Lockheed P-38 Lightning
| P-38 Lightning | |
|---|---|
 A P-38 Lightning warbird over Chino Airport in 2009 | |
| General information | |
| Type | |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Lockheed Corporation |
| Primary users | United States Army Air Forces |
| Number built | 10,037[1] |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1941–45 |
| Introduction date | July 1941[2] |
| First flight | 27 January 1939 |
| Retired | 1949 (United States Air Force) 1965 (Honduran Air Force)[3] |
| Developed into | Lockheed XP-49 Lockheed XP-58 |
The Lockheed P-38 Lightning is an American single-seat, twin piston-engined fighter aircraft that was used during World War II. Developed for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) by the Lockheed Corporation, the P-38 incorporated a distinctive twin-boom design with a central nacelle containing the cockpit and armament. Along with its use as a general fighter, the P-38 was used in various aerial combat roles, including as a highly effective fighter-bomber, a night fighter, and a long-range escort fighter when equipped with drop tanks.[4] The P-38 was also used as a bomber-pathfinder, guiding streams of medium and heavy bombers, or even other P-38s equipped with bombs, to their targets.[5] Used in the aerial reconnaissance role, the P-38 accounted for 90 percent of aerial film captured over Europe.[6][7][8] Although it was not designated a heavy fighter or a bomber destroyer by the USAAC, the P-38 filled those roles and more; unlike German heavy fighters crewed by two or three airmen, the P-38 with its lone pilot was nimble enough to compete with single-engine fighters.[9]
The P-38 was used most successfully in the Pacific and the China-Burma-India Theaters of Operations as the aircraft of America's top aces, Richard Bong (40 victories), Thomas McGuire (38 victories), and Charles H. MacDonald (27 victories). In the South West Pacific theater, the P-38 was the primary long-range fighter of United States Army Air Forces until the introduction of large numbers of P-51D Mustangs toward the end of the war.[10] Unusually for an early-war fighter design, both engines were supplemented by turbosuperchargers, making it one of the earliest Allied fighters capable of performing well at high altitudes.[11] The turbosuperchargers also muffled the exhaust, making the P-38's operation relatively quiet.[12] The Lightning was extremely forgiving in flight and could be mishandled in many ways, but the initial rate of roll in early versions was low relative to other contemporary fighters; this was addressed in later variants with the introduction of hydraulically boosted ailerons.[13] The P-38 was the only American fighter aircraft in large-scale production throughout American involvement in the war, from the Attack on Pearl Harbor to Victory over Japan Day.[14]
Design and development
[edit]The Lockheed Corporation designed the P-38 in response to a February 1937 specification from the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). Circular Proposal X-608 was a set of aircraft performance goals authored by First Lieutenants Benjamin S. Kelsey and Gordon P. Saville for a twin-engined, high-altitude "interceptor" having "the tactical mission of interception and attack of hostile aircraft at high altitude."[15] Forty years later, Kelsey explained that Saville and he drew up the specification using the word "interceptor" as a way to bypass the inflexible Army Air Corps requirement for pursuit aircraft to carry no more than 500 lb (230 kg) of armament including ammunition, and to bypass the USAAC restriction of single-seat aircraft to one engine. Kelsey was looking for a minimum of 1,000 lb (450 kg) of armament.[16] Kelsey and Saville aimed to get a more capable fighter, better at dog fighting and at high-altitude combat. Specifications called for a maximum airspeed of at least 360 mph (580 km/h) at altitude, and a climb to 20,000 ft (6,100 m) within six minutes,[17] the toughest set of specifications USAAC had ever presented. The unbuilt Vultee XP1015 design was offered to fill this requirement, but was not advanced enough to merit further investigation. A similar proposal for a single-engined fighter was issued at the same time, Circular Proposal X-609, in response to which the Bell P-39 Airacobra was designed.[18] Both proposals required liquid-cooled Allison V-1710 engines with turbosuperchargers and gave extra points for tricycle landing gear.


Lockheed formed a secretive engineering team to implement the project apart from the main factory; this approach later became known as Skunk Works.[19][20] The Lockheed design team, under the direction of Hall Hibbard and Clarence "Kelly" Johnson, considered a range of twin-engined configurations, including both engines in a central fuselage with push–pull propellers.[21]
The eventual configuration was rare in contemporary production fighter aircraft design, with the Dutch Fokker G.I heavy fighter, and the later Northrop P-61 Black Widow night fighter and Swedish SAAB 21 having a similar planform. The Lockheed team chose twin booms to accommodate the tail assembly, engines, and turbosuperchargers, with a central nacelle for the pilot and armament. The XP-38 gondola mockup was designed to mount two .50-caliber (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine guns with 200 rounds per gun (rpg), two .30-caliber (7.62 mm) Brownings with 500 rpg, and a United States Army Ordnance Department prototype T1 23 mm (.90 in) autocannon with a rotary magazine as a substitute for the nonexistent 25 mm Hotchkiss aircraft autocannon specified by Kelsey and Saville.[18] In the prototype YP-38s, an Army Ordnance Department T9 37 mm (1.46 in) autocannon (later designated as the M4 in production) with 15 rounds replaced the 23 mm T1.[22][23] The 15 rounds were in three five-round clips, an unsatisfactory arrangement according to Kelsey, and the T9/M4 did not perform reliably in flight. Further armament experiments from March to June 1941 resulted in the P-38E combat configuration of four M2 Browning machine guns, and one Hispano 20 mm (.79 in) autocannon with 150 rounds.[24]
Clustering all the armament in the nose was unusual in U.S. aircraft, which typically used wing-mounted guns with trajectories set up to crisscross at one or more points in a convergence zone. The P-38 cannon used heavier 20 mm rounds, creating a different trajectory, so it was inclined upward slightly more than the four machine guns such that the trajectories of the cannon rounds and .50-caliber bullets came together between 350 and 400 yards.[25] Nose-mounted guns did not suffer as much from having their useful ranges limited by pattern convergence, meaning that good pilots could shoot much farther. A Lightning could reliably hit targets at any range up to 1,000 yd (910 m), whereas the wing guns of other fighters were optimized for a specific range.[26] The rate of fire was about 650 rounds per minute for the 20×110 mm cannon round (130-gram shell) at a muzzle velocity of about 2,850 ft/s (870 m/s), and for the .50-caliber machine guns (43-gram rounds), about 850 rpm at 2,900 ft/s (880 m/s) velocity. Combined rate of fire was over 4,000 rpm with roughly every sixth projectile a 20 mm shell.[27] The duration of sustained firing for the 20 mm cannon was about 14 seconds, while the .50-caliber machine guns worked for 35 seconds if each magazine were fully loaded with 500 rounds, or for 21 seconds if 300 rounds were loaded to save weight for long-distance flying.
The Lockheed design incorporated tricycle undercarriage and a bubble canopy, and featured two 1,000 hp (750 kW) turbosupercharged 12-cylinder Allison V-1710 engines fitted with counter-rotating propellers to eliminate the effect of engine torque, with the turbochargers positioned behind the engines, the exhaust side of the units exposed along the dorsal surfaces of the booms.[28] Counter-rotation was achieved by the use of "handed" engines; the crankshafts of the engines turned in opposite directions, a relatively easy task for the V-1710 modular-design aircraft powerplant.[29]
The P-38 was the first American fighter to make extensive use of stainless steel and smooth, flush-riveted, butt-jointed aluminum skin panels.[30][page needed] It was also the first military airplane to fly faster than 400 mph (640 km/h) in level flight.[31][32]
XP-38 and YP-38 prototypes
[edit]Lockheed won the competition on 23 June 1937 with its Model 22 and was contracted to build a prototype XP-38[33] for US$163,000, though Lockheed's own costs on the prototype would add up to US$761,000.[34] Construction began in July 1938 in an old bourbon distillery purchased by Lockheed to house expanding operations. This secure and remote site was later identified by Johnson as the first of five Lockheed Skunk Works locations.[19][20][35] The XP-38 first flew on 27 January 1939 at the hands of Ben Kelsey.[36][Note 1]

Kelsey then proposed a speed dash to Wright Field on 11 February 1939 to relocate the aircraft for further testing. General Henry "Hap" Arnold, commander of the USAAC, approved of the record attempt and recommended a cross-country flight to New York. The flight set a speed record by flying from California to New York in seven hours and two minutes, not counting two refueling stops.[28] Kelsey flew conservatively for most of the way, working the engines gently, even throttling back during descent to remove the associated speed advantage. Bundled up against the cold, Arnold congratulated Kelsey at Wright Field during his final refueling stop, and said, "don't spare the horses" on the next leg.[38] After climbing out of Wright Field and reaching altitude, Kelsey pushed the XP-38 to 420 miles per hour (680 km/h).[39] Nearing his destination, Kelsey was ordered by Mitchel Field tower (Hempstead, New York) into a slow landing pattern behind other aircraft. Carburetor icing caused it to be brought down short of the Mitchel runway, and it was wrecked. However, on the basis of the record flight, the Air Corps ordered 13 YP-38s on 27 April 1939 for US$134,284 (~$2.31 million in 2023) each.[1][40] (The "Y" in "YP" was the USAAC's designation for service test, i.e. small numbers of early production aircraft, while the "X" in "XP" was for experimental.) Lockheed's chief test pilot, Tony LeVier, angrily characterized the accident as an unnecessary publicity stunt,[41] but according to Kelsey, the loss of the prototype, rather than hampering the program, sped the process by cutting short the initial test series. The success of the aircraft design contributed to Kelsey's promotion to captain in May 1939.[19]

Manufacture of YP-38s fell behind schedule, at least partly because of changes to meet the need for mass production, making them substantially different in construction from the prototype. Another factor was the sudden required expansion of Lockheed's facility in Burbank, taking it from a specialized civilian firm dealing with small orders to a large government defense contractor making Venturas, Harpoons, Lodestars, and Hudsons, and designing the Constellation for TWA. The first YP-38 was not completed until September 1940, with its maiden flight on 17 September.[43] The 13th and final YP-38 was delivered to the USAAC in June 1941; 12 aircraft were retained for flight testing and one for destructive stress testing. The YPs were substantially redesigned and differed greatly in detail from the hand-built XP-38. They were lighter and included changes in engine fit. The propeller rotation was reversed, with the blades spinning outward (away from the cockpit) at the top of their arc, rather than inward as before. This improved the aircraft's stability as a gunnery platform.[44]
High-speed compressibility problems
[edit]
Test flights revealed problems initially believed to be tail flutter. During high-speed flight approaching Mach 0.68, especially during dives, the aircraft's tail would begin to shake violently and the nose would tuck under (see Mach tuck), steepening the dive. Once caught in this dive, the fighter would enter a high-speed compressibility stall and the controls would lock up, leaving the pilot no option but to bail out (if possible) or remain with the aircraft until it got down to denser air, where he might have a chance to pull out. During a test flight in May 1941, USAAC Major Signa Gilkey managed to stay with a YP-38 in a compressibility lockup, riding it out until he recovered gradually using elevator trim.[28] Lockheed engineers were very concerned by this limitation, but first had to concentrate on filling the current order of aircraft. In late June 1941, the Army Air Corps was renamed the U.S. Army Air Forces (USAAF), and 65 Lightnings were finished for the service by September 1941, with more on the way for the USAAF, the Royal Air Force (RAF), and the Free French Air Force operating from England.
By November 1941, many of the initial assembly-line challenges had been met, which freed up time for the engineering team to tackle the problem of frozen controls in a dive. Lockheed had a few ideas for tests that would help them find an answer. The first solution tried was the fitting of spring-loaded servo tabs on the elevator trailing edge designed to aid the pilot when control yoke forces rose over 30 pounds-force (130 N), as would be expected in a high-speed dive. At that point, the tabs would begin to multiply the effort of the pilot's actions. Expert test pilot Ralph Virden was given a specific high-altitude test sequence to follow and was told to restrict his speed and fast maneuvering in denser air at low altitudes, since the new mechanism could exert tremendous leverage under those conditions. A note was taped to the instrument panel of the test craft underscoring this instruction. On 4 November 1941, Virden climbed into YP-38 #1 and completed the test sequence successfully, but 15 minutes later, was seen in a steep dive followed by a high-G pullout. The tail unit of the aircraft failed at about 3,500 ft (1,000 m) during the high-speed dive recovery; Virden was killed in the subsequent crash. The Lockheed design office was justifiably upset, but their design engineers could only conclude that servo tabs were not the solution for loss of control in a dive. Lockheed still had to find the problem; the Army Air Forces personnel were sure it was flutter and ordered Lockheed to look more closely at the tail.
In 1941, flutter was a familiar engineering problem related to a too-flexible tail, but the P-38's empennage was completely skinned in aluminum rather than fabric and was quite rigid. At no time did the P-38 suffer from true flutter.[45] To prove a point, one elevator and its vertical stabilizers were skinned with metal 63% thicker than standard, but the increase in rigidity made no difference in vibration. Army Lieutenant Colonel Kenneth B. Wolfe (head of Army Production Engineering) asked Lockheed to try external mass balances above and below the elevator, although the P-38 already had large mass balances elegantly placed within each vertical stabilizer. Various configurations of external mass balances were equipped, and dangerously steep test flights were flown to document their performance. Explaining to Wolfe in Report No. 2414, Kelly Johnson wrote, "the violence of the vibration was unchanged and the diving tendency was naturally the same for all conditions." The external mass balances did not help at all. Nonetheless, at Wolfe's insistence, the additional external balances were a feature of every P-38 built from then on.[46]
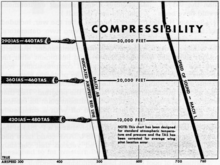
Johnson said in his autobiography[47] that he pleaded with National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics to do model tests in its wind tunnel. They already had experience of models thrashing around violently at speeds approaching those requested and did not want to risk damaging their tunnel. Gen. Arnold, head of Army Air Forces, ordered them to run the tests, which were done up to Mach 0.74.[48] The P-38's dive problem was revealed to be the center of pressure moving back toward the tail when in high-speed airflow. The solution was to change the geometry of the wing's lower surface when diving to keep lift within bounds of the top of the wing. In February 1943, quick-acting dive flaps were tried and proven by Lockheed test pilots. The dive flaps were installed outboard of the engine nacelles, and in action, they extended downward 35° in 1.5 seconds. The flaps did not act as a speed brake; they affected the pressure distribution in a way that retained the wing's lift.[49]
Late in 1943, a few hundred dive flap field-modification kits were assembled to give North African, European, and Pacific P-38s a chance to withstand compressibility and expand their combat tactics. The kits did not always reach their destination. In March 1944, 200 dive flap kits intended for the European Theater of Operations (ETO) P-38Js were destroyed in a mistaken identification incident in which an RAF fighter shot down the Douglas C-54 Skymaster (mistaken for a German Focke-Wulf Fw 200) taking the shipment to England. Back in Burbank, P-38Js coming off the assembly line in spring 1944 were towed out to the ramp and modified in the open air. The flaps were finally incorporated into the production line in June 1944 on the last 210 P-38Js. Despite testing having proved the dive flaps effective in improving tactical maneuvers, a 14-month delay in production limited their implementation, with only the final half of all Lightnings built having the dive flaps installed as an assembly-line sequence.[50]
Johnson later recalled:
I broke an ulcer over compressibility on the P-38 because we flew into a speed range where no one had ever been before, and we had difficulty convincing people that it wasn't the funny-looking airplane itself, but a fundamental physical problem. We found out what happened when the Lightning shed its tail and we worked during the whole war to get 15 more kn [28 km/h] of speed out of the P-38. We saw compressibility as a brick wall for a long time. Then we learned how to get through it.[51]
Buffeting was another early aerodynamic problem. Distinguishing it from compressibility was difficult, as both were reported by test pilots as "tail shake". Buffeting came about from airflow disturbances ahead of the tail; the airplane would shake at high speed. Leading-edge wing slots were tried, as were combinations of filleting between the wing, cockpit, and engine nacelles. Air-tunnel test number 15 solved the buffeting completely and its fillet solution was fitted to every subsequent P-38 airframe. Fillet kits were sent out to every squadron flying Lightnings. The problem was traced to a 40% increase in air speed at the wing-fuselage junction where the thickness/chord ratio was highest. An airspeed of 500 mph (800 km/h) at 25,000 ft (7,600 m) could push airflow at the wing-fuselage junction close to the speed of sound. Filleting solved the buffeting problem for the P-38E and later models.[45]

Another issue with the P-38 arose from its unique design feature of outwardly rotating (at the "tops" of the propeller arcs) counter-rotating propellers. Losing one of two engines in any twin-engined, non-centerline thrust aircraft on takeoff creates sudden drag, yawing the nose toward the dead engine and rolling the wingtip down on the side of the dead engine. Normal training in flying twin-engined aircraft when losing an engine on takeoff is to push the remaining engine to full throttle to maintain airspeed; if a pilot did that in the P-38, regardless of which engine had failed, the resulting engine torque and p-factor force produced a sudden, uncontrollable yawing roll, and the aircraft would flip over and crash. Eventually, procedures were taught to allow a pilot to deal with the situation by reducing power on the running engine, feathering the prop on the failed engine, and then increasing power gradually until the aircraft was in stable flight. Single-engined takeoffs were possible, though not with a full fuel and ammunition load.[52]
The engines were unusually quiet because the exhausts were muffled by the General Electric turbosuperchargers on the twin Allison V12s.[53] Early problems with cockpit temperature regulation occurred; pilots were often too hot in the tropical sun as the canopy could not be fully opened without severe buffeting, and were often too cold in Northern Europe and at high altitude, as the distance of the engines from the cockpit prevented easy heat transfer. Later variants received modifications (such as electrically heated flight suits) to solve these problems.[citation needed]
On 20 September 1939, before the YP-38s had been built and flight tested, the USAAC ordered 66 initial-production P-38 Lightnings, 30 of which were delivered to the (renamed) USAAF in mid-1941, but not all these aircraft were armed. The unarmed aircraft were subsequently fitted with four .50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns (instead of the two .50 in/12.7 mm and two .30 in/7.62 mm of their predecessors) and a 37 mm (1.46 in) cannon. They also had armored glass, cockpit armor, and fluorescent instrument lighting.[54] One was completed with a pressurized cabin on an experimental basis and designated XP-38A.[55] Due to reports the USAAF was receiving from Europe, the remaining 36 in the batch were upgraded with small improvements such as self-sealing fuel tanks and enhanced armor protection to make them combat-capable. The USAAF specified that these 36 aircraft were to be designated P-38D. As a result, no P-38Bs or P-38Cs were designated. The P-38D's main role was to work out bugs and give the USAAF experience with handling the type.[56]

In March 1940, the French and British, through the Anglo-French Purchasing Committee, ordered 667 P-38s for US$100M,[57] designated Model 322F for the French and Model 322B for the British. The aircraft was a variant of the P-38E. The overseas Allies wished for complete commonality of Allison engines with the large numbers of Curtiss P-40 Tomahawks both nations had on order, so they ordered the aircraft fitted with two right-handed engines (not counter-rotating) without turbosuperchargers.[58][Note 2] Performance was supposed to be 400 mph (640 km/h) at 16,900 ft (5,200 m).[59] After the fall of France in June 1940, the British took over the entire order and gave the aircraft the service name "Lightning". By June 1941, the War Ministry had cause to reconsider their earlier aircraft specifications based on experience gathered in the Battle of Britain and The Blitz.[60] British displeasure with the Lockheed order came to the fore in July, and on 5 August 1941, they modified the contract such that 143 aircraft would be delivered as previously ordered, to be known as "Lightning (Mark) I", and 524 would be upgraded to US-standard P-38E specifications with a top speed of 415 mph (668 km/h) at 20,000 ft (6,100 m) guaranteed, to be called "Lightning II", for British service.[60] Later that summer, an RAF test pilot reported back from Burbank with a poor assessment of the "tail flutter" situation, and the British cancelled all but three of the 143 Lightning Is.[60] As a loss around US$15M was involved, Lockheed reviewed their contracts and decided to hold the British to the original order. Negotiations grew bitter and stalled.[60] Everything changed after Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on 7 December 1941, after which the United States government seized some 40 of the Model 322s for West Coast defense;[61] subsequently all British Lightnings were delivered to the USAAF starting in January 1942. The USAAF lent the RAF three of the aircraft, which were delivered by sea in March 1942[62] and were test flown no earlier than May[63] at Cunliffe-Owen Aircraft Swaythling, the Aeroplane and Armament Experimental Establishment (A&AEE) and the Royal Aircraft Establishment.[60] The A&AEE example was unarmed, lacked turbochargers and restricted to 300 mph (480 km/h); though the undercarriage was praised and flight on one engine described as comfortable.[64] These three were subsequently returned to the USAAF; one in December 1942 and the others in July 1943.[62] Of the remaining 140 Lightning Is, 19 were not modified and were designated by the USAAF as RP-322-I ('R' for 'Restricted', because noncounter-rotating propellers were considered more dangerous on takeoff), while 121 were converted to counter-rotating V-1710F-2 engines without turbosuperchargers and designated P-322-II. All 121 were used as advanced trainers; a few were still serving that role in 1945.[63] A few RP-322s were later used as test modification platforms such as for smoke-laying canisters. The RP-322 was a fairly fast aircraft below 16,000 ft (4,900 m) and well-behaved as a trainer.[63][Note 3]
Many of the British order of 524 Lightning IIs were fitted with stronger F-10 Allison engines as they became available, and all were given wing pylons for fuel tanks or bombs. The upgraded aircraft were deployed to the Pacific as USAAC F-5A reconnaissance or P-38G fighter models, the latter used with great effect in the operation that shot down Admiral Yamamoto in April 1943. Robert Petit's G model named Miss Virginia was on that mission, borrowed by Rex Barber, who was later credited with the kill. Petit had already used Miss Virginia to defeat two Nakajima A6M2-N "Rufe" floatplanes in February and to heavily damage a Japanese submarine chaser in March, which he mistakenly claimed as a destroyer sunk. Murray "Jim" Shubin used a less powerful F model he named "Oriole" to down five confirmed and possibly six Zeros over Guadalcanal in June 1943 to become ace in a day.[65]
The British name was retained over Lockheed's original name 'Atalanta', the swift-running Greek goddess, following the company tradition of using mythological and celestial figures.[66]
Range extension
[edit]The strategic bombing proponents within the USAAF, nicknamed the Bomber Mafia by their ideological opponents, had established in the early 1930s a policy against research to create long-range fighters, which they thought would not be practical; this kind of research was not to compete for bomber resources. Aircraft manufacturers understood that they would not be rewarded if they installed subsystems on their fighters to enable them to carry drop tanks to provide more fuel for extended range. Lieutenant Kelsey, acting against this policy, risked his career in late 1941 when he convinced Lockheed to incorporate such subsystems in the P-38E model, without putting his request in writing. It is possible that Kelsey was responding to Colonel George William Goddard's observation that the US sorely needed a high-speed, long-range photo reconnaissance plane. Along with a change order specifying some P-38Es be produced with guns replaced by photoreconnaissance cameras, to be designated the F-4-1-LO, Lockheed began working out the problems of drop-tank design and incorporation. After the attack on Pearl Harbor, eventually about 100 P-38Es were sent to a modification center near Dallas, Texas, or to the new Lockheed assembly plant B-6 (today the Burbank Airport), to be fitted with four K-17 aerial photography cameras. All of these aircraft were also modified to be able to carry drop tanks. P-38Fs were modified, as well. Every Lightning from the P-38G onward was capable of being fitted with drop tanks straight off the assembly line.[67]
In March 1942, General Arnold made an off-hand comment that the US could avoid the German U-boat menace by flying fighters to the UK rather than packing them onto ships. President Roosevelt pressed the point, emphasizing his interest in the solution. Arnold was likely aware of the flying radius extension work being done on the P-38, which by this time had seen success with small drop tanks in the range of 150 to 165 US gal (570 to 620 L), the difference in capacity being the result of subcontractor production variation. Arnold ordered further tests with larger drop tanks in the range of 300 to 310 US gal (1,100 to 1,200 L); the results were reported by Kelsey as providing the P-38 with a 2,500-mile (4,000 km) ferrying range.[67] Because of available supply, the smaller drop tanks were used to fly Lightnings to the UK, the plan called Operation Bolero.
Led by two Boeing B-17 Flying Fortresses, the first seven P-38s, each carrying two small drop tanks, left Presque Isle Army Air Field in Maine on 23 June 1942 for RAF Heathfield in Scotland. Their first refueling stop was made in far northeast Canada at Goose Bay. The second stop was a rough airstrip in Greenland called Bluie West One, and the third refueling stop was in Iceland at Keflavik. Other P-38s followed this route with some lost in mishaps, usually due to poor weather, low visibility, radio difficulties, and navigational errors. Nearly 200 of the P-38Fs (and a few modified Es) were successfully flown across the Atlantic in July–August 1942, making the P-38 the first USAAF fighter to reach Britain and the first fighter ever to be delivered across the Atlantic under its own power.[68] Kelsey himself piloted one of the Lightnings, landing in Scotland on 25 July.[69]
Operational history
[edit]
The first unit to receive P-38s was the 1st Fighter Group. After the attack on Pearl Harbor, the unit joined the 14th Pursuit Group in San Diego to provide West Coast defense.[70]
Entry to the war
[edit]The first Lightning to see active service was the F-4 version, a P-38E in which the guns were replaced by four K17 cameras.[71] They joined the 8th Photographic Squadron in Australia on 4 April 1942.[44] Three F-4s were operated by the Royal Australian Air Force in this theater for a short period beginning in September 1942.
On 29 May 1942, 25 P-38s began operating in the Aleutian Islands in Alaska. The fighter's long range made it well-suited to the campaign over the almost 1,200-mile (1,900 km)-long island chain, and it was flown there for the rest of the war. The Aleutians were some of the most rugged environments available for testing the new aircraft under combat conditions. More Lightnings were lost due to severe weather and other conditions than enemy action; cases occurred where Lightning pilots, mesmerized by flying for hours over gray seas under gray skies, simply flew into the water. On 9 August 1942, two P-38Es of the 343rd Fighter Group, 11th Air Force, at the end of a 1,000-mile (1,600 km) long-range patrol, happened upon a pair of Japanese Kawanishi H6K "Mavis" flying boats and destroyed them,[44] making them the first Japanese aircraft to be shot down by Lightnings.
European theater
[edit]North Africa and Italy
[edit]
After the Battle of Midway, the USAAF began redeploying fighter groups to Britain as part of Operation Bolero and Lightnings of the 1st Fighter Group were flown across the Atlantic via Iceland. On 14 August 1942, Second Lieutenant Elza Shahan of the 27th Fighter Squadron, and Second Lieutenant Joseph Shaffer of the 33rd Squadron operating out of Iceland shot down a Focke-Wulf Fw 200 Condor over the Atlantic. Shaffer, flying either a P-40C or a P-39, scored the first hit, causing a fire on the Condor; Shahan in his P-38F finished it off with a high-speed gunnery pass.[72] This was the first Luftwaffe aircraft destroyed by the USAAF.[73]
After 347 sorties with no enemy contact, the 1st and 14th Fighter Groups transferred from the UK to the 12th Air Force in North Africa as part of the force being built up for Operation Torch. The Lightning's long range allowed the pilots to fly their fighters over the Bay of Biscay, skirting neutral Spain and Portugal to refuel in Morocco. The P-38s were initially based at Tafaroui Airfield in Algeria alongside P-40 Warhawks and the rest of the 12th Air Force. P-38s were first involved in North African combat operations on 11 November 1942. The first North African P-38 kill was on 22 November, when Lieutenant Mark Shipman of the 14th downed an Italian airplane with twin engines. Shipman later made two more kills – a Messerschmitt Bf 109 fighter and a very large Me 323 Gigant transport.[74]
Early results in the Mediterranean Theater of Operations were mixed. Some P-38 pilots scored multiple kills to become aces, while many others were shot down due to inexperience or tactical strictures. Overall, the P-38 suffered its highest losses in the Mediterranean Theater. The primary function of the P-38 in North Africa was to escort bombers,[75] but the fighters also targeted transport aircraft, and later in the campaign, they were sometimes tasked with ground-attack missions. When tied to bomber-escort duties, the P-38 squadrons were vulnerable to attack from above by German fighters, who selected the most advantageous position and timing. The initial tactical doctrine of the American units was for the P-38s to fly near the bombers at all times rather than to defend aggressively or to fly ahead and clear the airspace for the bombers, and many American pilots were downed because of this limitation. Losses mounted, and all available P-38s in the UK were flown over to North Africa to restore squadron strength.[74] After this painful experience, the American leadership changed tactics, and in February 1943, the P-38s were given free rein in their battles.[76]
The first German success against the P-38 was on 28 November 1942, when Bf 109 pilots of Jagdgeschwader 53 claimed seven Lightnings for no loss of their own.[76] Further one-sided German victories were noted on several occasions through January 1943.[77] The first P-38 pilots to achieve ace status were Virgil Smith of the 14th FG and Jack Illfrey of the 1st FG, both credited with five wins by 26 December. Smith got a sixth enemy aircraft on 28 December, but was killed two days later in a crash landing, likely after taking fire from Oberfeldwebel Herbert Rollwage of JG 53, who survived the war with at least 71 kills. This was Rollwage's first victory over a P-38, and his 35th claim at the time.[78]
The two squadrons of the 14th Fighter Group were reduced so badly in December 1942 that the 82nd FG was flown from the UK to North Africa to cover the shortage. The first kill by the 82nd was during a bomber-escort mission on 7 January 1943, when William J. "Dixie" Sloan broke formation and turned toward six attacking Bf 109s to shoot one of them down. Known for his maverick style, Sloan racked up 12 victories by July 1943.[78] After another heavy toll in January 1943, 14th FG had to be withdrawn from the front to reorganize, with surviving pilots sent home and the few remaining Lightnings transferred to the 82nd.[75] The 14th was out of action for three months, returning in May.[79]
On 5 April 1943, 26 P-38Fs of the 82nd claimed 31 enemy aircraft destroyed, helping to establish air superiority in the area and allegedly earning it the German nickname "der Gabelschwanz Teufel" – the Fork-tailed Devil, coming from a recently downed German aviator, as described by Life magazine in August 1943. However, the reliability of this attribution is doubtful as the clear intent of the article was to rehabilitate the P-38's reputation in the minds of the American public. No earlier independent or German attestation exists for this claim.[80] The P-38s remained active in the Mediterranean for the rest of the war, continuing to deliver and receive damage in combat. On 30 August 1943, 13 P-38s were shot down by German and Italian fighters while escorting B-26 and B-17 bombers on raids against targets in Italy.[81][82] On 2 September, 10 P-38s were shot down in combat with Bf 109s of JG 53, with four Bf 109s, including that of 67-victory ace Franz Schieß, who had been the leading "Lightning killer" in the Luftwaffe with 17 destroyed.[82][83]
The Mediterranean Theater had the first aerial combat between German fighters and P-38s. German fighter pilot appraisal of the P-38 was mixed. Some observers dismissed the P-38 as an easy kill, while others gave it high praise, a deadly enemy worthy of respect. Johannes Steinhoff, commander of JG 77 in North Africa, said that the unit's old Bf 109s were "perhaps, a little faster" than the P-38, but a dogfight with the twin-engined fighter was daunting because its turning radius was much smaller, and it could quickly get on the tail of the Bf 109. Franz Stigler, an ace with 28 kills, flew Bf 109s against the P-38 in North Africa. Stigler said the Lightning "could turn inside us with ease and they could go from level flight to climb almost instantaneously. We lost quite a few pilots who tried to make an attack and then pull up... One cardinal rule we never forgot was to avoid fighting the P-38 head on. That was suicide." Stigler said the best defense was to flick-roll the Bf 109 and dive, as the Lightning was slow in the first 10° of roll, and it was not as fast in a dive.[84] Herbert Kaiser, eventually a 68-kill ace, shot down his first P-38 in January 1943. Kaiser said that the P-38 should be respected as a formidable opponent, that it was faster and more maneuverable than the Bf 109G-6 model he flew, especially since the G-6 was slowed by underwing cannon pods. Johann Pichler, another high-scoring ace, said that the P-38 in 1943 was much faster in a climb than the Bf 109.[79] Kurt Bühligen, third-highest scoring German pilot on the Western front with 112 victories, recalled: "The P-38 fighter (and the B-24) were easy to burn. Once in Africa, we were six, and met eight P-38s and shot down seven. One sees a great distance in Africa and our observers and flak people called in sightings and we could get altitude first and they were low and slow."[85] General der Jagdflieger Adolf Galland was unimpressed with the P-38, declaring "it had similar shortcomings in combat to our Bf 110, our fighters were clearly superior to it."[86] Heinz Bäer said that P-38s "were not difficult at all. They were easy to outmaneuver and were generally a sure kill".[87]
On 12 June 1943, a P-38G, while flying a special mission between Gibraltar and Malta, or perhaps, just after strafing the radar station of Capo Pula, landed on the airfield of Capoterra (Cagliari), in Sardinia, from navigation error due to a compass failure. Regia Aeronautica chief test pilot Colonnello (Lieutenant Colonel) Angelo Tondi flew the captured aircraft to Guidonia airfield, where the P-38G was evaluated. On 11 August 1943, Tondi took off to intercept a formation of about 50 bombers, returning from the bombing of Terni (Umbria). Tondi attacked B-17G Bonny Sue, 42–30307, that fell off the shore of Torvaianica, near Rome, while six airmen parachuted out. According to US sources, he also damaged three more bombers on that occasion. On 4 September, the 301st BG reported the loss of B-17 "The Lady Evelyn," 42–30344, downed by "an enemy P-38".[88] War missions for that plane were limited, as the Italian petrol was too corrosive for the Lockheed's tanks.[89] Other Lightnings were eventually acquired by Italy for postwar service.

In a particular case when faced by more agile fighters at low altitudes in a constricted valley, Lightnings suffered heavy losses. On the morning of 10 June 1944, 96 P-38Js of the 1st and 82nd Fighter Groups took off from Italy for Ploiești, the third-most heavily defended target in Europe, after Berlin and Vienna.[90] Instead of bombing from high altitude as had been tried by the Fifteenth Air Force, USAAF planning had determined that a dive-bombing surprise attack, beginning at about 7,000 feet (2,100 m) with bomb release at or below 3,000 feet (900 m),[90] performed by 46 82nd Fighter Group P-38s, each carrying one 1,000-pound (500 kg) bomb, would yield more accurate results.[91] All of 1st Fighter Group and a few aircraft in 82nd Fighter Group were to fly cover, and all fighters were to strafe targets of opportunity on the return trip; a distance of some 1,255 miles (2,020 km), including a circuitous outward route made in an attempt to achieve surprise.[90] Some 85 or 86 fighters arrived in Romania to find enemy airfields alerted, with a wide assortment of aircraft scrambling for safety. P-38s shot down several, including heavy fighters, transports, and observation aircraft. At Ploiești, defense forces were fully alert, the target was concealed by smoke screen, and antiaircraft fire was very heavy, seven Lightnings were lost to antiaircraft fire at the target, and two more during strafing attacks on the return flight. German Bf 109 fighters from I./JG 53 and 2./JG 77 fought the Americans. Sixteen P-38s, called "Indieni cu două pene" (Indians with two feathers) by the Romanians, of the 71st Fighter Squadron were challenged by a large formation of Romanian IAR.81C fighters of the 6th Fighter Group. The fight took place below 300 feet (100 m) in a narrow valley and lasted 12 minutes.[92][93] Herbert Hatch saw two IAR 81Cs that he misidentified as Focke-Wulf Fw 190s hit the ground after taking fire from his guns, and his fellow pilots confirmed three more of his kills. Three of his victories were confirmed by gun camera. However, the outnumbered 71st Fighter Squadron took more damage than it dished out, losing nine aircraft. In all, the USAAF lost 22 aircraft on the mission. The Americans claimed 23 aerial victories. The Romanians and Germans lost five Bf 110s, four Ju 52s, and one Savoia-Marchetti SM.79 on the ground, as well as three Focke-Wulf Fw 58, three IAR 38, and three IAR.81C in the air.[94][95] Eleven enemy locomotives were strafed and left burning, and flak emplacements were destroyed, along with fuel trucks and other targets. Results of the bombing were not observed by the USAAF pilots because of the smoke. The dive-bombing mission profile was not repeated, though the 82nd Fighter Group was awarded the Presidential Unit Citation for its part.[96]
Western Europe
[edit]Experiences over Germany had shown a need for long-range escort fighters to protect the Eighth Air Force's heavy-bomber operations. The P-38Hs of the 55th Fighter Group were transferred to the Eighth in England in September 1943, and were joined by the 20th Fighter Group, 364th Fighter Group, and 479th Fighter Group soon after. P-38s and Spitfires escorted Flying Fortress raids over Europe.[97]
Because its distinctive shape was less prone to cases of mistaken identity and friendly fire,[98] Lieutenant General Jimmy Doolittle, commander of the 8th Air Force, chose to pilot a P-38 during the invasion of Normandy, so he could watch the progress of the air offensive over France.[99] At one point in the mission, Doolittle flick-rolled through a hole in the cloud cover, but his wingman, then–Major General Earle E. Partridge, was looking elsewhere and failed to notice Doolittle's quick maneuver, leaving Doolittle to continue on alone on his survey of the crucial battle. Of the P-38, Doolittle said that it was "the sweetest-flying plane in the sky".[100]

A little-known role of the P-38 in the European theater was that of fighter-bomber during the invasion of Normandy and the Allied advance across France into Germany. Assigned to the IX Tactical Air Command, the 370th Fighter Group and 474th Fighter Group and their P-38s initially flew missions from England, dive-bombing radar installations, enemy armor, troop concentrations, and flak towers, and providing air cover.[101] The 370th's group commander Howard F. Nichols and a squadron of his P-38 Lightnings attacked Field Marshal Günther von Kluge's headquarters in July 1944; Nichols himself skipped a 500 lb (230 kg) bomb through the front door.[102] The 370th later operated from Cardonville, France, and the 474th from various bases in France, flying ground-attack missions against gun emplacements, troops, supply dumps, and tanks near Saint-Lô in July and in the Falaise–Argentan area in August 1944.[101] The 370th participated in ground-attack missions across Europe until February 1945, when the unit changed over to the P-51 Mustang. The 474th operated out of bases in France, Belgium, and Germany in primarily the ground-attack missions until November–December 1945.[103]
After some disastrous raids in 1944 with B-17s escorted by P-38s and Republic P-47 Thunderbolts, Doolittle, then head of the U.S. Eighth Air Force, went to the Royal Aircraft Establishment, Farnborough, asking for an evaluation of the various American fighters. Test pilot Captain Eric Brown, Fleet Air Arm, recalled:
We had found out that the Bf 109 and the FW 190 could fight up to a Mach of 0.75, three-quarters the speed of sound. We checked the Lightning and it couldn't fly in combat faster than 0.68. So, it was useless. We told Doolittle that all it was good for was photoreconnaissance and had to be withdrawn from escort duties. And the funny thing is that the Americans had great difficulty understanding this because the Lightning had the two top aces in the Far East.[104]
After evaluation tests at Farnborough, the P-38 was kept in fighting service in Europe for a while longer. Although many failings were remedied with the introduction of the P-38J, by September 1944, all but one of the Lightning groups in the Eighth Air Force had converted to the P-51 Mustang. The Eighth Air Force continued to conduct reconnaissance missions using the F-5 variant.[70]
Pacific theater
[edit]
The P-38 was used most extensively and successfully in the Pacific Theater, where it proved more suited, combining exceptional range with the reliability of two engines for long missions over water. The P-38 was used in a variety of roles, especially escorting bombers at altitudes of 18,000–25,000 ft (5,500–7,600 m). The P-38 was credited with destroying more Japanese aircraft than any other USAAF fighter.[1] Freezing cockpit temperatures were not a problem at low altitude in the tropics. In fact, the cockpit was often too hot since opening a window while in flight caused buffeting by setting up turbulence through the tailplane. Pilots taking low-altitude assignments often flew stripped down to shorts, tennis shoes, and parachute. While the P-38 could not out-turn the A6M Zero and most other Japanese fighters when flying below 200 mph (320 km/h), its superior speed coupled with a good rate of climb meant that it could use energy tactics, making multiple high-speed passes at its target. In addition, its tightly grouped guns were even more deadly to lightly armored Japanese warplanes than to German aircraft. The concentrated, parallel stream of bullets allowed aerial victory at much longer distances than fighters carrying wing guns. Dick Bong, the United States' highest-scoring World War II air ace (40 victories in P-38s), flew directly at his targets to ensure he hit them, in some cases flying through the debris of his target (and on one occasion colliding with an enemy aircraft, which was claimed as a "probable" victory). The twin Allison engines performed admirably in the Pacific.

General George C. Kenney, commander of the USAAF 5th Air Force operating in New Guinea, could not get enough P-38s; they had become his favorite fighter in November 1942 when one squadron, the 39th Fighter Squadron of the 35th Fighter Group, joined his assorted P-39s and P-40s. The Lightnings established local air superiority with their first combat action on 27 December 1942.[105][106][107][108][109] Kenney sent repeated requests to Arnold for more P-38s, and was rewarded with occasional shipments, but Europe was a higher priority in Washington.[110] Despite their small force, Lightning pilots began to compete in racking up scores against Japanese aircraft.
On 2–4 March 1943, P-38s flew top cover for 5th Air Force and Australian bombers and attack aircraft during the Battle of the Bismarck Sea, in which eight Japanese troop transports and four escorting destroyers were sunk. Two P-38 aces from the 39th Fighter Squadron were killed on the second day of the battle: Bob Faurot and Hoyt "Curley" Eason (a veteran with five victories who had trained hundreds of pilots, including Dick Bong). In one notable engagement on 3 March 1943, P-38s escorted 13 B-17s (part of an attack including B-25 Mitchells and Beaufighters) as they bombed the Japanese convoy from a medium altitude of 7,000 ft (2,100 m), which dispersed the convoy formation and reduced their concentrated antiaircraft firepower. A B-17 was shot down and when Japanese Zero fighters machine-gunned some of the B-17 crew members who bailed out in parachutes, three P-38s promptly dived into action, claiming five Zeros.[111][112][113][114]
Killing of Admiral Yamamoto
[edit]Because of its ability to fly long distances, the Lightning figured in one of the most significant operations in the Pacific Theater – the interception, on 18 April 1943, of Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto, the architect of Japan's naval strategy in the Pacific including the attack on Pearl Harbor. When American codebreakers found out that he was flying to Bougainville Island to conduct a front-line inspection, 16 P-38G Lightnings were sent on a long-range fighter-intercept mission, flying 435 miles (700 km) from Guadalcanal at heights of 10 to 50 ft (3 to 20 m) above the ocean to avoid detection. The Lightnings met Yamamoto's two Mitsubishi G4M "Betty" fast bomber transports and six escorting Zeros just as they arrived at the island. The first Betty crashed in the jungle and the second ditched near the coast. The Americans lost one P-38. Japanese search parties found Yamamoto's body at the jungle crash site the next day.[115]
Service record
[edit]
The P-38's service record shows mixed results, which may reflect more on its employment than on flaws with the aircraft. The P-38's engine troubles at high altitudes only occurred with the Eighth Air Force. One reason for this was the inadequate cooling systems of the G and H models; the improved P-38 J and L had tremendous success flying out of Italy into Germany at all altitudes.[70] Until the -J-25 variant, P-38s were easily avoided by German fighters because of the lack of dive flaps to counter compressibility in dives. German fighter pilots not wishing to fight would perform the first half of a Split S and continue into steep dives because they knew the Lightnings would be reluctant to follow.
On the positive side, having two engines was a built-in insurance policy. Many pilots arrived safely back to base after having an engine failure en route or in combat. On 3 March 1944, the first Allied fighters reached Berlin on a frustrated escort mission. Lieutenant Colonel Jack Jenkins of 55th Fighter Group led the group of P-38H pilots, arriving with only half his force after flak damage and engine trouble took their toll. On the way into Berlin, Jenkins reported one rough-running engine, causing him to wonder if he would ever make it back. The B-17s he was supposed to escort never showed up, having turned back at Hamburg. Jenkins and his wingman were able to drop tanks and outrun enemy fighters to return home with three good engines between them.[116]

In the European Theater, P-38s made 130,000 sorties with a loss of 1.3% overall, comparing favorably with P-51s, which posted a 1.1% loss, considering that the P-38s were vastly outnumbered and suffered from poorly thought-out tactics. Most of the P-38 sorties were made in the period prior to Allied air superiority in Europe, when pilots fought against a very determined and skilled enemy.[117] Lieutenant Colonel Mark Hubbard, a vocal critic of the aircraft, rated it the third-best Allied fighter in Europe.[118] The Lightning's greatest virtues were long range, heavy payload, high speed, fast climb, and concentrated firepower. The P-38 was a formidable fighter, interceptor, and attack aircraft.
In the Pacific Theater, the P-38 downed over 1,800 Japanese aircraft, with more than 100 pilots becoming aces by downing five or more enemy aircraft.[115] American fuel supplies contributed to a better engine performance and maintenance record, and range was increased with leaner mixtures. In the second half of 1944, the P-38L pilots out of Dutch New Guinea were flying 950 mi (1,530 km), fighting for 15 minutes and returning to base.[119] Such long legs were invaluable until the P-47N and P-51D entered service.
Postwar operations
[edit]The end of the war left the USAAF with thousands of P-38s rendered obsolete by the jet age. Orders for 1,887 more were cancelled.[120] The last P-38s in service with the United States Air Force were retired in 1949.[121] One-hundred late-model P-38L and F-5 Lightnings were acquired by Italy through an agreement dated April 1946. Delivered, after refurbishing, at the rate of one per month, they finally were all sent to the Aeronautica Militare by 1952. The Lightnings served in the 4° Stormo and other units including 3° Stormo, flying reconnaissance over the Balkans, ground attack, naval cooperation, and air-superiority missions. Due to old engines, pilot errors, and lack of experience in operations, large numbers of P-38s were lost in at least 30 accidents, many of them fatal. Despite this, many Italian pilots liked the P-38 because of its excellent visibility on the ground and stability on takeoff. The Italian P-38s were phased out in 1956; none survived the scrapyard.[122]
Surplus P-38s were also used by other foreign air forces, with 12 sold to Honduras and 15 retained by China. Six F-5s and two unarmed black two-seater P-38s were operated by the Dominican Air Force based in San Isidro Airbase, Dominican Republic, in 1947. Most of the wartime Lightnings present in the continental U.S. at the end of the war were put up for sale for US$1,200 apiece; the rest were scrapped. P-38s in distant theaters of war were bulldozed into piles and abandoned or scrapped; very few avoided that fate.
The CIA "Liberation Air Force" flew one P-38M to support the 1954 Guatemalan coup d'etat. On 27 June 1954, this aircraft dropped napalm bombs that destroyed the British cargo ship SS Springfjord, which was loading Guatemalan cotton[123] and coffee[124] for Grace Line[125][failed verification] in Puerto San José.[126] In 1957, five Honduran P-38s bombed and strafed a village occupied by Nicaraguan forces during a border dispute between these two countries concerning part of Gracias a Dios Department.[127]
P-38s were popular contenders in the air races from 1946 through 1949, with brightly colored Lightnings making screaming turns around the pylons at Reno and Cleveland. Lockheed test pilot Tony LeVier was among those who bought a Lightning, choosing a P-38J model and painting it red to make it stand out as an air racer and stunt flyer. Lefty Gardner, former B-24 and B-17 pilot and associate of the Confederate Air Force, bought a mid-1944 P-38L-1-LO that had been modified into an F-5G. Gardner painted it white with red and blue trim and named it White Lightnin'; he reworked its turbo systems and intercoolers for optimum low-altitude performance and gave it P-38F-style air intakes for better streamlining. White Lightnin' was severely damaged in a crash landing following an engine fire on a transit flight, and was bought and restored with a brilliant polished-aluminum finish by the company that owns Red Bull. The aircraft is now located in Austria.
F-5s were bought by aerial survey companies and employed for mapping. From the 1950s on, the use of the Lightning steadily declined, and only a few more than two dozen still exist, with few still flying. One example is a P-38L owned by the Lone Star Flight Museum in Galveston, Texas, painted in the colors of Charles H. MacDonald's Putt Putt Maru. Two other examples are F-5Gs, which were owned and operated by Kargl Aerial Surveys in 1946, and are now located in Chino, California, at Yanks Air Museum, and in McMinnville, Oregon, at Evergreen Aviation Museum. The earliest-built surviving P-38, Glacier Girl, was recovered from the Greenland ice cap in 1992, 50 years after she crashed there on a ferry flight to the UK, and after a complete restoration, flew once again 10 years after her recovery.
Production
[edit]| Variant | Built or converted |
Comment |
|---|---|---|
| XP-38 | 1 | Prototype |
| YP-38 | 13 | Evaluation aircraft |
| P-38 | 30 | Initial production aircraft |
| XP-38A | 1 | Pressurized cockpit |
| P-38D | 36 | Fitted with self-sealing fuel tanks/armored windshield |
| P-38E | 210 | First combat-ready variant, revised armament |
| F-4 | 100+ | Reconnaissance aircraft based on P-38E |
| Model 322 | 3 | RAF order: twin right-hand props and no turbo |
| RP-322 | 147 | USAAF trainers |
| P-38F | 527 | First fully[citation needed] combat-capable P-38 fighter |
| F-4A | 20 | Reconnaissance aircraft based on P-38F |
| P-38G | 1,082 | Improved P-38F fighter |
| F-5A | 180 | Reconnaissance aircraft based on P-38G |
| XF-5D | 1 | A one-off converted F-5A |
| P-38H | 601 | Automatic cooling system; improved P-38G fighter |
| P-38J | 2,970 | New cooling and electrical systems |
| F-5B | 200 | Reconnaissance aircraft based on P-38J |
| F-5C | 123 | Reconnaissance aircraft converted from P-38J |
| F-5E | 705 | Reconnaissance aircraft converted from P-38J/L |
| P-38K | 2 | Paddle blade props; up-rated engines with a different propeller reduction ratio |
| P-38L-LO | 3,810 | Improved P-38J new engines; new rocket pylons |
| P-38L-VN | 113 | P-38L built by Vultee |
| F-5F | – | Reconnaissance aircraft converted from P-38L |
| P-38M | 75 | Night fighter converted from P-38L |
| F-5G | – | Reconnaissance aircraft converted from P-38L |
Over 10,000 Lightnings were manufactured, becoming the only U.S. combat aircraft that remained in continuous production throughout the duration of American participation in World War II. The Lightning had a major effect on other aircraft; its wing, in a scaled-up form, was used on the Lockheed Constellation.[129]
P-38D and P-38Es
[edit]Delivered and accepted Lightning production variants began with the P-38D model. The few "hand made" YP-38s initially contracted were used as trainers and test aircraft. No Bs or Cs were delivered to the government as the USAAF allocated the 'D' suffix to all aircraft with self-sealing fuel tanks and armor.[41] Many secondary but still initial teething tests were conducted using the earliest D variants.[41]
The first combat-capable Lightning was the P-38E (and its photo-recon variant the F-4) which featured improved instruments, electrical, and hydraulic systems. Part-way through production, the older Hamilton Standard Hydromatic hollow steel propellers were replaced by new Curtiss Electric duraluminum propellers. The definitive (and now famous) armament configuration was settled upon, featuring four .50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns with 500 rpg, and a 20 mm (.79 in) Hispano autocannon with 150 rounds.[130]
While the machine guns had been arranged symmetrically in the nose on the P-38D, they were "staggered" in the P-38E and later versions, with the muzzles protruding from the nose in the relative lengths of roughly 1:4:6:2. This was done to ensure a straight ammunition-belt feed into the weapons, as the earlier arrangement led to jamming.
The first P-38E rolled out of the factory in October 1941 as the Battle of Moscow filled the news wires of the world. Because of the versatility, redundant engines, and especially high-speed and high-altitude characteristics of the aircraft, as with later variants, over a hundred P-38Es were completed in the factory or converted in the field to a photoreconnaissance variant, the F-4, in which the guns were replaced by four cameras. Most of these early reconnaissance Lightnings were retained stateside for training, but the F-4 was the first Lightning to be used in action in April 1942.[citation needed]
P-38Fs and P-38Gs
[edit]After 210 P-38Es were built, they were followed, starting in February 1942, by the P-38F, which incorporated racks inboard of the engines for fuel tanks or a total of 2,000 lb (910 kg) of bombs. Early variants did not enjoy a high reputation for maneuverability, though they could be agile at low altitudes if flown by a capable pilot, using the P-38's forgiving stall characteristics to their best advantage. From the P-38F-15 model onwards, a "combat maneuver" setting was added to the P-38's Fowler flaps. When deployed at the 8° maneuver setting, the flaps allowed the P-38 to out-turn many contemporary single-engined fighters at the cost of some added drag. However, early variants were hampered by high aileron control forces and a low initial rate of roll,[131] and all such features required a pilot to gain experience with the aircraft,[41] which in part was an additional reason Lockheed sent its representative to England, and later to the Pacific Theater.
The aircraft was still experiencing extensive teething troubles, as well as being victimized by "urban legends", mostly involving inapplicable twin-engined factors which had been designed out of the aircraft by Lockheed.[41] In addition to these, the early versions had a reputation as a "widow maker" as it could enter an unrecoverable dive due to a sonic surface effect at high subsonic speeds. The 527 P-38Fs were heavier, with more powerful engines that used more fuel, and were unpopular in the air war in Northern Europe.[41] Since the heavier engines were having reliability problems and with them, without external fuel tanks, the range of the P-38F was reduced, and since drop tanks themselves were in short supply as the fortunes in the Battle of the Atlantic had not yet swung the Allies' way, the aircraft became relatively unpopular in minds of the bomber command planning staffs despite being the longest-ranged fighter first available to the 8th Air Force in sufficient numbers for long-range escort duties.[41] Nonetheless, General Spaatz, then commander of the 8th Air Force in the UK, said of the P-38F: "I'd rather have an airplane that goes like hell and has a few things wrong with it, than one that won't go like hell and has a few things wrong with it."[100]

The P-38F was followed in June 1942 by the P-38G, using more powerful Allisons of 1,400 hp (1,000 kW) each and equipped with a better radio. A dozen of the planned P-38G production were set aside to serve as prototypes for what became the P-38J with further uprated Allison V-1710F-17 engines (1,425 hp (1,063 kW) each) in redesigned booms, which featured chin-mounted intercoolers in place of the original system in the leading edge of the wings and more efficient radiators. Lockheed subcontractors, however, were initially unable to supply both of Burbank's twin production lines with a sufficient quantity of new core intercoolers and radiators. War Production Board planners were unwilling to sacrifice production, and one of the two remaining prototypes received the new engines, but retained the old leading-edge intercoolers and radiators.

As the P-38H, 600 of these stop-gap Lightnings with an improved 20 mm cannon and a bomb capacity of 3,200 lb (1,500 kg) were produced on one line beginning in May 1943 while the near-definitive P-38J began production on the second line in August 1943. The Eighth Air Force was experiencing high-altitude and cold-weather issues which, while not unique to the aircraft, were perhaps more severe as the turbosuperchargers upgrading the Allisons were having their own reliability issues, making the aircraft more unpopular with senior officers out of the line.[41] This was a situation unduplicated on all other fronts where the commands were clamoring for as many P-38s as they could get.[41] Both the P-38G and P-38H models' performances were restricted by an intercooler system integral to the wing's leading edge, which had been designed for the YP-38's less powerful engines. At the higher boost levels, the new engine's charge air temperature would increase above the limits recommended by Allison and would be subject to detonation if operated at high power for extended periods of time. Reliability was not the only issue, either. For example, the reduced power settings required by the P-38H did not allow the maneuvering flap to be used to good advantage at high altitude.[132] All these problems really came to a head in the unplanned P-38H and sped the Lightning's eventual replacement in the 8th Air Force; fortunately, the 15th Air Force was glad to get them.
Some P-38G production was diverted on the assembly line to F-5A reconnaissance aircraft. An F-5A was modified to an experimental two-seat reconnaissance configuration as the XF-5D, with a Plexiglas nose, two machine guns, and additional cameras in the tail booms.
P-38J, P-38L
[edit]
The P-38J was introduced in August 1943. The turbosupercharger intercooler system on previous variants had been housed in the leading edges of the wings and had proven vulnerable to combat damage and could burst if the wrong series of controls was mistakenly activated. In the P-38J series, the streamlined engine nacelles of previous Lightnings were changed to fit the intercooler radiator between the oil coolers, forming a "chin" that visually distinguished the J model from its predecessors. While the P-38J used the same V-1710-89/91 engines as the H model, the new core-type intercooler more efficiently lowered intake manifold temperatures and permitted a substantial increase in rated power. The leading edge of the outer wing was fitted with 55 US gal (210 L) fuel tanks, filling the space formerly occupied by intercooler tunnels, but these were omitted on early P-38J blocks due to limited availability.[133]
The final 210 J models, designated P-38J-25-LO, alleviated the compressibility problem through the addition of a set of electrically actuated dive recovery flaps just outboard of the engines on the bottom centerline of the wings. With these improvements, a USAAF pilot reported a dive speed of almost 600 mph (970 km/h), although the indicated air speed was later corrected for compressibility error, and the actual dive speed was lower.[134] Lockheed manufactured over 200 retrofit modification kits to be installed on P-38J-10-LO and J-20-LO already in Europe, but the USAAF C-54 carrying them was shot down by an RAF pilot who mistook the Douglas transport for a German Focke-Wulf Condor.[135] Unfortunately, the loss of the kits came during Lockheed test pilot Tony LeVier's four-month morale-boosting tour of P-38 bases. Flying a new Lightning named Snafuperman, modified to full P-38J-25-LO specifications at Lockheed's modification center near Belfast, LeVier captured the pilots' full attention by routinely performing maneuvers during March 1944 that common 8th Air Force wisdom held to be suicidal. It proved too little, too late, because the decision had already been made to re-equip with Mustangs.[52]
The P-38J-25-LO production block also introduced hydraulically boosted ailerons, one of the first times such a system was fitted to a fighter. This significantly improved the Lightning's rate of roll and reduced control forces for the pilot. This production block and the following P-38L model are considered the definitive Lightnings, and Lockheed ramped up production, working with subcontractors across the country to produce hundreds of Lightnings each month.
The P-38L was the most numerous variant of the Lightning, with 3,923 built, 113 by Consolidated-Vultee in their Nashville plant. It entered service with the USAAF in June 1944, in time to support the Allied invasion of France on D-Day. Lockheed production of the Lightning was distinguished by a suffix consisting of a production block number followed by "LO," for example "P-38L-1-LO", while Consolidated-Vultee production was distinguished by a block number followed by "VN," for example "P-38L-5-VN."
The P-38L was the first Lightning fitted with zero-length rocket launchers. Seven High Velocity Aircraft Rockets (HVARs) on pylons were placed beneath each wing, and later, five rockets were on each wing on "Christmas tree" launch racks, which added 1,365 lb (619 kg) to the aircraft.[136] The P-38L also had strengthened stores pylons to allow carriage of 2,000 lb (900 kg) bombs or 300 US gal (1,100 L) drop tanks.

Lockheed modified 200 P-38J airframes in production to become unarmed F-5B photo-reconnaissance aircraft, while hundreds of other P-38Js and P-38Ls were modified at Lockheed's Dallas Modification Center to become F-5Cs, F-5Es, F-5Fs, or F-5Gs. A few P-38Ls were field modified to become two-seat TP-38L familiarization trainers. During and after June 1948, the remaining J and L variants were designated ZF-38J and ZF-38L, with the "ZF" designator (meaning "obsolete fighter") replacing the "P for Pursuit" category.
Late-model Lightnings were delivered unpainted, per USAAF policy established in 1944. At first, field units tried to paint them, since pilots worried about being too visible to the enemy, but the reduction in weight and drag turned out to be a minor advantage in combat.
The P-38L-5, the most common subvariant of the P-38L, had a modified cockpit heating system consisting of a plug-socket in the cockpit into which the pilot could plug his heat-suit wire for improved comfort. These Lightnings also received the uprated V-1710-112/113 (F30R/L) engines, and this dramatically lowered the number of engine-failure problems experienced at high altitude so commonly associated with European operations.
P-38K
[edit]Two P-38Ks were developed from 1942 to 1943, one official and one an internal Lockheed experiment. The first was actually a battered RP-38E "piggyback" test mule previously used by Lockheed to test the P-38J chin intercooler installation, now fitted with paddle-bladed "high activity" Hamilton Standard Hydromatic propellers similar to those used on the P-47. The new propellers required spinners of greater diameter, and the mule's crude, hand-formed sheet steel cowlings were further stretched to blend the spinners into the nacelles. It retained its "piggyback" configuration that allowed an observer to ride behind the pilot. With Lockheed's AAF representative as a passenger and the maneuvering flap deployed to offset Army Hot Day conditions, the old "K-Mule" still climbed to 45,000 feet (14,000 m). With a fresh coat of paint covering its crude, hand-formed steel cowlings, this RP-38E acts as stand-in for the "P-38K-1-LO" in the model's only picture.[137]
The 12th G model originally set aside as a P-38J prototype was redesignated P-38K-1-LO and fitted with the aforementioned paddle-blade propellers and new Allison V-1710-75/77 (F15R/L) powerplants rated at 1,875 bhp (1,398 kW) at War Emergency Power. These engines were geared 2.36 to 1, unlike the standard P-38 ratio of 2 to 1. The AAF took delivery in September 1943, at Eglin Field. In tests, the P-38K-1 achieved 432 mph (695 km/h) at military power and was predicted to exceed 450 mph (720 km/h) at War Emergency Power with a similar increase in load and range. The initial climb rate was 4,800 ft (1,500 m)/min and the ceiling was 46,000 ft (14,000 m). It reached 20,000 ft (6,100 m) in five minutes flat; this with a coat of camouflage paint, which added weight and drag. Although it was judged superior in climb and speed to the latest and best fighters from all AAF manufacturers, the War Production Board refused to authorize P-38K production due to the two- to three-week interruption in production necessary to implement cowling modifications for the revised spinners and higher thrust line.[137] Some had also doubted Allison's ability to deliver the F15 engine in quantity.[138] As promising as it had looked, the P-38K project came to a halt.
Pathfinders, night-fighter, and other variants
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (January 2011) |
The Lightning was modified for other roles. In addition to the F-4 and F-5 reconnaissance variants, a number of P-38Js and P-38Ls were field modified as formation bombing "pathfinders" or "droopsnoots",[139] fitted with a Norden bombsight or an H2X radar system. Such pathfinders would lead a formation of other P-38s, each loaded with two 2,000 lb (907 kg) bombs; the entire formation releasing their ordnance when the pathfinder did.[140]

A number of Lightnings were modified as night fighters. Several field or experimental modifications with different equipment fits finally led to the "formal" P-38M night fighter, or Night Lightning. A total of 75 P-38Ls were modified to the Night Lightning configuration, painted flat-black with conical flash hiders on the guns, an AN/APS-6 radar pod below the nose, and a second cockpit with a raised canopy behind the pilot's canopy for the radar operator. The headroom in the rear cockpit was limited, requiring radar operators who were preferably short in stature.[141][page needed]
One of the initial production P-38s had its turbosuperchargers removed, with a secondary cockpit placed in one of the booms to examine how flight crews would respond to such an "asymmetric" cockpit layout.[142][page needed][143][page needed] One P-38E was fitted with an extended central nacelle to accommodate a tandem-seat cockpit with dual controls, and was later fitted with a laminar-flow wing.

Very early in the Pacific War, a scheme was proposed to fit Lightnings with floats to allow them to make long-range ferry flights. The floats would be removed before the aircraft went into combat. Concerns arose that saltwater spray would corrode the tailplane, so in March 1942, P-38E 41-1986 was modified with a tailplane raised some 16–18 in (41–46 cm), booms lengthened by 2 ft, and a rearward-facing second seat added for an observer to monitor the effectiveness of the new arrangement. A second version was crafted on the same airframe with the twin booms given greater sideplane area to augment the vertical rudders. This arrangement was removed and a final third version was fabricated that had the booms returned to normal length but the tail raised 33 in (84 cm). All three tail modifications were designed by George H. "Bert" Estabrook. The final version was used for a quick series of dive tests on 7 December 1942 in which Milo Burcham performed the test maneuvers and Kelly Johnson observed from the rear seat. Johnson concluded that the raised floatplane tail gave no advantage in solving the problem of compressibility. At no time was this P-38E testbed airframe actually fitted with floats, and the idea was quickly abandoned, as the U.S. Navy proved to have enough sealift capacity to keep up with P-38 deliveries to the South Pacific.[144]
Still another P-38E was used in 1942 to tow a Waco troop glider as a demonstration. However, there proved to be plenty of other aircraft, such as Douglas C-47 Skytrains, available to tow gliders, and the Lightning was spared this duty.
Standard Lightnings were used as crew and cargo transports in the South Pacific. They were fitted with pods attached to the underwing pylons, replacing drop tanks or bombs, that could carry a single passenger in a lying-down position, or cargo. This was a very uncomfortable way to fly. Some of the pods were not even fitted with a window to let the passenger see out or bring in light.
Lockheed proposed a carrier-based Model 822 version of the Lightning for the United States Navy. The Model 822 would have featured folding wings, an arresting hook, and stronger undercarriage for carrier operations. The Navy was not interested, as they regarded the Lightning as too big for carrier operations and did not like liquid-cooled engines; therefore, the Model 822 never went beyond the paper stage. However, the Navy did operate four land-based F-5Bs in North Africa, inherited from the USAAF and redesignated FO-1.
A P-38J was used in experiments with an unusual scheme for midair refueling, in which the fighter snagged a drop tank trailed on a cable from a bomber. The USAAF managed to make this work, but decided it was not practical. A P-38J was also fitted with experimental retractable snow-ski landing gear, but this idea never reached operational service, either.
After the war, a P-38L was experimentally fitted with armament of three .60 in (15.2 mm) machine guns. The .60 in (15.2 mm) caliber cartridge had been developed early in the war for an infantry anti-tank rifle, a type of weapon developed by a number of nations in the 1930s when tanks were lighter, but by 1942, armor was too tough for this caliber.
Another P-38L was modified after the war as a "super strafer", with eight .50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns in the nose and a pod under each wing with two .50 in (12.7 mm) guns, for a total of 12 machine guns. Nothing came of this conversion, either.
Variants
[edit]
- XP-38: United States Army Air Force designation for one prototype Lockheed Model 22 first flown in 1939[145]
- YP-38: Redesigned preproduction batch with armament, 13 built[145]
- P-38: First production variant with 0.5 in guns and a 37 mm cannon, 30 built[145][146]
- XP-38A: Thirtieth P-38 modified with a pressurized cockpit[145][146]
- Lightning I: Former Armée de l'air order for 667 aircraft (being reduced to 143 Lighting Is), it was taken by the Royal Air Force, three delivered to RAF, and the remainder of the order was delivered to USAAF. It used C-series V-1710-33 engines without turbochargers, and right-hand propeller rotation (not counter).[147][148]
- Lightning II: The Royal Air Force designation for a cancelled order of 524 aircraft using F-series V-1710 engines, the only one built was retained by the USAAF for testing. The rest of the order was completed as P-38F-13-LO, P-38F-15-LO, P-38G-13-LO, and P-38G-15-LO aircraft.[147][148]
- P-322-I: 22 Lightning Is of the 143 built were retained by the USAAF for training and testing. Most were unarmed, although some retained the Lighting I armament of two .50 cal and two .30 cal guns.[145][149]
- P-322-II: 121 Lightning Is were re-engined with the V-1710-27/-29 and used for training. Most were unarmed.[145][149]
- P-38B: Proposed variant of the P-38A, not built[145]
- P-38C: Proposed variant of the P-38A, not built[145]
- P-38D: Production variant with modified tailplane incidence, self-sealing fuel tanks, 36 built[145]
- P-38E: Production variant with revised hydraulic system, 20 mm cannon rather than the 37 mm of earlier variants, 210 built[145]
- P-38E Floatplane: A proposed floatplane variant of the P-38E with upswept tail booms and fitted with droppable and fuel-filled floats, one prototype was converted from P-38E 41-1986 with modified tail booms, but was not fitted with floats. It did not enter production.[150]
- P-38F: Production variant with inboard underwing racks for drop tanks or 2000 lb of bombs, 527 built[145]
- P-38G: Production variant with modified radio equipment, 1082 built[145]
- P-38H: Production variant capable of carrying 3200 lb of underwing bombs, improved intercooler design along with automatic oil radiator flaps, 601 built[145]
- P-38J: This production variant was built in 1943 with improvements to each batch, notably an increase of Hp that came with an improved turbocharger. It also included chin radiators, flat bullet-proof windshields, power-boosted ailerons, and increased fuel capacity* 2970 were built. Some were modified to pathfinder configuration and to F-5C, F-5E, and F-5F.[145]
- P-38K: With V-1710-75/77 (F15R/L) powerplants rated at 1875 hp (1,398 kW) at War Emergency Power, larger Hamilton Standard Paddle-bladed propellers were added to compensate for increased power, one was built* a single P-38E was additionally converted to the same propeller as the P-38K.[145]
- P-38L: With 1600 hp engines, 3923 were built, which included 113 built at Vultee* later conversions to pathfinders and F-5G were made.[145]
- TP-38L: Two P-38Ls were converted as tandem-seated operational trainers.[145]
- P-38M: Conversion of P-38L as a radar-equipped night-fighter[145]
- F-4: Photo-reconnaissance variant of the P-38E, 99 built[151]
- F-4A: Photo-reconnaissance variant of the P-38F, 20 built[151]
- F-5A: Reconnaissance variant of the P-38G, 181 built[151]
- F-5B: Reconnaissance variant of the P-38J, 200 were built, and four were later sent to the United States Navy as FO-1s.[151]
- F-5C: Reconnaissance variant of the P-38J, 123 conversions[151]
- XF-5D: Prone-observer variant, one conversion from a F-5A[151]
- F-5E: Reconnaissance variant converted from the P-38J and P-38L, 705 converted[151]
- F-5F: Reconnaissance variant conversions of the P-38L[151]
- F-5G: As reconnaissance variant conversions of the P-38L, they had a different camera configuration from the F-5F.[151]
- XFO-1: United States Navy designation for four F-5Bs operated for evaluation.[152]
Operators
[edit]- Military
Civil
Noted P-38s
[edit]
Yippee
[edit]The 5,000th Lightning built, a P-38J-20-LO, 44-23296, was painted bright vermilion red, and had the name YIPPEE painted on the underside of the wings in large white letters, as well as the signatures of hundreds of factory workers. This and other aircraft were used by a handful of Lockheed test pilots including Milo Burcham, Jimmie Mattern, and Tony LeVier in remarkable flight demonstrations, performing such stunts as slow rolls at treetop level with one prop feathered to dispel the myth that the P-38 was unmanageable.[153][154]
Surviving aircraft
[edit]Of the ten thousand aircraft built, there are 26 survivors of which ten are airworthy.
Noted P-38 pilots
[edit]Richard Bong and Thomas McGuire
[edit]
The American ace of aces and his closest competitor both flew Lightnings and tallied 40 and 38 victories, respectively.[155] Majors Richard I. "Dick" Bong and Thomas B. "Tommy" McGuire of the USAAF competed for the top position. Both men were awarded the Medal of Honor.
McGuire was killed in air combat in January 1945 over the Philippines, after accumulating 38 confirmed kills, making him the second-ranking American ace. Bong was rotated back to the United States as America's ace of aces, after making 40 kills, becoming a test pilot. He was killed on 6 August 1945, the day the atomic bomb was dropped on Japan, when his Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star jet fighter flamed out on take-off.

Charles Lindbergh
[edit]Charles Lindbergh became famous for his transatlantic solo flight before the war. By WWII he was a civilian working for Vought in the South Pacific area. He received preferential treatment as if a visiting colonel. In Hollandia, Lindbergh attached himself to the 475th Fighter Group which was flying P-38s. Although new to the aircraft, Lindbergh was instrumental in extending the range of the P-38 through improved throttle settings, or engine-leaning techniques, notably by reducing engine speed to 1,600 rpm, setting the carburetors for auto-lean and flying at 185 mph (298 km/h) indicated airspeed, which reduced fuel consumption to 70 gal/h, about 2.6 mpg. This combination of settings had been considered dangerous as it was believed this would upset the fuel mixture, causing an explosion.[156]
While with the 475th, he took part in a number of combat missions. On 28 July 1944, Lindbergh shot down a Mitsubishi Ki-51 "Sonia" flown by the veteran commander of the 73rd Independent Flying Chutai of the Imperial Japanese Army Captain Saburo Shimada. In an extended, twisting dogfight in which many of the participants ran out of ammunition, Shimada turned his aircraft directly toward Lindbergh, who was just approaching the combat area. Lindbergh fired in a defensive reaction brought on by Shimada's apparent head-on ramming attack. Hit by cannon and machine-gun fire, the "Sonia's" propeller visibly slowed, but Shimada held his course. Lindbergh pulled up at the last moment to avoid collision as the damaged "Sonia" went into a steep dive, hit the ocean, and sank. The unofficial kill was not entered in the 475th's war record. On 12 August 1944, Lindbergh left Hollandia to return to the United States.[157]
Charles MacDonald
[edit]The third-ranking American ace of the Pacific theater, Charles H. MacDonald, flew a Lightning against the Japanese and scored 27 kills[155] in his aircraft, the Putt Putt Maru.
Martin James Monti
[edit]Martin James Monti was an American pilot who defected to the Axis powers in a stolen F-5E Lightning, which was handed over to the Luftwaffe Zirkus Rosarius for testing afterward.
Robin Olds
[edit]Robin Olds was the last P-38 ace in the 8th Air Force and the last in the ETO. Flying a P-38J, he downed five German fighters on two separate missions over France and Germany. He subsequently transitioned to P-51s and scored seven more kills. After World War II, he flew F-4 Phantom IIs in Vietnam, ending his career as brigadier general with 16 kills.
John H. Ross
[edit]Ross is a decorated World War II pilot who flew 96 missions for the U.S. Army Air Forces under the U.S. 8th Air Force's 7th Reconnaissance Group in the 22nd Reconnaissance Squadron. Ross flew the Lockheed P-38 Lightning as a photo-reconnaissance pilot out of RAF Mount Farm in England during the war. He received 11 medals and was awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross twice for missions that were integral to Allied victory at the Battle of the Bulge.
Antoine de Saint-Exupéry
[edit]
At midday on 31 July 1944, noted aviation pioneer and writer Antoine de Saint-Exupéry (Night Flight, Wind, Sand and Stars and The Little Prince) vanished in his P-38 of the French Armée de l'Air's Groupe de Chasse II/33, after departing Borgo-Porreta, Corsica. His health, both physically and mentally, had been deteriorating. Saint-Exupéry was said to be intermittently subject to depression and talk had arisen of taking him off flying status.[158][159][Note 4] He was on a flight over the Mediterranean, from Corsica to mainland France, in an unarmed F-5B photo-reconnaissance variant of the P-38J,[Note 5] described as being a "war-weary, nonairworthy craft".[160]
In 2000, a French scuba diver found the partial remnants of a Lightning spread over several thousand square meters of the Mediterranean seabed off the coast of Marseille. In April 2004, the recovered component serial numbers were confirmed as being from Saint-Exupéry's F-5B Lightning. Only a small amount of the aircraft's wreckage was recovered.[161] In June 2004, the recovered parts and fragments were given to the Air and Space Museum of France in Le Bourget, Paris, where Saint-Exupéry's life is commemorated in a special exhibit.[162]
In 1981 and also in 2008, two Luftwaffe fighter pilots, respectively Robert Heichele and Horst Rippert, separately claimed to have shot down Saint-Exupéry's P-38.[163][164][165] Both claims were unverifiable and possibly self-promotional, as neither of their units' combat records of action from that period made any note of such a shoot-down.[166][167]
Specifications (P-38L)
[edit]



Data from Lockheed P-38H/J/L Pilot's Flight Operating Instructions,[169] P-38H/J/L Pilot's Flight Operating Instructions[170]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 37 ft 10 in (11.53 m)
- Wingspan: 52 ft 0 in (15.85 m)
- Height: 12 ft 10 in (3.91 m)
- Wing area: 327.5 sq ft (30.43 m2)
- Aspect ratio: 8.26[171]
- Airfoil: root: NACA 23016; tip: NACA 4412[172]
- Empty weight: 12,800 lb (5,806 kg) [171]
- Gross weight: 17,500 lb (7,938 kg) [171]
- Max takeoff weight: 21,600 lb (9,798 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Allison V-1710 (-111 left hand rotation and -113 right hand rotation) V-12 liquid-cooled turbo-supercharged piston engine, 1,600 hp (1,200 kW) each WEP at 60 inHg (2.032 bar) and 3,000 rpm
- Propellers: 3-bladed Curtiss electric constant-speed propellers (LH and RH rotation)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 414 mph (666 km/h, 360 kn) on Military Power: 1,425 hp (1,063 kW) at 54 inHg (1.829 bar), 3,000 rpm and 25,000 ft (7,620 m)[173]
- Cruise speed: 275 mph (443 km/h, 239 kn)
- Stall speed: 105 mph (169 km/h, 91 kn)
- Combat range: 1,300 mi (2,100 km, 1,100 nmi)
- Ferry range: 3,300 mi (5,300 km, 2,900 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 44,000 ft (13,000 m)
- Rate of climb: 4,750 ft/min (24.1 m/s)
- Lift-to-drag: 13.5
- Wing loading: 53.4 lb/sq ft (261 kg/m2) [171]
- Power/mass: 0.16 hp/lb (0.26 kW/kg)
- Drag area: 8.78 sq ft (0.82 m2)[171]
- Zero-lift drag coefficient: 0.0268[171]
Armament
- Guns:
- 1× Hispano M2(C) 20 mm cannon with 150 rounds
- 4× M2 Browning machine gun 0.50 in (12.7 mm) machine guns with 500 rpg.
- Rockets: 4× M10 three-tube 4.5 in (112 mm) M8 rocket launchers; or:
- Bombs:
- Inner hardpoints:
- 2× 2,000 lb (907 kg) bombs or drop tanks; or
- 2× 1,000 lb (454 kg) bombs or drop tanks, plus either
- 4× 500 lb (227 kg) bombs or
- 4× 250 lb (113 kg) bombs; or
- 6× 500 lb (227 kg) bombs; or
- 6× 250 lb (113 kg) bombs
- Outer hardpoints:
- 10× 5 in (127 mm) HVARs (High Velocity Aircraft Rockets); or
- 2× 500 lb (227 kg) bombs; or
- 2× 250 lb (113 kg) bombs
- Inner hardpoints:
Popular culture
[edit]
Harley Earl arranged for several of his designers to view a YP-38 prototype shortly before World War II, and its design directly inspired the tail fins of the 1948–1949 Cadillac.[174]
The P-38 was also the inspiration for Raymond Loewy and his design team at Studebaker for the 1950 and 1951 model-year Studebakers.[175]
The whine of the speeder bike engines in Return of the Jedi was partly achieved by recording the engine noise of a P-38, combined with that of a North American P-51 Mustang.[176]
The popular eight-bit video game "1942" puts the player in command of a P-38 flying over the Pacific, fighting against Japanese Zeros and the Nakajima G10N bomber. The game was made by Japanese company Capcom, intended for Western markets, and finishes with the player raiding Tokyo.
Notable appearances in media
[edit]See also
[edit]Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- Bristol Beaufighter – (United Kingdom)
- de Havilland Mosquito – (United Kingdom)
- Focke-Wulf Fw 187 Falke – (German Reich)
- Fokker G.I – (Netherlands)
- Hughes XF-11 – (United States)
- Kawasaki Ki-96 – (Japan)
- Messerschmitt Me 210 – (Nazi Germany)
- Mitsubishi Ki-83 – (Japan)
- Nakajima J5N – (Japan)
- Northrop P-61 Black Widow – (United States)
- Westland Whirlwind – (United Kingdom)
Related lists
- List of aircraft of World War II
- List of fighter aircraft
- List of Lockheed aircraft
- List of military aircraft of the United States
Notes
[edit]- ^ The 1939 edition of the German Aviation Manual already contained a detailed drawing and a close-up photograph of this prototype along with detailed information on the engines, and indicated that its maximum speed was supposed to be 640–680 km/h (400–420 mph). Dimensions, equipment, and weaponry were indicated as unknown.[37]
- ^ Turbosuperchargers were not secret nor restricted by the United States government. Related designs were known from French and Swiss firms. France and the UK did not want turbosuperchargers; they had never employed them and they knew the American ones were in short supply and did not want delivery delayed[59]
- ^ Some of the fastest postwar racing P-38s were virtually identical in layout to the P-322-II.
- ^ Saint-Exupéry suffered recurring pain and immobility from previous injuries due to his numerous aircraft crashes, to the extent that he could not dress himself in his own flight suit. After his death, vague suggestions were made that his disappearance was the result of suicide rather than an aircraft failure or combat loss.[citation needed]
- ^ He was flying a P-38-F-5B-1-LO, 42-68223, c/n 2734.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Donald 1997, p. 581.
- ^ Master Sgt. John DeShetler (20 November 2006), 'Lightning' strikes 1st Pursuit Group, United States Air Force
- ^ "Honduran Air Force". aeroflight.co.uk. Retrieved: 10 October 2010.
- ^ Johnsen 2003, p. 75, chptr. 4 "Its ability to carry two 150-gallon or 300-gallon drop made it a natural for long range escort duties...".
- ^ "P-38 Lightning". National Museum of the United States Air Force. Retrieved 21 January 2007.
- ^ The P-38: When Lightning Strikes, Lockheed Martin
- ^ Don Kieth (2023). Richard Bong: America's #1 Ace Fighter Pilot of World War. Penguin Publishing Group. ISBN 9780593187302.
90 percent of all aerial reconnaissance film taken during the war in Europe was captured by smooth-flying P-38s
- ^ "Lockheed P-38L Lightning - N3800L". EAA Museum. Retrieved 7 January 2025.
By some accounts, P-38 photo missions brought back 80 to 90 percent of all aerial recon photos from that period...
- ^ Levine 1992, p. 18.
- ^ Stanaway 1998, p. [page needed].
- ^ USAAF 1 1945, p. 7, "Two turbo-superchargers give the Allison engines sea level horsepower at extremely high altitudes.".
- ^ Blake 2020, Chptr. 8, p. 300, "…the P-38 was a very quiet plane, because its exhaust exited through the turbosuperchargers on top of the plane…".
- ^ Gunston 1980, p. 133.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. xvi.
- ^ Bodie 2001, pp. 16–17.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 14.
- ^ Hanson, Dave. "Lockheed P-38 Lightning." Dave's Warbirds. Retrieved: 21 January 2007.
- ^ a b Bodie 2001, p. 19.
- ^ a b c Bodie 2001, p. 51.
- ^ a b Current Biography Yearbook. H. W. Wilson Co. 1969. p. 199.
At that time, Lockheed did not as yet have a formal engineering building, and so Johnson and his staff improvised a development plant using unoccupied corners in hangars and an old distillery. The results of this 'skunk works' approach was the legendary P-38 Lightning.
- ^ "XP-38 Design Drawings: A diagram of the configurations considered for the prototype." Archived 18 December 2006 at the Wayback Machine P-38 National Association & Museum. Retrieved: 21 January 2007.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 44.
- ^ Chinn, George (1951). "37-mm Automatic Guns". The Machine Gun. Vol. 3. Washington D.C., USA: United States Government Printing Office. p. 31. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
Gun, Automatic 37-mm T9- The T2 gun was modified... until eventually a gun designated T9 was ready for test. In September 1939 this gun was mounted... in P-38 and P-39 fighter planes... which was standardized as the M4.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 80.
- ^ AN 01-75-2 P-38 gunsight manual, Section IV, page 21
- ^ Coggins 2000, p. 31.
- ^ Grahame, Arthur (January 1944). "The Facts About Fighter-Plane Firepower". Popular Science. pp. 76–83, 186. Grahame says the Lightning shoots 168 rounds per second (combined cannon and MG), the weight of fire being 547 lb/minute (9.1 lb/second). The 20 mm cannon fires at 2850 ft/sec muzzle velocity, projectile weight 0.29 lb (130 grams), at 650 rpm (10.8 rps). The .50 caliber machine gun fires at 2900 ft/sec, weight of projectile 800 grains (51.8 grams), at 850 rev/min.
- ^ a b c "Lockheed P-38 Lightning." aviation-history.com. Retrieved: 21 January 2007.
- ^ "Handbook of Operation and Maintenance-Allison V1710 type engines" (PDF). Allison division, General Motors. 1943.
- ^ Loftin, L.K. Jr. 1985 "Quest for Performance: The Evolution of Modern Aircraft. NASA SP-468". Archived 13 June 2006 at the Wayback Machine NASA Scientific and Technical Information Branch. Washington. Retrieved: 22 April 2006.
- ^ Thornborough & Davis 1988, p. 8.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 245.
- ^ O'Leary, Michael. "Conquering the Sky!" Air Classics, April 2005. Retrieved: 26 January 2007.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 32.
- ^ Kocivar, Ben (6 October 1964). "Collier Trophy". Look. Vol. 28, no. 20. p. 36.
He calls his development plants 'skunk works'. There have been five of them – the first, an abandoned distillery.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 33.
- ^ Schnitzler, R., G.W. Feuchter and R. Schulz, eds. Handbuch der Luftfahrt (Manual of Aviation) (in German). Munich: J.F. Lehmanns Verlag, 1939. pg386-7
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 36.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 40.
- ^ Knaack 1988, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Caidin 1983, p. [page needed].
- ^ Parker 2013, pp. 59, 75–76.
- ^ "About the P-38: Early Years." P-38 National Association & Museum. Retrieved: 21 January 2007.
- ^ a b c "Collections Database: Lockheed P-38J-10-LO Lightning." National Air and Space Museum. Retrieved: 6 February 2009.
- ^ a b Bodie 2001, p. 58.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 57.
- ^ Johnson & Smith 1985, p. 74.
- ^ Erikson, Albert L. "Wind-Tunnel Investigation of Devices for Improving The Diving Characteristics of Airplanes." NACA MR No. 3F12, Summary.
- ^ Bodie 2001, pp. 174–175.
- ^ Ethell 1984, p. 14.
- ^ Goebel, Greg. "The Lockheed P-38 Lightning." vectorsite.net, Version 1.3. Retrieved: 21 January 2007.
- ^ a b Bodie 2001, p. 210.
- ^ Kaplan & Saunders 1991, p. 56.
- ^ Baugher, Joe. "Lockheed P-38 Lightning." Archived 26 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine Joe Baugher's Encyclopedia of American Military Aircraft, 13 June 1999. Retrieved: 29 January 2007.
- ^ Baugher, Joe. "Lockheed XP-38A Lightning." Joe Baugher's Encyclopedia of American Military Aircraft, 13 June 1999. Retrieved: 29 January 2007.
- ^ Baugher, Joe. "Lockheed P-38D Lightning." Joe Baugher's Encyclopedia of American Military Aircraft, 13 June 1999. Retrieved: 29 January 2007.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 46.
- ^ Bodie 2001, pp. 45, 47.
- ^ a b Baugher, Joe. "Lightning I for RAF." Joe Baugher's Encyclopedia of American Military Aircraft, 2 December 2002. Retrieved: 29 January 2007.
- ^ a b c d e Bodie 2001, p. 60.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 63.
- ^ a b Bodie 2001, p. 61.
- ^ a b c Bodie 2001, p. 64.
- ^ Mason 2010, pp. 204–205.
- ^ Bodie 2001, pp. 111–116.
- ^ Yenne 1987, p. 60.
- ^ a b Bodie 2001, pp. 89–91.
- ^ McFarland & Newton 2006, p. 103.
- ^ Bodie 2001, pp. 101–102.
- ^ a b c Baugher, Joe. "P-38 in European Theatre." Joe Baugher's Encyclopedia of American Military Aircraft, 13 June 1999. Retrieved: 4 February 2007.
- ^ Maloney, Edward T. Lockheed P-38 "Lightning", Aero Series Vol. 19, Fallbrook, California: Aero Publishers, Inc., 1968. p. 4.
- ^ Stanaway & Mellinger 2001, p. 43.
- ^ Stanaway 1998, p. [page needed].
- ^ a b Stanaway 2014, p. 71.
- ^ a b Blake 2012, p. 14.
- ^ a b Stanaway 2014, p. 72.
- ^ Bergström 2019, pp. 315–316.
- ^ a b Stanaway 2014, p. 73.
- ^ a b Stanaway 2014, p. 74.
- ^ Gray, William P. (16 August 1943). "P-38: Lockheed's Twin-tailed Fighter Lives Down Its Hoodoo to Sweep Enemy Skies". Life. p. 51.
- ^ Shores et al. 2018, pp. 321–323.
- ^ a b Scutts 1994, p. 61.
- ^ Shores et al. 2018, pp. 326–329.
- ^ Laurier 2016, p. 54.
- ^ Sims 1980, pp. 134–135.
- ^ Galland 1954, p. [page needed].
- ^ Rymaszewski, Michael (July 1994). "Playing Your Aces". Computer Gaming World. p. 102.
- ^ Garello, Giancarlo. Prede di guerra. Aerei jugoslavi, inglesi, statunitensi, belgi 1940–1943. Torino: La Bancarella Aeronautica, 2007. p. 68 No ISBN. (in Italian)
- ^ Dimensione cielo. Caccia Assalto 3 – aerei italiani nella 2a guerra mondiale (in Italian). Rome: Edizioni Bizzarri, 1973. No ISBN. p. 72.
- ^ a b c Cesarani & Kavanaugh 2004, pp. 234–235.
- ^ Stanaway 1998, pp. 43–46.
- ^ Hatch 2000, pp. 59–67.
- ^ "Dan Vizanti, despre IAR 80 și bătălia din 10 iunie 1944". ziare.com (in Romanian). 9 June 2009.
- ^ Neulen 2005, pp. 113–114.
- ^ "IAR 80 contra P 38 – 10 iunie 1944 – rapoarte despre misiune – USAAF". iar80flyagain.org (in Romanian). 14 July 2022.
- ^ "Mission No. 702 / 10 June 1944 / Romana Americana Oil Refinery, Ploesti, Rumania". 82ndfightergroup.com. Archived from the original on 9 October 2011. Retrieved 27 August 2009.
- ^ Spick 1983, p. 94.
- ^ Tillman 2004, p. 8.
- ^ "Interview with General James H. Doolittle". Hotlinecy.com. Retrieved: 6 February 2009.
- ^ a b Of Men and Stars: A History of Lockheed Aircraft Corporation, 1913–1957. Burbank, California: Lockheed Aircraft Corporation, 1958. p. 11.
- ^ a b "Army Air Corps, World War II: 370th Fighter Group". Living History Group. Retrieved: 14 December 2009.
- ^ Achtung Jabos! The Story of the IX TAC. Stars and Stripes Publications, Information and Education Division, Special and Informational Services, ETOUSA, 1944.
- ^ "474th Fighter Group - WWII - World War II - Army Air Forces".
- ^ Thompson & Smith 2008, p. 240.
- ^ Kenney 1987, pp. 171–173.
- ^ Hearn 2008, p. 86.
- ^ Schom 2004, p. 310.
- ^ Stanaway 1997, pp. 7–8.
- ^ McFarland 1997, p. 33.
- ^ Bruning 2003, p. 124.
- ^ Gillison 1962, pp. 692–693.
- ^ Spinetta 2007, p. [page needed].
- ^ Watson 1950, pp. 129–165.
- ^ Gamble 2010, p. 310.
- ^ a b Stanaway 1997, p. 14.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 223.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 214.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 217.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 234.
- ^ Berliner 2011, p. 14.
- ^ "P-38 Lightning." Bvhcenter.org, 9 June 2011.
- ^ Sgarlato, Nico. "I P-38 Italiani. (in Italian)". Aerei Nella Storia n.21, December 2000.
- ^ "Memorandum for: Chief WH, CIA Subject: Bombing of British ship SS Springfjord." Central Intelligence Agency, 1 July 1955. The three-page memorandum is stamped: "CIA Historical Review Program, Release as Sanitized, 2003"
- ^ Villagrán Kramer 1993–2004, p. 151.
- ^ Lloyd, Selwyn (5 July 1954), "Aircraft Attacks", Parliamentary Debates (Hansard), vol. 529, cc 1769-1772, archived from the original on 25 December 2012, retrieved 16 August 2012.
- ^ King, J. C. "Memorandum for: Office of the General Council: Subject: S. S. Springfjord." Central Intelligence Agency, 25 July 1958. The two-page memorandum is stamped: "CIA Historical Review Program, Release as Sanitized, 2003".
- ^ Hagedorn, Daniel P. (July–November 1986). "From Caudillos to COIN". Air Enthusiast. No. 33. pp. 55–70.
- ^ Lockheed P-38L Lightning. National Museum of the United States Air Force. Retrieved: 16 October 2016.
- ^ Johnson & Smith 1985, p. [page needed].
- ^ Spick 2002, p. 224.
- ^ "WWII Aircraft Performance: P-38F Tactical Trials". Final Report on Tactical Suitability of the P-38F Type Airplane, 6 March 1943. Retrieved: 19 January 2009.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 166.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 172.
- ^ Baugher, Joe. "Lockheed P-38J Lightning." Joe Baugher's Encyclopedia of American Military Aircraft, 5 June 1999. Retrieved: 29 January 2007.
- ^ Bodie 2001, p. 208.
- ^ Cross 1969, p. [page needed].
- ^ a b Bodie 2001, pp. 169–171.
- ^ "P38K." P-38 Lightning online, 21 October 2007. Retrieved: 6 February 2009.
- ^ Donald 2004, p. 145.
- ^ Lightning Modifications & Derivatives / Postwar v2.0.7 1 February 2021 Greg Goebel
- ^ Jeffrey L. Ethell (1983). P-38 Lightning. Danvers, MA, USA: Crown. ISBN 9780517552476.
...the 418th, 419th and 421st Night Fighter Squadron were given P-38s.
- ^ Cross 1969.
- ^ Cross, Roy (1968). Lockheed P-38 Lightning. John W. Caler Publications. ISBN 9780858800038. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
Another experiment was the modification of P-38 40-744 for pilot asymmetric flight tests...
- ^ Bodie 2001, pp. 118–121.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Andrade 1979, pp. 146–147.
- ^ a b Kinzey 1998, p. 33.
- ^ a b Andrade 1979, p. 245.
- ^ a b Kinzey 1998, p. 27.
- ^ a b Kinzey 1998, p. 28.
- ^ Davis 1990, p. 15.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Andrade 1979, pp. 99–100.
- ^ Andrade 1979, p. 191.
- ^ Cefaratt 2002, pp. 15, 39, 141.
- ^ Frey 2004, p. 61.
- ^ a b Sherman, Stephen (June 1999), "PTO/CBI Pilots of WWII, Top American aces of the Pacific & CBI", acepilots.com., archived from the original on 26 March 2006, retrieved 8 May 2007
- ^ Kirkland 2003, pp. 29–35.
- ^ "Charles Lindbergh and the 475th Fighter Group." Lightning Strikes. Retrieved: 10 October 2010.
- ^ Schiff 2006, pp. 430–433.
- ^ Schiff 2006, pp. 436–437.
- ^ Cate 1970, p. [page needed].
- ^ Cyvoct, Brian. "Riou Island's F-5B Lightning, Rhône's delta, France. Pilot: Commander Antoine de Saint-Exupéry." Archived 21 April 2008 at the Wayback Machine Aero-relic.org, 2004.
- ^ "Antoine de Saint-Exupéry aurait été abattu par un pilote allemand" (in French). Le Monde, 15 March 2008.
- ^ Schiff 2006, pp. 438–439.
- ^ "Wartime author mystery 'solved'." BBC News, 17 March 2008.
- ^ Tagliabuet, John. "Clues to the Mystery of a Writer Pilot Who Disappeared." The New York Times, 11 April 2008.
- ^ Beale, Nick. "Saint-Exupéry Entre Mythe et Réalité "(in French). Aero Journal, No. 4, 2008, pp. 78–81.
- ^ "Archive sources for Luftwaffe activity over Southern France on 30 and 31 July 1944." Archived 5 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine Ghost Bombers. Retrieved: 30 August 2011.
- ^ United States Air Force Museum Guidebook 1987, p. 54.
- ^ Lockheed P-38H/J/L Pilot's Flight Operating Instructions. USAAF. 1944. ISBN 9781411690134. Retrieved 9 January 2020.
- ^ Lockheed P-38H/J/L Pilot's Flight Operating Instructions (PDF). United States Army Air Force. 1944. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 July 2012. Retrieved 9 January 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f "Appendix A (continued), Table III" Archived 12 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine. Characteristics of Illustrative Aircraft, 1939–80, Quest for Performance: The Evolution of Modern Aircraft. NASA.
- ^ Lednicer, David. "The Incomplete Guide to Airfoil Usage". m-selig.ae.illinois.edu. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- ^ Crosby 2003, p. 96.
- ^ Lamm & Holls 1996, p. 110.
- ^ "The P-38 prowls the highway." Hemmings Motor News, courtesy of Studebaker. Retrieved: 14 December 2009.
- ^ "Sound Design of Star Wars." filmsound.org, 3 January 2012. Quote: "The sound of a Speeder Bike was achieved by mixing together the recorded sounds of a P-51 Mustang airplane, a P-38 Lockheed Interceptor, and then recording them."
Bibliography
[edit]- Andrade, John M. (1979). U.S. Military Aircraft Designations and Serials since 1909. Leicester, England: Midland Counties Publications. ISBN 978-0-904597-22-6.
- Bearman, Matt (April 2018). "Lockheed Consternation: Compressibility & the P-38 Lightning, Pt. 3". The Aviation Historian (23): 18–30. ISSN 2051-1930.
- Bergström, Christer [in Swedish] (2019). Black cross/red star : air war over the Eastern Front. Volume 4, Stalingrad to Kuban 1942-1943. Eskilstuna: Vaktel Books. ISBN 978-91-88441-21-8.
- Berliner, Don (2011). Surviving fighter aircraft of World War Two : a global guide to location and types. Barnsley, South Yorkshire: Pen & Sword Aviation. ISBN 978-1-84884-265-6.
- Blake, Steve (2012). P-38 Lightning Aces of the 82nd Fighter Group. Botley, Oxford: Bloomsbury. ISBN 978-1-78096-871-1.
- Blake, Steven (4 October 2020). Lightning Strikes: The Lockheed P-38. Stroud, UK: Fonthill Media. ISBN 978-1-78155-788-4. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- Bodie, Warren M. (2001) [1991]. The Lockheed P-38 Lightning: The Definitive Story of Lockheed's P-38 Fighter. Hayesville, North Carolina: Widewing Publications. ISBN 978-0-9629359-5-4.
- Bruning, John R. (2003). Jungle ace : Col. Gerald R. Johnson, the USAAF's top fighter leader of the Pacific War (1st The warriors ed.). Washington, D.C.: Brassey's. ISBN 978-1-61234-086-9.
- Caidin, Martin (1983). Fork-tailed Devil. New York: Ballantine Books. ISBN 978-0-345-31292-1.
- Cate, Curtis (1970). Antoine de Saint-Exupéry: His Life and Times. Saint-Laurent, Québec: Longmans Canada Limited. ISBN 978-1-55778-291-5.
- Cefaratt, Gil (2002). Lockheed : the people behind the story (Limited ed.). Paducah, Ky.: Turner Pub. pp. 15, 39, 141. ISBN 978-1-56311-847-0.
- Cesarani, David; Kavanaugh, Sarah (2004). Holocaust : critical concepts in historical studies. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-31871-6.
- Coggins, Edward V. (2000). Wings That Stay On. Turner. p. 31. ISBN 978-1-56311-568-4.
- Crosby, Francis (2003). A Handbook of Fighter Aircraft Featuring photographs from the Imperial War Museum. London: Hermes House. ISBN 978-0-681-34256-9.
- Cross, Roy (1969). Lockheed P-38 Lightning technical manual. Dandenong, Victoria, Australia: Kookaburra technical publications, John W. Caler Publications. OCLC 898545364.
- Davis, Larry (1990). P-38 Lightning In Action. Squadron/Signal Publications. ISBN 978-0-89747-255-5.
- Donald, David (1997). The encyclopedia of world aircraft (Updated ed.). Leicester: Blitz Editions. ISBN 978-1-85605-375-4.
- Donald, David (2004). "Warplane Classic: Lockheed P-38 Lightning 'Fork-tailed Devil'". International Air Power Review. Vol. 14. ISBN 978-1-880588-85-7. ISSN 1473-9917.
- Ethell, Jeffrey (1984). The Great book of World War II airplanes. New York: Bonanza Books. ISBN 978-0-517-45993-5.
- Frey, Royal D. (2004). Flying American combat aircraft of WWII : 1939-45 (1st ed.). Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books. ISBN 978-0-8117-3124-9.
- Galland, Adolf (1954). The First and The Last. Cutchogue, New York: Buccaneer Books. ISBN 978-0-89966-728-7.
- Gamble, Bruce (2010). Fortress Rabaul : the battle for the Southwest Pacific, January 1942-April 1943. Minneapolis: Zenith Press. ISBN 978-0-7603-2350-2.
- Gillison, Douglas (1962). Royal Australian Air Force 1939–1942. Canberra: Australian War Memorial. pp. 692–693. OCLC 2000369. Retrieved 24 October 2021.
- Gunston, Bill (1980). Aircraft of World War 2. New York: Crescent Books. ISBN 978-0-517-31680-1.
- Hatch, Herbert (2000). An Ace and his Angel : Memoirs of a World War II Fighter Pilot. Paducah, Kentucky: Turner Publishing Company. ISBN 978-1-56311-574-5.
- Hearn, Chester G. (2008). Air Force : an illustrated history : the U.S. Air Force from the 1910s to the 21st century. Minneapolis, Minn.: Zenith Press. ISBN 978-0-7603-3308-2.
- Johnsen, Frederick (2003). Steve Gansen (ed.). Weapons of the Eighth Air Force. St. Paul, MN: MBI. ISBN 978-0-7603-1340-4. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- Johnson, Clarence L.; Smith, Maggie (1985). Kelly: More Than My Share of it All. Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution Press. ISBN 978-0-87474-564-1.
- Kaplan, Philip; Saunders, Andy (1991). Little friends : the fighter pilot experience in World War II England (1st ed.). New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-58434-8.
- Kenney, George C. (1987). General Kenney reports : a personal history of the Pacific War. Washington, D.C.: DIANE. ISBN 978-0-912799-44-5.
- Kinzey, Bert (1998). Detail & Scale Volume 57 P-38 Lighting Part I XP-38 through P-38H. Squadron/Signal Publications. ISBN 978-1-888974-10-2.
- Kirkland, Richard C. (2003). War pilot : true tales of combat and adventure (First ed.). Novato, Calif.: Presidio. ISBN 978-0-345-45812-4.
- Knaack, Marcelle S. (1988). Encyclopedia of US Air Force aircraft and missile systems / 2 Post World War II bombers, 1945-1973. Washington, DC: Office of Air Force History, US Air Force. ISBN 978-0-912799-59-9.
- Lamm, Michael; Holls, Dave (1996). A century of automotive style : 100 years of American car design. Stockton, Calif.: Lamm-Morada Pub. Co. ISBN 978-0-932128-07-2.
- Laurier, Jim (2016). Fighter! : Ten Killer Planes of World War II. Minneapolis, Minnesota: Voyageur Press. ISBN 978-0-7603-5301-1.
- Levine, Alan J. (1992). The Strategic Bombing of Germany, 1940–1945. Greenwood. ISBN 978-0-275-94319-6.
- Mason, Tim (2010). The secret years : flight testing at Boscombe Down 1935-1945. Manchester: Crécy. ISBN 978-1-902109-14-5.
- McFarland, Stephen Lee (1997). A concise history of the U.S. Air Force (Air Force fiftieth anniversary commemorative ed.). Washington, D.C.: Air Force History and Museums Program, United States Air Force. ISBN 978-0-16-049208-2.
- McFarland, Stephen Lee; Newton, Wesley Philips (2006). To command the sky : the battle for air superiority over Germany, 1942-1944. Tuscaloosa: University of Alabama Press. ISBN 978-0-8173-5346-9.
- Neulen, Hans Werner (2005). In the skies of Europe : air forces allied to the Luftwaffe, 1939-1945. Ramsbury: Crowood. ISBN 978-1-86126-799-3.
- Parker, Dana T. (2013). Building Victory: Aircraft Manufacturing in the Los Angeles Area in World War II. Cypress, California. ISBN 978-0-9897906-0-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Scutts, Jerry (1994). Bf 109 Aces of North Africa and the Mediterranean. Aircraft of the Aces. Vol. 2. London, UK: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-85532-448-0.
- Schiff, Stacy (2006) [1994]. Saint-Exupéry: A Biography. New York: Henry Holt. ISBN 978-0-679-40310-4. Archived from the original on 13 May 2016. Retrieved 20 September 2023.
- Schom, Alan (2004). The Eagle and the Rising Sun : the Japanese-American war, 1941-1943, Pearl Harbor through Guadalcanal. New York: W.W. Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-04924-4.
- Shores, Christopher; Massimello, Giovanni; Guest, Russell; Olynyk, Frank; Bock, Winfried; Thomas, Andy (2018). A History of the Mediterranean Air War 1940–1945: Volume Four: Sicily and Italy to the Fall of Rome: 14 May, 1943 –5 June, 1944. London: Grub Street. ISBN 978-1-911621-10-2.
- Sims, Edward H. (1980). Fighter tactics and strategy, 1914-1970 (2nd ed.). Fallbrook, Calif.: Aero Pub. ISBN 978-0-8168-8795-8.
- Spick, Mike (1983). Fighter pilot tactics : the techniques of daylight air combat. Cambridge: Patrick Stephens. ISBN 978-0-85059-617-5.
- Spick, Mike (2002). The Illustrated Directory of Fighters. St. Paul, Minnesota: Salamander Books. ISBN 978-0-7603-1343-5.
- Spinetta, Lawrence (November 2007). "Battle of the Bismarck Sea". World War II. ISSN 0898-4204. Retrieved 2 August 2013.
- Stanaway, John (1997). P-38 Lightning Aces of the Pacific and CBI. New York: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-85532-633-0.
- Stanaway, John (1998). P-38 Lightning aces of the ETO/MTO. London: Osprey Aerospace. ISBN 978-1-85532-698-9.
- Stanaway, John; Mellinger, George (2001). P-39 Airacobra aces of World War 2. Oxford: Osprey Aviation. ISBN 978-1-84176-204-3.
- Stanaway, John (2014). P-38 Lightning Aces 1942–43. Aircraft of the Aces. Vol. 120. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-78200-334-2.
- Thompson, J. Steve; Smith, Peter C. (2008). Air combat manoeuvres : the technique and history of air fighting for flight simulation. Hersham: Classic. ISBN 978-1-903223-98-7.
- Thornborough, Anthony M.; Davis, Peter E. (1988). Lockheed blackbirds. Surrey: I. Allan. ISBN 978-0-7110-1794-8.
- Tillman, Barrett (2004). Brassey's D-Day encyclopedia : the Normandy invasion A-Z (1st ed.). Washington, D.C.: Brassey's. ISBN 978-1-57488-760-0.
- Villagrán Kramer, Francisco (1993–2004). Biografía política de Guatemala. [Guatemala]: FLACSO-Guatemala-Costa Rica. ISBN 978-99939-72-01-3.
- Watson, Richard L. (1950). The Pacific: Guadalcanal to Saipan, August 1942 to July 1944 (IV ed.). University of Chicago Press. OCLC 9990462000. Retrieved 24 October 2021.
- Yenne, Bill (1987). Lockheed. Crescent Books. ISBN 978-0-517-60471-7.
- Pilot Training Manual for the P-38 Lightning. Winston-Salem, North Carolina, USA: Headquarters AAF, Office of Flying Safety, Safety Education Division. 1 August 1945. ISBN 978-0-359-08811-9. Archived from the original on 6 January 2022. Retrieved 6 January 2022.
External links
[edit]- "German Pilots Renamed It: Gabelschwanz Teufel (Fork-tailed Devil)", Popular Science, September 1943
- The short film P-38: Flight Characteristics is available for free viewing and download at the Internet Archive.
- "The Lockheed Lightning" a 1943 Flight article
- "Jap-hunting without a Gun!" a 1943 Lockheed advertisement in Flight
- "Lockheed Lightning (P-38/J)"[permanent dead link] a 1944 Flight article
- "Lockheed Lightning (P-38L-5-LO)"[permanent dead link] Cutaway view
- [1] P-38 Association and Museum
- Pilot training manual for the Lightning P-38 – The Museum of Flight Digital Collections
