Königsberg
 Königsberg Castle before World War I; ruined in WWII, ruins demolished in 1968–1969 on Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev's orders[1][2] | |
Königsberg was a port city on the south eastern corner of the Baltic Sea. It is today known as Kaliningrad and is part of Russia. | |
| Coordinates | 54°42′41.3″N 20°30′33.5″E / 54.711472°N 20.509306°E |
|---|---|
| History | |
| Founded | 1255 |
| Abandoned | 1945 |
| Associated with | Sambians, Germans, Poles, Jews, Russians, Lithuanians |
| Events | World War II |
| Site notes | |
| Ownership | State of the Teutonic Order, Poland, Prussia, Russia, Germany |
Königsberg (/ˈkɜːnɪɡzbɜːrɡ/; German: [ˈkøːnɪçsbɛʁk] ⓘ; lit. 'King's mountain'; Polish: Królewiec; Lithuanian: Karaliaučius; Baltic Prussian: Kunnegsgarbs; Russian: Кёнигсберг, romanized: Kyónigsberg, IPA: [ˈkʲɵnʲɪɡzbʲɪrk]) is the historic German and Prussian name of the medieval city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussian settlement Twangste[3] by the Teutonic Knights during the Baltic Crusades. It was named in honour of King Ottokar II of Bohemia, who led a campaign against the pagan Old Prussians, a Baltic tribe.[4]
A Baltic port city, it successively became the capital of the State of the Teutonic Order, the Duchy of Prussia and the provinces of East Prussia and Prussia. Königsberg remained the coronation city of the Prussian monarchy from 1701 onwards, though the capital was Berlin. From the thirteenth to the twentieth centuries on, the inhabitants spoke predominantly German, although the city also had a profound influence upon the Lithuanian and Polish cultures. It was a publishing center of Lutheran literature; this included the first Polish translation of the New Testament, printed in the city in 1551, as well as the first book in Lithuanian and the first Lutheran catechism, both printed in Königsberg in 1547.
A university city, home of the Albertina University (founded in 1544), Königsberg developed into an important German intellectual and cultural center, being the residence of Simon Dach, Immanuel Kant, Käthe Kollwitz, E. T. A. Hoffmann, David Hilbert, Agnes Miegel, Hannah Arendt, Michael Wieck, and others. It was the easternmost large city in Germany until World War II. Between the wars, it was in the exclave of East Prussia, separated from Germany by the Polish Corridor.
The city was heavily damaged by Allied bombing in 1944 and during the Battle of Königsberg in 1945, when it was occupied by the Red Army. The Potsdam Agreement of 1945 placed it provisionally under Soviet administration, and it was annexed by the Soviet Union on 9 April 1945. Its small Lithuanian population was allowed to remain, but the Germans were expelled. The city was largely repopulated with Russians and, to a lesser degree, Ukrainians and Belarusians from the Soviet Union after the ethnic cleansing. It was renamed Kaliningrad in 1946, in honour of Soviet Communist functionary Mikhail Kalinin. The city's historic centre was subsequently demolished by the Soviet government.[1][2][5][6][7]
It is now the capital of Russia's Kaliningrad Oblast, an exclave bordered in the north by Lithuania and in the south by Poland. In the Final Settlement treaty of 1990, Germany renounced all claims to the city.[a]
Name
[edit]The first mention of the present-day location in chronicles indicates it as the place of a village of fishermen and hunters. When the Teutonic Order began the Northern Crusades, they built a wooden fortress, and later a stone fortress, calling it "Conigsberg", which later morphed into "Königsberg". The literal meaning of this is 'King's mountain', in apparent honour of King Ottokar II of Bohemia,[4] who led one of the Teutonic campaigns.
In Polish, it is called Królewiec, in Lithuanian Karaliaučius (calques of the original German name).[9]
History
[edit]Sambians
[edit]Königsberg was preceded by a Sambian — or Old Prussian — fort known as Twangste (Prussian word tvinksta means a pond made by a dam),[10] as well as several Old Prussian settlements including the fishing village and port Lipnick and the farming villages Sakkeim and Trakkeim.
Arrival of the Teutonic Order
[edit]
During the conquest of the Prussian Sambians by the Teutonic Knights in 1255, Twangste was destroyed and replaced with a new fortress known as Conigsberg. This name meant "King's Hill" (Latin: castrum Koningsberg, Mons Regius, Regiomontium), honoring King Ottokar II of Bohemia who paid for the erection of the first fortress there during the Prussian Crusade.[11][12] Northwest of this new Königsberg Castle arose an initial settlement, later known as Steindamm, roughly 7 kilometres (4 mi) from the Vistula Lagoon.[13]
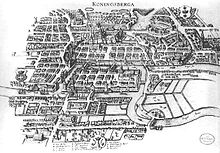
The Teutonic Order used Königsberg to fortify their conquests in Samland and as a base for campaigns against pagan Lithuania. Under siege during the Prussian uprisings in 1262–63, Königsberg Castle was relieved by the Master of the Livonian Order.[14][15] Because the initial northwestern settlement was destroyed by the Prussians during the rebellion, rebuilding occurred in the southern valley between the castle hill and the Pregolya River. This new settlement, Altstadt, received Culm rights in 1286. Löbenicht, a new town directly east of Altstadt between the Pregolya River and the Schlossteich, received its own rights in 1300. Medieval Königsberg's third town was Kneiphof, which received town rights in 1327 and was located on an island of the same name in the Pregolya, south of Altstadt.

Within the state of the Teutonic Order, Königsberg was the residence of the marshal, one of the chief administrators of the military order.[16] The city was also the seat of the Bishopric of Samland, one of the four dioceses into which Prussia had been divided in 1243 by the papal legate, William of Modena. Adalbert of Prague became the main patron saint of Königsberg Cathedral, a landmark of the town of Kneiphof.
Königsberg joined the Hanseatic League in 1340 and developed into an important port for the south-eastern Baltic region, trading goods throughout Prussia, the Kingdom of Poland, and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The chronicler Peter of Dusburg probably wrote his Chronicon terrae Prussiae in Königsberg from 1324 to 1330.[17] After the Teutonic Order's victory over pagan Lithuanians in the 1348 Battle of Strėva, Grand Master Winrich von Kniprode established a Cistercian nunnery in the city.[18] Aspiring students were educated in Königsberg before continuing on to higher education elsewhere, such as Prague or Leipzig.[17]
Although the Knights suffered a crippling defeat in the Battle of Grunwald, Königsberg remained under the control of the Teutonic Knights throughout the Polish-Lithuanian-Teutonic War. Livonian knights replaced the Prussian branch's garrison at Königsberg, allowing them to participate in the recovery of towns occupied by Władysław II Jagiełło's troops.[19]
Polish sovereignty
[edit]
In 1440, Königsberg became a founding member of the anti-Teutonic Prussian Confederation. In 1454 the Confederation rebelled against the Teutonic Knights and asked the Polish king, Casimir IV Jagiellon, to incorporate Prussia into the Kingdom of Poland; the king agreed, and signed an act of incorporation.[20] The local mayor pledged allegiance to the Polish king during the incorporation in March 1454.[21] This marked the beginning of the Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466) between the State of the Teutonic Order and the Kingdom of Poland. The city, known in Polish as Królewiec, became the seat of the short-lived Królewiec Voivodeship.[22] King Casimir IV authorized the city to mint Polish coins.[23] While Königsberg three towns initially joined the rebellion, Altstadt and Löbenicht soon rejoined the Teutonic Knights and defeated Kneiphof (Knipawa) in 1455. Grand Master Ludwig von Erlichshausen fled from the crusaders' capital at Castle Marienburg (Malbork) to Königsberg in 1457; the city's magistrate presented Erlichshausen with a barrel of beer out of compassion.[24] In 1465, a landing force from Polish-allied Elbląg destroyed the shipyard near Altstadt, preventing the Teutonic Knights from rebuilding their fleet until the end of the war.[25]
Following the Second Peace of Thorn (1466) — which ended the Thirteen Years' War — the reduced monastic state became a fief of the Kingdom of Poland, and Königsberg became the new capital.[26][27] The grand masters took over the marshal's quarters. During the Polish-Teutonic War (1519–1521), Königsberg was besieged without success[28] by Polish forces led by Grand Crown Hetman Mikołaj Firlej. The city itself opposed the Teutonic Knights' war against Poland and demanded peace.
Duchy of Prussia
[edit]
Through the preachings of the Bishop of Samland, Georg von Polenz, Königsberg became predominantly Lutheran during the Protestant Reformation.[29] After summoning a quorum of the Knights to Königsberg, Grand Master Albert of Brandenburg (a member of the House of Hohenzollern) secularised the Teutonic Knights' remaining territories in Prussia in 1525 and converted to Lutheranism.[30] By paying feudal homage to his uncle, King Sigismund I of Poland, Albert became the first duke of the new Duchy of Prussia, a fief of Poland.[22]
While the Prussian estates quickly allied with the duke, the Prussian peasantry would only swear allegiance to Albert in person at Königsberg, seeking the duke's support against the oppressive nobility.[citation needed][clarification needed] After convincing the rebels to lay down their arms, Albert had several of their leaders executed.[31]
Königsberg, the capital, became one of the biggest cities and ports of Ducal Prussia, having considerable autonomy, a separate parliament and currency. While German continued to be the official language, the city served as a vibrant center of publishing in both Polish and Lithuanian.[citation needed] The city flourished through the export of wheat, timber, hemp, and furs,[32] as well as pitch, tar, and fly ash.[33] The city acted as an intermediary in maritime trade between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Netherlands, England and France.[34] Many Poles, including noblemen and Polish Jews, came to the city for trade.[34] The 17th-century stock exchange included a painting depicting a townswoman buying goods from a Pole and a Dutchman, embracing the notion that the city's prosperity was based on trade with the East and West, particularly Poland and the Netherlands.[34]
Königsberg was one of the few Baltic ports regularly visited by more than one hundred ships annually in the latter 16th century, along with Gdańsk and Riga.[35] The University of Königsberg, founded by Duke Albert in 1544 and receiving token royal approval from King Sigismund II Augustus in 1560,[22] became a center of Protestant teaching. The university had a profound impact on the development of Lithuanian culture, and several important Lithuanian writers attended the Albertina (see Lithuanians section below). Poles, including several notable figures, were also among the staff and students of the university (see Poles section below). The university was also the preferred educational institution of the Baltic German nobility.

With the growth of the Scottish diaspora in Poland, the first acquisition of citizenship in the city by a Scotsman occurred in 1561.[36]
On several occasions the city got into disputes with the Prussian Dukes and sought intervention and confirmation of its rights from the Polish authorities. In 1566, the city's rights were extended and the Prussian dukes were not allowed to interfere in the city's internal affairs by the Polish Royal Commissioners.[37] In 1635, Polish King Władysław IV Vasa granted the city the right to organize its military defense against a possible Swedish attack in exchange for exemption from paying taxes to Prussian dukes.[38] King Władysław IV was hosted in the city very grandly during his visits in 1635 and 1636.[39] He appointed Jerzy Ossoliński as the Polish governor of the duchy in 1636. Ossoliński resided in the city and completed the fortification of the city against a potential Swedish attack.[39]
The capable Duke Albert was succeeded by his feeble-minded son, Albert Frederick. Anna, daughter of Albert Frederick, married Elector John Sigismund of Brandenburg, who was granted the right of succession to Prussia on Albert Frederick's death in 1618. From this time the Electors of Brandenburg, the rulers of Brandenburg-Prussia, governed the Duchy of Prussia.[citation needed]
Brandenburg-Prussia
[edit]When Imperial and then Swedish armies overran Brandenburg during the Thirty Years' War of 1618–1648, the Hohenzollern court fled to Königsberg. On 1 November 1641, Elector Frederick William persuaded the Prussian diet to accept an excise tax.[40] In the Treaty of Königsberg of January 1656, the elector recognised his Duchy of Prussia as a fief of Sweden. In the Treaty of Wehlau in 1657, however, he negotiated the release of Prussia from Polish sovereignty in return for an alliance with Poland. The 1660 Treaty of Oliva confirmed Prussian independence from both Poland and Sweden.
In 1661 Frederick William informed the Prussian diet that he possessed jus supremi et absoluti domini, and that the Prussian Landtag could convene with his permission.[41] The Königsberg burghers, led by Hieronymus Roth of Kneiphof, opposed "the Great Elector's" absolutist claims, and actively rejected the Treaties of Wehlau and Oliva, seeing Prussia as "indisputably contained within the territory of the Polish Crown".[42] Delegations from the city's burghers went to the Polish king, John II Casimir Vasa, who initially promised aid, but then failed to follow through.[42] The town's residents attacked the elector's troops while local Lutheran priests held masses for the Polish king and for the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.[42] However, Frederick William succeeded in imposing his authority after arriving with 3,000 troops in October 1662 and training his artillery on the town.[42] Refusing to request mercy, Roth went to prison in Peitz until his death in 1678.[41]
The Prussian estates which swore fealty to Frederick William in Königsberg on 18 October 1663[43] refused the elector's requests for military funding, and Colonel Christian Ludwig von Kalckstein sought assistance from neighbouring Poland. After the elector's agents had abducted Kalckstein, he was executed in 1672. The Prussian estates' submission to Frederick William followed; in 1673 and 1674 the elector received taxes not granted by the estates and Königsberg received a garrison without the estates' consent.[44] The economic and political weakening of Königsberg strengthened the power of the Junker nobility within Prussia.[45]
Königsberg long remained a center of Lutheran resistance to Calvinism within Brandenburg-Prussia; Frederick William forced the city to accept Calvinist citizens and property-holders in 1668.[46]
Kingdom of Prussia
[edit]
By the act of coronation in Königsberg Castle on 18 January 1701, Frederick William's son, Elector Frederick III, became Frederick I, King in Prussia. The elevation of the Duchy of Prussia to the Kingdom of Prussia was possible because the Hohenzollerns' authority in Prussia was independent of Poland and the Holy Roman Empire. Since "Kingdom of Prussia" was increasingly used to designate all of the Hohenzollern lands, former ducal Prussia became known as the Province of Prussia (1701–1773), with Königsberg as its capital. However, Berlin and Potsdam in Brandenburg were the main residences of the Prussian kings.
The city was wracked by plague and other illnesses from September 1709 to April 1710, losing 9,368 people, or roughly a quarter of its populace.[47] On 13 June 1724, Altstadt, Kneiphof, and Löbenicht amalgamated to formally create the larger city Königsberg. Suburbs that subsequently were annexed to Königsberg include Sackheim, Rossgarten, and Tragheim.[13]

From 1734, during the War of the Polish Succession, Polish King Stanisław Leszczyński stayed in the city, and several prominent Polish officials, including Franciszek Maksymilian Ossoliński, and voivodes Antoni Michał Potocki, Piotr Jan Czapski and Andrzej Morsztyn, formed an informal political committee in support of Leszczyński there in 1734.[48] After the arrival of more Leszczyński's supporters in 1735, the city was the main center of authority and court of King Stanisław Leszczyński.[49] After his defeat in the war, Leszczyński signed an act of renunciation of the Polish crown in the city on 26 January 1736, and then left the city for France on 27 March 1736.[50]
Russian occupation
[edit]During the Seven Years' War (1756–1763), the Russian Empire decided to go to war with the Kingdom of Prussia and annex the territory and city, which was then to be offered to Poland as part of a territorial exchange desired by Russia.[51] Russia occupied and annexed Königsberg in January 1758 with no resistance, and the Prussian estates pledged allegiance to Russia.[52] The economic growth of the following years was based on the supply of arms to the Russian army and boosted trade with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.[53] By the terms of the Treaty of Saint Petersburg (signed 5 May 1762), Russia relinquished its claim to Königsberg and it reverted back to Prussian control.[42][54]
Kingdom of Prussia after 1773
[edit]After the First Partition of Poland in 1772, Königsberg became the capital of the newly formed province of East Prussia in 1773, which replaced the Province of Prussia in 1773. By 1800 the city was approximately five miles (8.0 km) in circumference and had 60,000 inhabitants, including a military garrison of 7,000, making it one of the most populous German cities of the time.[55]
After Prussia's defeat at the hands of Napoleon Bonaparte in 1806 during the War of the Fourth Coalition and the subsequent occupation of Berlin, King Frederick William III of Prussia fled with his court from Berlin to Königsberg.[56] The city was a centre for political resistance to Napoleon. To foster liberalism and nationalism among the Prussian middle class, the "League of Virtue" was founded in Königsberg in April 1808. The French forced its dissolution in December 1809, but its ideals were continued by the Turnbewegung of Friedrich Ludwig Jahn in Berlin.[57] Königsberg officials, such as Johann Gottfried Frey, formulated much of Stein's 1808 Städteordnung, or new order for urban communities, which emphasised self-administration for Prussian towns.[58] The East Prussian Landwehr was organised from the city after the Convention of Tauroggen.[59]
In 1819 Königsberg had a population of 63,800.[60] It served as the capital of the united Province of Prussia from 1824 to 1878, when East Prussia was merged with West Prussia. It was also the seat of the Regierungsbezirk Königsberg, an administrative subdivision.[61]
Led by the provincial president Theodor von Schön and the Königsberger Volkszeitung newspaper, Königsberg was a stronghold of liberalism against the conservative government of King Frederick William IV.[62] During the revolution of 1848, there were 21 episodes of public unrest in the city;[63] major demonstrations were suppressed.[64] Königsberg became part of the German Empire in 1871 during the Prussian-led unification of Germany. A sophisticated-for-its-time series of fortifications around the city that included fifteen forts was completed in 1888.[65]
The extensive Prussian Eastern Railway linked the city to Breslau (Wrocław), Thorn (Toruń), Insterburg, Eydtkuhnen, Tilsit, and Pillau. In 1860 the railway connecting Berlin with St. Petersburg was completed and increased Königsberg's commerce. Extensive electric tramways were in operation by 1900; and regular steamers plied the waterways to Memel, Tapiau and Labiau, Cranz, Tilsit, and Danzig (Gdańsk). The completion of a canal to Pillau in 1901 increased the trade of Russian grain in Königsberg, but, like much of eastern Germany, the city's economy was generally in decline.[66] The city was an important entrepôt for Scottish herring. in 1904 the export peaked at more than 322 thousand barrels.[67] By 1900 the city's population had grown to 188,000, with a 9,000-strong military garrison.[13] By 1914 Königsberg had a population of 246,000;[68] Jews flourished in the culturally pluralistic city.[69]
Weimar Republic
[edit]
Following the defeat of the Central Powers in World War I, Imperial Germany was replaced with the democratic Weimar Republic. The Kingdom of Prussia ended with the abdication of the Hohenzollern monarch, Wilhelm II, and the kingdom was succeeded by the Free State of Prussia. Königsberg and East Prussia, however, were separated from the rest of Weimar Germany following the restoration of independent Poland and the creation of the Polish Corridor. Due to the isolated geographical situation after World War I the German Government supported several large infrastructure projects: 1919 Airport "Devenau" (the first civil airport in Germany), 1920 "Deutsche Ostmesse" (a new German trade fair; including new hotels and radio station), 1929 reconstruction of the railway system including the new central railway station and 1930 opening of the North station.
Nazi Germany
[edit]In 1932 the local paramilitary SA had already started to terrorise their political opponents. On the night of 31 July 1932 there was a bomb attack on the headquarters of the Social Democrats in Königsberg, the Otto-Braun-House. The Communist politician Gustav Sauf was killed, and the executive editor of the Social Democrat "Königsberger Volkszeitung", Otto Wyrgatsch, and the German People's Party politician Max von Bahrfeldt were severely injured. Members of the Reichsbanner were attacked and the local Reichsbanner Chairman of Lötzen (Giżycko), Kurt Kotzan, was murdered on 6 August 1932.[70][71]
Following Adolf Hitler's coming to power, Nazis confiscated Jewish shops and, as in the rest of Germany, a public book burning was organised, accompanied by antisemitic speeches in May 1933 at the Trommelplatz square. Street names and monuments of Jewish origin were removed, and signs such as "Jews are not welcomed in hotels" started appearing. As part of the state-wide "aryanisation" of the civil service Jewish academics were ejected from the university.[72]
In July 1934, Hitler made a speech in the city in front of 25,000 supporters.[73] In 1933 the NSDAP alone received 54% of votes in the city.[73] After the Nazis took power in Germany, opposition politicians were persecuted and newspapers were banned. The Otto-Braun-House was requisitioned and became the headquarters of the SA, which used the house to imprison and torture opponents. Walter Schütz, a communist member of the Reichstag, was murdered there.[74] Many who would not co-operate with the rulers of Nazi Germany were sent to concentration camps and held prisoner there until their death or liberation.

In 1935, the Wehrmacht designated Königsberg as the Headquarters for Wehrkreis I (under the command of General der Artillerie Albert Wodrig), which took in all of East Prussia.[citation needed] According to the census of May 1939, Königsberg had a population of 372,164.[75]
In World War II both Königsberg and Berlin had large Fernschreibstellen (teleprinter offices) for the German Army which collected morning messages each day from regional or local centres to be sent in long messages to headquarters. They also had a Geheimschreibstube or cipher room where plaintext messages could be encrypted on Lorenz SZ40/42 machines. If sent by radio rather than landline they were intercepted and decrypted at Bletchley Park in England, where they were known as Fish. Some messages were daily returns, and some were between Hitler and his generals; both were valuable to Allied intelligence. Königsberg had links over the Eastern Front.[76]
Persecution of Jews under the Nazi regime
[edit]Prior to the Nazi era, Königsberg was home to a third of East Prussia's 13,000 Jews. Under Nazi rule, the Polish and Jewish minorities were classified as Untermenschen and persecuted by the authorities. The city's Jewish population shrank from 3,200 in 1933 to 2,100 in October 1938. The New Synagogue of Königsberg, constructed in 1896, was destroyed during Kristallnacht (9 November 1938); 500 Jews soon fled the city.
After the Wannsee Conference of 20 January 1942, Königsberg's Jews began to be deported to various Nazi concentration camps:[77] The SS sent the first and largest group of Jewish deportees, comprising 465 Jewish men, women and children, from Königsberg and East Prussia to the Maly Trostenets extermination camp near Minsk on 24 June 1942. Almost all were murdered soon after their arrival. Additional transports from Königsberg to the Theresienstadt ghetto and Auschwitz took place until 1945.[78]
In 1944–1945, the Germans operated a sub-camp of the Stutthof concentration camp in Königsberg, where they imprisoned around 500 Jews as forced labour.[79] In 1939, the Germans also established a forced labour camp for Romani people in the city.[80]
Persecution of Poles during World War II
[edit]
In September 1939, with the German invasion of Poland underway, the Polish consulate in Königsberg was attacked (which constituted a violation of international law), its workers arrested and sent to concentration camps where several of them died.[81] Polish students at the local university were captured, tortured and finally executed.[81] Other victims included local Polish civilians guillotined for petty violations of German law and regulations such as buying and selling meat.[81] Nevertheless, the Polish resistance movement was active in the city, which served as one of the region's main transfer points for smuggled Polish underground press.[82]
In September 1944 69,000 slave labourers were registered in the city (not counting prisoners of war), with most of them working on the outskirts; within the city were 15,000 slave labourers.[83] All of them were denied freedom of movement, forced to wear a "P" sign, if Poles, or "Ost" sign, if they were from the Soviet Union, and were watched by special units of the Gestapo and Wehrmacht.[83] They were denied basic spiritual and physical needs and food, and suffered from famine and exhaustion.[83] The conditions of the forced labour were described as "tragic", especially for Poles and Soviets, who were treated harshly by their German overseers. Ordered to paint German ships with toxic paints and chemicals, they were neither given gas-masks nor was there any ventilation in facilities where they worked, supposedly to expedite construction, while the substances evaporated in temperatures as high as 40 Celsius. As a result, there were cases of sudden illness or death during the work.[83]
Destruction in World War II
[edit]In 1944, Königsberg suffered heavy damage from British bombing attacks and burned for several days. The historic city center, especially the original quarters Altstadt, Löbenicht, and Kneiphof were destroyed, including the cathedral, the castle, all churches of the old city, the old and the new universities, and the old shipping quarters.[84]

Many people fled from Königsberg ahead of the Red Army's advance after October 1944, particularly after word spread of the Soviet atrocities at Nemmersdorf.[85][86] In early 1945, Soviet forces, under the command of the Polish-born Soviet Marshal Konstantin Rokossovsky, besieged the city that Hitler had envisaged as the home for a museum holding all the Germans had 'found in Russia'.[87] In Operation Samland, General Baghramyan's 1st Baltic Front, now known as the Samland Group, captured Königsberg in April.[88] Although Hitler had declared Königsberg an "invincible bastion of German spirit", the Soviets captured the city after a three-month-long siege. A temporary German breakout had allowed some of the remaining civilians to escape via train and naval evacuation from the nearby port of Pillau. Königsberg, which had been declared a "fortress" (Festung) by the Germans, was fanatically defended.[89]
On 21 January, during the Red Army's East Prussian Offensive, mostly Polish and Hungarian Jews from Seerappen, Jesau, Heiligenbeil, Schippenbeil, and Gerdauen (subcamps of Stutthof concentration camp) were gathered in Königsberg by the Nazis. Up to 7,000 of them were forced on a death march to Sambia: those that survived were subsequently executed at Palmnicken.[77]
On 9 April – one month before the end of the war in Europe – the German military commander of Königsberg, General Otto Lasch, surrendered the remnants of his forces, following the three-month-long siege by the Red Army. For this act, Lasch was condemned to death, in absentia, by Hitler.[90] At the time of the surrender, military and civilian dead in the city were estimated at 42,000, with the Red Army claiming over 90,000 prisoners.[91] Lasch's subterranean command bunker is preserved as a museum in today's Kaliningrad.[92]
About 120,000 survivors remained in the ruins of the devastated city. The German civilians were held as forced labourers until 1946. Only the Lithuanians, a small minority of the pre-war population, were collectively allowed to stay.[93] Between October 1947 and October 1948, about 100,000 Germans were forcibly moved to Germany.[94][need quotation to verify] The remaining 20,000 German residents were expelled in 1949–50.[95]
According to Soviet documents, there were 140,114 German inhabitants in September 1945 in the region that later became the Kaliningrad Oblast, thereof 68,014 in Königsberg. Between April 1947 and May 1951, according to Soviet documents, 102,407 were deported to the Soviet occupation zone of Germany. How many of the deportees were from the city of Königsberg does not become apparent from Soviet records. It is estimated that 43,617 Germans were in the city in the spring of 1946.[96] According to German historian Andreas Kossert, there were about 100,000 to 126,000 German civilians in the city at the time of Soviet conquest, and of these only 24,000 survived to be deported in 1947. Hunger accounted for 75% of the deaths, epidemics (especially typhoid fever) for 2.6% and violence for 15%, according to Kossert.[97]
Soviet Kaliningrad
[edit]Under the Potsdam Agreement of 1 August 1945, the city became part of the Soviet Union pending the final determination of territorial borders at an anticipated peace settlement. This final determination eventually took place on 12 September 1990 when the Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany was signed. The excerpt from the initial agreement pertaining to the partition of East Prussia, including the area surrounding Königsberg, is as follows (note that Königsberg is spelt "Koenigsberg" in the original document):
VI. CITY OF KOENIGSBERG AND THE ADJACENT AREA
The Conference examined a proposal by the Soviet Government that pending the final determination of territorial questions at the peace settlement, the section of the western frontier of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics which is adjacent to the Baltic Sea should pass from a point on the eastern shore of the Bay of Danzig to the east, north of Braunsberg – Goldep, to the meeting point of the frontiers of Lithuania, the Polish Republic and East Prussia.The Conference has agreed in principle to the proposal of the Soviet Government concerning the ultimate transfer to the Soviet Union of the city of Koenigsberg and the area adjacent to it as described above, subject to expert examination of the actual frontier.
The President of the United States and the British Prime Minister supported the proposal of the Conference at the forthcoming peace settlement.[98]

Königsberg was renamed Kaliningrad in 1946 after the Chairman of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR Mikhail Kalinin, although Kalinin was unrelated to the city, and there were already cities named in honour of Kalinin in the Soviet Union, namely Kalinin (now Tver) and Kaliningrad (now Korolev, Moscow Oblast).[99][100]
Some historians speculate that it may have originally been offered to the Lithuanian SSR because the resolution from the conference specifies that Kaliningrad's border would be at the (pre-war) Lithuanian frontier. The remaining German population was forcibly expelled between 1947 and 1948. The annexed territory was populated with Soviet citizens, mostly ethnic Russians but to a lesser extent also Ukrainians and Belarusians.[101]
The German language was replaced with the Russian language. In 1950, there were 1,165,000 inhabitants, which was only half the number of the pre-war population.
From 1953 to 1962, a monument to Stalin stood on Victory Square. In 1973, the town hall was turned into the House of Soviets. In 1975, the trolleybus was launched again. In 1980, a concert hall was opened in the building of the former Lutheran Church of the Holy Family. In 1986, the Kreuzkirche building was transferred to the Russian Orthodox Church.
For foreigners, the city was completely closed and, with the exception of rare visits of friendship from neighboring Poland, it was practically not visited by foreigners.[102][103]

The old city was not restored, and the ruins of the Königsberg Castle were demolished in the late 1960s,[1] on Leonid Brezhnev's personal orders,[1][2] despite the protests of architects, historians, local historians and ordinary residents of the city.[5][6][7]
The "reconstruction" of the oblast, threatened by hunger in the immediate post-war years, was carried out through an ambitious policy of oceanic fishing[104] with the creation of one of the main fishing harbours of the USSR in Kaliningrad city. Fishing not only fed the regional economy but also was a basis for social and scientific development, in particular oceanography.[105]
In 1957, an agreement was signed and later came into force which delimited the border between Polish People's Republic (Soviet satellite state at the time) and the Soviet Union.[106][107]
The region was added as a semi-exclave to the Russian SFSR; since 1946 it has been known as the Kaliningrad Oblast. According to some historians, Stalin created it as an oblast separate from the Lithuanian SSR because it further separated the Baltic states from the West.[108] Others think that the reason was that the region was far too strategic for the USSR to leave it in the hands of another SSR other than the Russian one.[105] The names of the cities, towns, rivers, and other geographical features were changed to Russian names.
The area was administered by the planning committee of the Lithuanian SSR, although it had its own Communist Party committee.[citation needed] In the 1950s, Nikita Khrushchev offered the entire Kaliningrad Oblast to the Lithuanian SSR but Antanas Sniečkus refused to accept the territory because it would add at least a million ethnic Russians to Lithuania proper.[101][109]
In 2010, the German magazine Der Spiegel published a report claiming that Kaliningrad had been offered to Germany in 1990 (against payment). The offer was not seriously considered by the West German government which, at the time, saw reunification with East Germany as a higher priority.[110] However, this story was later denied by Mikhail Gorbachev.[111]
Demographics
[edit]Following the Christianization of the region, the vast majority of the population was Catholic, and after the Reformation, the majority of the population belonged to the Evangelical Church of Prussia. A majority of its parishioners were Lutherans, although there were also Calvinists.
- Number of inhabitants, by year
- 1400: 10,000
- 1663: 40,000
- 1819: 63,869
- 1840: 70,839
- 1855: 83,593
- 1871: 112,092
- 1880: 140,909
- 1890: 172,796
- 1900: 189,483 (including the military), among whom were 8,465 Roman Catholics and 3,975 Jews.[112]
- 1905: 223,770, among whom were 10,320 Roman Catholics, 4,415 Jews and 425 Poles.[113]
- 1910: 245,994
- 1919: 260,895
- 1925: 279,930, among whom were 13,330 Catholics, 4,050 Jews and approximately 6,000 others.[114]
- 1933: 315,794
- 1939: 372,164
- 1945: 73,000
Jews
[edit]
The Jewish community in the city had its origins in the 16th century, with the arrival of the first Jews in 1538. The first synagogue was built in 1756. A second, smaller synagogue which served Orthodox Jews was constructed later, eventually becoming the New Synagogue.
The Jewish population of Königsberg in the 18th century was fairly low, although this changed as restrictions[115] became relaxed over the course of the 19th century. In 1756 there were 29 families of "protected Jews" in Königsberg, which increased to 57 by 1789. The total number of Jewish inhabitants was less than 500 in the middle of the 18th century, and around 800 by the end of it, out of a total population of almost 60,000 people.[116]
The number of Jewish inhabitants peaked in 1880 at about 5,000, many of whom were migrants escaping pogroms in the Russian Empire. This number declined subsequently so that by 1933, when the Nazis took over, the city had about 3,200 Jews. As a result of antisemitism and persecution in the 1920s and 1930s two-thirds of the city's Jews emigrated, mostly to the US and Great Britain. Those who remained were shipped by the Germans to concentration camps in two waves; first in 1938 to various camps in Germany, and the second in 1942 to the Theresienstadt concentration camp in occupied Czechoslovakia, Kaiserwald concentration camp in occupied Latvia, as well as camps in Minsk in the occupied Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic.[117]
Lithuanians
[edit]The Lithuanian Duke Butautas was baptized in Königsberg in 1365.[118] In the 14th century Vytautas the Great was residing in Königsberg following his retreat from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and 31 Samogitian nobles visited him in 1390 to recognize him as their ruler and concluded a peace and trade treaty.[118]
The University of Königsberg was an important center of Protestant Lithuanian culture and studies.[119] Abraomas Kulvietis and Stanislovas Rapalionis are also seen as important early Lithuanian scholars, who also were one of the co-founders of the University of Königsberg.[119][118] Daniel Klein published the first Lithuanian grammar book in Königsberg in 1653. Königsberg was closely related to the Lithuanian culture, and had an important impact in founding the literary language and national press of Lithuania. Despite persecution and intensive Germanisation, about 9 percent of the city was Lithuanian by the end of the 19th century.[120] Quite many Lithuanian publications were published by Königsberg's printing presses.[118]
Poles
[edit]
Poles were among the first professors of the University of Königsberg,[121] which received the royal Law of Privilege from King Sigismund II Augustus of Poland on 28 March 1560.[122] University of Königsberg lecturers included Hieronim Malecki (theology), Maciej Menius (astronomy) and Jan Mikulicz-Radecki (medicine).[123] Jan Kochanowski and Stanislaw Sarnicki were among the first students known to be Polish, later Florian Ceynowa, Wojciech Kętrzynski[124] and Julian Klaczko studied in Königsberg.[125] For 24 years Celestyn Myślenta (who first registered at the University as "Polonus") was a seven time rector of the university,[126] while Maciej Menius was a three times rector.[127] From 1728 there was a "Polish Seminar" at the seminary of Protestant theology, which operated until the early 1930s and had developed a number of pastors, including Krzysztof Celestyn Mrongovius and August Grzybowski.[123][128] Duke Albert of Prussia established a press in Königsberg that issued thousands of Polish pamphlets and religious books. During the Reformation Königsberg became a place of refuge for Polish Protestant adherents, a training ground for Polish Protestant clergy and a source of Polish Protestant literature.[129] In 1564 Jan Mączyński issued his Polish-Latin lexicon at Königsberg.[130]

According to historian Janusz Jasiński, based on estimates obtained from the records of St. Nicholas's Church, during the 1530s Lutheran Poles constituted about one quarter of the city population. This does not include Polish Catholics or Calvinists who did not have centralised places of worship until the 17th century, hence records that far back for these two groups are not available.[116]
From the 16th to 20th centuries, the city was a publishing center of Polish-language literature, especially religious literature. In 1545 in Königsberg a Polish catechism was printed by Jan Seklucjan.[131][132] In 1551 the first translation of the New Testament in Polish came out, issued by Stanisław Murzynowski.[131] Murzynowski's collections of sermons were delivered by Eustachy Trepka and in 1574 by Hieronim Malecki. The works of Mikolaj Rej were printed here by Seklucjan.[133] Maciej Stryjkowski announced in Königsberg the publication of his Kronika Polska, Litewska, Żmudzka, i wszystkiej Rusi ("A Chronicle of Poland, Lithuania, Samogitia and all Rus").[134]
Although formally the relationship of these lands with Poland stopped at the end of the 17th century, in practice the Polish element in Königsberg played a significant role for the next century, until the outbreak of World War II. Before the second half of the 19th century many municipal institutions (e.g. courts, magistrates) employed Polish translators, and there was a course in Polish at the university.[135] Polish books were issued as well as magazines with the last one being the Kalendarz Staropruski Ewangelicki (Old Prussian Evangelical Calendar) issued between 1866 and 1931.[42] In the 1840s, a local branch of the Polish Democratic Society was founded.[136] The city played an important role in the January Uprising, as it was one of the main supply centres for Polish underground movement, with about 10 companies of Königsberg smuggling arms and ammunition for Polish insurgents. There was a complex Polish resistance network built in the city, including figures such as Kazimierz Szulc and Piotr Drzewiecki. In 1876, Wojciech Kętrzyński wrote that the city retained a significant Polish community and the local population had pro-Polish sentiments, writing: "In Königsberg [...] a Pole among Germans today still finds sympathetic hearts, hearts that nourish sympathy for him".[137] At that time, between 25 and 30 percent of the city's population was Polish.[137][138]
During the Protestant Reformation the oldest church in Königsberg, St. Nicholas, was opened for non-Germans, especially Lithuanians and Poles.[139] Services for Lithuanians started in 1523, and by the mid-16th century also included ones for Poles.[140] By 1603 it had become a solely Polish-language church as Lithuanian service was moved to St. Elizabeth. In 1880 St. Nicholas was converted to a German-language church; weekly Polish services remained only for Masurians in the Prussian Army, although those were halted in 1901.[141] The church was bombed in 1944, further damaged in 1945, and the remaining ruins were demolished after the war in 1950.[142] The Königsberg Cathedral also hosted Polish-language services until the 18th century.
Culture and society
[edit]Notable people
[edit]Königsberg was the birthplace of the mathematician Christian Goldbach and the writer E.T.A. Hoffmann,[143] as well as the home of the philosopher Immanuel Kant,[144] who lived there virtually all his life and rarely travelled more than ten miles (16 km) away from the city.[145] Kant entered the university of Königsberg at age 16 and was appointed to a chair in metaphysics there in 1770 at the age of 46. While working there he published his Critique of Pure Reason (arguing that knowledge arises from the application of innate concepts to sensory experience) and his Metaphysics of Morals which argues that virtue is acquired by the performance of duty for its own sake.[146] In 1736, the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler used the arrangement of the city's bridges and islands as the basis for the Seven Bridges of Königsberg Problem, which led to the mathematical branches of topology and graph theory. In 1862, David Hilbert was baptised in Königsberg and educated there;[147] he established himself as one of the world's most influential mathematicians by the turn of the century.[148] Noted South African baboon rescuer Rita Miljo (1931–2012) grew up in Königsberg.[149] The distinguished biochemist and Nobel prizewinner Fritz Lipmann (1899–1986) was born in Königsberg.
Languages
[edit]The language of government and high culture was German. The Low Prussian dialect was widely spoken, but is now a moribund language as its refugee speakers are elderly and dying out. As the capital of the region of East Prussia which was a multi-ethnic territory, diverse languages such as Latvian, Lithuanian, Polish, and Yiddish were commonly heard on the streets of Königsberg. Old Prussian, a Baltic language, died out in the 18th century.
Arts
[edit]
In the Königsstraße (King Street) stood the Academy of Art with a collection of over 400 paintings. About 50 works were by Italian masters; some early Dutch paintings were also to be found there.[150] At the King's Gate stood statues of King Ottakar I of Bohemia, Albert of Prussia, and Frederick I of Prussia. Königsberg had a magnificent Exchange (completed in 1875) with fine views of the harbour from the staircase. Along Bahnhofsstraße ("Station Street") were the offices of the famous Royal Amber Works – Samland was celebrated as the "Amber Coast". There was also an observatory fitted up by the astronomer Friedrich Bessel, a botanical garden, and a zoological museum. The "Physikalisch", near the Heumarkt, contained botanical and anthropological collections and prehistoric antiquities. Two large theatres built during the Wilhelmine era were the Stadttheater (municipal theatre) and the Apollo.
Königsberg Castle
[edit]
Königsberg Castle was one of the city's most notable structures. The former seat of the Grand Masters of the Teutonic Knights and the Dukes of Prussia, it contained the Schloßkirche, or palace church, where Frederick I was crowned in 1701 and William I in 1861. It also contained the spacious Moscowiter-Saal, one of the largest halls in the German Reich, and a museum of Prussian history.
Education
[edit]Königsberg became a center of education when the Albertina University was founded by Duke Albert of Prussia in 1544. The university was opposite the north and east side of the Königsberg Cathedral. Lithuanian scholar Stanislovas Rapalionis, one of the founding fathers of the university, was the first professor of theology.[151]
Multiculturalism
[edit]As a consequence of the Protestant Reformation, the 1525 and subsequent Prussian church orders called for providing religious literature in the languages spoken by the recipients.[152] Duke Albrecht thus called in a Danzig (Gdańsk) book printer, Hans Weinreich, who was soon joined by other book printers, to publish Lutheran literature not only in German and (New) Latin, but also in Latvian, Lithuanian, Old Prussian and Polish.[153] The expected readership were inhabitants of the duchy, religious refugees, Lutherans in Poland (including neighbouring Warmia) and Lithuania as well as Lutheran priests from Poland and Lithuania called in by the duke.[152] Königsberg thus became a centre for printing German, Polish and Lithuanian books:[154] In 1530, the first Polish translation of Luther's Small Catechism was published by Weinrich.[155] In 1545, Weinreich published two Old Prussian editions of the catechism, which are the oldest printed and second-oldest books in that language after the handwritten 14th-century "Elbing dictionary".[156] The first Lithuanian-language book, Simple Words of Catechism by Martynas Mažvydas, was also printed in Königsberg, published by Weinreich in 1547.[157] Further Polish- and Lithuanian-language religious and non-religious prints followed. One of the first newspapers in Polish was published in Königsberg in the years 1718–1720, the Poczta Królewiecka.[158] The city remained an important Polish printing center until the early 20th century, with the last Polish book printed in 1931.[159]
Sports
[edit]Football clubs which played in Königsberg included VfB Königsberg and SV Prussia-Samland Königsberg. Lilli Henoch, the world record holder in the discus, shot put, and 4 × 100 meters relay events was born in Königsberg,[160] as was Eugen Sandow, dubbed the "father of modern bodybuilding". Segelclub RHE, Germany's oldest sailing club, was founded in Königsberg in 1855. The club still exists, and is now headquartered in Hamburg.
Cuisine
[edit]
Königsberg was well known within Germany for its unique regional cuisine.[citation needed] A popular dish from the city was Königsberger Klopse, which is still made today in some specialist restaurants in the now Russian city and elsewhere in present-day Germany.
Other food and drink native to the city included:
- Königsberger Marzipan
- Kopskiekelwein, a wine made from blackcurrants or redcurrants
- Bärenfang
- Ochsenblut, literally "ox blood", a champagne-burgundy cocktail mixed at the popular Blutgericht pub, which no longer exists (the pub was located in the north wing of Königsberg Castle, which was demolished in 1968)
- Königsberger Fleck or Königsberg-style tripe soup, made with the addition of bone marrow and root vegetables
Fortifications
[edit]
The fortifications of Königsberg consist of numerous defensive walls, forts, bastions and other structures. They make up the First and the Second Defensive Belt, built in 1626–1634 and 1843–1859, respectively.[65] The 15-metre-thick First Belt was erected due to Königsberg's vulnerability during the Polish–Swedish wars.[65] The Second Belt was largely constructed on the place of the first one, which was in a bad condition.[65] The new belt included twelve bastions, three ravelins, seven spoil banks and two fortresses, surrounded by water moat.[65] Ten brick gates served as entrances and passages through defensive lines and were equipped with moveable bridges.[65]
There was a Bismarck tower just outside Königsberg, on the Galtgarben, the highest point on the Sambia Peninsula. It was built in 1906 and destroyed by German troops sometime in January 1945 as the Soviets approached.[162][163]
See also
[edit]- List of people from Königsberg
- Königsberger Klopse, traditional German menu
- Königsberger Marzipan, traditional type of marzipan
- Seven Bridges of Königsberg, a topology problem
- Kaliningrad (Königsberg) question
- Königsberger Paukenhund, traditional kettle drum dog of the Prussian infantry
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ a b c d Ryabushev, Alexander (11 November 2008). "Калининградские руины еще немного подождут". Nezavisimaya Gazeta (in Russian). Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ a b c Artamonova, Alexandra (7 June 2018). "Raze and rebuild: Kaliningrad's battle to preserve its complex post-war cityscape". The Calvert Journal. Retrieved 5 January 2021.
- ^ Haga, Mitsuru (2020). "Vertical lands and horizontal gods: is East "East" and West "West"?". Intercultural Relations. 2 (8): 10. doi:10.12797/RM.02.2020.08.01. ISSN 2544-2139.
The old Prussian settlement of Twangste was conquered by the Teutonic Knights in 1225 and became the German city of Königsberg.
- ^ a b Bradbury, Jim (2004). Routledge Companion to Medieval Warfare. p. 75. ISBN -0-203-64466-2.
- ^ a b "Калининградская архитектура". Archived from the original on 30 July 2012. // archikld.ru
- ^ a b О восстановлении послевоенного Калининграда 1946—1953 гг. Archived 25 September 2020 at the Wayback Machine // klgd.ru
- ^ a b Клемешев А. П.; Калининградский государственный университет (2004). На перекрёстке культур: русские в Балтийском регионе. Выпуск 7. Часть 2. КГУ. pp. 206–207.
- ^ Stankevičius, Augustas (10 January 2025). "Moscow accuses Lithuanian president of 'territorial claims' on Kaliningrad". lrt.lt. Retrieved 20 January 2025.
- ^ "Караляучус — Краловиц — Кёнигсберг — Калининград" (in Russian). Deutsche Welle. 29 April 2005.
- ^ Silvija Ozola. Churches — Building Dominances of the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia Urban Centres in the 17th Century // ART TEMPUS / Mg. art., Mg. paed. Zeltite Barsevska. — Daugavpils : Institute of Art, Daugavpils University, 2014. — V. 2. — P. 11. — ISSN 2255-9396.
- ^ Biskup
- ^ Koch, Hannsjoachim Wolfgang (1978). A history of Prussia. Longman P4
- ^ a b c Baedeker, p. 174
- ^ Seward, p. 107
- ^ Turnbull, p. 13
- ^ Christiansen, p. 205
- ^ a b Christiansen, p. 224
- ^ Christiansen, p. 222
- ^ Urban, pp. 225–226
- ^ Górski 1949, p. 54.
- ^ Górski 1949, pp. 71–72.
- ^ a b c Podbereski 2010, p. 113.
- ^ Górski 1949, p. 63.
- ^ Koch, p. 19
- ^ "Kalendarz dat: 1465". Dzieje.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 19 June 2024.
- ^ Górski 1949, pp. 96–97, 214–215.
- ^ Christiansen, p. 243
- ^ Urban, p. 254
- ^ Koch, p. 33
- ^ Christiansen, p. 247
- ^ Koch, p. 34
- ^ Koch, p. 44
- ^ Kirby, Northern Europe, p. 8
- ^ a b c Jasiński 2005, p. 131.
- ^ Kirby, Northern Europe, p. 13
- ^ Feduszka, Jacek (2009). "Szkoci i Anglicy w Zamościu w XVI-XVIII wieku". Czasy Nowożytne (in Polish). Vol. 22. Zarząd Główny Polskiego Towarzystwa Historycznego. p. 52. ISSN 1428-8982.
- ^ Małłek 1992, pp. 249–250.
- ^ Małłek 1992, p. 252.
- ^ a b Małłek 1992, p. 253.
- ^ Koch, p. 46
- ^ a b Koch, Hannsjoachim Wolfgang (1978). A history of Prussia. Longman. p. 56.
- ^ a b c d e f Jasiński, Janusz (1994). Historia Królewca: szkice z XIII-XX stulecia. Książnica Polska. pp. 80, 103–104. ISBN 83-85702-03-2.
- ^ Clark, p. 53
- ^ Koch, p. 57
- ^ Holborn, 1648–1840, p. 61
- ^ Clark, pp. 121–2
- ^ Kirby, Northern Europe, p. 352
- ^ Ciesielski, Tomasz (2010). "Prusy Wschodnie w trakcie polskiej wojny sukcesyjnej i wojny siedmioletniej". In Gieszczyński, Witold; Kasparek, Norbert (eds.). Wielkie wojny w Prusach. Działania militarne między dolną Wisłą a Niemnem na przestrzeni wieków (in Polish). Dąbrówno. pp. 108–109. ISBN 978-83-62552-00-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Ciesielski, p. 110
- ^ Ciesielski, p. 113
- ^ Ciesielski, p. 118
- ^ Ciesielski, p. 165
- ^ Ciesielski, p. 166
- ^ Zammito, John H. (2002). Kant, Herder, and the birth of anthropology. University of Chicago Press. p. 392. ISBN 978-0-226-97859-8.
- ^ For comparison: Berlin ca. 170,000, Cologne and Frankfurt ca. 50,000 each, and Munich ca. 30,000.
- ^ Koch, p. 160
- ^ Koch, p. 192
- ^ Holborn, 1648–1840, p. 401
- ^ Clark, p. 361
- ^ Holborn, 1840–1945, p. 8
- ^ Hauf, R (1980) The Prussian administration of the district of Königsberg, 1871–1920, Quelle & Meyer, Wiebelsheim P21
- ^ Clark, pp. 440–2
- ^ Clark, p. 476
- ^ Holborn, 1840–1945, p. 51
- ^ a b c d e f "The Past..." Museum of the World Ocean. Archived from the original on 10 March 2011. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- ^ Kirby, The Baltic World, p. 303
- ^ "Annual Statistics". scottishherringhistory.uk.
- ^ Kirby, The Baltic World, p. 205
- ^ Clark, p. 584
- ^ Matull, Wilhelm (1973). "Ostdeutschlands Arbeiterbewegung: Abriß ihrer Geschichte, Leistung und Opfer" (PDF) (in German). Holzner Verlag. p. 350.
- ^ Die aufrechten Roten von Königsberg Der Spiegel, 28 June 2009 (in German)
- ^ Janusz Jasinski, Historia Krolewca, 1994, page 251-252
- ^ a b Janusz Jasinski, Historia Krolewca, 1994, page 249
- ^ Matull, page 357
- ^ GRC, p. 37
- ^ Gannon, Paul (2006). Colossus: Bletchley Park's Greatest Secret. London: Atlantic Books. pp. 207, 208. ISBN 1-84354-330-3.
- ^ a b Ostpreussen.net
- ^ "Memorial Plaque to the Victims of the First Deportation from Königsberg". Information Portal to European Sites of Remembrance. Berlin, Germany: Stiftung Denkmal für die ermordeten Juden Europas. Retrieved 18 July 2019.
- ^ Gliński, Mirosław. "Podobozy i większe komanda zewnętrzne obozu Stutthof (1939–1945)". Stutthof. Zeszyty Muzeum (in Polish). 3: 173. ISSN 0137-5377.
- ^ "Lager für Sinti und Roma Königsberg". Bundesarchiv.de (in German). Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- ^ a b c Janusz Jasinski, Historia Krolewca (1994), p. 256
- ^ Chrzanowski, Bogdan (2022). Polskie Państwo Podziemne na Pomorzu w latach 1939–1945 (in Polish). Gdańsk: IPN. p. 57. ISBN 978-83-8229-411-8.
- ^ a b c d Janusz Jasinski, Historia Krolewca, 1994, p. 257.
- ^ Gilbert, M (1989) Second World War, Weidenfeld and Nicolson, London, P582-3
- ^ Berlin , Antony Beevor
- ^ A Writer at War Vasily Grossman, Edited & Translated by Antony Beevor and Luba Vinoradova, Pimlico, 2006
- ^ Gilbert, M (1989) Second World War, Weidenfeld and Nicolson, London, P291
- ^ Jukes.Stalin's Generals, p. 30
- ^ Beevor, A (2002) Berlin: The Downfall 1945 Penguin Books. p. 91.
- ^ Gilbert, M (1989) Second World War, Weidenfeld and Nicolson, London, P660
- ^ Hastings, M (2005) 2nd ed Armageddon: The Battle for Germany 1944–45, Pan Macmillan, P291
- ^ "visitkaliningrad.com". visitkaliningrad.com. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ^ Eaton, Nicole. "Building a Soviet City: the Transformation of Königsberg". Wilson Center.
- ^ Berger, Stefan (13 May 2010). "How to be Russian with a Difference? Kaliningrad and its German Past". Geopolitics. 15 (2): 345–366. doi:10.1080/14650040903486967. S2CID 143378878.
- ^ Michael Wieck: A Childhood Under Hitler and Stalin: Memoirs of a "Certified Jew," University of Wisconsin Press, 2003, ISBN 0-299-18544-3, Hans Lehndorff: East Prussian Diary, A Journal of Faith, 1945–1947 London 1963
- ^ Bernhard Fisch and Marina Klemeševa, "Zum Schicksal der Deutschen in Königsberg 1945–1948 (im Spiegel bislang unbekannter russischer Quellen)", Zeitschrift für Ostmitteleuropa-Forschung Bd. 44 Nr. 3 (1995), pages 394, 395, 399.
- ^ Andreas Kossert, Ostpreußen. Geschichte und Mythos, 2007 Pantheon Verlag, PDF edition, p. 347. Peter B. Clark (The Death of East Prussia. War and Revenge in Germany's Easternmost Province, Andover Press 2013, PDF edition, p. 326) refers to Professor Wilhelm Starlinger, the director of the city's two hospitals that cared for typhus patients, who estimated that out of a population of about 100,000 in April 1945, some 25,000 had survived by the time large-scale evacuations began in 1947. This estimate is also mentioned by Richard Bessel, "Unnatural Deaths", in: The Illustrated Oxford History of World War II, edited by Richard Overy, Oxford University Press 2015, pp. 321 to 343 (p. 336).
- ^ "The Potsdam Declaration". 2 August 1945. Archived from the original on 19 July 2001. Retrieved 2 April 2009 – via ibiblio.
- ^ Кёнигсберг мог стать Балтийском. Archived 1 February 2022 at the Wayback Machine // klgd.ru
- ^ Кёнигсберг-Калининград. Поиск самоидентификации. Archived 6 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine // klgd.ru
- ^ a b Milan Bufon (11 April 2014). The New European Frontiers: Social and Spatial (Re)Integration Issues in Multicultural and Border Regions. Cambridge Scholars Publishing. p. 98. ISBN 978-1-4438-5936-3.
- ^ Социально-экономическая география Балтийского региона. // window.edu.ru
- ^ Калининград: От реликта России до процветающего города Прибалтики («The Independent», Великобритания). Archived 27 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine // newkaliningrad.ru
- ^ Roqueplo O: La Russie et son Miroir d'Extrême-Occident, Langues'O, HAL, 2018
- ^ a b Roqueplo O: La Russie et son miroir d'Extrême-Occident, 2018
- ^ "Russia (USSR) / Poland Treaty (with annexed maps) concerning the Demarcation of the Existing Soviet–Polish State Frontier in the Sector Adjoining the Baltic Sea 5 March 1957" (PDF). Retrieved 2 April 2009.
- ^ For other issues of the frontier delimitation see "Maritime boundary delimitation agreements and other material". Retrieved 2 April 2009.
- ^ Weinberg, Gerhard L. (2005). Visions of Victory: The hopes of eight World War II leaders. Cambridge University Press. p. 114. ISBN 978-0-521-85254-8.
- ^ Krickus, Richard J. (2002). "2. Kaliningrad under Soviet and Russian Rule". The Kaliningrad Question. Lanham, Maryland, United States: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-7425-1705-9 – via Google Books.
- ^ Wiegrefe, Klaus (22 May 2010). Müller von Blumencron, Mathias; Mascolo, Georg (eds.). "Zeitgeschichte: Historischer Ballast" [Contemporary History: Historical Ballast]. Der Spiegel (in German). Hamburg, Germany: Spiegel-Berlag. ISSN 2195-1349. Archived from the original on 14 October 2017.
- ^ Berger, Stefan (31 July 2010). Rusbridger, Alan (ed.). "Should Kant's home once again be German?". The Guardian. London, England, United Kingdom. ISSN 1756-3224. OCLC 60623878. Archived from the original on 6 February 2021.
- ^ Meyers Konversations-Lexikon. 6th edition, vol. 11, Leipzig and Vienna 1908, p. 387 (in German).
- ^ Gemeindelexikon für das Königreich Preußen. Heft 1, Verlag des Königlichen Statistischen Landesamtes, Berlin 1907, p. 118 + 119 (in German).
- ^ Der Große Brockhaus, 15th edition, vol. 10 (Leipzig 1931), p. 382 (in German).
- ^ Reade, Cyril (2007). Mendelssohn to Mendelsohn: Visual Case Studies of Jewish Life in Berlin. Peter Lang. pp. 49–50. ISBN 978-3-03910-531-1.
- ^ a b Jasiński, Janusz (1994). Historia Królewca: szkice z XIII-XX stulecia. Olsztyn: Ksiaznica Polska. p. 172. ISBN 83-85702-03-2.
- ^ Danny, Isabel (2009). The Fall of Hitler's Fortress City: The Battle for Königsberg, 1945. Casemate Publishers. pp. 64–74. ISBN 978-1-935149-20-0.
- ^ a b c d Matulevičius, Algirdas. "Karaliaučiaus lietuviai". Visuotinė lietuvių enciklopedija (in Lithuanian). Retrieved 29 November 2024.
- ^ a b Walenty Piłat (1998). W kre̢gu kultur bałtyckich. Wyższa Szkoła Pedagogiczna. p. 82. ISBN 978-83-87315-15-3.
- ^ Furmonavicius, Darius (March 2003). Koenigsberg/Karaliaucius/Kaliningrad region: Settlement of sovereignty will end Second World War (PDF). Nashville, TN: EUSA 8th International Conference. p. 2.
- ^ Jerzy Oleksiński (1972). Bard ziemi mazurskiej. Nasza Księgarnia.
- ^ Janusz Małłek (1987). Dwie części Prus: studia z dziejów Prus Książęcych i Prus Królewskich w XVI i XVII wieku. Wydawn. Pojezierze. p. 193. ISBN 978-83-7002-302-7.
- ^ a b Harold Ellis; Sir Roy Calne; Christopher Watson (2011). Lecture Notes: General Surgery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 268. ISBN 978-1-118-29379-9.
- ^ Uniwersytet im. Adama Mickiewicza w Poznaniu, Instytut Historii (1996). Studia historica Slavo-Germanica. Wydawn. Naukowe im. A. Mickiewicza. p. 5. ISBN 83-232-0761-5.
- ^ Wrzesiński, Wojciech; Achremczyk, Stanisław (1993). Królewiec a Polska: praca zbiorowa. Ośrodek Badań Naukowych. p. 126.
- ^ Wrzesiński, Wojciech; Achremczyk, Stanisław (1993). Królewiec a Polska: praca zbiorowa. Ośrodek Badań Naukowych. p. 85.
- ^ Czerniakowska, Malgorzata (1992). "Menius, Maciej". In Nowak, Zbigniew (ed.). Słownik biograficzny Pomorza Nadwiślańskiego. Vol. Supplement I. Gdańskie Towarzystwo Naukowe. pp. 199–201.
- ^ Wrzesiński, Wojciech; Achremczyk, Stanisław (1993). Królewiec a Polska: praca zbiorowa. Ośrodek Badań Naukowych. pp. 81, 126.
- ^ The Cambridge History of Poland: From the Origins to Sobieski (To 1696) By W. F. Reddaway, J. H. Penson, O. Halecki, R. Dyboski Cambridge 1950 Page 325
- ^ Adam Zamoyski Polish Way: A Thousand-Year History of the Poles and Their Culture Hippocrene Books New York 1987 Page 117
- ^ a b Krašovec, Jože (1988). Interpretation Der Bibel. Continuum International Publishing Group. p. 1223. ISBN 1-85075-969-3.
- ^ The Cambridge History of Poland: From the Origins to Sobieski (To 1696) By W. F. Reddaway, J. H. Penson, O. Halecki, R. Dyboski Cambridge 1950 Page 331
- ^ Lipinski, Roman (2004). "Individualism and the Sense of Solidarity". In Lienenmann-Perrin, Christine; Vroom, H.M.; Michael Weinrich (eds.). Contextuality in Reformed Europe: The Mission of the Church in the Transformation of European Culture. Rodopi. p. 245.
- ^ Morfill, Richard (1883). Slavonic literature. Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge. p. 202.
- ^ Sławomir Augusiewicz; Janusz Jasiński; Tadeusz Oracki (2005). Wybitni Polacy w Królewcu: XVI-XX wiek. Wydawnictwo "Littera". p. 46. ISBN 978-83-89775-03-0.
- ^ Jasiński 2005, p. 127.
- ^ a b Jasiński 2005, pp. 123–132.
- ^ Borzyszkowski, Józef (2006). ""Wybitni Polacy w Królewcu XVI-XX wiek", Sławomir Augusiewicz, Janusz Jasiński, Tadeusz Oracki, Olsztyn 2005: [recenzja]". Komunikaty Mazursko-Warmińskie (Review) (in Polish). 2 (1): 297–300.
- ^ Albinus, Robert (1985). Lexikon der Stadt Königsberg/Pr. und Umgebung. Leer: Gerhard Rautenberg. p. 304. ISBN 3-7921-0320-6.
- ^ Müller, Gerhard; Seebass, Gottfried (1994). Andreas Osiander. Gesamtausgabe. Schriften und Briefe 1549 bis August 1551. Vol. 9. Gütersloh: Mohn. p. 109. ISBN 3-579-00133-7.
- ^ Gause II, p. 693
- ^ Podbereski 2010, pp. 113–117.
- ^ . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 13 (11th ed.). 1911.
- ^ . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 15 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 662–672.
- ^ Lewis, Rick. 2005. 'Kant 200 Years On'. Philosophy Now. No. 49.
- ^ Guyer P, "Introduction. The starry heavens and the moral law" in Guyer P (ed) The Cambridge Companion to Kant and Modern Philosophy. Cambridge University Press. Cambridge. 2006 pp3-5.
- ^ Reid, Constance (1996). "Youth". Hilbert. New York: Springer. pp. 1–8. ISBN 0387946748.
- ^ O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F. (November 2014). "David Hilbert". MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive. Scotland: University of St Andrews. Retrieved 26 January 2025.
- ^ Schudel, Matt (28 July 2012). "Rita Miljo, Founder of South African Baboon Sanctuary, Dies at 81". The Washington Post. Washington, D.C. Archived from the original on 4 July 2022. Retrieved 4 July 2022.
- ^ Baedeker, p. 176
- ^ Zinkevičius, p.32
- ^ a b Bock, Vanessa (2004). "Die Anfänge des polnischen Buchdrucks in Königsberg. Mit einem Verzeichnis der polnischen Drucke von Hans Weinreich und Alexander Augezdecki". In Axel E. Walter (ed.). Königsberger Buch- und Bibliotheksgeschichte. Cologne: Böhlau. pp. 127–155, esp. p. 127-131.
- ^ Komorowski, Manfred (2004). "Eine Bibliographie Königsberger Drucke vor 1800 – Utopie oder reelle Chance?". In Axel E. Walter (ed.). Königsberger Buch- und Bibliotheksgeschichte. Cologne: Böhlau. pp. 169–186, esp. p. 170.
Bock, Vanessa (2004). "Die Anfänge des polnischen Buchdrucks in Königsberg. Mit einem Verzeichnis der polnischen Drucke von Hans Weinreich und Alexander Augezdecki". In Axel E. Walter (ed.). Königsberger Buch- und Bibliotheksgeschichte. Cologne: Böhlau. pp. 127–155, esp. p. 127-131. - ^ Kirby, Northern Europe, p. 88
- ^ Bock, Vanessa (2004). "Die Anfänge des polnischen Buchdrucks in Königsberg. Mit einem Verzeichnis der polnischen Drucke von Hans Weinreich und Alexander Augezdecki". In Axel E. Walter (ed.). Königsberger Buch- und Bibliotheksgeschichte. Cologne: Böhlau. pp. 127–155, esp. p. 131-132.
- ^ Grosse, Rudolf; Wellmann, Hans (1996). Textarten im Sprachwandel. Nach der Erfindung des Buchdrucks. Heidelberg: Winter. p. 65.
- ^ Kaunas, Domas (2004). "Die Rolle Königsbergs in der Geschichte des litauischen Buches". In Axel E. Walter (ed.). Königsberger Buch- und Bibliotheksgeschichte. Cologne: Böhlau. pp. 157–167, esp. p. 158.
- ^ Zieniukowa, J (2007). "On the History of Polish Language in Königsberg". Acta Baltico-Slavica. Archeologia, Historia, Ethnographia, et Linguarum Scientia. 31: 325–337.
- ^ Podbereski 2010, p. 114.
- ^ Joseph M. Siegman (1992). The International Jewish Sports Hall of Fame. SP Books. ISBN 1-56171-028-8. Retrieved 2 November 2011.
- ^ "Museums of Kaliningrad". Tourism Kaliningrad. Archived from the original on 25 December 2010. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- ^ de:Bismarckturm Bismarck towers (German Wikipedia)
- ^ Galtgarben (German Wikipedia)
Sources
[edit]- Baedeker, Karl (1904). Baedeker's Northern Germany. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. p. 395.
- Biskup, Marian. Königsberg gegenüber Polen und dem Litauen der Jagiellonen zur Zeit des Mittelalters (bis 1525) in Królewiec a Polska Olsztyn 1993 (in German)
- Bötticher, Adolf (1897). Die Bau- und Kunstdenkmäler der Provinz Ostpreußen. Heft VII. Königsberg (in German). Königsberg: Rautenberg. p. 395.
- Christiansen, Erik (1997). The Northern Crusades. London: Penguin Books. p. 287. ISBN 0-14-026653-4.
- Clark, Christopher (2006). Iron Kingdom: The Rise and Downfall of Prussia 1600–1947. Cambridge: Belknap Press of Harvard. p. 776. ISBN 0-674-02385-4.
- Clark, Peter B. (2013). The Death of East Prussia — War and Revenge in Germany's Easternmost Province. US: Andover Press. ISBN 978-1-481935-75-3.
- Gause, Fritz: Die Geschichte der Stadt Königsberg in Preußen. Three volumes, Böhlau, Cologne 1996, ISBN 3-412-08896-X (in German).
- Górski, Karol (1949). Związek Pruski i poddanie się Prus Polsce: zbiór tekstów źródłowych (in Polish and Latin). Poznań: Instytut Zachodni.
- Holborn, Hajo (1964). A History of Modern Germany: 1648–1840. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. p. 556.
- Holborn, Hajo (1982). A History of Modern Germany: 1840–1945. Princeton: Princeton University Press. p. 844. ISBN 0-691-00797-7.
- Jasiński, Janusz (2005). "Polska a Królewiec". Komunikaty Mazursko-Warmińskie (in Polish). 2 (1).
- Kirby, David (1990). Northern Europe in the Early Modern Period: The Baltic World, 1492–1772. London: Longman. ISBN 0-582-00410-1.
- Kirby, David (1999). The Baltic World, 1772–1993: Europe's Northern Periphery in an Age of Change. London: Longman. ISBN 0-582-00408-X.
- Małłek, Janusz (1992). "Polityka miasta Królewca wobec Polski w latach 1525–1701". Komunikaty Mazursko-Warmińskie (in Polish). No. 3–4.
- "Juden in Königsberg" (in German). Ostpreussen.net. 12 December 2006. Retrieved 5 March 2008.
- Podbereski, Wacław (2010). "Królewiec – Koenigsberg – Kaliningrad". Znad Wilii (in Polish). Vol. 4, no. 44. p. 113. ISSN 1392-9712.
- Turnbull, Stephen (2003). Crusader Castles of the Teutonic Knights (1): The red-brick castles of Prussia 1230–1466. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. p. 64. ISBN 1-84176-557-0.
- Urban, William (2003). The Teutonic Knights: A Military History. London: Greenhill Books. p. 290. ISBN 1-85367-535-0.
- Wieck, Michael (2003). A Childhood Under Hitler and Stalin: Memoirs of a "Certified Jew. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 0-299-18544-3.
- Zinkevičius, Zigmas (2008). Mažosios Lietuvos indėlis į lietuvių kultūrą. Vilnius: Mokslo ir enciklopedijų leidybos institutas. p. 286. ISBN 978-5-420-01621-3.
External links
[edit]- Photoarchaeology of Kneiphof
- Kaliningrad Photo Gallery – Reisebilder aus Königsberg
- The Film Königsberg is dead, France/Germany 2004 by Max & Gilbert (in German and English)
- Territory's history from 1815 to 1945 (in German)
- Interactive Map with photos of Königsberg and modern Kaliningrad Archived 29 July 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- Site with 400+ side-by-side photos of 1939/2005 identical locations in Königsberg/Kaliningrad (in Russian and German)
- Northeast Prussia 2000: Travel Photos
- Adreßbuch der Haupt- und Residenzstadt Königsberg., Адресная книга Кёнигсберга. (нем. яз.)(1770–1941)