House of Councillors
35°40′35.5″N 139°44′40.5″E / 35.676528°N 139.744583°E
House of Councillors 参議院 Sangiin | |
|---|---|
| 213th Session of the National Diet | |
| Type | |
| Type | of the National Diet |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 248 |
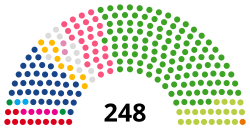 | |
Political groups | Government (143)
Opposition (92)
Unaffiliated (11)
Vacant (1)
|
| Committees | 17 committees |
Length of term | 6 years |
| Salary | President: ¥2,170,000/m Vice President: ¥1,584,000/m Members: ¥1,294,000/m |
| Elections | |
| Parallel voting: Single non-transferable vote (148 seats) Party-list proportional representation (100 seats) Staggered elections | |
First election | 20 April 1947 |
Last election | 10 July 2022 |
Next election | On or before 27 July 2025 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Chamber of the House of Councillors | |
| Website | |
| www | |
| This article is part of a series on |
 |
|---|
|
|
The House of Councillors (参議院, Sangiin) is the upper house of the National Diet of Japan. The House of Representatives is the lower house. The House of Councillors is the successor to the pre-war House of Peers. If the two houses disagree on matters of the budget, treaties, or the nomination of the prime minister, the House of Representatives can insist on its decision. In other decisions, the House of Representatives can override a vote of the House of Councillors only by a two-thirds majority of members present.
The House of Councillors has 248 members who each serve six-year terms, two years longer than those of the House of Representatives. Councillors must be at least 30 years old, compared with 25 years old in the House of Representatives. The House of Councillors cannot be dissolved, and terms are staggered so that only half of its membership is up for election every three years. Of the 121 members subject to election each time, 73 are elected from 45 districts by single non-transferable vote (SNTV) and 48 are elected from a nationwide list by proportional representation (PR) with open lists.[1]
Roles and responsibilities
[edit]
The power of House of Councillors is very similar to the Canadian Senate or the Irish Seanad.[2] In central issues, there is a "supremacy of the House of Representatives" (ja:衆議院の優越, Shūgiin no yūetsu). In the election of the prime minister, the ratification of international treaties, and on passing the budget, a decision by the House of Representatives always overrides dissent from the House of Councillors. Only the lower house can pass votes of no-confidence against the cabinet. All other legislation requires either the approval by majorities in both houses, an agreement in the conference committee of both houses or an additional override vote by two-thirds majority in the House of Representatives.[3][4] However, no single party has ever won a two-thirds majority in the House of Representatives under the current constitution, although the LDP came close several times, as did the DPJ in 2009. In other words, controlling a majority in the House of Councillors and one third of the House of Representatives is enough for a united opposition to be able to block the passage of legislation. For certain important administrative nominations by the cabinet, the approval of both houses is required (although the laws containing this requirement could be changed by two-thirds lower house override as a "nuclear option"); and constitutional amendment proposals need two-thirds majorities in both the houses of the Diet to be submitted to the people in a national referendum.[2]
One additional constitutional role of the House of Councillors is to serve as functioning fully elected emergency legislature on its own during lower house election campaigns: While the House of Representatives is dissolved, the National Diet can't be convened, and therefore no law can be passed in regular procedure; but in urgent cases requiring parliamentary action (e.g. election management, provisional budgets, disaster response), an emergency session (緊急集会, kinkyū shūkai) of the House of Councillors can still be invoked to take provisional decisions for the whole Diet. Such decisions will become invalid unless confirmed by the House of Representatives as soon as the whole Diet convenes again.
The basic stipulations on the role of the House of Councillors are subject of chapter IV of the constitution.[5] Laws and rules containing more detailed provisions on parliamentary procedures and the relations between the two houses include the National Diet Law (国会法, Kokkai-hō),[6] the conference committee regulations (両院協議会規程, ryōin-kyōgikai kitei),[7] and the rules of each house (衆議院/参議院規則, Shūgiin/Sangiin kisoku).[8]
Constitutional practice
[edit]In practice, governments often tried to ensure legislative majorities, either by forming coalition governments with safe legislative majorities in the first place or by negotiating with part of the opposition, or avoided to submit bills with no prospects of passage,[9] so the House of Councillors rarely voted against the decisions reached by the lower house for much of postwar history: As the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), founded in 1955, often held majorities in both houses or was sufficiently close to control both houses together with independents and micro-parties for a long period, inter-chamber disagreement was rare during most of the 1955 System.
After the opposition victory in the 1989 election, the relative importance of the House of Councillors initially increased, as the LDP continued to govern alone and did not hold a two-thirds majority in the House of Representatives. Crucial legislation had to be negotiated with parts of the opposition. The most prominent example was the so-called "PKO Diet" (ja:PKO国会, PKO Kokkai) of 1992 when the LDP negotiated and passed the peace-keeping operations bill with centre-left/right-of-JSP opposition parties (DSP and Kōmeitō) against fierce opposition from JSP and JCP; the PKO law became the base for the Self-Defense Forces' first (ground) deployment abroad as part of the UN mission in Cambodia. After the 1993 House of Representatives election, with the exception of a brief minority government in 1994, coalition governments or the confidence and supply arrangement during the restored LDP single-party government ensured legislative government majorities until the opposition victory in the 1998 House of Councillors election which led to the formation of another coalition government by 1999.
The legislative two-thirds override power of the House of Representatives was never used between 1950s and 2008 when the LDP-Kōmeitō coalition government had lost the House of Councillors majority in the 2007 election, but did control a two-thirds majority in the House of Representatives since 2005. After that, it has been used somewhat more frequently (see ja:衆議院の再議決, Shūgin no saikaketsu, ~"Override decisions by the House of Representatives" for a list). If a government controls a two-thirds majority in the House of Representatives and is willing to use it, the House of Councillors can only delay a bill, but not prevent passage.
Opposition control of the House of Councillors is often summarized by the term nejire Kokkai (ja:ねじれ国会, "twisted" or "skewed" Diet). Setting aside the immediate postwar years, when many governments were in the minority in the upper house, but the strongest force, the centrist Ryokufūkai, was not in all-out opposition to either centre-left or centre-right governments and willing to cooperate, the Diet was "twisted" from 1989 to 1993, 1998–1999, 2007–2009, and most recently 2010–2013.
"Gridlock" and reform proposals
[edit]In recent years, many constitutional revision advocates call for reforming the role of the House of Councillors ("carbon copy" of the House of Representatives or "recalcitrant naysayer") or abolishing it altogether to "prevent political paralysis", after the recently more frequent twisted Diets have seen an increase in inter-chamber friction/"political nightmare"s.[10][11] Examples of high-stakes, internationally noted conflicts in recent twisted Diets:
- In 2008, two nominees for BoJ governor by the Fukuda Cabinet (Toshirō Mutō, Kōji Tanami) were rejected by the DPJ-led opposition in the House of Councillors, and the SDF naval support mission for NATO/OEF in the Indian Ocean had to be interrupted for one month while the extension of the anti-terrorism law was delayed by the extended legislative proceedings necessary to override the House of Councillors rejection.
- In 2011, the Kan Cabinet struggled to pass a renewable energy bill and a bond ceiling increase (unlike the budget itself subject to the normal legislative procedure) against the LDP-led opposition majority in the House of Councillors until it negotiated a deal with the LDP in exchange for child allowance reform and the cabinet's resignation which Kan had already announced, but conditioned on the passage of the bills.[12][13]
Membership and elections
[edit]Article 102 of the Japanese Constitution provided that half of the councillors elected in the first House of Councillors election in 1947 would be up for re-election three years later in order to introduce staggered six-year terms.
The House initially had 250 seats. Two seats were added to the House in 1970 after the agreement on the repatriation of Okinawa, increasing the House to a total of 252.[14] Legislation aimed at addressing malapportionment that favoured less populated prefectures was introduced in 2000; this resulted in ten seats being removed (five each at the 2001 and 2004 elections), bringing the total number of seats to 242.[14] Further reforms to address malapportionment took effect in 2007 and 2016, but did not change the total number of members in the house.[14]
From 1947 to 1983, the House had 100 seats allocated to a national block (全国区, zenkoku-ku), of which fifty seats were allocated in each election.[14] It was originally intended to give nationally prominent figures a route to the House without going through local electioneering processes.[citation needed] Some national political figures, such as feminists Shidzue Katō and Fusae Ichikawa and former Imperial Army general Kazushige Ugaki, were elected through the block, along with a number of celebrities such as comedian Yukio Aoshima (later Governor of Tokyo), journalist Hideo Den and actress Yūko Mochizuki.[citation needed] Shintaro Ishihara won a record 3 million votes in the national block in the 1968 election.[citation needed] The national block was last seen in the 1980 election and was replaced with a nationwide proportional representation block in the 1983 election.[14] The national proportional representation block was reduced to 96 members in the 2000 reforms.[14]
Current composition
[edit]This section needs to be updated. (April 2024) |

| |||||||||
| Caucus (English name)[16] (domestic name) |
Parties | Members | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Term | Total | ||||||||
| 29 July 2019 – 28 July 2025 (elected 2019, up 2025) |
26 July 2022 – 25 July 2028 (elected 2022, up 2028) | ||||||||
| PR | SNTV/FPTP | Subtotal | PR | SNTV/FPTP | Subtotal | ||||
| Government | 25 | 39 | 64 | 24 | 51 | 75 | 139 | ||
| Liberal Democratic Party Jiyūminshutō |
Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) | 19 | 32 | 51 | 18 | 44 | 62 | 113 | |
| Komeito Kōmeitō |
Komeito | 6 | 7 | 13 | 6 | 7 | 13 | 26 | |
| Opposition | 22 | 25 | 47 | 24 | 18 | 42 | 89 | ||
| The Constitutional Democratic Party of Japan and Social Democratic Party Rikken-minshu / Shamin / Mushozoku |
Constitutional Democratic Party (CDP) Social Democratic Party (SDP) Independents |
9 | 15 | 24 | 8 | 9 | 17 | 41 | |
| Nippon Ishin (Japan Innovation Party) and Free Education For All Nippon Ishin no Kai / Kyōiku mushō-ka o jitsugen suru Kai |
Nippon Ishin no Kai Free Education For All (FEFA) |
3 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 12 | 18 | |
| Democratic Party For the People and The Shin-Ryokufukai Kokumin-minshutō / Shin-Ryokufūkai |
Democratic Party For the People (DPFP) Independents |
3 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 11 | |
| Japanese Communist Party Nihon Kyōsantō |
Japanese Communist Party (JCP) | 4 | 3 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 10 | |
| Reiwa Shinsengumi Reiwa Shinsengumi |
Reiwa Shinsengumi | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 5 | |
| The Party to Protect People from NHK NHK kara kokumin o mamoru tō |
The Party to Protect the People from NHK | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | |
| Okinawa Whirlwind Okinawa no Kaze |
Okinawa Social Mass Party | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Independents (government & opposition) | 1 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 10 | ||
| Independents Members not affiliated with any parliamentary caucus |
LDP 1 (President) CDP 1 (Vice President) Sanseitō 1 Independents 8 | ||||||||
| Total | 48 | 69 | 117 | 49 | 72 | 121 | 238 | ||
| Vacant: the Iwate seat in the 2022 class (by-election due October 27, 2024), 6 more majoritarian seats, three from Tokyo and one each from Kanagawa, Osaka and Wakayama (no by-elections before 2025), three proportional seats (to be filled by runners-up shortly) |
N/A | 2 | 5 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 10 | |
For a list of individual members, see the List of members of the Diet of Japan#House of Councillors.
Latest election
[edit]List of House of Councillors regular elections
[edit]20th century
[edit]| Election | Cabinet | Prime Minister | Date | Turnout | Total seats |
Elected seats |
Term expiration date |
Majority party / Seats share | Emperor (Reign) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Yoshida I | Shigeru Yoshida | 20 April 1947 | 61.12% | 250 | 250 | 2 May 1953 | Socialist | 47 | 18.80% | Shōwa (1926–1989)
| |
| 2nd | Yoshida III | 4 June 1950 | 72.19% | 125 | 3 June 1956 | Liberal | 76 | 30.40% | ||||
| 3rd | Yoshida IV | 24 April 1953 | 63.18% | 2 May 1959 | 93 | 37.20% | ||||||
| 4th | I. Hatoyama III | Ichirō Hatoyama | 8 July 1956 | 62.11% | 7 July 1962 | Liberal Democratic | 122 | 48.80% | ||||
| 5th | Kishi II | Nobusuke Kishi | 2 June 1959 | 58.75% | 1 June 1965 | 132 | 52.80% | |||||
| 6th | Ikeda II | Hayato Ikeda | 1 July 1962 | 68.22% | 7 July 1968 | 142 | 56.80% | |||||
| 7th | Satō I | Eisaku Satō | 4 July 1965 | 67.02% | 1 July 1971 | 140 | 55.77% | |||||
| 8th | Satō II | 7 July 1968 | 68.94% | 7 July 1974 | 142 | 54.80% | ||||||
| 9th | Satō III | 27 June 1971 | 59.24% | 252 | 126 | 10 July 1977 | 131 | 52.61% | ||||
| 10th | K. Tanaka II | Kakuei Tanaka | 7 July 1974 | 73.20% | 7 July 1980 | 126 | 50.40% | |||||
| 11th | T. Fukuda | Takeo Fukuda | 10 July 1977 | 68.49% | 9 July 1983 | 124 | 49.79% | |||||
| 12th | Ōhira II | Masayoshi Ōhira | 22 June 1980 | 74.54% | 7 July 1986 | 135 | 54.00% | |||||
| 13th | Nakasone I | Yasuhiro Nakasone | 26 June 1983 | 57.00% | 9 July 1989 | 137 | 54.36% | |||||
| 14th | Nakasone II (R2) | 6 July 1986 | 71.36% | 7 July 1992 | 143 | 56.74% | ||||||
| 15th | Uno | Sōsuke Uno | 23 July 1989 | 65.02% | 252 | 126 | 22 July 1995 | 109 | 43.25% | Akihito (Heisei) (1989–2019)
| ||
| 16th | Miyazawa | Kiichi Miyazawa | 26 July 1992 | 50.72% | 25 July 1998 | 107 | 42.46% | |||||
| 17th | Murayama | Tomiichi Murayama | 23 July 1995 | 44.52% | 22 July 2001 | 111 | 44.04% | |||||
| 18th | Hashimoto II (R) | Ryutaro Hashimoto | 12 July 1998 | 58.84% | 25 July 2004 | 103 | 40.87% | |||||
| Election | Cabinet | Prime Minister | Date | Turnout | Total seats |
Elected seats |
Term expiration date |
Majority party / Seats share | Emperor (Reign) | |||
21st century
[edit]| Election | Cabinet | Prime Minister | Date | Turnout | Total seats |
Elected seats |
Term expiration date |
Majority party / Seats share | Emperor (Reign) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19th | Koizumi I | Junichiro Koizumi | 29 July 2001 | 56.44% | 247 | 121 | 28 July 2007 | Liberal Democratic | 111 | 44.93% | Akihito (Heisei) (1989–2019)
| |
| 20th | Koizumi II | 11 July 2004 | 56.57% | 242 | 25 July 2010 | 115 | 47.52% | |||||
| 21st | S. Abe I | Shinzo Abe | 29 July 2007 | 58.64% | 28 July 2013 | Democratic | 109 | 45.04% | ||||
| 22nd | Kan | Naoto Kan | 11 July 2010 | 57.92% | 25 July 2016 | 106 | 43.80% | |||||
| 23rd | S. Abe II | Shinzo Abe | 21 July 2013 | 52.61% | 28 July 2019 | Liberal Democratic | 115 | 47.52% | ||||
| 24th | S. Abe III (R1) | 10 July 2016 | 54.70% | 25 July 2022 | 121 | 50.00% | ||||||
| 25th | S. Abe IV (R1) | 21 July 2019 | 48.80% | 245 | 124 | 28 July 2025 | 113 | 46.12% | Naruhito (Reiwa) (2019–present)
| |||
| 26th | Kishida II | Fumio Kishida | 10 July 2022 | 52.05% | 248 | 25 July 2028 | 119 | 47.98% | ||||
| Election | Cabinet | Prime Minister | Date | Turnout | Total seats |
Elected seats |
Term expiration date |
Majority party / Seats share | Emperor (Reign) | |||
See also
[edit]- President of the House of Councillors
- List of current members of the House of Councillors
- List of districts of the House of Councillors of Japan
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- Specific
- ^ Hayes 2009, p. 50
- ^ a b Fahey, Rob (18 July 2019). "Japan Explained: The House of Councilors - Tokyo Review". Archived from the original on 16 April 2021. Retrieved 9 April 2021.
- ^ House of Representatives: Diet functions: Diagram of (the) Legislative Procedure Archived 2021-09-12 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Thies M.F., Yanai Y. (2013) Governance with a Twist: How Bicameralism Affects Japanese Lawmaking. In: Pekkanen R., Reed S.R., Scheiner E. (eds) Japan Decides 2012. Palgrave Macmillan, London.
- ^ Text (in unreformed script) Archived 2021-10-17 at the Wayback Machine and English translation Archived 2021-03-08 at the Wayback Machine, Wikisource
- ^ Text Archived 2021-06-28 at the Wayback Machine and English translation Archived 2021-10-16 at the Wayback Machine, House of Councillors
- ^ Text Archived 2021-05-12 at the Wayback Machine, House of Councillors
- ^ HC rules: Text Archived 2021-11-09 at the Wayback Machine and English translation Archived 2021-11-20 at the Wayback Machine, House of Councillors; HR rules: Text Archived 2021-09-23 at the Wayback Machine, House of Representatives.
- ^ Thies M.F., Yanai Y. (2014): Bicameralism vs. Parliamentarism: Lessons from Japan's Twisted Diet, Journal of Electoral Studies 30 (2), 60-74. (J-STAGE Archived 2021-09-13 at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ Reiko, Oyama (30 June 2015). "The Rightful Role of the House of Councillors". nippon.com (Nippon Foundation). Archived from the original on 18 October 2021. Retrieved 9 April 2021.
- ^ Takenaka Harukata, July 20, 2011: Why Japanese Politics Is at a Standstill Archived 2021-09-12 at the Wayback Machine, nippon.com (Nippon Foundation), retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ Risa Maeda, Shinichi Saoshiro, Reuters, July 5, 2011: Japan opposition sets conditions for energy bill Archived 2021-09-12 at the Wayback Machine, retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ Hiroko Tabuchi, The New York Times, August 23, 2011: Japan's Prime Minister Likely to Resign, Minister Says Archived 2021-09-12 at the Wayback Machine, retrieved September 12, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f 参議院議員選挙制度の変遷 [Changes to the electoral system of the House of Councillors] (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 27 July 2018. Retrieved 12 December 2016.
- ^ "会派名及び会派別所属議員数". 参議院 House of Councillors, The National Diet of Japan. 2024. Retrieved 2024-10-21.
- ^ "Strength of the Political Groups in the House of Councillors". House of Councillors. Retrieved 2022-12-23.
- Bibliography
- Hayes, L. D., 2009. Introduction to Japanese Politics. 5th ed. New York: M.E. Sharpe. ISBN 978-0-7656-2279-2
External links
[edit]- House of Councillors Website (in English)
- House of Councillors internet TV - Official site (in Japanese)
