Lesser woolly horseshoe bat
| Lesser woolly horseshoe bat | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Rhinolophidae |
| Genus: | Rhinolophus |
| Species: | R. beddomei
|
| Binomial name | |
| Rhinolophus beddomei Andersen, 1905
| |
| |
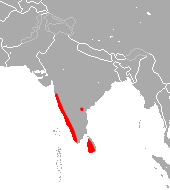
| Lesser woolly horseshoe bat range | |
The lesser woolly horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus beddomei), also called Beddome's horseshoe bat, is a species of bat in the family Rhinolophidae. It is found in India and Sri Lanka. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, caves, and urban areas.
Taxonomy and etymology
[edit]It was described as a new species in 1905 by Danish mammalogist Knud Andersen.[2] The eponym for the species name "beddomei" is Colonel Richard Henry Beddome, a British officer and naturalist who spent a good deal of his career in India.[3] Beddome was the collector of the holotype for this species. The holotype was collected in the Wayanad district of India.[2] As Rhinolophus is quite speciose, it is divided into closely related "species groups." Andersen placed the lesser woolly horseshoe bat in the philippensis species group,[2] but Simmons includes it in the trifoliatus species group.[4] Some authors have considered it a subspecies of the woolly horseshoe bat; since 1992, it has usually been accorded full species status.[5]
Description
[edit]The bat's head and body length is 7 centimetres (2.8 in), with a forearm 6 centimetres (2.4 in) long and a wingspan of 33 centimetres (13 in). Females are larger than males. Pelage is rough-textured and woolly. Body completely dark grayish brown, upper side grizzled. Wing membrane blackish brown. The ears are prominent, well-fluted, and pointy and nose-leaf is complex with a distinctive shape.
Biology and ecology
[edit]It is nocturnal, using echolocation to navigate in the dark. It echolocates at frequencies of 31.0–38.3kHz; its frequencies of maximum energy are 38.5 and 38.7 kHz. Its call duration is 48.2–58.0 seconds.[6]
References
[edit]- ^ Srinivasulu, B.; Srinivasulu, C. (2019). "Rhinolophus beddomei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T40023A22061859. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T40023A22061859.en. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ a b c Andersen, K. (1905). "XXVIII.—On the Bats of the Rhinolophus philippinensis Group, with Descriptions of Five new Species". Journal of Natural History. 16 (92): 243–257. doi:10.1080/03745480509443674.
- ^ Beolens, B.; Watkins, M.; Grayson, M. (2009). The eponym dictionary of mammals. JHU Press. p. 34. ISBN 9780801895333.
- ^ Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M., eds. (2005). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Topál, G.; Csorba, G. (1992). "The subspecific division of Rhinolophus luctus Temminck, 1835, and the taxonomic status of R. beddomei Andersen, 1905 (Mammalia, Chiroptera)" (PDF). Miscellanea Zoologica Hungarica. 7: 101–116.
- ^ Raghuram, H.; Jain, M.; Balakrishnan, R. (2014). "Species and acoustic diversity of bats in a palaeotropical wet evergreen forest in southern India". Current Science: 631–641.

