George Ștefănescu

George Ștefănescu-Râmnic (20 April 1914 – 29 October 2007) was a contemporary Romanian-German painter.
Radu Carneci wrote of him in 1984:
George Ștefănescu is a great colorist who dares bring together intense colours, as though recalling the fauvistes' age. He does it with a secret harmony descended from both the knowledge of the graphics' progress and from the inheritance creatively used, of painting on glass and other folk Romanian arts.
Thus, the painter has reached a synthesis of the artistic work, with the colour, though important as it is, left in the second plane, meant to support and illustrate the idea.
In this case, the colour plays the same part as with flowers – luring us so that we may better feel their essences, their fragrance.[1]
Biography
[edit]Early life
[edit]George Ștefănescu was born in 1914 in the commune of Plăinești (now Dumbrăveni, Vrancea County), between the cities of Focșani and Râmnicu Sărat. His father Gheorghe was descended from an Aromanian family from Bitola, Macedonia. His mother, Sanda, born Cățănaru, was originally from the commune of Crucea de Jos, Vrancea County. From 1926 to 1933 he attended the secondary school in Râmnicu Sărat. His art teacher recommended him to the church painter Constantinescu and he became the latter's apprentice after school. In 1933, after receiving his baccalaureate, he moved to Bucharest. He took lessons with the painter Ion Theodorescu-Sion, a noted personality in the Romanian art world, for the entrance examination of the Academy of Creative Arts. From 1933 to 1936 he studied at the Academy of Creative Arts in Bucharest in the class of the painter Nicolae Dărăscu.

In 1936, he had his first solo exhibition in a Bucharest art gallery, and also took a study trip to Vrancea and Balcic. In 1937 he attended artillery officer's school, had an exhibition in Craiova with the writer Ion Ionescu; the latter presented his novel Oameni cu buche ("Men with books" / "Literate men"). That year, he also began to sketch designs for women's clothing and fashion accessories for a Bucharest fashion house. He worked for the construction company SONACO, became a member of Sindicatul Artiștilor din România (the Union of Romanian Artists, which included painters, sculptors and graphic artists) and because a student at the well-known private art seminar "Zapan". His professors there were well-known painters such as Lucian Grigorescu, Platon Cazanovici, and Mihail Gheorghiță.
In 1938, together with the fresco painter Alexandru Mazilescu he worked painting murals. In Bukovina, he had the opportunity to observe the well-known wall paintings of the painted monasteries. From 1940 to 1944 he served in the Romanian military during World War II, with a corps that advanced as far as Crimea. During the Axis retreat, his horse stepped on a mine, which exploded, killing the horse, and leaving him with a serious head wound that, for over a decade, left him unable to distinguish colors, which mean that he could not paint and had to seek other work. In 1945 he participated in seminars in theatre directing and set design at ARLUS, led by Professor Ion Sava. He was the teacher of the painter Zwy Milshtein.[citation needed]
In 1946–1947 he was employed at the film production company Filmul Popular, who had a laboratory in Bucharest on Strada Scaune. He worked with some Hungarian specialists to modernize this film laboratory, eventually becoming head of the laboratory. As a result, he was assigned to modernize a film laboratory in Mogoșoaia, owned by the National Tourism Office (Oficiul National de Turism, ONT). The Mogoșoaia laboratory had been wrecked in the bombardament toward the end of the War. This time, he had to do the job without professional Hungarian help.
During his time at the ONT laboratory (1948–1951), he also founded his own advertising studio for the film industry.
In 1951–1955, Ștefănescu worked for the state ministry of electrical power, as director of the electro chain stores of the country. In 1956, though, he started his own design studio in Bucharest. Around 1957, his health stabilized, and under the encouragement of the painter Nicolae Darascu, his former professor and later friend, he began again to paint. In summer 1957, he resumed painting landscapes near Bucharest (Cernica, Pasărea, Băneasa, Mogoșoaia).
Municipal Theater Bucharest
[edit]
In 1958 he took a position as production director at the Lucia Sturdza-Bulandra Municipal Theater (now Bulandra Theatre) in Bucharest and became a member of the Union of Creative Artists of Romania (Uniunea Artistilor Plastici din România, UAP). The director of the theater, the actress Lucia Sturdza-Bulandra, Grande Dame of the Bucharest theatre at this time, knew him as a student of Ion Sava, a theatre professor teaching directing and set design, and in 1959 gave him the order for the stage design for the drama Când vei fi întrebat ("When You'll Be Asked") of the playwright Dorel Dorian. Ștefănescu created the decor and costumes. That year, he also took a study trip to Timișoara and surrounding areas in western Romania, where he painted mostly landscapes and portraits of farmer.
In 1960 he was commissioned to execute a portrait of Tony Bulandra, husband of Lucia Sturdza Bulandra and probably Romania's best known actor at the time, for the museum of the National Theatre Bucharest. He also did set design and costumes for the play Mamouret by Jean Sermet and toured with the Bulandra company to Budapest and elsewhere in Hungary, after which he stayed on another month in Budapest to settle tour matters. He took the opportunity to paint oil and watercolor paintings, to draw, and to befriend Hungarian painters. After his return to Bucharest, these works were exhibited in Bucharest in the hall of Sala Izvor, the main hall of the Bulandra Theatre.
Ștefănescu's studio
[edit]In 1961, Ștefănescu did set design and costumes for Mihail Beniuc's play Întoarcerea ("The Return"). The UAP granted him his own studio in the Gheorghe Tattarescu Memorial Museum, and he had another solo exhibition at the Sala Izvor. The following year, he did stage design and costumes for A. I. Ștefănescu's (no relation) inquisitorial courtroom drama Camera fierbinte ("The hot room" or "The hot chamber") and had another solo exhibition in the theater, exhibiting stage settings, blueprints of costumes, oil paintings, watercolors and drawings.
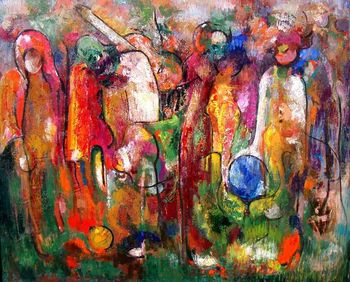
Misu Weinberg, one of Romania's most influential art collectors visited Ștefănescu's studio, beginning a fruitful relationship that lasted until Weinberg's death. Weinberg displayed Ștefănescu's works in the company of works by such Romanian masters as Theodor Pallady, Gheorghe Petrascu, Iser and others, raising Ștefănescu's visibility among collectors, many of whom Weinberg accompanied to Ștefănescu's studio.
In 1963, Ștefănescu continued his set design and costume work with Război și pace (War and Peace) by Alfred Neumann, Erwin Piseator, and Guntram Prüfer, based on the Tolstoy novel. This production was the first in Romania to combine traditional stage settings with the photographic slide projection. The same year, he also designed sets for the Portretul (The Portrait) by Alexandru Voitin, and took a study trip to the Black Sea coast near Tuzla. In 1964, he participated in the biennial stage design salon in Bucharest and executed stage setting blueprints for the play "Fii cuminte Cristofor" ("Behave, Christopher") by Aurel Baranga.
In 1965, he participated in the annual salon of the creative arts sponsored by the City of Bucharest and had a solo exhibition at the Gheorghe Tattarescu Museum. The exhibition catalogue had a foreword by Nestor Ignat and text by Misu Weinberg. That year, he also made a study visit to Sighișoara, followed by further travel the next year to the Black Sea coast of Bulgaria, where he painted many watercolors and to the Danube Delta and to the Romanian Black Sea coast.

In 1967, he returned to stage and costume design, for the play Poetul și revoluţia ("The Poet and the Revolution") about Vladimir Mayakovsky, script by Valeriu Moisescu and Dinu Negreanu. He also did stage design for Luceafărul (The Morning Star) by Barbu Ștefănescu Delavrancea, and staged it again as an open air sound and light show at the Mogoșoaia Palace. In May 1967, he participated in the spring salon of the City of Bucharest in Herăstrău Park. Later that year he paid working visits to the Danube Delta and to Sibiu.
In May 1968, Ștefănescu had a solo exhibition of oil and watercolour paintings in the exhibition room of the Gheorghe Tattarescu Museum, with the texts of the exhibition catalogue written by Florin Colonaș. Around this time, Ștefănescu's paintings first show the egg-shaped elements that soon became a significant characteristic of his painting. His paintings drew the attention of the "pope" among the Romanian art critics, Professor Petru Comarnescu. He also continued his stage design and costumes, for the play Sfârșitul pământului (The End of the World) by Victor Eftimiu.
He participated in the 1969 City of Bucharest salon of the creative arts, and designed stage costumes for the Bulandra Theatre's production of Ghosts by Henrik Ibsen.[2] He participated in the December 1969 – February 1970 exhibition "Art roumain contemporain" in the gallery Baccache in Beirut, Lebanon and paid a study visit to Brașov.
The 1970s
[edit]In 1970, Ștefănescu had a solo exhibition at Simeza Gallery in Bucharest. He continued his theatre work, designing costumes for the Georges Feydeau farce Puricele în ureche (Une puce à l'oreille, A Flea in her Ear); stage design was by Liviu Ciulei. He did stage design for the play Contrapuncte (Counterpoints) by Paul Everac and costume design for the film Pădurea spânzuraţilor (Forest of the Hanged) directed by Liviu Ciulei. He also paid a study visit to Sibiu and Sighişoara. His work was included in a touring exhibition, "Romanian Art", in Lüdenscheid, Germany, Orly, France, Vienna, and the Watts Art Gallery in New York City.

In 1971, he again participated in the salon of the creative arts, at the Romanian Atheneum in Bucharest, and in 1972 as the creative arts salon in the Dalles Gallery, Bucharest. In the latter year, he did stage design and costumes for the play Patru oameni fără nume (Four Nameless Men) by Radu Bădilă, and costumes for the play Povestiri din pădurea vieneză (Tales from the Vienna Woods) by Ödön von Horvath directed by Nicolae Alexandru Toscani.[3]
In 1973, he had another solo exhibition at the Simeza Gallery; Traian Stoica wrote the foreword for the exhibition catalogue. That year, he was awarded the Ordinul "Meritul Cultural", the order of cultural merit. In 1974, he did stage design for the play Între noi nu a fost decât tăcerea – (Between Us There Has Been Only Silence) by Lia Crișan; this was the last of his theater activities; after this time, he devoted himself entirely to painting; his studio in this period became a meeting place for artists, critics and collectors. He participated again that year in the salon for the creative arts at the Gallery Dalles, and the next year in the exhibition 12 Rumänische Maler ("12 Romanian Painters") in Hamburg, and made two study journeys, one to Czechoslovakia and the other to Mediaș and Bazna.
In 1976, his solo exhibition in Bucharest's Gallery Căminul Artei had a catalogue featuring critical texts by university professor of arts Dan Grigorescu and artist and critic Virgil Mocanu. He paid a study visit to Breaza, a health resort preferred by painters. The next few years he focused on painting, with an eye toward a large exhibition; he paid study visits to Bazna, Buziaș and Covasna.

In 1979, he participated again in the City of Bucharest salon for the creative arts at Gallery Dalles, after which he had a solo exhibition at the Art Gallery of the City of Bucharest (Galeriile de Artă ale Municipiului București). The foreword to the exhibition catalogue was, again, but Dan Grigorescu, who also delivered a speech to open the exhibition. Ștefănescu also participated in the Contemporary East European Paintings exhibition in Tokyo, Japan.[4]
The 1980s
[edit]In 1980, Ștefănescu participated once again in the City of Bucharest salon for the creative arts at the Dalles Gallery, and paid a study visit to Covasna. In the next two years, he traveled again to Covasna, as well as to Azuga and to Bistrița-Năsăud County. In 1983, he had a solo exhibition in the Art Gallery of the City of Bucharest (Galeriile de Artă ale Municipiului București). Among those who contributed to the exhibition catalogue were museum expert Gheorghe Cosma and poet and journalist Radu Carneci.
Around this time, Ștefănescu's work began to be seen a bit more in the West, and he began to garner more press attention. In 1984, he had solo exhibitions in Willebroek, Belgium and Werdohl, West Germany.[5] In 1985, this was followed by a solo exhibition at the Hagenring Gallery in Hagen, West Germany . Two years later, in 1987, the Meridiane publishing house published a monograph about Ștefănescu in the series Romanian Painters. Texts were written by the art historian Adriana Bobu (living in Paris). A report by the art expert Constanța Iliescu concerning his painting The dancers was published in the trade press in the series of articles "Comori de Artă ale Capitalei" ("Art treasures of the Capital"). In a Chinese-language magazine on Romania, several pages were dedicated to his painting. In 1988 in the trade magazine ARTA, the art critic Theodor Redlow dedicated several pages to Ștefănescu including colour pictures of his work.[6]
Life in Germany
[edit]
Stefanescu moved to Germany in 1989. That year he had exhibitions in Harsewinkel and Ennepetal, with an opening speech by the art critic Hermann Hirschberg. The following year, he had several exhibitions in Bremen, one at the Gallery Helmar H. Veltzke with an introduction by journalist and art historian Hans Peter Labonte, one at the Galeria Art Gallery, and an exhibition "George Ștefănescu – Neue Wege – Neue Bilder" ("New paths, new pictures") in the Queens Hotel in Bremen, with texts by Hans Peter Labonte. His work was also covered that year in Romanian writer and art lover Dorina Munteanu's book Mărturisiri și reflecţii ale unui colecţionar de arta ("Confessions and reflections of an art collector"). Finally, in December 1990, the exhibition "Vater und Sohn im Spiegel der Kunst" ("Father and Son in the Mirror of Art") in Lüdinghausen was introduced by Dr. Jenny Sarrazin, the official responsible for cultural affairs in the district of Coesfeld.
In 1991, he participated in the exhibition "9 Künstler aus Lüdinghausen" ("9 artists from Lüdinghausen") in the Lüdinghausen castle Burg Vischering; the foreword to the exhibition catalogue was written by Dr. Falco Herleman.[7] 1992 Dülmen: Exhibition "Neue Wege – Neue Bilder". Bocholt and Ahaus exhibition with the Hamalandkreis. 1994–1995 Solo exhibition : private collection : Skillykorn / Singapore. One of his pictures was included in Romanian school books together with pictures of other Romanian art classics.
1996–1997 Solo exhibition in the Gallery Noran / Lüdinghausen / Münster (Westfalen) and the Gallery Wöhrle / Hamm. 1998 Solo exhibitions : Haus Hünenburg / Bremen, Gallery Käthner Böke / Leer and Gallery NORAN / Lüdinghausen. 1999 Solo exhibition Sparkasse Lüdinghausen.
2003 Solo exhibition : "Der Grosse Vogel" in the Gallery Klostermühle Heiligeberg and Volksbank Achim.[8] 2004 Solo exhibition "Licht und Farbe".[9]
Selected works
[edit]- 1936 – Natura moartă cu muscată , Germany, Private collection
- 1936 – Peisaj la Balcic, Romania, Private collection [1]
- 1951 – Natură moartă – Still life, Romania, Private collection [2]
- 1967 – Autoportret- Self portrait, Romania, Private collection [3]
- 1967 – Sighişoara – Schäßburg, Romania, Private collection [4]
- 1968 – La scăldat, Romania, Private collection [5]
- 1975 – Crucifixion, Romania, Private collection [6]
- 1980 – Harlekin, Romania, Private collection [7]
- 1982 – Allegorie, Germany, Private collection [8]
- 1993 – Gedankensturm, Germany, Private collection [9]
- 1999 – Das Gespräch, Germany, Private collection [10]
- 2002 – Frau in blau, Germany, Private collection [11]
Notes
[edit]- ^ Radu Carneci : Exhibition in Willebroek Belgium Archived 2007-09-28 at the Wayback Machine, Exhibition catalogue. 1984.
- ^ Ibsen : Das Theaterstück "Gespenster", Teatrul Lucia Sturdza Bulandra.
- ^ Ödön von Horvath : Das Theaterstück "Geschichten aus dem Wiener Wald" Archived 2007-09-26 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Contemporary East European Paintings : Ausstellungskatalog Archived 2007-09-28 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Ausstellungen in Belgien und Deutschland: Ausstellungskatalog Archived 2007-09-28 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Theodor Redlow : Profil George Stefanescu Archived 2007-09-28 at the Wayback Machine – Revista "Arta" Anul XXXV Nr.3/1988 – p.10.
- ^ Dr.Falco Herleman : Ausstellung in der Burg Vischering Archived 2007-09-28 at the Wayback Machine. In: Ausstellungskatalog. 1991.
- ^ Der Grosse Vogel : Ausstellung in der Galerie Klostermühle Heiligeberg Archived 2007-09-29 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Licht und Farbe : Ausstellung in Lüdinghausen.
References
[edit]- Adriana Bobu: George Ștefănescu – Kunstmonographie in der Reihe "Rumänische Maler", Verlag Meridiane, Bucharest 1987. [12]
- Künstausstellung in der Burg Vischering, 1991. [13]
- Künstlerlexikon für Münster und Umgebung, 1996. [14]
External links
[edit]- (in Romanian) Official site
- George Ștefănescu-Râmnic in Wikiart
- (in Romanian) Biography Archived 2011-07-19 at the Wayback Machine
