Florida Senate
Florida Senate | |
|---|---|
| Florida Legislature | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
Term limits | 2–3 terms (8 years)[a] |
| History | |
| Founded | May 26, 1845 |
| Preceded by | Legislative Council of the Territory of Florida |
New session started | November 19, 2024 |
| Leadership | |
President pro tempore | |
Minority Leader | |
| Structure | |
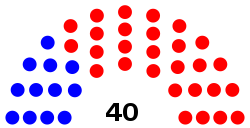
| Seats | 40 |
 | |
Political groups | Majority
Minority
|
Length of term | 4 years[a] |
| Authority | Article III, Constitution of Florida |
| Salary | $29,697.00/year + per diem (Subsistence & Travel)[1] |
| Elections | |
Last election | November 5, 2024 (20 seats) |
Next election | November 3, 2026 (20 seats) |
| Redistricting | Legislative control |
| Motto | |
| In God We Trust | |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Senate Chamber Florida Capitol Tallahassee, Florida | |
| Website | |
| The Florida Senate | |
| Constitution | |
| Constitution of Florida | |
| Rules | |
| The Florida Senate Rules | |
| Footnotes | |
 |
|---|
The Florida Senate is the upper house of the Florida Legislature, the state legislature of the U.S. state of Florida, the Florida House of Representatives being the lower house. Article III, Section 1 of the Constitution of Florida, adopted in 1968, defines the role of the Legislature and how it is to be constituted.[2] The Senate is composed of 40 members, each elected from a single-member district with a population of approximately 540,000 residents. The Senate Chamber is located in the State Capitol building.
Following the November 2022 elections, Republicans hold a supermajority in the chamber with 28 seats; Democrats are in the minority with 12 seats.[3]
Terms
[edit]Article III, of the Florida Constitution, defines the terms for state legislators. The Constitution requires state senators from odd-numbered districts to be elected in the years that end in numbers of which are multiples of four. Senators from even-numbered districts are required to be elected in even-numbered years the numbers of which are not multiples of four.[4]
To reflect the results of the U.S. census and the redrawing of district boundaries, all seats are up for election in redistricting years, with some terms truncated as a result. Thus, senators in odd-numbered districts were elected to two-year terms in 2022 (following the 2020 census), and senators in even-numbered districts will be elected to two-year terms in 2032 (following the 2030 census).
Legislators take office immediately upon election.
Term limits
[edit]In 1992, Florida voted to enact eight-year term limit for state officials. In 1995, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in U.S. Term Limits, Inc. v. Thornton that states could not enact congressional term limits.[5][6]
Qualifications
[edit]Florida legislators must be at least twenty-one years old, an elector and resident of their district, and must have resided in Florida for at least two years prior to election.[2]
Legislative session
[edit]
Each year during which the Legislature meets constitutes a new legislative session.
Regular legislative session
[edit]The Florida Legislature meets in a 60-day regular legislative session each year. Regular sessions in odd-numbered years must begin on the first Tuesday after the first Monday in March. Under the State Constitution, the Legislature can begin even-numbered year regular sessions at a time of its choosing.[4]
Special session
[edit]Special legislative sessions may be called by the governor, by a joint proclamation of the Senate president and House speaker, or by a three-fifths vote of all legislators. During a special session, the Legislature may only address legislative business that is within the purpose or purposes stated in the proclamation calling the session.[4]
Powers and process
[edit]The Florida Statutes are the codified statutory laws of the state.[7]
Leadership
[edit]The Senate is headed by the Senate President, who controls the agenda along with the Speaker of the House and Governor.[citation needed]
- President: Ben Albritton (R)
- President Pro Tempore: Jason Brodeur (R)
- Majority Leader: Jim Boyd (R)
- Minority Leader: Jason Pizzo (D)
Composition
[edit]| Affiliation | Party (Shading indicates majority caucus)
|
Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Democratic | Vacant | ||
| End of 2020–22 legislature | 23 | 16 | 39 | 1 |
| Start of previous (2022–24) legislature | 28 | 12 | 40 | 0 |
| End of previous legislature | ||||
| Start of current (2024–26) legislature | 28 | 12 | 40 | 0 |
| Latest voting share | 70% | 30% | ||
Members, 2024–2026
[edit]*Elected in a special election.
District map
[edit]
Past composition of the Senate
[edit]See also
[edit]- Florida State Capitol
- Florida Senate Majority Office
- Government of Florida
- List of presidents of the Florida Senate
- List of Florida state legislatures
- Major parties:
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "The 2017 Florida Statutes F.S. 11.13 Compensation of members". Florida Legislature.
- ^ a b "Florida Statutes". Florida Legislature. Retrieved October 26, 2022.
- ^ "Senators". Florida Senate.
- ^ a b c "The Florida Constitution". Florida Legislature.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Kevin Derby (February 11, 2016). "Florida Backs Article V Convention for Constitutional Amendment on Congressional Term Limits". Sunshine State News.
- ^ "Vote Yes On Amendment No. 9 To Begin Limiting Political Terms". Sun-Sentinel. October 27, 1992. Archived from the original on July 18, 2018. Retrieved December 6, 2017.
- ^ "Statutes & Constitution: Online Sunshine". Florida Legislature. Retrieved September 26, 2013.
- ^ And previous terms of service, if any.

