had shifted to a liberal score (Quinn–Martin = −1.940; Bailey = −1.188) by the 1993–94 term, his last. The median justice (shown with a yellow background line) was Byron White (orange line) for most of the time from 1969 to 1989, Sandra Day O’Connor (dark brown line) from 1999 to 2005, Anthony Kennedy (green line) from 2006 to 2017, John Roberts (black line) in 2018 and 2019, and, perhaps, both Brett Kavanaugh (green line) and John Roberts since 2020.[47]
The graphs show that since the 1938 term every chief justice (black lines), except Earl Warren and John Roberts (since about 2020), has had a more conservative ideological lean than the median justice on the Court.
Career liberal voting percentage by issue area from 1946–2017
[edit]The following sortable table[a] lists the lifetime percentage liberal scores of Supreme Court justices as compiled in the Supreme Court Database.[48][49] The table shows data for justices whose service began at or after the 1946 term; the data ends with the 2016–2017 term.
In the Supreme Court Database, liberal represents the voting direction of the justices across the various issue areas. It is most appropriate in the areas of criminal procedure, civil rights, and First Amendment cases, where it signifies pro-defendant votes in criminal procedure cases, pro-women, or pro-minorities in civil rights cases, and pro-individual against the government in First Amendment cases. In takings clause cases, a pro-government/anti-owner vote is considered liberal. In labor union cases, pro-union votes against both individuals and the government are considered liberal, and in economic cases, the term represents pro-government votes against challenges to federal regulatory authority and pro-competition, anti-business, pro-liability, pro-injured person, and pro-bankruptcy decisions. In federalism and federal taxation cases, the term indicates pro-national government positions.
- No. (justice number) – order that Supreme Court justice was appointed
- Justice – justice's name
- Year confirmed – year confirmed to the Supreme Court
- Position – Chief Justice or Associate Justice
- Criminal procedure – a higher number means pro-defendant votes in cases involving the rights of persons accused of crime, except for the due process rights of prisoners.
- Civil rights – a higher number means more votes permitting intervention on freedom cases which pertain to classifications based on race (including Native Americans), age, indigence, voting, residence, military, or handicapped status, sex, or alienage.
- First Amendment – a higher number reflects votes that advocate individual freedoms with regard to speech.
- Union – a higher number means pro-union votes in cases involving labor activity.
- Economic – a higher number means more votes against commercial business activity, plus litigation involving injured persons or things, employee actions concerning employers, zoning regulations, and governmental regulation of corruption other than that involving campaign spending.
- Federalism – a higher number means votes for a larger, more empowered government in conflicts between the federal and state governments, excluding those between state and federal courts, and those involving the priority of federal fiscal claims.
- Federal taxes – a higher number means more votes widening the government's ability to define and enforce tax concepts and policies in cases involving the Internal Revenue Code and related statutes.
Note: A highlighted row indicates that the Justice is currently serving on the Court.
| No. | Justice | Year confirmed | Year departed | Position | Criminal procedure | Civil rights | First amendment | Union | Economic | Federalism | Federal taxes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 85 | Fred M. Vinson | 1946 | 1953 | Chief Justice | 27.0% | 45.3% | 26.2% | 34.1% | 59.9% | 51.5% | 74.5% |
| 86 | Tom C. Clark | 1949 | 1967 | Associate Justice | 32.1% | 53.5% | 37.1% | 61.9% | 72.5% | 51.3% | 74.8% |
| 87 | Sherman Minton | 1949 | 1956 | Associate Justice | 23.1% | 36.2% | 27.0% | 55.9% | 62.0% | 53.3% | 75.6% |
| 88 | Earl Warren | 1953 | 1969 | Chief Justice | 73.3% | 81.0% | 83.5% | 70.2% | 81.3% | 72.1% | 80.0% |
| 89 | John Marshall Harlan II | 1955 | 1971 | Associate Justice | 37.8% | 42.0% | 44.2% | 53.8% | 36.7% | 50.0% | 70.6% |
| 90 | William J. Brennan Jr. | 1956 | 1990 | Associate Justice | 76.2% | 82.5% | 84.5% | 65.8% | 69.8% | 66.3% | 70.3% |
| 91 | Charles Evans Whittaker | 1957 | 1962 | Associate Justice | 39.8% | 44.2% | 36.5% | 40.5% | 33.6% | 52.4% | 63.2% |
| 92 | Potter Stewart | 1958 | 1981 | Associate Justice | 44.9% | 48.4% | 63.0% | 57.3% | 45.0% | 56.5% | 66.4% |
| 93 | Byron White | 1962 | 1993 | Associate Justice | 32.9% | 55.2% | 39.2% | 62.6% | 59.3% | 66.9% | 84.7% |
| 94 | Arthur Goldberg | 1962 | 1965 | Associate Justice | 75.0% | 98.0% | 96.2% | 61.1% | 63.2% | 53.3% | 77.3% |
| 95 | Abe Fortas | 1965 | 1969 | Associate Justice | 81.5% | 82.1% | 79.5% | 60.0% | 72.2% | 64.3% | 46.7% |
| 96 | Thurgood Marshall | 1967 | 1991 | Associate Justice | 80.1% | 84.5% | 83.4% | 68.9% | 63.0% | 68.6% | 74.2% |
| 97 | Warren E. Burger | 1969 | 1986 | Chief Justice | 19.0% | 37.4% | 30.9% | 43.3% | 45.0% | 66.7% | 72.1% |
| 98 | Harry Blackmun | 1970 | 1994 | Associate Justice | 42.3% | 62.1% | 56.2% | 61.8% | 55.0% | 67.4% | 74.4% |
| 99 | Lewis F. Powell Jr. | 1972 | 1987 | Associate Justice | 28.4% | 40.3% | 46.1% | 51.1% | 45.6% | 59.0% | 56.1% |
| 100 | William Rehnquist[b] | 1972 | 1986 | Associate Justice | 14.1% | 24.1% | 18.1% | 48.9% | 43.5% | 29.1% | 62.5% |
| 101 | John Paul Stevens | 1975 | 2010 | Associate Justice | 66.9% | 64.3% | 66.9% | 63.9% | 56.2% | 56.9% | 59.4% |
| 102 | Sandra Day O'Connor | 1981 | 2006 | Associate Justice | 26.4% | 45.4% | 41.8% | 42.7% | 46.5% | 48.3% | 58.9% |
| (100) | William Rehnquist[b] | 1986 | 2005 | Chief Justice | 19.6% | 30.6% | 26.1% | 33.3% | 49.4% | 46.1% | 77.8% |
| 103 | Antonin Scalia | 1986 | 2016 | Associate Justice | 27.4% | 30.6% | 30.5% | 33.8% | 46.2% | 52.0% | 69.7% |
| 104 | Anthony Kennedy | 1988 | 2018 | Associate Justice | 33.3% | 44.0% | 46.0% | 39.7% | 44.6% | 56.3% | 81.0% |
| 105 | David Souter | 1990 | 2009 | Associate Justice | 57.2% | 69.3% | 70.8% | 58.8% | 54.2% | 64.8% | 70.7% |
| 106 | Clarence Thomas | 1991 | — | Associate Justice | 22.4% | 25.0% | 32.2% | 30.8% | 46.2% | 47.4% | 58.7% |
| 107 | Ruth Bader Ginsburg | 1993 | 2020 | Associate Justice | 62.3% | 70.0% | 69.4% | 72.2% | 56.6% | 60.6% | 80.6% |
| 108 | Stephen Breyer | 1994 | 2022 | Associate Justice | 55.6% | 69.7% | 55.8% | 77.1% | 50.0% | 67.7% | 79.4% |
| 109 | John Roberts | 2005 | — | Chief Justice | 31.1% | 42.4% | 50.0% | 41.2% | 44.5% | 73.2% | 90.9% |
| 110 | Samuel Alito | 2006 | — | Associate Justice | 18.6% | 38.8% | 39.0% | 31.3% | 42.4% | 68.4% | 81.8% |
| 111 | Sonia Sotomayor | 2009 | — | Associate Justice | 66.9% | 70.7% | 67.7% | 61.5% | 50.0% | 63.0% | 100.0% |
| 112 | Elena Kagan | 2010 | — | Associate Justice | 62.5% | 71.9% | 68.0% | 66.7% | 50.0% | 75.0% | 80.0% |
| 113 | Neil Gorsuch[c] | 2017 | — | Associate Justice | 0.0% | 50.0% | 100.0% | No cases | 33.3% | No cases | No cases |
| 114 | Brett Kavanaugh | 2018 | — | Associate Justice | |||||||
| 115 | Amy Coney Barrett | 2020 | — | Associate Justice | |||||||
| 116 | Ketanji Brown Jackson | 2022 | — | Associate Justice |
- ^ To sort, click on the arrow in the header. To sort by multiple columns, click on the first column's sort arrow, then shift-click on subsequent columns' sort arrows.
- ^ a b William Rehnquist's terms as associate justice and chief justice are listed separately.
- ^ Percentages for Neil Gorsuch may be misleading since he had participated in only a few cases through 2017.
See also
[edit]- Judicial activism
- Judicial appointment history for United States federal courts
- Judicial Common Space
- Judicial discretion
- Judicial restraint
- List of justices of the Supreme Court of the United States
- Martin-Quinn score
- Models of judicial decision making
- Segal–Cover score
References
[edit]- ^ Segal, Jeffrey A.; Spaeth, Harold J. (2002). The Supreme Court and the Attitudinal Model Revisited. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521783514.
- ^
Epstein, Lee; Martin, Andrew D. (2012). "Is the Roberts Court Especially Activist? A Study of Invalidating (and Upholding) Federal, State, and Local Laws" (PDF). Emory Law Journal. 61: 737–758. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 9, 2012. Retrieved December 10, 2012.
…for Justices appointed since 1952, Epstein & Landes's findings parallel ours: the vast majority were opportunistic restraintists (activists), willing to uphold laws that were consistent with their policy preferences and strike those that were not.
- ^
Clark, Tom S.; Montagnes, B. Pablo; Spenkuch, Jörg L. (2022). "Politics from the Bench? Ideology and Strategic Voting in the U.S. Supreme Court" (PDF). Journal of Public Economics. 214: 104726. doi:10.1016/j.jpubeco.2022.104726. Retrieved October 30, 2022.
The evidence we present suggests that justices vote strategically, at least in part, to affect precedent.
- ^ Segal, Jeffrey A.; Timpone, Richard J.; Howard, Robert M. (2000). "Buyer Beware? Presidential Success through Supreme Court Appointments". Political Research Quarterly. 53 (3): 557–573. doi:10.1177/106591290005300306. S2CID 153646562.
- ^ Pinello, Daniel R. (1999). "Linking Party to Judicial Ideology in American Courts: A Meta-Analysis". The Justice System Journal. 20 (3): 219–254. JSTOR 27976992. Retrieved December 14, 2022.
- ^ a b Epstein, Lee; Martin, Andrew D.; Nelson, Michael J. (July 1, 2024). Provisional Data Report on the 2023 Term (PDF) (Report). Retrieved November 17, 2024.
- ^ a b c Devins, Neal; Baum, Lawrence (2017). "Split definitive: How party polarization turned the Supreme Court into a partisan court". The Supreme Court Review. 2016 (1). University of Chicago Law School: 301–365. doi:10.1086/691096. S2CID 142355294. Retrieved November 13, 2022.
- ^ Baum, Lawrence; Devins, Neal (2019). The company they keep: How partisan divisions came to the Supreme Court (PDF). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0190278052.
- ^ Epstein, Lee (2024). "Partisanship 'All the Way Down' on the US Supreme Court". Pepperdine Law Review. 51 (3): 489–514. Retrieved November 17, 2024.
- ^ Liptak, Adam (July 2, 2024). "In a Volatile Term, a Fractured Supreme Court Remade America". New York Times. New York. Retrieved December 16, 2024.
- ^ Thomson-DeVeaux, Amelia; Bronner, Laura (July 5, 2022). "The Supreme Court's Partisan Divide Hasn't Been This Sharp In Generations". Five Thirty Eight. Retrieved December 16, 2024.
It's now abundantly clear that Trump's appointees are in control of this court, and they're not searching for consensus. In fact, the divide between the court's Republican and Democratic appointees is deeper than it's been in the modern era.
- ^ Bonica, Adam; Sen, Maya (Winter 2021). "Estimating Judicial Ideology". Journal of Economic Perspectives. 35 (1): 97–118. doi:10.1257/jep.35.1.97. S2CID 234063775.
- ^ Segal, Jeffrey A.; Cover, Albert D. (June 1989). "Ideological Values and the Votes of U.S. Supreme Court Justices" (PDF). American Political Science Review. 83 (2): 557–565. doi:10.2307/1962405. JSTOR 1962405.
- ^ Segal, Jeffrey A.; Epstein, Lee; Cameron, Charles M.; Spaeth, Harold J. (August 1995). "Ideological Values and the Votes of U.S. Supreme Court Justices Revisited" (PDF). The Journal of Politics. 57 (3). Southern Political Science Association: 812–823. doi:10.2307/2960194. JSTOR 2960194. S2CID 145385646.
- ^ Epstein, Lee; Walker, Thomas G.; Dixon, William J. (November 1989). "The Supreme Court and Criminal Justice Disputes: A Neo-Institutional Perspective" (PDF). American Journal of Political Science. 33 (4): 825–841. doi:10.2307/2111111. JSTOR 2111111. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 21, 2010. Retrieved December 10, 2012.
- ^ Bonica, Adam; Chilton, Adam S.; Goldin, Jacob; Rozema, Kyle; Sen, Maya (2017). "Measuring judicial ideology using law clerk hiring". American Law and Economics Review. 19 (1): 129–161. doi:10.1093/aler/ahw013. hdl:10.1093/aler/ahw012. Retrieved February 8, 2021.
- ^ Grofman, Bernard; Brazill, Timothy J. (2002). "Identifying the median justice on the Supreme Court through multidimensional scaling: Analysis of 'natural courts' 1953–1991" (PDF). Public Choice. 112: 55–79. doi:10.1023/A:1015601614637. S2CID 17435544.
- ^ Poole, Keith (July 10, 2003). "The Unidimensional Supreme Court". Retrieved November 27, 2012.
The bottom line is that the current Court is basically unidimensional.
- ^ a b Ruger, Theodore W. (2005). "Justice Harry Blackmun and the Phenomenon of Judicial Preference Change" (PDF). Missouri Law Review. 70: 1209. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 1, 2010. Retrieved December 10, 2012.
- ^ Martin, Andrew D.; Quinn, Kevin M. (2007). "Assessing Preference Change on the US Supreme Court" (PDF). The Journal of Law, Economics, & Organization. 23 (2): 365–385. doi:10.1093/jleo/ewm028. hdl:2027.42/116217.
- ^ Epstein, Lee; Martin, Andrew D.; Quinn, Kevin M.; Segal, Jeffrey A. (2007). "Ideological Drift among Supreme Court Justices: Who, When, and How Important?" (PDF). Northwestern University Law Review. 101 (4): 1483–1503.
- ^ Jackman, Simon (2011). "Statistical Inference, Classical and Bayesian". In Badie, Bertrand; Berg-Schlosser, Dirk; Morlino, Leonardo (eds.). International Encyclopedia of Political Science. doi:10.4135/9781412959636.n585. ISBN 9781412959636. Archived from the original on November 12, 2013.
- ^ Martin, Andrew D.; Quinn, Kevin M. (2002). "Dynamic Ideal Point Estimation via Markov Chain Monte Carlo for the U.S. Supreme Court, 1953–1999" (PDF). Political Analysis. 10 (2): 134–153. doi:10.1093/pan/10.2.134.
- ^ Martin, Andrew D.; Quinn, Kevin M. (May 2, 2001). "The Dimensions of Supreme Court Decision Making: Again Revisiting The Judicial Mind". Presented at the 2001 Meeting of the Midwest Political Science Association. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.24.1490.
- ^ Martin, Andrew D.; Quinn, Kevin M.; Epstein, Lee (2005). "The Median Justice on the United States Supreme Court". North Carolina Law Review. 83: 1275–1322.
- ^ a b Silver, Nate (March 29, 2012). "Supreme Court May Be Most Conservative in Modern History". FiveThirtyEight.
- ^ Martin, Andrew; Quinn, Kevin. "Martin–Quinn scores: measures".
- ^ Black, Duncan (February 1948). "On the rationale of group decision-making". Journal of Political Economy. 56 (1): 23–34. doi:10.1086/256633. JSTOR 1825026. S2CID 153953456.
- ^ a b c Bailey, Michael A. (2013). "Is Today's Court the Most Conservative in Sixty Years? Challenges and Opportunities in Measuring Judicial Preferences". The Journal of Politics. 75 (3): 821–834. doi:10.1017/S0022381613000443. Retrieved July 14, 2022.
- ^ Bailey, Michael A.; Maltzman, Forrest (2011). The constrained court: law, politics, and the decisions justices make. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0691151052.
- ^ Clinton, Joshua; Jackman, Simon; Rivers, Douglas (May 2004). "The Statistical Analysis of Roll Call Data" (PDF). American Political Science Review. 98 (2): 355. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.186.3440. doi:10.1017/S0003055404001194. S2CID 7487820.
- ^ Epstein, Lee; Martin, Andrew D.; Segal, Jeffrey A.; Westerland, Chad (May 2007). "The Judicial Common Space" (PDF). Journal of Law, Economics, and Organization. 23 (2): 303–325. doi:10.1093/jleo/ewm024. hdl:10.1093/jleo/ewm024. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 8, 2010. Retrieved December 10, 2012.
The [Nominate] Common Spaces scores are bounded below by −1 and above by 1, whereas the Martin–Quinn scores are theoretically unbounded (currently, they range from about –6 [Justice Douglas] to 4 [Justice Thomas]).
- ^ Bailey, Michael A. (July 2007). "Comparable Preference Estimates across Time and Institutions for the Court, Congress, and Presidency" (PDF). American Journal of Political Science. 51 (3): 433–448. doi:10.1111/j.1540-5907.2007.00260.x.
- ^ "Updated Bridge Ideal Points for 1950 to 2020 (updated May 2021)". Retrieved July 14, 2022.
- ^ Ho, Daniel E.; Quinn, Kevin M. (June 2010). "How Not to Lie with Judicial Votes: Misconceptions, Measurement, and Models" (PDF). California Law Review. 98 (3): 813–876. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 9, 2010. Retrieved December 10, 2012.
- ^ Carroll, Royce; Lewis, Jeffrey B.; Lo, James; Poole, Keith T.; Rosenthal, Howard (November 2009). "Comparing Nominate and Ideal: Points of Difference and Monte Carlo Tests" (PDF). Legislative Studies Quarterly. 34 (4): 555–591. doi:10.3162/036298009789869727. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 30, 2013. Retrieved December 10, 2012.
- ^ "Supreme Court Procedures". United States Courts. Retrieved December 8, 2020.
- ^ "The Supreme Court at Work: The Term and Caseload". United States Supreme Court. Retrieved September 12, 2021.
Plenary review, with oral arguments by attorneys, is currently granted in about 80 of those cases each Term, and the Court typically disposes of about 100 or more cases without plenary review.
- ^
Johnson, Benjamin B. (2022). "The origins of Supreme Court question selection" (PDF). Columbia Law Review. 122 (3): 793–864.
The modern Court has effectively abandoned the traditional judicial role of deciding cases in favor of targeting preselected questions. This arrangement may serve the Court's institutional interests, but it also pulls the Court into politics.
- ^ Farnsworth, Ward (September 2007). "The Use and Limits of Martin–Quinn Scores to Assess Supreme Court Justices, with Special Attention to the Problem of Ideological Drift". Northwestern University Law Review. 101 (4): 1891–1903. SSRN 1000986.
- ^ McGuire, Kevin T.; Vanberg, Georg; Smith Jr., Charles E.; Caldeira, Gregory A. (October 2009). "Measuring Policy Content on the U.S. Supreme Court" (PDF). The Journal of Politics. 71 (4): 1305–1321. doi:10.1017/s0022381609990107. S2CID 54045434.
- ^ Hurley, Lawrence; Chung, Andrew; Allen, Jonathan (March 23, 2021). "The 'shadow docket': How the U.S. Supreme Court quietly dispatches key rulings". Reuters.
- ^ Liptak, Adam (July 24, 2010). "Court Under Roberts Is Most Conservative in Decades". The New York Times.
- ^ Epstein, Lee; Landes, William M.; Posner, Richard A. (2013). "How Business Fares in the Supreme Court" (PDF). Minnesota Law Review. 97: 1431–1472.
We find that five of the ten Justices who, over the span of our study (the 1946 through 2011 Terms), have been the most favorable to business are currently serving, with two of them ranking at the very top among the thirty-six Justices in our study.
- ^
Thomson-DeVeaux, Amelia; Bronner, Laura (July 5, 2022). "The Supreme Court's Partisan Divide Hasn't Been This Sharp In Generations". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved October 31, 2022.
The data emphasizes that the court is deeply polarized along partisan lines — perhaps more than it's ever been.
- ^ Mangan, Dan; Breuninger, Kevin. "Ketanji Brown Jackson sworn in as Supreme Court justice, replacing Stephen Breyer". CNBC. Retrieved October 12, 2022.
- ^ Liptak, Adam (June 18, 2021). "The Supreme Court's Newest Justices Produce Some Unexpected Results". The New York Times.
- ^ Epstein, Lee; Walker, Thomas G.; Staudt, Nancy; Hendrickson, Scott; Roberts, Jason (November 1, 2017). "The U.S. Supreme Court Justices Database". Archived from the original on November 18, 2017. Retrieved April 3, 2024.
- ^ Spaeth, Harold J.; Epstein, Lee; Martin, Andrew D.; Segal, Jeffrey A.; Ruger, Theodore J.; Benesh, Sara C. "2023 Supreme Court Database". 2023 Release 01. Retrieved April 3, 2024.
External links
[edit]- Questioning Supreme Court Nominees About Their Views on Legal or Constitutional Issues: A Recurring Issue – a June 23, 2010 Congressional Research Service report for Congress