J wave
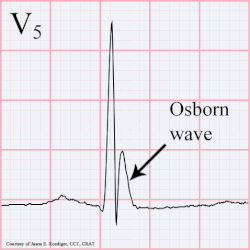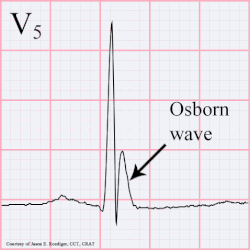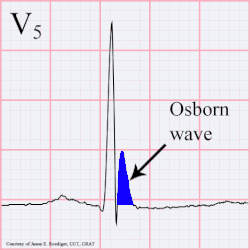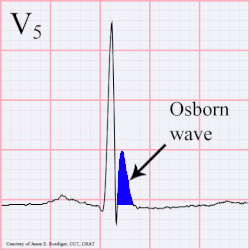

A J wave — also known as Osborn wave, camel-hump sign, late delta wave, hathook junction, hypothermic wave,[1] K wave, H wave or current of injury — is an abnormal electrocardiogram finding.[2]
J waves are positive deflections occurring at the junction between the QRS complex and the ST segment,[3][4] where the S point, also known as the J point, has a myocardial infarction-like elevation.
Causes
[edit]They are usually observed in people suffering from hypothermia with a temperature of less than 32 °C (90 °F),[5] though they may also occur in people with very high blood levels of calcium (hypercalcemia), brain injury, vasospastic angina, acute pericarditis, or they could also be a normal variant.[citation needed] Osborn waves on ECG are frequent during targeted temperature management (TTM) after cardiac arrest, particularly in patients treated with 33 °C.[6] Osborn waves are not associated with increased risk of ventricular arrhythmia, and may be considered a benign physiological phenomenon, associated with lower mortality in univariable analyses.[6]
History
[edit]The prominent J deflection attributed to hypothermia was first reported in 1938 by Tomaszewski. These waves were then definitively described in 1953 by John J. Osborn (1917–2014) and were named in his honor.[7] Over time, the wave has increasingly been referred to as a J wave, though is still sometimes referred to as the Osborn wave in most part due to Osborn's article in the American Journal of Physiology on experimental hypothermia.[8]
References
[edit]- ^ Aydin M, Gursurer M, Bayraktaroglu T, Kulah E, Onuk T (2005). "Prominent J wave (Osborn wave) with coincidental hypothermia in a 64-year-old woman". Tex Heart Inst J. 32 (1): 105. PMC 555838. PMID 15902836.
- ^ Maruyama M, Kobayashi Y, Kodani E, et al. (2004). "Osborn waves: history and significance". Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 4 (1): 33–9. PMC 1501063. PMID 16943886. Archived from the original on 2011-06-15. Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- ^ "ecg_6lead018.html". Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- ^ "THE MERCK MANUAL OF GERIATRICS, Ch. 67, Hyperthermia and Hypothermia, Fig. 67-1". Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- ^ Marx, John (2010). Rosen's emergency medicine: concepts and clinical practice 7th edition. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier. p. 1869. ISBN 978-0-323-05472-0.
- ^ a b Hadziselimovic, Edina; Thomsen, Jakob Hartvig; Kjaergaard, Jesper; Køber, Lars; Graff, Claus; Pehrson, Steen; Nielsen, Niklas; Erlinge, David; Frydland, Martin; Wiberg, Sebastian; Hassager, Christian (July 2018). "Osborn waves following out-of-hospital cardiac arrest—Effect of level of temperature management and risk of arrhythmia and death". Resuscitation. 128: 119–125. doi:10.1016/j.resuscitation.2018.04.037. PMID 29723608.
- ^ Osborn, J. J. (1953). "Experimental hypothermia: Respiratory and blood pH changes in relation to cardiac function". Am J Physiol. 175 (3): 389–398. doi:10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.175.3.389. PMID 13114420.
- ^ Serafi, S.; Vliek, C.; Taremi, M. (2011). "Osborn waves in a hypothermic patient". Journal of Community Hospital Internal Medicine Perspectives. 1 (4). Article: 10742. doi:10.3402/jchimp.v1i4.10742. PMC 3714046. PMID 23882340.
