5'-Guanylyl imidodiphosphate
Appearance
(Redirected from Gpp(NH)p)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Guanosine 5′-(tetrahydrogen 4-imidotriphosphate)
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O5-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2-Amino-6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl} tetrahydrogen 2-imidotriphosphate | |
| Other names
GppNHp; GppNP; GMP-Pnp; GDP-NP
Guanylyl imidodiphosphate 5-Guanylylimidodiphosphate 5′-Guanylyliminodiphosphonate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H17N6O13P3 | |
| Molar mass | 522.196 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
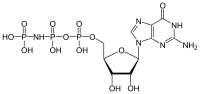
5'-Guanylyl imidodiphosphate (GDPNP) is a purine nucleotide. It is an analog of guanosine triphosphate in which one of the oxygen atoms is replaced with an amine, producing a non-hydrolyzable functional group. Guanylyl imidodiphosphate binds tightly to G-proteins in the presence of Mg2+.[2] Guanylyl imidodiphosphate is a potent stimulator of adenylate cyclase.[2] It is often used in studies of protein synthesis.[3][4]
References
[edit]- ^ Guanosine 5′-β,γ-imidotriphosphate trisodium salt hydrate at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ a b Guanylyl imidodiphosphate at PubChem
- ^ Miller, J.D. & Walter, P. (1993). "A GTPase Cycle in Initiation of Protein Translocation Across the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane". Ciba Foundation Symposium 176 - the GTPase Superfamily. Novartis Foundation Symposia. Vol. 176. pp. 147–163. doi:10.1002/9780470514450.ch10. ISBN 9780470514450. PMID 8299417.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Connolly, T.; et al. (1991). "Requirement of GTP hydrolysis for dissociation of the signal recognition particle from its receptor". Science. 252 (5009): 1171–1173. Bibcode:1991Sci...252.1171C. doi:10.1126/science.252.5009.1171. PMID 1851576. S2CID 42899156.
