Étienne Guibourg
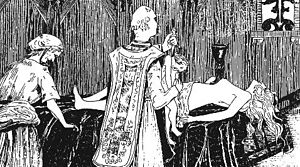
The Abbé Étienne Guibourg (c. 1610 – January 1686) was a French Roman Catholic abbé and occultist who was involved in the affaire des poisons, during the reign of Louis XIV. He has been variously described as a "defrocked" or "renegade" priest, and is said to have also had a good knowledge of chemistry.[1] He is best known for performing a series of Black Mass rituals with Catherine Monvoisin for Madame de Montespan.
Early life and ecclesiastic career
[edit]Guibourg claimed to be the illegitimate son of Henri de Montmorency.[2]
He was the sacristan of the Saint-Marcel church at Saint-Denis which was later destroyed during the French Revolution but described as being "the most beautiful of the parish churches of the town of Saint-Denis".[3] He was formerly the chaplain to the Comte de Montgomery.
Despite his position, he is said to have kept a long-term mistress, Jeanne Chanfrain, with whom he had several children.
Black Masses
[edit]According to later accounts, confessions and trials, Guibourg performed a series of Black Masses with Catherine Monvoisin (known as La Voisin). The most famous of these were performed for Madame de Montespan around 1672-3. Montague Summers gives an account of one such ritual:[2]
A long black velvet pall was spread over the altar, and upon this the royal mistress laid herself in a state of perfect nudity. Six black candles were lit, the celebrant robed himself in a chasuble embroidered with esoteric characters wrought in silver, the gold paten and chalice were placed upon the naked belly of the living altar [...] All was silent save for the low monotonous murmur of the blasphemous liturgy [...] An assistant crept forward bearing an infant in her arms. The child was held over the altar, a sharp gash across the neck, a stifled cry, and warm drops fell into the chalice and streamed upon the white figure beneath. The corpse was handed to la Voisin, who flung it callously into an oven fashioned for that purpose which glowed white-hot in its fierceness.
Summers provides a further account of the incantation used by Guibourg himself:[2]
Astaroth, Asmodeus, princes of friendship and love, I invoke you to accept the sacrifice, this child that I offer you, for the things I ask of you. They are that the friendship and love of the King and the Dauphin may be assured to me, that I may be honoured by all the princes and princesses of the Court, that the King deny me nothing I ask whether it be for my relatives or for any of my household.
Accounts suggest that La Voisin performed rituals with a number of priests (including at least one whose work was uncovered by Church authorities, forcing him into exile) as well as Guibourg. It is unlikely Guibourg took part in all of La Voisin's Black Masses. It is alleged, upon her arrest, investigators discovered the corpses of 2,500 infants buried in her yard, allegedly sacrificed the same way as in Guibourg's ritual. Allegedly, La Voisin had paid prostitutes for their infants for use in the rituals.[2] Eleanor Herman, in her book Sex with Kings, claims that the police, given reports of "babies' bones", uncovered the remains of 2,500 infants in La Voisin's garden.[4] However, Anne Somerset disputes this in her book The Affair of the Poisons and states there is no mention of the garden being searched for human remains.[5]
Arrest and sentence
[edit]In 1680, Françoise Filastre, under interrogation in connection with the poison affair, claimed that Guibourg had performed Black Masses. Guibourg was arrested and confessed to this and to other crimes.[6]
He was sentenced to life imprisonment and sequestration and died in prison in 1686.
In fiction
[edit]- He is portrayed in a novel by Judith Merkle Riley: The Oracle Glass (1994).
- He is portrayed as Father Etienne Gibbourg in the second season of the French-Canadian television series Versailles (2017) by Ned Dennehy.
- In Scott Snyder's "Batman: The Black Mirror" (Detective Comics #871–881) the villainous character The Dealer alternatively goes by the pseudonym Etienne Guibourg in reference to the Abbé.
References
[edit]- ^ Legends, Monsters, Or Serial Murderers?: The Real Story Behind an Ancient Crime by Dirk C. Gibson (ABC-CLIO, 2012)
- ^ a b c d Geography of Witchcraft by Montague Summers (1927; reprint Kessinger Publishing, 2003)
- ^ Saint Denis: a town in the Middle Ages
- ^ Herman, Eleanor (2009). Sex with kings : 500 years of adultery, power, rivalry, and revenge. 3M Cloud Library (1st ed.). [Place of publication not identified]: HarperCollins. p. 113. ISBN 978-0-06-175155-4. OCLC 973737952.
- ^ Somerset, Anne (2004). The affair of the poisons : murder, infanticide, and Satanism at the court of Louis XIV (1st U.S. ed.). New York: St. Martin's Press. p. 162. ISBN 0-312-33017-0. OCLC 55511430.
- ^ The Affair of the Poisons: Murder, Infanticide, and Satanism at the Court of Louis XIV by Anne Somerset (St. Martin's Press, 2003) ISBN 0-312-33017-0
Sources
[edit]- Hugh Noel Williams - Madame de Montespan and Louis XIV, 1910.
- Excerpts from Bastille trial records of Guibourg and LaVoisin (French and English translation)
