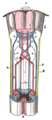
Spinocerebellar tracts
| Spinocerebellar tracts | |
|---|---|
 Spinocerebellar tracts are labeled in blue at right. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tractus spinocerebellaris |
| MeSH | D020824 |
| NeuroNames | 1978 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The spinocerebellar tracts are nerve tracts originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum. The two main tracts are the dorsal spinocerebellar tract, and the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Both of these tracts are located in the peripheral region of the lateral funiculi (white matter columns).[1] Other tracts are the rostral spinocerebellar tract, and the cuneocerebellar tract (posterior external arcuate fibers).[2]
They carry proprioceptive, and cutaneous information to the cerebellum, where movement can be coordinated.[1]
Origins of proprioceptive information
[edit]Proprioceptive information is obtained by Golgi tendon organs and muscle spindles.
- Golgi tendon organs consist of a fibrous capsule enclosing tendon fascicles and bare nerve endings that respond to tension in the tendon by causing action potentials in type Ib afferents. These fibers are relatively large, myelinated, and quickly conducting.
- Muscle spindles monitor the length within muscles and send information via faster Ia afferents. These axons are larger and faster than type Ib (from both nuclear bag fibers and nuclear chain fibers) and type II afferents (solely from nuclear chain fibers).
All of these neurons are sensory (first order, or primary) and have their cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia. They pass through Rexed laminae layers I-VI of the posterior grey column (dorsal horn) to form synapses with second order or secondary neurons in layer VII just beneath the dorsal horn.
Tracts
[edit]The main spinocerebellar tracts are the dorsal and the ventral spinocerebellar tracts.[1]
| Division | Peripheral Process of First Order the Neuron | Region of Innervation |
|---|---|---|
| dorsal (posterior) spinocerebellar tract | from muscle spindle (primarily) and Golgi tendon organs | ipsilateral caudal aspect of the body and legs |
| ventral (anterior) spinocerebellar tract | from Golgi tendon organs | ipsilateral caudal aspect of the body and legs |
| Cuneocerebellar tract | from muscle spindle (primarily) and Golgi tendon organs | ipsilateral arm |
| Rostral spinocerebellar tract | from Golgi tendon organs | ipsilateral arm |
Dorsal spinocerebellar tract
[edit]The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (posterior spinocerebellar tract, Flechsig's fasciculus, Flechsig's tract) conveys proprioceptive information from proprioceptors in the skeletal muscles and joints to the cerebellum.[3]
It is part of the somatosensory system and runs in parallel with the ventral spinocerebellar tract. It carries proprioceptive information from muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs of ipsilateral part of trunk and lower limb. Proprioceptive information is taken to the spinal cord via central processes of dorsal root ganglia (first order neurons). These central processes travel through the posterior grey column where they synapse with second order neurons of Clarke's nucleus. Axon fibers from Clarke's Nucleus convey this proprioceptive information in the spinal cord in the peripheral region of the lateral funiculus ipsilaterally. The fibers continue to course through the medulla oblongata of the brainstem, at which point they pass through the inferior cerebellar peduncle and into the cerebellum, where unconscious proprioceptive information is processed.
This tract involves two neurons and ends up on the same side of the body.
The terms Flechsig's fasciculus and Flechsig's tract are named after German neuroanatomist, psychiatrist and neuropathologist Paul Flechsig.
Ventral spinocerebellar tract
[edit]The ventral spinocerebellar tract (or anterior spinocerebellar tract) conveys proprioceptive information from the body to the cerebellum. Historically, it has also been known as Gowers' column (or fasciculus or tract), after Sir William Richard Gowers.
It is part of the somatosensory system and runs in parallel with the dorsal spinocerebellar tract. Both these tracts involve two neurons. The ventral spinocerebellar tract will cross to the opposite side of the body first in the spinal cord as part of the anterior white commissure and then cross again to end in the cerebellum (referred to as a "double cross"), as compared to the dorsal spinocerebellar tract, which does not decussate, or cross sides, at all through its path.
The ventral tract (under L2/L3) gets its proprioceptive/fine touch/vibration information from a first order neuron, with its cell body in a dorsal ganglion. The axon runs via the fila radicularia to the dorsal horn of the grey matter. There it makes a synapse with the dendrites of two neurons: they send their axons bilaterally to the ventral border of the lateral funiculi. The fibers of the ventral spinocerebellar tract then enters the cerebellum via the superior cerebellar peduncle. This is in contrast with the dorsal spinocerebellar tract (C8 - L2/L3), which only has 1 unilateral axon that has its cell body in Clarke's column (only at the level of C8 - L2/L3).
Originates from ventral horn at lumbosacral spinal levels. Axons first cross midline in the spinal cord and run in the ventral border of the lateral funiculi. These axons ascend to the pons where they join the superior cerebellar peduncle to enter the cerebellum. Once in the deep white matter of the cerebellum, the axons recross the midline, give off collaterals to the globose and emboliform nuclei, and terminate in the cortex of the anterior lobe and vermis of the posterior lobe.
Comparison with dorsal spinocerebellar tract
[edit]When the dorsal roots are cut in a cat performing a step cycle, peripheral excitation is lost, and the dorsal spinocerebellar tract has no activity; the ventral spinocerebellar tract continues to show activity. This suggests that the dorsal spinocerebellar tract carries sensory information to the spinocerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncle during movement (since the inferior peduncle is known to contain fibres from the dorsal tract), and that the ventral spinocerebellar tract carries internally generated motor information about the movement through the superior cerebellar peduncle.[4]
Posterior external arcuate fibers
[edit]The posterior external arcuate fibers (dorsal external arcuate fibers or cuneocerebellar tract)[5] take origin in the accessory cuneate nucleus, and pass to the inferior cerebellar peduncle of the same side. The term "cuneocerebellar tract" is also used to describe exteroceptive and proprioceptive components that take origin in the gracile and cuneate nuclei; they pass to the inferior cerebellar peduncle of the same side.[6]
The posterior external arcuate fibers carry proprioceptive information from the upper limbs and neck. It is an analogue to the dorsal spinocerebellar tract for the upper limbs.[7] In this context, the "cuneo-" derives from the accessory cuneate nucleus, not the cuneate nucleus. (The two nuclei are related in space, but not in function.)
It is uncertain whether fibers are continued directly from the gracile and cuneate fasciculi into the inferior peduncle.
Rostral spinocerebellar tract
[edit]The rostral spinocerebellar tract is a tract which transmits information from the golgi tendon organs of the cranial half of the body to the cerebellum.[8] It terminates bilaterally in the anterior lobe of the cerebellum (lower cerebellar peduncle) after travelling ipsilaterally from its origin in the cervical portion of the spinal cord.[9][10] It reaches the cerebellum partly through the brachium conjunctivum (superior cerebellar peduncle) and partly through the restiform body (inferior cerebellar peduncle).[10]
Pathway for dorsal and spinocuneocerebellar tracts
[edit]The sensory neurons synapse in the posterior thoracic nucleus also known as Clarke's nucleus.
This is a column of relay neuron cell bodies within the medial gray matter within the spinal cord in layer VII (just beneath the dorsal horn), specifically between T1-L3. These neurons then send axons up the spinal cord, and project ipsilaterally to medial zones of the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncle.
Below L3, relevant neurons pass into the gracile fasciculus (usually associated with the dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway) until L3 where they synapse with the posterior thoracic nucleus (leading to considerable caudal enlargement).
The neurons in the accessory cuneate nucleus have axons leading to the ipsilateral cerebellum via the inferior cerebellar peduncle.
Pathway for ventral and rostral spinocerebellar tracts
[edit]Some neurons of the ventral spinocerebellar tract instead form synapses with neurons in layer VII of L4-S3. Most of these fibers cross over to the contralateral lateral funiculus via the anterior white commissure and through the superior cerebellar peduncle. The fibers then often cross over again within the cerebellum to end on the ipsilateral side. For this reason the tract is sometimes termed the "double-crosser."
The Rostral Tract synapses at the dorsal horn lamina (intermediate gray zone) of the spinal cord and ascends ipsilaterally to the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncle
Additional images
[edit]-
Decussation of pyramids.
-
Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view.
-
Deep dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view.
-
Dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view.
-
Dissection of brain-stem. Dorsal view.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Standring, Susan (2016). Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Digital version (Forty-first ed.). New York: Elsevier Limited. p. 431. ISBN 9780702052309.
- ^ Haines, Duane E.; Mihailoff, Gregory A. (2018). Fundamental neuroscience for basic and clinical applications (5th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier. p. 162. ISBN 9780323396325.
- ^ Adel K. Afifi Functional Neuroanatomy pag.51 ISBN 970-10-5504-7
- ^ Jessell, Thomas M.; Kandel, Eric R.; Schwartz, James H. (2000). Principles of neural science. New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-8385-7701-6.
- ^ Sabyasachi Sircar (2007). Principles of Medical Physiology. Stuttgart: Georg Thieme Verlag. p. 608. ISBN 978-1-58890-572-7.
- ^ Cooke, J. D. (October 1971). "Origin and termination of cuneocerebellar tract". Experimental Brain Research. 13 (4): 339–358. doi:10.1007/bf00234336. PMID 5123642. S2CID 23836263.
- ^ Fix, James D. (2002). Neuroanatomy. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 133. ISBN 978-0-7817-2829-4.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2008-04-30. Retrieved 2019-10-02.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Ben Greenstein, Adam Greedstein (2000). Color atlas of neuroscience: neuroanatomy and neurophysiology. ISBN 0-86577-710-1.
- ^ a b "Rostral spinocerebellar tract". The Neuroscience Lexicon. Retrieved 19 May 2013.[dead link]
Further reading
[edit]- OSCARSSON, O.; UDDENBERG, N. (1 May 1965). "Properties of Afferent Connections to the Rostral Spinocerebellar Tract in the Cat". Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. 64 (1–2): 143–153. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04163.x. PMID 14347272.
External links
[edit]- hier-804 at NeuroNames
- hier-805 at NeuroNames
- hier-793 at NeuroNames - dorsal external arcuate fibers
- hier-800 at NeuroNames - cuneocerebellar tract
- Anatomyatlases Plate17327
- NIF Search - Anterior Spinocerebellar Tract via the Neuroscience Information Framework