Dhanmondi Thana
Dhanmondi
ধানমন্ডি | |
|---|---|
Neighbourhood and Thana | |
 Skyline of Dhanmondi, Bangladesh | |
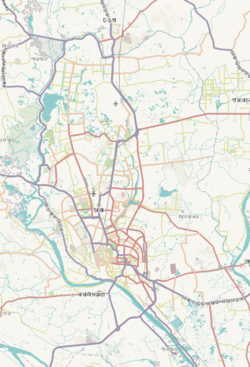
 Expandable map of Dhanmondi Thana | |
| Coordinates: 23°44.7′N 90°22.6′E / 23.7450°N 90.3767°E | |
| Country | |
| Division | Dhaka Division |
| District | Dhaka District |
| Area | |
• Total | 4.34 km2 (1.68 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 23 m (75 ft) |
| Population | |
• Total | 101,937 |
| • Density | 23,000/km2 (61,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+6 (BST) |
| Postal code | 1209[3] |
| Area code | 02[4] |
| Notable sport teams | Sheikh Jamal |
Dhanmondi (Bengali: ধানমন্ডি) is an upscale residential and commercial neighbourhood and a thana (police jurisdiction) in Dhaka, Bangladesh, known for its central location, cultural vibrancy and being home to the country's founder, Sheikh Mujibur Rahman.[5] Dhanmondi Thana falls within the administrative areas of both the Dhaka North and Dhaka South city corporations. It fully encompasses wards 49 and partially includes wards 47 and 48.[2][6]
The origins of Dhanmondi can be traced back to the early 1950s, when the Government of East Pakistan developed it as a centrally planned residential area catering to the city's elites.
History
[edit]During the British colonial period, the area that is now Dhanmondi had a canal next to it and was primarily used for cultivation, interspersed with a few settlements. It was known for its rice (ধান, dhan in Bengali) and other grain seed markets. The term mandi in Persian and Urdu refers to a market or bazaar, hence the area came to be known as Dhanmondi.[7] By the 19th century, the canal dried up, making the market there less significant. Dhanmondi subsequently became forested and remained that way until the mid-twentieth century.[8]
In 1950, the government of East Pakistan acquired roughly 500 acres of agricultural and horticultural land, and leveled and divided it into plots, each approximately one bigha (0.33 acres) in size. These plots were allocated to ministers, government officials, public figures, professionals, and businesspeople based on specific criteria. The Dhaka Improvement Trust (DIT), established in 1956, oversaw the development of public amenities, construction of roads, and implementation of other infrastructure projects. Wide roads were laid out in a grid pattern, with vegetation planted along roadsides and in public areas. Plots were leased to allottees for 99 years at a rate of ৳5,000 per bigha. While initially the DIT strictly designated Dhanmondi plots for residential purposes, by 1972, this rule was considerably relaxed to the extent that it was virtually not enforced anymore.[9]
Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, regarded as the founding father of Bangladesh, resided in Dhanmondi at road no. 32. He was assassinated along with most of his family at his residence on 15 August 1975. Today, his former residence has been converted into a memorial museum.[9]
Over the decades Dhanmondi evolved into a chic, miniature city, with hospitals to malls, schools, banks, offices and universities. After the liberation war, its neighbourhoods primarily consisted of two-story houses.[10] Dhanmondi Thana was formed in 1976.[11]
Geography
[edit]Dhanmondi Thana covers 4.34 km2 (1.68 sq mi), bordered by Mohammadpur Thana to the north, New Market Thana to the east and the south, Hazaribagh Thana to the south and the west. Sher-e-Bangla Nagar and Kalabagan thanas occupies the eastern border.[11]
Demographics
[edit]In the 2022 Bangladeshi census, Dhanmondi Thana recorded a total population of 101,937, distributed between the two city corporations. The Dhaka North section housed 75,148 residents, whereas Dhaka South accommodated 26,789 residents, with a combined total of 27,487 households and an average household size of 3.7 members. [2] The recorded population in 2022 reflects a decrease from the 2011 figures, which stood at 147,643 individuals.[6]
Points of interest
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2024) |
The most important roads in Dhanmondi are Road no. 27, Satmasjid Road and Mirpur Road.
Dhanmondi Lake
[edit]The lakeside walkway at Dhanmondi Lake is overlooked by the Rabindra Sarobar, an open-air amphitheater near the Road 8 bridge, where dramas, concerts, and various cultural programs are held from time to time by both amateur and professional artistes, especially during major festivals and holidays.
Exotic and delicious snack stalls along the lakeside, particularly on Road 2 (opposite the entrance to Bangladesh Rifles), Road 5 (on an island accessible only by foot bridges from two sides), Road 8 (near the amphitheater) and Road 32 (opposite the residence of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman), offer a variety of snacks and beverages, aimed at city dwellers during the day. These places are gathered by a lot of people, mostly around late afternoon, due to its popularity.
During festivals such as Pohela Baishakh, Independence Day and Eid, moving around Dhanmondi can be difficult due to crowding.
Banks
[edit]Almost every bank operating in the country has an outlet in Dhanmondi. Foreign banks such as HSBC and Standard Chartered also have branches there, with HSBC and Standard Chartered having multiple ATM booths within the area.
Restaurants
[edit]Dhanmondi is known for its wide range of expensive restaurants and cafes that mostly cluster around Satmasjid Road. Several local and international fast food chains in the country have outlets in this area. Most of these restaurants were opened in 2010s.
Dhanmondi is home to many renowned food chains, especially fast food.
Education
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2015) |
Over the last fifteen years, a large number of outstanding schools, colleges and private universities have been developed around the area.
Government Laboratory High School, BCSIR School, Birshreshtha Noor Mohammad Public School, Birshreshtha Munshi Abdur Rouf Public School, Viqarunnisa Noon School, YWCA Higher Secondary School etc are some of the renowned schools in this area. Many well-known English medium schools in the country, such as Scholastica (Junior Section), South Breeze, Sunbeams,[citation needed] Oxford International School Main Campus and Junior Dhanmondi Campus,[12] Mastermind, Maple Leaf International school, Marie Curie School, Dhanmondi Tutorial, Sunnydale, European Standard School (ESS), Scholars School and College are located here.
Colleges like Dhaka College, Hamdard Public College, Ideal College and Dhaka City College are located here. Among the universities, University Of Development Alternative (UODA), the University of Liberal Arts Bangladesh, United International University, Daffodil International University, Eastern University, People's University of Bangladesh, World University of Bangladesh, Stamford University, University of Asia Pacific are the most well-known and can be quite luxurious and expensive.
Gallery
[edit]-
Bridge over Dhanmondi Lake
-
Dhanmondi Lake.
-
Dhanmondi 32 bridge in 1966
-
Shops and restaurants at Satmasjid Road
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Geographic coordinates of Dhaka, Bangladesh". DATEANDTIME.INFO. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
- ^ a b c National Report (PDF). Population and Housing Census 2022. Vol. 1. Dhaka: Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. November 2023. p. 386. ISBN 978-9844752016.
- ^ "Bangladesh Postal Code". Dhaka: Bangladesh Postal Department under the Department of Posts and Telecommunications of the Ministry of Posts, Telecommunications and Information Technology of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. 19 October 2024.
- ^ "Bangladesh Area Code". China: Chahaoba.com. 18 October 2024.
- ^ Allchin, Joseph (15 March 2014). "Bangladesh property: Dhaka's growing high-end market". Financial Times. Nikkei Inc. Retrieved 9 May 2024.
- ^ a b National Report (PDF). Population & Housing Census 2011. Vol. 2. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 September 2017. Retrieved 9 May 2024.
- ^ Hossain, Nazir (April 1995). Kiṃbadantira Ḍhākā কিংবদন্তির ঢাকা [Dhaka in Legends] (in Bengali) (3rd ed.). Dhaka: Three Star Cooperative Multipurpose Society Limited. p. 106. LCCN 95905768. OCLC 33970022.
- ^ Mamoon, Muntassir (2008). ঢাকা: স্মৃতি বিস্মৃতির নগরী [Dhaka: City of Memory and Oblivion] (in Bengali). Dhaka: Ananya Prakashani. p. 137. ISBN 984-412-104-3.
- ^ a b Islam, Sirajul (2012). "Dhanmondi". In Sirajul Islam; Miah, Sajahan; Khanam, Mahfuza; Ahmed, Sabbir (eds.). Banglapedia: the National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Online ed.). Dhaka, Bangladesh: Banglapedia Trust, Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. ISBN 984-32-0576-6. OCLC 52727562. OL 30677644M. Retrieved 28 December 2024.
- ^ "আবাসিকের ঐতিহ্য হারাচ্ছে ধানমন্ডি" [Dhanmondi losing its residential tradition]. Prothom Alo (in Bengali). 6 January 2016. Retrieved 15 August 2022.
- ^ a b Ahmed, Syed Shabbir (2012). "Dhanmondi Thana". In Sirajul Islam; Miah, Sajahan; Khanam, Mahfuza; Ahmed, Sabbir (eds.). Banglapedia: the National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Online ed.). Dhaka, Bangladesh: Banglapedia Trust, Asiatic Society of Bangladesh. ISBN 984-32-0576-6. OCLC 52727562. OL 30677644M. Retrieved 28 December 2024.
- ^ "Contact Details." Oxford International School. Retrieved 20 September 2015. "Main Campus (Attached Centre of Cambridge International Examination for CIPP, CLSP, Check Point, O Level and A Level examinations) House # 34, Road # 27 (old), New 16, Dhanmondi R/A, Dhaka-1209, "