Hamamatsu
Hamamatsu
浜松市 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| Nickname: "City of Music" | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
 Location of Hamamatsu in Shizuoka Prefecture | |||||||||
| Coordinates: 34°42′39″N 137°43′39″E / 34.71083°N 137.72750°E | |||||||||
| Country | Japan | ||||||||
| Region | Chūbu (Tōkai) | ||||||||
| Prefecture | Shizuoka | ||||||||
| Government | |||||||||
| • Mayor | Yusuke Nakano | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• Total | 1,558.06 km2 (601.57 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population (September 1, 2023) | |||||||||
• Total | 780,128 | ||||||||
| • Density | 500/km2 (1,300/sq mi) | ||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) | ||||||||
| Phone number | 53-457-2111 | ||||||||
| Address | 103-2 Motoshiro-chō, Chūō-ku, Hamamatsu-shi, Shizuoka-ken 430-8652 | ||||||||
| Climate | Cfa | ||||||||
| Website | www | ||||||||
| Symbols | |||||||||
| Bird | Japanese bush warbler | ||||||||
| Flower | Mikan | ||||||||
| Tree | Pine | ||||||||
Hamamatsu (浜松市, Hamamatsu-shi) is a city located in western Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan. In September 2023, the city had an estimated population of 780,128 in 340,591 households,[1] making it the prefecture's largest city, with a population density of 500/km2 (1,300/sq mi) over the total urban area of 1,558.06 km2 (601.57 sq mi).
Overview
[edit]Hamamatsu is a member of the World Health Organization's Alliance for Healthy Cities (AFHC).[2]
History
[edit]Prehistoric ages
[edit]The area now comprising Hamamatsu has been settled since prehistoric times, with numerous remains from the Jōmon period and Kofun period having been discovered within the present city limits, including the Shijimizuka site shell mound and the Akamonue Kofun ancient tomb.
Ancient ages
[edit]In the Nara period, it became the capital of Tōtōmi Province.
Feudal period
[edit]During the Sengoku period, Hamamatsu Castle was the home of future shōgun Tokugawa Ieyasu.
-
Takane Castle
-
Battle of Mikatagahara (1573)
Early modern ages
[edit]Hamamatsu flourished during the Edo period under a succession of daimyō rulers as a castle town, and as a post town on the Tōkaidō highway connecting Edo with Kyoto.
Late modern ages
[edit]After the Meiji Restoration, Hamamatsu became a short-lived prefecture from 1871 to 1876, after which it was united with Shizuoka Prefecture. Hamamatsu Station opened on the Tōkaidō Main Line in 1889.
The same year, with the establishment of the modern municipalities system, Hamamatsu became a town.
- July 1, 1911: Hamamatsu is upgraded from a town to a city
- 1918: Rice riots of 1918 affect Hamamatsu
- 1921: The village of Tenjinchō merges with Hamamatsu
- 1926: Imperial Japanese Army Hamamatsu Air Base opens
- 1933: Imperial Japanese Army Flight School opens
- 1936: The villages of Hikuma and Fujizuka merge with Hamamatsu
- December 7, 1944: Tonankai earthquake causes much damage
- June 1945: Hamamatsu largely destroyed by US air raids
-
Hirokoji Street in the 1930s
-
Nippon Gakki Seizo Kabushiki Kaisha headquarter & factory (1935)
Contemporary ages
[edit]- 1948: Hamamatsu Incident, ethnic rioting of Zainichi Korean residents.
- 1951: The villages of Aratsu, Goto, and Kawarin merge with Hamamatsu
- 1954: Eight villages in Hamana District merge with Hamamatsu
- 1955: The village of Miyakoda merges with Hamamatsu
- 1957: The village of Irino merges with Hamamatsu
- 1960: The village of Seto merges with Hamamatsu
- 1961: The village of Shinohara merges with Hamamatsu
- 1965: The village of Shonai merges with Hamamatsu
- May 1, 1990: Hamamatsu Arena opened
- January 1, 1991: The village of Kami in Hamana District merges with Hamamatsu.
- April 1, 1991: The first Hamamatsu International Piano Competition was held.
- May 1, 1994: Act City Tower opened.
- October 1, 1995: Hamamatsu Museum of Musical Instruments opened.
- April 1, 1996: Hamamatsu is designated a core city by the central government.
- June 1, 1996: Hamamatsu City Fruit Park opened.
- April 1, 1997: Hamamatsu is designated as an Omnibus Town.
- April 1, 1998: Act City Musical School opened.
- April 3, 2000: Shizuoka University of Art and Culture opened.
- July 1, 2001: The city's 90th anniversary is commemorated
- August 1, 2002: Launched the conference on Pan-Hamanako Designated City Simulation.
- April 1, 2003: Shizuoka New Kawafuji National High School Competition was held.
- June 1, 2003: Launched Tenryūgawa-Hamanako Region Merger Conference.
- April 8 – October 11, 2004: Pacific Flora 2004 (Shizuoka International Garden and Horticulture Exhibition) was held at Hamanako Garden Park.
- July 1, 2005: Hamamatsu absorbed the cities of Hamakita and Tenryū; the town of Haruno (from Shūchi District), the towns of Hosoe, Inasa and Mikkabi (all from Inasa District), the towns of Misakubo and Sakuma, the village of Tatsuyama (all from Iwata District), and the towns of Maisaka and Yūtō (both from Hamana District) were merged into Hamamatsu.[3][4] Inasa District and Iwata District were both dissolved as a result of this merger. Therefore, there are no more villages left in Shizuoka Prefecture.
- April 1, 2007: Hamamatsu became a city designated by government ordinance by the central government.
Cityscapes
[edit]-
City views from Hamamatsu Castle
-
CBD of Hamamatsu
-
Part of Hamamatsu Skyline
-
Skyline of Hamamatsu
-
Yūrakugai
-
Night view of Hamamatsu
Geography
[edit]




Hamamatsu is 260 kilometres (160 mi) southwest of Tokyo.[5]
Hamamatsu consists of a flat plain and the Mikatahara Plateau in the south, and a mountainous area in the north. It is roughly bordered by Lake Hamana to the west, the Tenryū River to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the south.
Climate
[edit]The climate in southern Hamamatsu has a humid subtropical climate with cool to mild winters with little snowfall; however, it is windy in winter because of the dry monsoon called Enshū no Karakaze, which is unique to the region. The climate in northern Hamamatsu is much harsher because of foehn winds. Summer is hot with the highest temperature often exceeds 35 degrees in the Tenryu-ku area, while it snows in winter.
| Climate data for Hamamatsu (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1882−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.7 (69.3) |
23.6 (74.5) |
24.9 (76.8) |
28.1 (82.6) |
31.8 (89.2) |
36.7 (98.1) |
39.2 (102.6) |
41.1 (106.0) |
36.6 (97.9) |
32.1 (89.8) |
27.8 (82.0) |
23.2 (73.8) |
41.1 (106.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 10.6 (51.1) |
11.5 (52.7) |
15.0 (59.0) |
19.6 (67.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
26.6 (79.9) |
30.3 (86.5) |
31.8 (89.2) |
28.8 (83.8) |
23.6 (74.5) |
18.6 (65.5) |
13.2 (55.8) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.3 (43.3) |
6.8 (44.2) |
10.3 (50.5) |
15.0 (59.0) |
19.3 (66.7) |
22.6 (72.7) |
26.3 (79.3) |
27.8 (82.0) |
24.9 (76.8) |
19.6 (67.3) |
14.2 (57.6) |
8.8 (47.8) |
16.8 (62.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 2.4 (36.3) |
2.7 (36.9) |
5.7 (42.3) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.3 (59.5) |
19.4 (66.9) |
23.4 (74.1) |
24.7 (76.5) |
21.5 (70.7) |
16.2 (61.2) |
10.4 (50.7) |
4.8 (40.6) |
13.1 (55.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −6.0 (21.2) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
0.0 (32.0) |
4.7 (40.5) |
10.4 (50.7) |
15.3 (59.5) |
16.8 (62.2) |
12.4 (54.3) |
3.8 (38.8) |
0.1 (32.2) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 59.2 (2.33) |
76.8 (3.02) |
147.1 (5.79) |
179.2 (7.06) |
191.9 (7.56) |
224.5 (8.84) |
209.3 (8.24) |
126.8 (4.99) |
246.1 (9.69) |
207.1 (8.15) |
112.6 (4.43) |
62.7 (2.47) |
1,843.2 (72.57) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 5.9 | 6.5 | 9.8 | 10.4 | 10.8 | 13.1 | 11.9 | 8.4 | 11.9 | 10.9 | 7.5 | 6.3 | 113.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 57 | 56 | 59 | 65 | 70 | 78 | 77 | 76 | 74 | 72 | 64 | 61 | 67 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 206.6 | 187.8 | 201.9 | 199.7 | 205.1 | 148.1 | 176.3 | 211.4 | 166.7 | 162.6 | 171.8 | 200.1 | 2,237.9 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[6] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Sakuma, Hamamatsu (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1978−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.8 (64.0) |
23.0 (73.4) |
26.3 (79.3) |
31.9 (89.4) |
34.1 (93.4) |
36.9 (98.4) |
40.2 (104.4) |
39.6 (103.3) |
37.3 (99.1) |
33.6 (92.5) |
25.7 (78.3) |
23.0 (73.4) |
40.2 (104.4) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 9.7 (49.5) |
11.1 (52.0) |
14.9 (58.8) |
20.2 (68.4) |
24.8 (76.6) |
27.5 (81.5) |
31.3 (88.3) |
32.9 (91.2) |
28.9 (84.0) |
23.2 (73.8) |
17.3 (63.1) |
11.8 (53.2) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.1 (37.6) |
4.3 (39.7) |
7.9 (46.2) |
13.1 (55.6) |
17.9 (64.2) |
21.5 (70.7) |
25.2 (77.4) |
26.3 (79.3) |
22.8 (73.0) |
16.9 (62.4) |
10.6 (51.1) |
5.2 (41.4) |
14.6 (58.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −1.5 (29.3) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
2.3 (36.1) |
7.2 (45.0) |
12.4 (54.3) |
17.3 (63.1) |
21.3 (70.3) |
22.3 (72.1) |
19.0 (66.2) |
12.8 (55.0) |
6.2 (43.2) |
0.7 (33.3) |
9.9 (49.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −7.1 (19.2) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
3.3 (37.9) |
9.0 (48.2) |
15.3 (59.5) |
16.4 (61.5) |
9.8 (49.6) |
2.4 (36.3) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 71.0 (2.80) |
97.6 (3.84) |
184.1 (7.25) |
193.5 (7.62) |
192.0 (7.56) |
265.6 (10.46) |
339.1 (13.35) |
225.9 (8.89) |
320.9 (12.63) |
223.5 (8.80) |
120.8 (4.76) |
78.1 (3.07) |
2,344 (92.28) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 6.5 | 6.7 | 9.9 | 10.2 | 10.7 | 13.0 | 13.6 | 11.0 | 11.7 | 10.6 | 7.2 | 6.8 | 117.9 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 152.9 | 167.1 | 187.4 | 194.0 | 194.0 | 138.0 | 156.4 | 187.4 | 148.2 | 163.1 | 151.7 | 142.4 | 1,982.5 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[7][8] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
[edit]Per Japanese census data,[9] the population of Hamamatsu has been increasing over the past 70 years.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1940 | 434,253 | — |
| 1950 | 494,296 | +13.8% |
| 1960 | 568,214 | +15.0% |
| 1970 | 631,284 | +11.1% |
| 1980 | 698,982 | +10.7% |
| 1990 | 751,509 | +7.5% |
| 2000 | 786,306 | +4.6% |
| 2010 | 800,912 | +1.9% |
| 2020 | 790,718 | −1.3% |
Foreign population
[edit]
Hamamatsu has a significant non-Japanese population. The population of Nikkei foreigners, especially Brazilians, increased after a 1990 change in Japanese immigration law allowed them to work in Japan. At one point, Hamamatsu had the largest Brazilian Nikkei population of any Japanese city.[10] Many foreigners work in the manufacturing sector, taking temporary jobs in Honda, Suzuki, and Yamaha plants.[5] As of 2008[update] the number of non-Japanese in Hamamatsu was 33,332,[11] and by 2010 the number exceeded 30,000. The city has a lot of Portuguese signage. It includes a Brazilian school, and many businesses catering to Brazilians display Brazilian flags.[10] However, Natsuko Fukue of The Japan Times wrote in 2010 that many foreign children have difficulty integrating to society in Hamamatsu because "Japanese and foreign communities live largely separate from one another."[5]
The foreign population dropped significantly in the aftermath of the global financial crisis in 2008, with the Hamamatsu city government offering aid for some foreign nationals to return to their home countries.[12] The foreign population was estimated as 25,084 as of August 1, 2019, per official city statistics.[13]
Neighboring municipalities
[edit]Government
[edit]
Hamamatsu has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city legislature of 46 members. The city contributes 15 members to the Shizuoka Prefectural Assembly.
Wards
[edit]Hamamatsu is administratively divided into three wards:
| Name | Area (km2) | Population (Oct 2023) | Pop Density |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chūō-ku (中央区) | 268.45 | 608,145 | |
| Hamana-ku (浜名区) | 345.77 | 155,996 | |
| Tenryū-ku (天竜区) | 943.84 | 24,515 |
Reorganization
[edit]On 1 January 2024, the number of wards will be reduced from seven to three as part of a municipal reorganization. Naka-ku, Higashi-ku, Nishi-ku, Minami-ku and Kita-ku will be merged into a new Chūō-ku, Hamakita-ku and Kita-ku will become Hamana-ku, while Tenryu-ku will remain unchanged. The reorganization was initially approved by a referendum held on April 7, 2019.[14]
Economy
[edit]


Hamamatsu has been famous as an industrial city, especially for musical instruments and motorcycles. It also has been known for fabric industry, but most of those companies and factories went out of business in the 1990s. As of 2010, Greater Hamamatsu, Hamamatsu Metropolitan Employment Area, has a GDP of US$54.3 billion.[15][16] 2014 Hamamatsu's GDP per capita(PPP) was US$41,470.[17]
Companies headquartered in Hamamatsu
[edit]- Enkei Corporation[18]
- Hamamatsu Photonics K.K.[19]
- Kawai Musical Instruments Mfg.
- Roland Corporation
- Suzuki Motor Co.
- Tōkai Gakki (also known as Tokai Guitars Company Ltd.)
- Yamaha Corporation
Companies founded in Hamamatsu
[edit]Media
[edit]Radio stations
[edit]- FM Haro! (JOZZ6AB FM, 76.1 MHz)
- K-MIX (JOKU FM, 78.4 MHz)
- NHK FM (JOPK FM, 82.1 MHz)
- SBS Radio (1404 kHz / 94.7 MHz)
- (in Portuguese) Radio Phoenix (internet)[20]
Transportation
[edit]


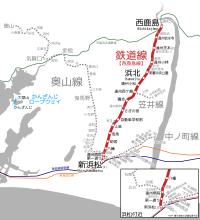

Airways
[edit]Airport
[edit]There are no civilian airports in Hamamatsu. Shizuoka Airport (34°47′46″N 138°11′22″E / 34.796111°N 138.189444°E) is the closest, located 43 kilometres (27 mi) from Hamamatsu Station, between Makinohara and Shimada.
Chūbu Centrair International Airport in Aichi Prefecture, located about 87 kilometres (54 mi)[21] west of the city, is the second closest.
Railways
[edit]High-Speed Rail
[edit]- Tōkaidō Shinkansen: - Hamamatsu -
- JR Central Hamamatsu workshop: maintenance facility for the Tōkaidō Shinkansen[22]
Conventional Lines
[edit]- Tōkaidō Main Line: - Tenryūgawa • Hamamatsu • Takatsuka • Maisaka • Bentenjima -
- Iida Line: - Izumma • Kamiichiba • Urakawa • Hayase • Shimokawai • Chūbu-Tenryū • Sakuma • Aizuki • Shironishi • Mukaichiba • Misakubo • Ōzore • Kowada -
- Enshū Railway Line: - Shin-Hamamatsu • Dai-Ichi-dōri • Enshū-Byōin • Hachiman • Sukenobu • Enshū-Hikuma • Enshū-Kamijima • Jidōsha-Gakkō-Mae • Saginomiya • Sekishi • Enshū-Nishigasaki • Enshū-Komatsu • Hamakita • Misono-Chūō-kōen • Enshū-Kobayashi • Enshū-Shibamoto • Enshū-Gansuiji • Nishi-Kajima
- Tenryū Hamanako Line: - Tenryū-Futamata • Futamata-Hommachi • Nishi-Kajima • Gansuiji • Miyaguchi • Fruit Park • Miyakoda • Hamamatsudaigakumae • Kanasashi • Kigakōkōmae • Kiga • Nishi-Kiga • Sunza • Hamanako-Sakume • Higashi-Tsuzuki • Tsuzuki • Mikkabi • Okuhamanako • Ona -
Roads
[edit]Expressways
[edit] Tōmei Expressway (Hamamatsu interchange, Hamamatsu Nishi interchange, and Mikkabi interchange)
Tōmei Expressway (Hamamatsu interchange, Hamamatsu Nishi interchange, and Mikkabi interchange) Shin-Tōmei Expressway
Shin-Tōmei Expressway
Hiways
[edit] San-en Nanshin Expressway (under construction)
San-en Nanshin Expressway (under construction)
Bypasses
[edit]- Hamamatsu Bypass
- Hamana Bypass
Japan National Highways
[edit]Education
[edit]


Colleges and universities
[edit]- Hamamatsu Gakuin University
- Hamamatsu University
- Hamamatsu University School of Medicine
- Seirei Christopher University
- Seisa University, Hamamatsu campus
- Shizuoka University (Faculty of Engineering and Faculty of Informatics)
- Shizuoka University of Art and Culture
- Tokoha University, Hamamatsu campus
Primary and secondary schools
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (July 2019) |
Senior high schools operated by Shizuoka Prefecture:
- Shizuoka Prefectural Hamamatsu North High School (静岡県立浜松北高等学校)
- Shizuoka Prefectural Hamamatsu Nishi (West) Senior and Junior High Schools (静岡県立浜松西高等学校・中等部)
- Shizuoka Prefectural Hamamatsu East High School (静岡県立浜松東高等学校)
- Shizuoka Prefectural Hamamatsu South High School (静岡県立浜松南高等学校)
- Shizuoka Prefectural Kiga High School (静岡県立気賀高等学校)
- Shizuoka Prefectural Kohoku High School (静岡県立浜松湖東高等学校)
- Shizuoka Prefectural Mikkabi High School (静岡県立三ヶ日高等学校)
There is one senior high school operated by the city government: Hamamatsu Municipal Senior High School
Elementary and junior high schools are operated by the city government. As of 2008[update], the city had 117 public elementary schools and 52 public junior high schools.[23]
Multicultural education
[edit]The city has the following Brazilian international schools:
- Escola Brasil (former Escola Brasileira de Hamamatsu) – Primary and secondary school[24]
- Escola Alegria de Saber – Primary and secondary school[24]
- Escola Alcance – Primary school[24]
It has one combined Peruvian school (ペルー学校) and Brazilian primary school, Mundo de Alegría.[24][25]
The city formerly hosted other Brazilian schools, Colégio Pitágoras Brasil and Escola Cantinho Feliz.[26]
As of May 1, 2009, the municipal elementary and junior high schools had 1,638 non-Japanese students.[27] As of 2008[update], there were 932 Brazilians enrolled in Hamamatsu's municipal elementary and junior high schools: 646 Brazilians were enrolled in 61 public elementary schools, and 286 Brazilians were enrolled in 38 public junior high schools.[23]
Within public schools Brazilian students have the same academic programs and take the same classes as Japanese nationals.[23] Special teachers and assistants work with foreign students at municipal elementary and junior high schools with significant numbers of non-Japanese enrolled.[28] In particular the schools use their part-time interpreters to assist Brazilian students. The interpreters are not formal teachers, yet Tsutsumi Angela Aparecida of Hamamatsu's Burajiru Fureai Kai wrote that "[t]heir assistance has become very useful".[23] Toshiko Sugino of the National Defense Academy of Japan wrote that the municipal and prefectural schools in Hamamatsu "follow traditional views of education and enforce rigid school rules" despite the reputation of open-mindedness in the residents of Hamamatsu, causing some foreigners to send their non-Japanese children to foreign private schools.[29]
As of 2008, many Brazilian parents have difficulty in deciding whether to send their children to Japanese schools or Brazilian schools, and it is common for Brazilian children attending Japanese schools to switch to a Brazilian school and vice versa.[23] By 2010, many Brazilian parents had lost their jobs due to an economic decline, and many were unable to afford the Brazilian school monthly tuitions of ¥30,000 to ¥40,000.[5]
As of 2010, about 50% of Brazilians of high school age in Hamamatsu do not attend high school. The inability to afford high school and difficulty with Japanese resulted in lower high school attendance rates. Hamamatsu NPO Network Center has made efforts to increase school attendance.[5]
In Hamamatsu volunteers and a non-profit organization have established Japanese-language classes and native language classes for foreign children.[28]
Local attractions
[edit]- Act City Tower Observatory: Hamamatsu's only skyscraper, situated next to JR Hamamatsu Station, is a symbol of the city. It was designed to resemble a harmonica, a reminder that Hamamatsu is sometimes known as the "City of Music". The building houses shopping and a food court, the Okura Hotel, and an observatory on the 45th floor overlooking all of central Hamamatsu, even down to the sand dunes at the shore.
- Chopin Monument This is a 1:1-scale replica of the famous Art Nouveau bronze statue of Chopin by the famed artist Wacław Szymanowski. The original is in Hamamatsu's sister city, Warsaw.
- Gosha Suwa Shrine is a Beppyo shrine in the city. It was formed from a merger of two shrines that were too damaged by the Bombing of Hamamatsu in World War II to be independent.[30]
- Hamamatsu Castle: Hamamatsu Castle Park stretches from the modern city hall building to the north. The castle is located on a hill in the southeast corner of the park, near city hall. It was built by Tokugawa Ieyasu. His rule marks the beginning of the Edo period. Tokugawa Ieyasu lived here from 1571 to 1588. There is a small museum inside, which houses some armor and other relics of the period, as well as a miniature model of how the city might have looked 400 years ago. North of the castle is a large park with a Japanese garden, a koi pond, a ceremonial teahouse, and some commons areas.
- Nakatajima Sand Dunes: one of the three largest sand dune areas in Japan
- Hamamatsu Flower Park
- Hamamatsu Fruit Park
- Hamamatsu Municipal Zoo
- Iinoya-gū shrine
- Motoshirochō Tōshō-gū shrine
-
Hamamatsu Castle
-
Nakatajima Sand Dunes
-
Hamanako Garden Park
-
Hamamatsu Wedding Central Park
-
Lake Hamana
-
Hamamatsu Pacific Ocean
-
Lake Hamana PALPAL
Culture
[edit]
Festivals
[edit]Akiha Fire Festival
[edit]- Haruno, Tenryu-ku: December
Long ago, Mount Akiha was believed to have supernatural powers to prevent fires. Bow and arrow, sword, and fire dances are performed at the Akiha Shrine. At the Akiha Temple, a firewalking ceremony is performed where both believers and spectators celebrate the festival.
Enshū Dainenbutsu
[edit]- Saigagake Museum, Hamamatsu City: July 15
When a family commemorates the first Obon holidays after the death of a loved one, they may request that a dainenbutsu (Buddhist chanting ritual) be performed outside their house. This is one of the local performing arts of the region. The group always forms a procession in front of the house led by a person carrying a lantern and marches to the sound of flutes, Japanese drums and cymbals.
Hamamatsu Kite Festival
[edit]- Naka-ku, Minami-ku, others: May
Hamamatsu Kite Festival is also called Hamamatsu Festival. Hamamatsu Kite Festival held from May 3 to May 5 each year, includes a Tako Gassen, or kite fight, and luxuriously decorated palace-like floats. The festival originated about 430 years ago, when the lord of Hamamatsu Castle celebrated the birth of his first son by flying kites. In the Meiji Era, the celebration of the birth of a first son by flying Hatsu Dako, or the first kite, became popular, and this tradition has survived in the form of Hamamatsu Kite Festival. During the nights of Hamamatsu Kite Festival, people parade downtown carrying over 70 yatai, or palace-lake floats, that are beautifully decorated while playing Japanese traditional festival music. The festival reaches its peak when groups representing the city's various districts compete by energetically marching through the downtown streets.
Hamakita Hiryu Festival
[edit]- Hamakita-ku: June
This festival is held in honor of Ryujin, the god believed to be associated with the Tenryū River, and features a wide variety of events such as the Hamakita takoage (kite flying) event and the Hiryu himatsuri (flying dragon fire festival) which celebrates water, sound, and flame.
Hamamatsu International Piano Competition
[edit]- November
This festival celebrates Hamamatsu's history as a city of musical instruments and music, and brings dozens of the best young pianists from all over the world. It has been held triennially since 1991 at the Act City Concert Hall and Main Hall.
Hamakita Man'yō Festival
[edit]- Hamakita-ku, Hamamatsu: October
This event takes place in Man'yō-no-Mori Park to commemorate the Man'yō period and introduce its culture. As part of the festival, people reenact the ancient past by wearing traditional clothes from the Heian period and presenting Japanese poetry readings.
Inasa Puppet Festival
[edit]- Inasa, Kita-ku: November
One of the few puppet festivals held in Japan, featuring 60 performances of about 30 plays by puppet masters from all over the country. The shows provide a full day of enjoyment for both children and adults.
Princess Road Festival
[edit]- Hosoe, Kita-ku: April
This reenactment of a procession made by the princess in her palanquin along with her entourage of over 100 people including maids, samurai, and servants makes for a splendid scene beneath the cherry blossoms along the Toda River. In the Edo period, princesses enjoyed traveling this road which came to be known as a hime kaidō (princess road).
Samba Festival
[edit]The Hamamatsu Samba Festival is held in the city.[31]
Shoryu Weeping Ume Blossom Festival
[edit]- Inasa, Kita-ku: late February to late March
In Ryusui Garden there is a stream with seven small waterfalls and about 80 weeping ume trees pruned to give the appearance of dragons riding on clouds to the heavens. There are also 200 young trees planted along the mountainside.
Sports
[edit]| Club | Sport | League | Venue | Established |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chunichi Dragons | Baseball | Ce.League | Vantelin Dome Nagoya, Hamamatsu Baseball Stadium | 1936 |
| San-en NeoPhoenix | Basketball | B.League | Toyohashi City General Gymnasium, Hamamatsu Arena | 1965 |
| Honda FC | Soccer | Japan Football League (JFL) | Honda Miyakoda Soccer Stadium | 1971 |
| Agleymina Hamamatsu | Futsal | F.League | Hamamatsu Arena | 1996 |
| Breath Hamamatsu | Volleyball | V.League | Hamamatsu Arena | 2012 |
-
Hamamatsu stadium
Football
[edit]- Honda FC which plays Japan Football League (third division) games at their own Miyakoda Soccer Stadium. Honda competed in the Japan Soccer League's First Division from 1981 to 1991, but chose to relegate itself and not compete in the professional divisions due to parent company Honda's choice to retain team ownership. Many Hamamatsu football fans prefer to follow Júbilo Iwata, across the Tenryū River in Iwata. Júbilo maintains a club shop within Hamamatsu.
- Volare FC Hamamatsu, an autonomous club who competed in the Tokai Regional Football League Division 2 in 2011, flouted plans to either overtake Honda FC or merge with it, but it finished last in the Tokai League and was relegated. Hamamatsu University also keeps a team in the said division, but college teams cannot be promoted to the top three tiers.
Basketball
[edit]- SAN-EN NeoPhoenix plays in the B.League, Japan's first division of professional basketball. The team plays its home games at the Toyohashi City General Gymnasium.
The Hamamatsu Arena was one of the host arenas of the 2006 FIBA World Championship.
Hamamatsu 3x3 FIBA: Placed Second at FIBA World Tour Final in ABU Dhabi in 2016. (Bikramjit Gill, Inderbir Gill, Chiro Kheda)
Women's volleyball
[edit]Hamamatsu was one of the host cities of the official 2010 Women's Volleyball World Championship.
International relations
[edit]Sister cities
[edit]Hamamatsu has ratified Music Culture Exchange Treaty with the following cities (however, of the following Rochester is the only official sister city):
| City | Country | State | Since |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porterville | California | February 16, 1981 (once a sister city of Hosoe, Hamamatsu assumed the sister city honors in 1981) | |
| Camas | Washington | September 29. 1981 (once a sister city of Mikkabi, Hamamatsu assumed the sister city honors in 1981) | |
| Chehalis | Washington | October 22, 1990 (once a sister city of Inasa, Hamamatsu assumed the sister city honors in 1998) | |
| Rochester | New York | October 12, 2006 (once a sister city of Hamamatsu assumed the Music Culture Exchange Treaty honors in 1996) |
Twinned cities
[edit]Hamamatsu is twinned with:
| City | Country | State | Since |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warsaw | Masovian Voivodeship | February 22, 1990[32] | |
| Manaus | Amazonas | June 20, 2008 | |
| Taipei | Special municipality | July 31, 2013 | |
| Bologna | Emilia-Romagna | April 23, 2014 | |
| Bandung | West Java | December 19, 2014 |
Friendship cities
[edit]| City | Country | State | Since |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shenyang | Liaoning | August 28, 2010 | |
| Hangzhou | Zhejiang | April 6, 2012 |
Notable people
[edit]- Hiroshi Amano, 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics winner
- Haruhi Aiso, singer, songwriter
- Barasui, manga artist
- Yuri Chinen, J-pop talent, singer
- Yōsuke Fujigaya, professional football player
- Yuji Fujimoto, politician
- Ken Fujita, professional football player
- Hironoshin Furuhashi, Olympic swimmer
- Kazuhiro Furuhashi, anime movie director
- Tatsuya Furuhashi, professional football player
- Taketoshi Gotoh, professional baseball player
- Akari Hibino, voice actress
- Coco Hayashi, voice actress
- Soichiro Honda, engineer, industrialist, founder of Honda Motor Company
- Yusuke Inuzuka, professional football player
- Yasuhide Ito, composer
- Toshio Kakei, actor
- Takeshi Kamo, Olympic football player
- Yoko Kando, Olympic swimmer
- Naoyuki Kato, illustrator
- Genichi Kawakami, former president of Yamaha
- Keisuke Kinoshita, movie director
- Naoyuki Kinoshita, art historian
- Sanae Kobayashi, voice actress
- Shigetatsu Matsunaga, professional football player
- Takuya Matsuura, professional football player
- Kanako Momota, J-pop singer and leader of Momoiro Clover Z
- Kiiti Morita, mathematician
- Ken Namba, composer
- Jiro Ono, renowned sushi chef
- Yuki Oshitani, professional football player
- Ken'ya Ōsumi, dancer
- Keisuke Ota, professional football player
- Yoshiaki Ota, professional football player
- Fumiya Sankai, Vlogger and actor in the Philippines, recording artist, and a businessman
- Kentaro Sato, composer
- Shinichiro Sawai, movie director, screenwriter
- Goro Shimura, mathematician
- Ryu Shionoya, politician
- Hideto Suzuki, professional football player
- Koji Suzuki, science-fiction writer
- Michio Suzuki, founder of Suzuki Motors
- Yasutomo Suzuki, politician, mayor of Hamamatsu
- Saya Takagi, actress
- Kenjiro Takayanagi, engineer, pioneer in development of the television
- Nobuhiro Takeda, professional football player
- Kenji Tsuruta, manga artist
- Kōji Tsuruta, actor
- Azumi Uehara, J-pop singer
- Hiromi Uehara, Jazz composer, pianist
- Tetsuya Wakuda, Japanese-Born Australian Chef
- Kosuke Yamamoto, professional football player
- Masaaki Yanagishita, professional football player
- Kisho Yano, professional football player
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Hamamatsu City official statistics (in Japanese)
- ^ Alliance for Healthy Cities official home page
- ^ 浜松市. "合併の経緯". 浜松市公式ホームページ (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-02-07.
平成17年7月1日、浜松市、浜北市、天竜市、舞阪町、雄踏町、細江町、引佐町、三ヶ日町、春野町、佐久間町、水窪町及び龍山村の12市町村が合併して、新しい浜松市が誕生しました。
- ^ 住民基本台帳人口移動報告年報 [Annual Report on Population Movement in the Basic Resident Register] (in Japanese). 総務庁統計局. 2005. p. 142.
Tenryu-shi, Hamakita-shi, Haruno-cho, Tatsuyama-mura, Sakuma-cho, Misakubo-cho, Maisaka-cho, Yuto-cho, Hosoe-cho, Inasa-cho, and Mikkabi-cho were incorporated into Hamamatsu-shi as of July 1, 2005.
- ^ a b c d e Fukue, Natsuko. "Nonprofit brings together foreign, Japanese residents in Hamamatsu" (Archive). The Japan Times. March 13, 2010. Retrieved on October 12, 2015.
- ^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved May 19, 2021.
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved April 26, 2022.
- ^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved April 26, 2022.
- ^ Hamamatsu population statistics
- ^ a b Sugino, Toshiko (National Defense Academy of Japan). "Linguistic Challenges and Possibilities of Immigrants In Case of Nikkei Brazilians in Japan" (Country Note on Topics for Breakout Session 4) (Archive). Centre for Education Research and Innovation (CERI), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development See list of reports. p. 1/8. Retrieved on October 12, 2015.
- ^ Aparecida, Tsutsumi Angela (Burajiru Fureai Kai). "The Contradiction Between "Being and Seeming" Reinforces Low Academic Performance " (Archive). US-China Education Review B 2 (2012) p. 217-223. CITED: p. 217.
- ^ Tabuchi, Hiroko (2009-04-22). "Japan Pays Foreign Workers to Go Home, Forever". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2018-03-06.
- ^ Hamamatsu City official statistics (in Japanese)
- ^ "行政区の再編について".
- ^ Yoshitsugu Kanemoto. "Metropolitan Employment Area (MEA) Data". Center for Spatial Information Science, The University of Tokyo.
- ^ Conversion rates – Exchange rates – OECD Data
- ^ "Global Metro Monitor". 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Corporate Outline Archived 2019-09-15 at the Wayback Machine." Enkei Corporation. Retrieved on June 5, 2018.
- ^ "Headquarters Archived 2016-04-20 at the Wayback Machine." Hamamatsu Photonics. Retrieved on February 17, 2015.
- ^ "Radio Phoenix – CONECTOU...TÁ NA PHOENIX". Radiophoenix.jp. Archived from the original on 2013-03-25. Retrieved 2013-03-26.
- ^ From Chūbu Centrair International Airport to Hamamatsu station (34°42′14″N 137°44′05″E / 34.703866°N 137.734759°E) (surveying http://vldb.gsi.go.jp/sokuchi/surveycalc/bl2stf.html Archived 2008-05-18 at the Wayback Machine (in Japanese))
- ^ Semmens, Peter (1997). High Speed in Japan: Shinkansen - The World's Busiest High-speed Railway. Sheffield, UK: Platform 5 Publishing. p. 58. ISBN 1-872524-88-5.
- ^ a b c d e Aparecida, Tsutsumi Angela (Burajiru Fureai Kai). "The Contradiction Between "Being and Seeming" Reinforces Low Academic Performance" (Archive). US-China Education Review B 2 (2012) p. 217-223. CITED: p. 218.
- ^ a b c d "Escolas Brasileiras Homologadas no Japão" (Archive). Embassy of Brazil in Tokyo. Retrieved on October 13, 2015.
- ^ "Ubicación y Acceso." Mundo de Alegría. Retrieved on October 24, 2015. "〒431–0102 Shizuoka-ken Hamamatsu-shi Nishi-ku Yuto-cho Ubumi 9611-1" – Japanese address: "住所 〒431-0102 静岡県 浜松市 西区 雄踏町 宇布見 9611-1"
- ^ "Escolas Brasileiras Homologadas no Japão" (Archive). Embassy of Brazil in Tokyo. February 7, 2008. Retrieved on October 13, 2015.
- ^ Kitawaki, Yasuyuki (北脇保之) (Former mayor of Hamamatsu, Director of the Center for Multilingual Multicultural Education and Research, Tokyo University of Foreign Studies (CEMMER, 東京外国語大学多言語・多文化教育研究センター)). "A Japanese approach to municipal diversity management: The case of Hamamatsu City" (Archive). Managing Diversity: Stronger Communities, Better Cities. Information about the book (Archive). At the Council of Europe website. Retrieved on October 12, 2015. PDF p. 7-8/13.
- ^ a b Kitawaki, Yasuyuki (北脇保之) (Former mayor of Hamamatsu, Director of the Center for Multilingual Multicultural Education and Research, Tokyo University of Foreign Studies (CEMMER, 東京外国語大学多言語・多文化教育研究センター)). "A Japanese approach to municipal diversity management: The case of Hamamatsu City" (Archive). Managing Diversity: Stronger Communities, Better Cities. Information about the book (Archive). At the Council of Europe website. Retrieved on October 12, 2015. PDF p. 8/13.
- ^ Sugino, Toshiko (National Defense Academy of Japan). "Linguistic Challenges and Possibilities of Immigrants In Case of Nikkei Brazilians in Japan" (Country Note on Topics for Breakout Session 4) (Archive). Centre for Education Research and Innovation (CERI), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (See list of reports). p. 4/8. Retrieved on October 12, 2015.
- ^ "Gosha Shrine/Suwa Shrine | iN HAMAMATSU.COM". www.inhamamatsu.com. Retrieved 2023-11-07.
- ^ Kitawaki, Yasuyuki (北脇保之) (Former mayor of Hamamatsu, Director of the Center for Multilingual Multicultural Education and Research, Tokyo University of Foreign Studies (CEMMER, 東京外国語大学多言語・多文化教育研究センター)). "A Japanese approach to municipal diversity management: The case of Hamamatsu City" (Archive). Managing Diversity: Stronger Communities, Better Cities. Information about the book (Archive). At the Council of Europe website. Retrieved on October 12, 2015. PDF p. 9/13.
- ^ "Miasta partnerskie Warszawy". um.warszawa.pl (in Polish). Biuro Promocji Miasta. 2005-05-04. Archived from the original on October 11, 2007. Retrieved 2008-08-29.
External links
[edit]- Official website (in Japanese)
- Hamamatsu City official website (in English)
- In Hamamatsu
 Hamamatsu travel guide from Wikivoyage
Hamamatsu travel guide from Wikivoyage Geographic data related to Hamamatsu at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Hamamatsu at OpenStreetMap- Hamamatsu Daisuki Net (I love Hamamatsu) Archived 2009-09-12 at the Wayback Machine (in English)











































