Time-of-flight mass spectrometry


Time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOFMS) is a method of mass spectrometry in which an ion's mass-to-charge ratio is determined by a time of flight measurement. Ions are accelerated by an electric field of known strength.[1] This acceleration results in an ion having the same kinetic energy as any other ion that has the same charge. The velocity of the ion depends on the mass-to-charge ratio (heavier ions of the same charge reach lower speeds, although ions with higher charge will also increase in velocity). The time that it subsequently takes for the ion to reach a detector at a known distance is measured. This time will depend on the velocity of the ion, and therefore is a measure of its mass-to-charge ratio. From this ratio and known experimental parameters, one can identify the ion.
Theory
[edit]
The potential energy of a charged particle in an electric field is related to the charge of the particle and to the strength of the electric field:
| 1 |
where Ep is potential energy, q is the charge of the particle, and U is the electric potential difference (also known as voltage).
When the charged particle is accelerated into time-of-flight tube (TOF tube or flight tube) by the voltage U, its potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. The kinetic energy of any mass is:
| 2 |
In effect, the potential energy is converted to kinetic energy, meaning that equations (1) and (2) are equal
| 3 |
| 4 |
The velocity of the charged particle after acceleration will not change since it moves in a field-free time-of-flight tube. The velocity of the particle can be determined in a time-of-flight tube since the length of the path (d) of the flight of the ion is known and the time of the flight of the ion (t) can be measured using a transient digitizer or time to digital converter.
Thus,
| 5 |
and we substitute the value of v in (5) into (4).
| 6 |
Rearranging (6) so that the flight time is expressed by everything else:
| 7 |
Taking the square root yields the time,
| 8 |
These factors for the time of flight have been grouped purposely. contains constants that in principle do not change when a set of ions are analyzed in a single pulse of acceleration. (8) can thus be given as:
| 9 |
where k is a proportionality constant representing factors related to the instrument settings and characteristics.
(9) reveals more clearly that the time of flight of the ion varies with the square root of its mass-to-charge ratio (m/q).
Consider a real-world example of a MALDI time-of-flight mass spectrometer instrument which is used to produce a mass spectrum of the tryptic peptides of a protein. Suppose the mass of one tryptic peptide is 1000 daltons (Da). The kind of ionization of peptides produced by MALDI is typically +1 ions, so q = e in both cases. Suppose the instrument is set to accelerate the ions in a U = 15,000 volts (15 kilovolt or 15 kV) potential. And suppose the length of the flight tube is 1.5 meters (typical). All the factors necessary to calculate the time of flight of the ions are now known for (8), which is evaluated first of the ion of mass 1000 Da:
| 10 |
Note that the mass had to be converted from daltons (Da) to kilograms (kg) to make it possible to evaluate the equation in the proper units. The final value should be in seconds:
which is about 28 microseconds. If there were a singly charged tryptic peptide ion with 4000 Da mass, and it is four times larger than the 1000 Da mass, it would take twice the time, or about 56 microseconds to traverse the flight tube, since time is proportional to the square root of the mass-to-charge ratio.
Delayed extraction
[edit]Mass resolution can be improved in axial MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer where ion production takes place in vacuum by allowing the initial burst of ions and neutrals produced by the laser pulse to equilibrate and to let the ions travel some distance perpendicularly to the sample plate before the ions can be accelerated into the flight tube. The ion equilibration in plasma plume produced during the desorption/ionization takes place approximately 100 ns or less, after that most of ions irrespectively of their mass start moving from the surface with some average velocity. To compensate for the spread of this average velocity and to improve mass resolution, it was proposed to delay the extraction of ions from the ion source toward the flight tube by a few hundred nanoseconds to a few microseconds with respect to the start of short (typically, a few nanosecond) laser pulse. This technique is referred to as "time-lag focusing" [3] for ionization of atoms or molecules by resonance enhanced multiphoton ionization or by electron impact ionization in a rarefied gas and "delayed extraction"[4][5][6] for ions produced generally by laser desorption/ionization of molecules adsorbed on flat surfaces or microcrystals placed on conductive flat surface.
Delayed extraction generally refers to the operation mode of vacuum ion sources when the onset of the electric field responsible for acceleration (extraction) of the ions into the flight tube is delayed by some short time (200–500 ns) with respect to the ionization (or desorption/ionization) event. This differs from a case of constant extraction field where the ions are accelerated instantaneously upon being formed. Delayed extraction is used with MALDI or laser desorption/ionization (LDI) ion sources where the ions to be analyzed are produced in an expanding plume moving from the sample plate with a high speed (400–1000 m/s). Since the thickness of the ion packets arriving at the detector is important to mass resolution, on first inspection it can appear counter-intuitive to allow the ion plume to further expand before extraction. Delayed extraction is more of a compensation for the initial momentum of the ions: it provides the same arrival times at the detector for ions with the same mass-to-charge ratios but with different initial velocities.
In delayed extraction of ions produced in vacuum, the ions that have lower momentum in the direction of extraction start to be accelerated at higher potential due to being further from the extraction plate when the extraction field is turned on. Conversely, those ions with greater forward momentum start to be accelerated at lower potential since they are closer to the extraction plate. At the exit from the acceleration region, the slower ions at the back of the plume will be accelerated to greater velocity than the initially faster ions at the front of the plume. So after delayed extraction, a group of ions that leaves the ion source earlier has lower velocity in the direction of the acceleration compared to some other group of ions that leaves the ion source later but with greater velocity. When ion source parameters are properly adjusted, the faster group of ions catches up to the slower one at some distance from the ion source, so the detector plate placed at this distance detects simultaneous arrival of these groups of ions. In its way, the delayed application of the acceleration field acts as a one-dimensional time-of-flight focusing element.
Reflectron TOF
[edit]

The kinetic energy distribution in the direction of ion flight can be corrected by using a reflectron.[7][8] The reflectron uses a constant electrostatic field to reflect the ion beam toward the detector. The more energetic ions penetrate deeper into the reflectron, and take a slightly longer path to the detector. Less energetic ions of the same mass-to-charge ratio penetrate a shorter distance into the reflectron and, correspondingly, take a shorter path to the detector. The flat surface of the ion detector (typically a microchannel plate, MCP) is placed at the plane where ions of same m/z but with different energies arrive at the same time counted with respect to the onset of the extraction pulse in the ion source. A point of simultaneous arrival of ions of the same mass-to-charge ratio but with different energies is often referred as time-of-flight focus. An additional advantage to the re-TOF arrangement is that twice the flight path is achieved in a given length of the TOF instrument.
Ion gating
[edit]A Bradbury–Nielsen shutter is a type of ion gate used in TOF mass spectrometers and in ion mobility spectrometers, as well as Hadamard transform TOF mass spectrometers.[9] The Bradbury–Nielsen shutter is ideal for fast timed ion selector (TIS)—a device used for isolating ions over narrow mass range in tandem (TOF/TOF) MALDI mass spectrometers.[10]
Orthogonal acceleration time-of-flight
[edit]

Continuous ion sources (most commonly electrospray ionization, ESI) are generally interfaced to the TOF mass analyzer by "orthogonal extraction" in which ions introduced into the TOF mass analyzer are accelerated along the axis perpendicular to their initial direction of motion. Orthogonal acceleration combined with collisional ion cooling allows separating the ion production in the ion source and mass analysis. In this technique, very high resolution can be achieved for ions produced in MALDI or ESI sources. Before entering the orthogonal acceleration region or the pulser, the ions produced in continuous (ESI) or pulsed (MALDI) sources are focused (cooled) into a beam of 1–2 mm diameter by collisions with a residual gas in RF multipole guides. A system of electrostatic lenses mounted in high-vacuum region before the pulser makes the beam parallel to minimize its divergence in the direction of acceleration. The combination of ion collisional cooling and orthogonal acceleration TOF [12][13] has provided significant increase in resolution of modern TOF MS from few hundred to several tens of thousand without compromising the sensitivity.
Hadamard transform time-of-flight mass spectrometry
[edit]Hadamard transform time-of flight mass spectrometry (HT-TOFMS) is a mode of mass analysis used to significantly increase the signal-to-noise ratio of a conventional TOFMS.[14] Whereas traditional TOFMS analyzes one packet of ions at a time, waiting for the ions to reach the detector before introducing another ion packet, HT-TOFMS can simultaneously analyze several ion packets traveling in the flight tube.[15] The ions packets are encoded by rapidly modulating the transmission of the ion beam, so that lighter (and thus faster) ions from all initially-released packets of mass from a beam get ahead of heavier (and thus slower) ions.[16] This process creates an overlap of many time-of-flight distributions convoluted in form of signals. The Hadamard transform algorithm is then used to carry out the deconvolution process which helps to produce a faster mass spectral storage rate than traditional TOFMS and other comparable mass separation instruments.[14]
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (May 2008) |
Tandem time-of-flight
[edit]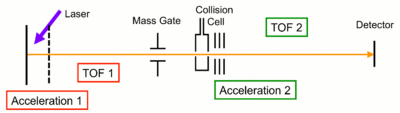
Tandem time-of-flight (TOF/TOF) is a tandem mass spectrometry method where two time-of-flight mass spectrometers are used consecutively.[17][18][19][20] To record full spectrum of precursor (parent) ions TOF/TOF operates in MS mode. In this mode, the energy of the pulse laser is chosen slightly above the onset of MALDI for specific matrix in use to ensure the compromise between an ion yield for all the parent ions and reduced fragmentation of the same ions. When operating in a tandem (MS/MS) mode, the laser energy is increased considerably above MALDI threshold. The first TOF mass spectrometer (basically, a flight tube which ends up with the timed ion selector) isolates precursor ions of choice using a velocity filter, typically, of a Bradbury–Nielsen type, and the second TOF-MS (that includes the post accelerator, flight tube, ion mirror, and the ion detector) analyzes the fragment ions. Fragment ions in MALDI TOF/TOF result from decay of precursor ions vibrationally excited above their dissociation level in MALDI source (post source decay [21]). Additional ion fragmentation implemented in a high-energy collision cell may be added to the system to increase dissociation rate of vibrationally excited precursor ions. Some designs include precursor signal quenchers as a part of second TOF-MS to reduce the instant current load on the ion detector.
Quadrupole time-of-flight
[edit]Quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (QToF-MS) has a similar configuration to a tandem mass spectrometer with a mass-resolving quadrupole and collision cell hexapole, but instead of a second mass-resolving quadrupole, a time-of-flight mass analyzer is used.[22][23] Both quadrupoles can operate in RF mode only to allow all ions to pass through to the mass analyzer with minimal fragmentation.[22] To increase spectral detail, the system takes advantage of collision-induced dissociation. Once the ions reach the flight tube, the ion pulser sends them upwards towards the reflectron and back down into the detector. Since the ion pulser transfers the same kinetic energy to all molecules, the flight time is dictated by the mass of the analyte.
QToF is capable of measuring mass to the 4th decimal place and is frequently used for pharmaceutical and toxicological analysis as a screening method for drug analogues.[24] Identification is done by collection of the mass spectrum and comparison to tandem mass spectrum libraries.[25]
Detectors
[edit]A time-of-flight mass spectrometer (TOFMS) consists of a mass analyzer and a detector. An ion source (either pulsed or continuous) is used for lab-related TOF experiments, but not needed for TOF analyzers used in space, where the sun or planetary ionospheres provide the ions. The TOF mass analyzer can be a linear flight tube or a reflectron. The ion detector typically consists of microchannel plate detector or a fast secondary emission multiplier (SEM) where first converter plate (dynode) is flat.[26] The electrical signal from the detector is recorded by means of a time to digital converter (TDC) or a fast analog-to-digital converter (ADC). TDC is mostly used in combination with orthogonal-acceleration (oa)TOF instruments.
Time-to-digital converters register the arrival of a single ion at discrete time "bins"; a combination of threshold triggering and constant fraction discriminator (CFD) discriminates between electronic noise and ion arrival events. CFD converts nanosecond-long Gaussian-shaped electrical pulses of different amplitudes generated on the MCP's anode into common-shape pulses (e.g., pulses compatible with TTL/ESL logic circuitry) sent to TDC. Using CFD provides a time point correspondent to a position of peak maximum independent of variation in the peak amplitude caused by variation of the MCP or SEM gain. Fast CFDs of advanced designs have the dead times equal to or less than two single-hit response times of the ion detector (single-hit response time for MCP with 2-5 micron wide channels can be somewhere between 0.2 ns and 0.8 ns, depending on the channel angle) thus preventing repetitive triggering from the same pulse. Double-hit resolution (dead time) of modern multi-hit TDC can be as low as 3-5 nanosecond.
The TDC is a counting detector – it can be extremely fast (down to a few picosecond resolution), but its dynamic range is limited due to its inability to properly count the events when more than one ion simultaneously (i.e., within the TDC dead time) hit the detector. The outcome of limited dynamic range is that the number of ions (events) recorded in one mass spectrum is smaller compared to real number. The problem of limited dynamic range can be alleviated using multichannel detector design: an array of mini-anodes attached to a common MCP stack and multiple CFD/TDC, where each CFD/TDC records signals from individual mini-anode. To obtain peaks with statistically acceptable intensities, ion counting is accompanied by summing of hundreds of individual mass spectra (so-called hystograming). To reach a very high counting rate (limited only by duration of individual TOF spectrum which can be as high as few milliseconds in multipath TOF setups), a very high repetition rate of ion extractions to the TOF tube is used. Commercial orthogonal acceleration TOF mass analyzers typically operate at 5–20 kHz repetition rates. In combined mass spectra obtained by summing a large number of individual ion detection events, each peak is a histogram obtained by adding up counts in each individual bin. Because the recording of the individual ion arrival with TDC yields only a single time point, the TDC eliminates the fraction of peak width determined by a limited response time of both the MCP detector and preamplifier. This propagates into better mass resolution.
Modern ultra-fast 10 GSample/sec analog-to-digital converters digitize the pulsed ion current from the MCP detector at discrete time intervals (100 picoseconds). Modern 8-bit or 10-bit 10 GHz ADC has much higher dynamic range than the TDC, which allows its usage in MALDI-TOF instruments with its high peak currents. To record fast analog signals from MCP detectors one is required to carefully match the impedance of the detector anode with the input circuitry of the ADC (preamplifier) to minimize the "ringing" effect. Mass resolution in mass spectra recorded with ultra-fast ADC can be improved by using small-pore (2-5 micron) MCP detectors with shorter response times.
Applications
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (May 2008) |
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) is a pulsed ionization technique that is readily compatible with TOF MS.
Atom probe tomography also takes advantage of TOF mass spectrometry.
Photoelectron photoion coincidence spectroscopy uses soft photoionization for ion internal energy selection and TOF mass spectrometry for mass analysis.
Secondary ion mass spectrometry commonly utilizes TOF mass spectrometers to allow parallel detection of different ions with a high mass resolving power.
Stefan Rutzinger proposed using TOF mass spectrometry with a cryogenic detector for the spectrometry of heavy biomolecules.[27]
History of the field
[edit]This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (August 2010) |
An early time-of-flight mass spectrometer, named the Velocitron, was reported by A. E. Cameron and D. F. Eggers Jr, working at the Y-12 National Security Complex, in 1948. The idea had been proposed two years earlier, in 1946, by W. E. Stephens of the University of Pennsylvania in a Friday afternoon session of a meeting, at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, of the American Physical Society.[28][29]
References
[edit]- ^ Stephens W. E. (1946). "A Pulsed Mass Spectrometer with Time Dispersion". Phys. Rev. 69 (11–12): 691. Bibcode:1946PhRv...69R.674.. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.69.674.2.
- ^ US 2847576, Lawrence, Ernest O., "Calutron system", published 1958-08-12, assigned to US, Atomic Energy Commission
- ^ Wiley, W. C.; McLaren, I. H. (1955). "Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer with Improved Resolution". Review of Scientific Instruments. 26 (12): 1150. Bibcode:1955RScI...26.1150W. doi:10.1063/1.1715212.
- ^ V. S. Antonov; V. S. Letokhov & A. N. Shibanov (1980). "Formation of molecular ions as a result of irradiation of the surface of molecular crystals". Pis'ma Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 31: 471.
- ^ JETP Lett. 31: 441.
{{cite journal}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Brown, R. S.; Lennon, J. J. (1995). "Mass resolution improvement by incorporation of pulsed ion extraction in a matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization linear time-of-flight mass spectrometer". Anal. Chem. 67 (13): 1998–2003. doi:10.1021/ac00109a015. PMID 8694246.
- ^ Mamyrin, B. A.; Karataev, V. I.; Shmikk, D. V.; Zagulin, V. A. (1973). "The mass-reflectron, a new nonmagnetic time-of-flight mass spectrometer with high resolution". Sov. Phys. JETP. 37: 45. Bibcode:1973JETP...37...45M.
- ^ US 4072862, Mamyrin, Boris A.; Karataev, Valery I. & Shmikk, Dmitry V., "Time-of-flight mass spectrometer", published 1978-02-07
- ^ U.S. patent 6,664,545
- ^ U.S. patent 6,489,610
- ^ U.S. patent 7,230,234
- ^ Dodonov, A. F., Chernushevich, I. V., Dodonova, T. F., Raznikov, V. V., Tal’rose, V. L. Inventor’s Certificate No. 1681340A1, USSR, February 25, 1987.
- ^ A.F. Dodonov, I.V. Chernushevich and V.V. Laiko, Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (1994) ACS Symposium Series 549, Chap. VII.
- ^ a b Richard N., Zare (2003). "Hadamard Transform Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry: More Signal, More of the Time" (PDF). Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 42 (1): 30–35. doi:10.1002/anie.200390047. PMID 19757587 – via Wiley-VCH.
- ^ Ansgar, Brock (1999). "Characterization of a Hadamard transform time-of-flight mass spectrometer" (PDF). Review of Scientific Instruments. 71 (3): 1306–1318. Bibcode:2000RScI...71.1306B. doi:10.1063/1.1150456 – via American Institute of Physics.
- ^ Ansgar, Brock; Rodriguez, Nestor; Zare, Richard N. (1998). "Hadamard Transform Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry". Analytical Chemistry. 70 (18): 3735–3741. doi:10.1021/ac9804036.
- ^ U.S. patent 5,206,508
- ^ U.S. patent 7,196,324
- ^ Medzihradszky KF, Campbell JM, Baldwin MA, Falick AM, Juhasz P, Vestal ML, Burlingame AL (2000). "The characteristics of peptide collision-induced dissociation using a high-performance MALDI-TOF/TOF tandem mass spectrometer". Anal. Chem. 72 (3): 552–8. doi:10.1021/ac990809y. PMID 10695141.
- ^ Vestal ML, Campbell JM (2005). "Tandem Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry". Biological Mass Spectrometry. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 402. pp. 79–108. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(05)02003-3. ISBN 9780121828073. PMID 16401507.
- ^ Spengler B.; Kirsch D.; Kaufmann R. (1991). "Metastable decay of peptides and proteins in matrix-assisted laser-desorption mass spectrometry". Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry. 5 (4): 198–202. Bibcode:1991RCMS....5..198S. doi:10.1002/rcm.1290050412.
- ^ a b Allen, Darren R.; McWhinney, Brett C. (August 2019). "Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry: A Paradigm Shift in Toxicology Screening Applications". The Clinical Biochemist. Reviews. 40 (3): 135–146. doi:10.33176/AACB-19-00023 (inactive 2024-11-02). ISSN 0159-8090. PMC 6719743. PMID 31530964.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ Chernushevich, Igor V.; Loboda, Alexander V.; Thomson, Bruce A. (August 2001). "An introduction to quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry". Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 36 (8): 849–865. Bibcode:2001JMSp...36..849C. doi:10.1002/jms.207. ISSN 1076-5174. PMID 11523084.
- ^ Noble, Carolina; Weihe Dalsgaard, Petur; Stybe Johansen, Sys; Linnet, Kristian (April 2018). "Application of a screening method for fentanyl and its analogues using UHPLC-QTOF-MS with data-independent acquisition (DIA) in MS E mode and retrospective analysis of authentic forensic blood samples". Drug Testing and Analysis. 10 (4): 651–662. doi:10.1002/dta.2263. PMID 28834382.
- ^ Marin, S. J.; Sawyer, J. C.; He, X.; Johnson-Davis, K. L. (2014-12-12). "Comparison of Drug Detection by Three Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Platforms". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 39 (2): 89–95. doi:10.1093/jat/bku134. ISSN 0146-4760. PMID 25505058.
- ^ U.S. patent 7,446,327
- ^ Rutzinger, Stefan. "Development and Application of a Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometer with a Cryogenic Detector for the Spectrometry of Heavy Biomolecules".
- ^ Campana, Joseph E. (1987). "Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry: a Historical Overview". Instrumentation Science & Technology. 16 (1): 1–14. Bibcode:1987IS&T...16....1C. doi:10.1080/10739148708543625. ISSN 1073-9149.
- ^ Mirsaleh-Kohan, Nasrin; Robertson, Wesley D.; Compton, Robert N. (2008). "Electron ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry: Historical review and current applications". Mass Spectrometry Reviews. 27 (3): 237–285. Bibcode:2008MSRv...27..237M. doi:10.1002/mas.20162. ISSN 0277-7037. PMID 18320595.
Bibliography
[edit]- Cotter, Robert J. (1994). Time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Columbus, OH: American Chemical Society. ISBN 978-0-8412-3474-1.
- Ferrer, Imma; Thurman, E. M. (2009). Liquid chromatography-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry: Principles, Tools and Applications for Accurate Mass Analysis. New York, NJ: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-13797-0.
- Ferrer, Imma; Thurman, E. M. (2005). "Measuring the Mass of an Electron by LC/TOF-MS: A Study of "Twin Ions"". Anal Chem. 77 (10): 3394–3400. doi:10.1021/ac0485942. PMID 15889935.
- A. E. Cameron & D. F. Eggers Jr (1948). "An ion "velocitron"". Rev Sci Instrum. 19 (9): 605–607. Bibcode:1948RScI...19..605C. doi:10.1063/1.1741336.
- W. E. Stephens (1946). "A pulsed mass spectrometer with time dispersion". Bull Am Phys Soc. 21 (2): 22.












