Dorking chicken
 A silver-grey Dorking cock | |
| Conservation status | FAO (2007): endangered-maintained[1]: 122 |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | United Kingdom[2] |
| Traits | |
| Weight | |
| Skin colour | white |
| Egg colour | white or tinted[4] |
| Comb type | single or rose-comb[3]: 99 |
| Classification | |
| APA | Large fowl: English[5] Bantam: Single comb clean legged[5] |
| EE | recognised[6] |
| PCGB | Soft feather: heavy[7] |
| |
The Dorking is a British breed of domestic chicken.[8] It is named after the town of Dorking, in Surrey in southern England.[4]
History
[edit]The Dorking is among the oldest British chicken breeds. It has sometimes been suggested that it derives from five-toed (rather than the usual four-toed) chickens brought to Britain by the Romans in the first century AD,[9][10] but it is not known whether the Romans brought poultry with them, nor if they found five-toed poultry when they arrived.[4] The Roman writer Columella, active at that time, mentions five-toed hens as being the best breeding-stock: "they are reckoned the most generous which have five toes".[11]: 342
The Dorking originated in the southern home counties in south-east England, and is named after the market town of Dorking, in Surrey, from where birds were sent to the markets of London. It was the principal meat breed supplied to the metropolis until it was displaced by the Sussex in the early part of the twentieth century; it also became popular as an exhibition bird.[8] It was among the breeds shown at the first poultry show, at London Zoo in 1845.[3]: 289
The Dorking was included in the first poultry standard, The Standard of Excellence in Exhibition Poultry, edited by William Bernhardt Tegetmeier and published in 1865 by the original Poultry Club of Great Britain.[12] In the late nineteenth century, separate breed societies formed for the various colour varieties; two of these merged to form the Dorking Club, and a Scottish Dorking Club also formed. By about the time of the Second World War, none of these remained active.[8] Interest in the breed had decreased rapidly, and it drew close to extinction. The Dorking Club was restarted in 1970.[8]
Three colour varieties – coloured, silver-grey and white – were included in the first Standard of Perfection of the American Poultry Association in 1874; the red was added in 1995.[5] Three bantam varieties – coloured, silver-grey and rose-comb white – were added in 1960.[5]
Characteristics
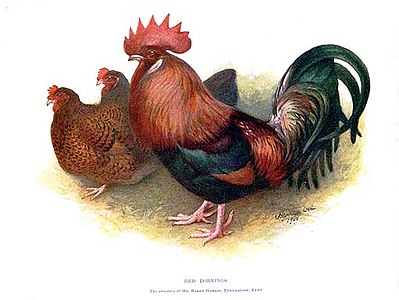
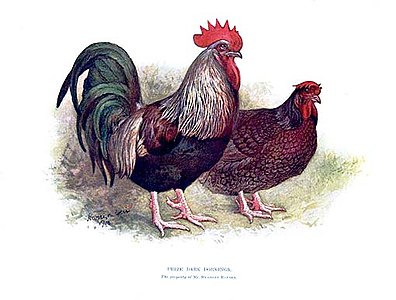
[edit]The Dorking has a rectangular body with short, five-toed legs. As with all single comb poultry, the comb points may require protection in extremely cold weather. Dorkings are well known for their versatility as a breed for both egg and meat production. It is one of the few breeds with red earlobes that produces a white-shelled egg. The skin colour beneath the feathers is white. The weight is 4.55–6.35 kg (10–14 lb) for cocks, 3.60–5.00 kg (8–11 lb) for cockerels and 3.60–4.55 kg (8–10 lb) for hens.[13] There are five recognised colour varieties: white, silver-grey, red, dark and cuckoo.[13]
Gallery
[edit]- Illustrations by Harrison Weir
-
Coloured Dorking
-
White Dorking
-
Red Dorkings
-
Prize Dark Dorkings
See also
[edit]- Dorking Cockerel, public art in Dorking, England that depicts the Dorking chicken
References
[edit]- ^ Barbara Rischkowsky, D. Pilling (eds.) (2007). List of breeds documented in the Global Databank for Animal Genetic Resources, annex to The State of the World's Animal Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. ISBN 9789251057629. Accessed November 2017.
- ^ Chickens. Poultry Club of Great Britain. Archived 9 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f Victoria Roberts (2008). British poultry standards: complete specifications and judging points of all standardized breeds and varieties of poultry as compiled by the specialist breed clubs and recognised by the Poultry Club of Great Britain. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 9781405156424.
- ^ a b c Dorking Archived 7 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Rare Breeds Survival Trust. Accessed November 2017.
- ^ a b c d APA Recognized Breeds and Varieties: As of January 1, 2012. American Poultry Association. Archived 4 November 2017.
- ^ Liste des races et variétés homologuée dans les pays EE (28.04.2013). Entente Européenne d’Aviculture et de Cuniculture. Archived 16 June 2013.
- ^ Breed Classification. Poultry Club of Great Britain. Archived 12 June 2018.
- ^ a b c d David Scrivener (2014). Popular Poultry Breeds. Ramsbury: Crowood. ISBN 9781847979711.
- ^ Sidney Hubert Lewer (1924). British Poultry and Poultry Keeping. London: Feathered World.
- ^ Janet Vorwald Dohner (2001), The Encyclopedia of Historic and Endangered Livestock and Poultry Breeds, Yale University Press, pp. 421–423, ISBN 0-300-08880-9
- ^ Lucius Junius Moderatus Columella (trans. Anon.) (1745). L. Junius Moderatus Columella of Husbandry, in Twelve Books: and his book, concerning Trees. Translated into English, with illustrations from Pliny, Cato, Varro, Palladius and other ancient and modern authors London: A. Millar.
- ^ William Bernhard Tegetmeier (editor) (1865). The Standard of Excellence in Exhibition Poultry, authorized by the Poultry Club. London: Groombridge and Sons, for the Poultry Club. 56 pp.
- ^ a b The Dorking Club Archived 28 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Poultry Club of Great Britain.
Further reading
[edit]- Thomas William Sturges (1911). The Poultry Manual: A Complete Guide for the Breeder and Exhibitor, second edition. London: Macdonald and Evans.