Dlusskyidris
| Dlusskyidris Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
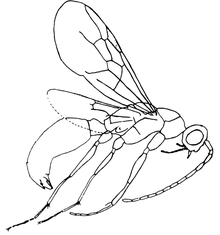
| |
| Illustration of D. zherichini | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Subfamily: | †Sphecomyrminae |
| Tribe: | †Sphecomyrmini |
| Genus: | †Dlusskyidris Bolton, 1994 |
| Species: | †D. zherichini
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Dlusskyidris zherichini (Dlussky, 1975)
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Dlusskyidris is an extinct genus of ant in the Formicidae subfamily Sphecomyrminae, and is one of the five genera placed in the tribe Sphecomyrmini. The genus contains a single described species, Dlusskyidris zherichini, and is known from three Late Cretaceous fossils which have been found in northern Russia.
History and classification
[edit]The three males of Dlusskyidris have been identified from adults that are preserved as inclusions in Taymyr amber.[1] The ambers of the peninsula occur in the upper levels of the Kheta Formation, which is exposed in a number of locations in the Taimyr region. Age estimates of the Kheta Formation are between the Coniacian and Santonian, and the ambers are found consistently in the uppermost units, giving a Santonian age range for the inclusions.[2][3] The Dlusskyidris adults were collected from the Yantardakh locality,[1] which is approximately 3 km (1.9 mi) upstream from the confluence of the Maimecha River with the Kheta River, on the bank of the Maimecha.[2][3] Based on the flora and fauna of the Ledyanaya and Mutino formations which surround the Kheta Formation, the paleoforest likely has a humid and warm temperate climate with the trees growing along river banks. While the resin producing trees have not been identified, the resins were likely dropped into the river systems and buried quickly in deltaic sediments.[2][4]
The three males were first studied by Russian paleoentomologist Gennady Dlussky, who published the genus and species description in a 1975 paper. In that paper Dlussky named the genus "Palaeomyrmex" and the species "Palaeomyrmex zherichini". However the genus name Palaeomyrmex had already been used over a hundred years earlier by Oswald Heer for Palaeomyrmex prodromus. Due to the name being preoccupied, the species was moved to the new genus name Dlusskyidris in 1994 by Barry Bolton.[5]
Russian paleoentomologist K. S. Perfilieva re-examined the holotype and paratype fossils 2011. Perfilieva noted that the visibility of the wings and the refractive index of the amber had been altered due to years of storage in castor oil.[1] The oil had seeped into the amber, filling in air bubbles and making the wings nearly invisible under light microscope examination.[1]
Description
[edit]The Dlusskyidris males are distinguished from other Sphecomyrminae males based on several features. There are spurs present on the tibias of the hind and mid legs.[5] The tergite of the end abdominal segment is triangular in shape, as is the subgenital plate. There are well developed cerci on the abdomen, the parameres are narrow with slight curving in the middle and pointed tips.[5]
In Dlussky's original description, he considered the wing venation primitive and similar to that of Armaniidae genera with complete cells 1r+2r, 3r and 2rm. Perfilieva noted however that two different versions of the venation were presented by Dlussky.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e Perfilieva, K.S. (2011). "New Data on the Wing Morphology of the Cretaceous Sphecomyrminae Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)". Paleontological Journal. 45 (3): 275–283. Bibcode:2011PalJ...45..275P. doi:10.1134/S0031030111030117. ISSN 0031-0301. S2CID 83899478.
- ^ a b c Perkovsky, E.E.; Makarkin, V.N. (2015). "First confirmation of spongillaflies (Neuroptera: Sisyridae) from the Cretaceous". Cretaceous Research. 56: 363–371. Bibcode:2015CrRes..56..363P. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.06.003.
- ^ a b Makarkin, VN; Perkovsky, E.E. (2016). "An interesting new species of Sisyridae (Neuroptera) from the Upper Cretaceous Taimyr amber". Cretaceous Research. 63: 170–176. Bibcode:2016CrRes..63..170M. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2016.03.010.
- ^ Poinar, G.O. Jr. (1992). Life in Amber. Stanford University Press. p. 59. ISBN 0-8047-2001-0.
- ^ a b c Grimaldi, D.; Agosti, D.; Carpenter, J. M. (1997). "New and rediscovered primitive ants (Hymenoptera, Formicidae) in Cretaceous amber from New Jersey, and their phylogenetic relationships". American Museum Novitates (3208): 1–43.
