Surgery
Surgery[a] is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance (cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies.
The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical operations typically require a surgical team that typically consists of the surgeon, the surgical assistant, an anaesthetist (often also complemented by an anaesthetic nurse), a scrub nurse (who handles sterile equipment), a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist, while procedures that mandate cardiopulmonary bypass will also have a perfusionist. All surgical procedures are considered invasive and often require a period of postoperative care (sometimes intensive care) for the patient to recover from the iatrogenic trauma inflicted by the procedure. The duration of surgery can span from several minutes to tens of hours depending on the specialty, the nature of the condition, the target body parts involved and the circumstance of each procedure, but most surgeries are designed to be one-off interventions that are typically not intended as an ongoing or repeated type of treatment.
In British colloquialism, the term "surgery" can also refer to the facility where surgery is performed, or simply the office/clinic of a physician,[1] dentist or veterinarian.[2]
Definitions
[edit]
As a general rule, a procedure is considered surgical when it involves cutting of a person's tissues or closure of a previously sustained wound. Other procedures that do not necessarily fall under this rubric, such as angioplasty or endoscopy, may be considered surgery if they involve "common" surgical procedure or settings, such as use of antiseptic measures and sterile fields, sedation/anesthesia, proactive hemostasis, typical surgical instruments, suturing or stapling. All forms of surgery are considered invasive procedures; the so-called "noninvasive surgery" ought to be more appropriately called minimally invasive procedures, which usually refers to a procedure that utilizes natural orifices (e.g. most urological procedures) or does not penetrate the structure being excised (e.g. endoscopic polyp excision, rubber band ligation, laser eye surgery), are percutaneous (e.g. arthroscopy, catheter ablation, angioplasty and valvuloplasty), or to a radiosurgical procedure (e.g. irradiation of a tumor).[citation needed]
Types of surgery
[edit]Surgical procedures are commonly categorized by urgency, type of procedure, body system involved, the degree of invasiveness, and special instrumentation.
- Based on timing:[citation needed]
- Elective surgery is done to correct a non-life-threatening condition, and is carried out at the person's convenience, or to the surgeon's and the surgical facility's availability.
- Semi-elective surgery is one that is better done early to avoid complications or potential deterioration of the patient's condition, but such risk are sufficiently low that the procedure can be postponed for a short period time.
- Emergency surgery is surgery which must be done without any delay to prevent death or serious disabilities or loss of limbs and functions.
- Based on purpose:[citation needed]
- Exploratory surgery is performed to establish or aid a diagnosis.
- Therapeutic surgery is performed to treat a previously diagnosed condition.
- Curative surgery is a therapeutic procedure done to permanently remove a pathology.
- Plastic surgery is done to improve a body part's function or appearance.
- Reconstructive plastic surgery is done to improve the function or subjective appearance of a damaged or malformed body part.[3]
- Cosmetic surgery is done to subjectively improve the appearance of an otherwise normal body part.[4]
- Bariatric surgery is done to assist weight loss when dietary and pharmaceutical methods alone have failed.
- Non-survival surgery, or terminal surgery, is where Euthanasia is performed while the subject is under Anesthesia so that the subject will not regain conscious pain perception.[5] This type of surgery is usually done in Animal testing experiments.[6]
- By type of procedure:
- Amputation involves removing an entire body part, usually a limb or digit; castration is the amputation of testes; circumcision is the removal of prepuce from the penis or clitoral hood from the clitoris (see female circumcision). Replantation involves reattaching a severed body part.
- Resection is the removal of all or part of an internal organ and/or connective tissue. A segmental resection specifically removes an independent vascular region of an organ such as a hepatic segment, a bronchopulmonary segment or a renal lobe.[7] Excision is the resection of only part of an organ, tissue or other body part (e.g. skin) without discriminating specific vascular territories. Exenteration is the complete removal of all organs and soft tissue content (especially lymphoid tissues) within a body cavity.
- Extirpation is the complete excision or surgical destruction of a body part.[8]
- Ablation is destruction of tissue through the use of energy-transmitting devices such as electrocautery/fulguration, laser, focused ultrasound or freezing.
- Repair involves the direct closure or restoration of an injured, mutilated or deformed organ or body part, usually by suturing or internal fixation. Reconstruction is an extensive repair of a complex body part (such as joints), often with some degrees of structural/functional replacement and commonly involves grafting and/or use of implants.
- Grafting is the relocation and establishment of a tissue from one part of the body to another. A flap is the relocation of a tissue without complete separation of its original attachment, and a free flap is a completely detached flap that carries an intact neurovascular structure ready for grafting onto a new location.
- Bypass involves the relocation/grafting of a tubular structure onto another in order to reroute the content flow of that target structure from a specific segment directly to a more distal ("downstream") segment.
- Implantation is insertion of artificial medical devices to replace or augment existing tissue.
- Transplantation is the replacement of an organ or body part by insertion of another from a different human (or animal) into the person undergoing surgery. Harvesting is the resection of an organ or body part from a live human or animal (known as the donor) for transplantation into another patient (known as the recipient).
- By organ system: Surgical specialties are traditionally and academically categorized by the organ, organ system or body region involved. Examples include:
- Cardiac surgery — the heart and mediastinal great vessels;
- Thoracic surgery — the thoracic cavity including the lungs;
- Gastrointestinal surgery — the digestive tract and its accessory organs;
- Vascular surgery — the extra-mediastinal great vessels and peripheral circulatory system;
- Urological surgery — the genitourinary system;
- ENT surgery — ear, nose and throat, also known as head and neck surgery when including the neck region;
- Oral and maxillofacial surgery — the oral cavity, jaws, and face;
- Neurosurgery — the central nervous system, and;
- Orthopedic surgery — the musculoskeletal system.
- By degree of invasiveness of surgical procedures:
- Conventional open surgery (such as a laparotomy) requires a large incision to access the area of interest, and directly exposes the internal body cavity to the outside.
- Minimally-invasive surgery involves much smaller surface incisions or even natural orifices (nostril, mouth, anus or urethra) to insert miniaturized instruments within a body cavity or structure, as in laparoscopic surgery or angioplasty.
- Hybrid surgery uses a combination of open and minimally-invasive techniques, and may include hand ports or larger incisions to assist with performance of elements of the procedure.
- By equipment used:
- Laser surgery involves use of laser ablation to divide tissue instead of a scalpel, scissors or similar sharp-edged instruments.
- Cryosurgery uses low-temperature cryoablation to freeze and destroy a target tissue.
- Electrosurgery involves use of electrocautery to cut and coagulate tissue.
- Microsurgery involves the use of an operating microscope for the surgeon to see and manipulate small structures.
- Endoscopic surgery uses optical instruments to relay the image from inside an enclosed body cavity to the outside, and the surgeon performs the procedure using specialized handheld instruments inserted through trocars placed through the body wall. Most modern endoscopic procedures are video-assisted, meaning the images are viewed on a display screen rather than through the eyepiece on the endoscope.
- Robotic surgery makes use of robotics such as the Da Vinci or the ZEUS robotic surgical systems, to remotely control endoscopic or minimally-invasive instruments.
Terminology
[edit]- Resection and excisional procedures start with a prefix for the target organ to be excised (cut out) and end in the suffix -ectomy. For example, removal of part of the stomach would be called a subtotal gastrectomy.
- Procedures involving cutting into an organ or tissue end in -otomy. A surgical procedure cutting through the abdominal wall to gain access to the abdominal cavity is a laparotomy.
- Minimally invasive procedures, involving small incisions through which an endoscope is inserted, end in -oscopy. For example, such surgery in the abdominal cavity is called laparoscopy.
- Procedures for formation of a permanent or semi-permanent opening called a stoma in the body end in -ostomy, such as creation of a colostomy, a connection of colon and the abdominal wall. This prefix is also used for connection between two viscera, such as how an esophagojejunostomy refers to a connection created between the esophagus and the jejunum.
- Plastic and reconstruction procedures start with the name for the body part to be reconstructed and end in -plasty. For example, rhino- is a prefix meaning "nose", therefore a rhinoplasty is a reconstructive or cosmetic surgery for the nose. A pyloroplasty refers to a type of reconstruction of the gastric pylorus.
- Procedures that involve cutting the muscular layers of an organ end in -myotomy. A pyloromyotomy refers to cutting the muscular layers of the gastric pylorus.
- Repair of a damaged or abnormal structure ends in -orraphy. This includes herniorrhaphy, another name for a hernia repair.
- Reoperation, revision, or "redo" procedures refer to a planned or unplanned return to the operating theater after a surgery is performed to re-address an aspect of patient care. Unplanned reasons for reoperation include postoperative complications such as bleeding or hematoma formation, development of a seroma or abscess, anastomotic leak, tissue necrosis requiring debridement or excision, or in the case of malignancy, close or involved resection margins that may require re-excision to avoid local recurrence. Reoperation can be performed in the acute phase, or it can be also performed months to years later if the surgery failed to solve the indicated problem. Reoperation can also be planned as a staged operation where components of the procedure are performed or reversed under separate anesthesia.
Description of surgical procedure
[edit]Setting
[edit]Inpatient surgery is performed in a hospital, and the person undergoing surgery stays at least one night in the hospital after the surgery. Outpatient surgery occurs in a hospital outpatient department or freestanding ambulatory surgery center, and the person who had surgery is discharged the same working day.[9] Office-based surgery occurs in a physician's office, and the person is discharged the same day.[10]
At a hospital, modern surgery is often performed in an operating theater using surgical instruments, an operating table, and other equipment. Among United States hospitalizations for non-maternal and non-neonatal conditions in 2012, more than one-fourth of stays and half of hospital costs involved stays that included operating room (OR) procedures.[11] The environment and procedures used in surgery are governed by the principles of aseptic technique: the strict separation of "sterile" (free of microorganisms) things from "unsterile" or "contaminated" things. All surgical instruments must be sterilized, and an instrument must be replaced or re-sterilized if it becomes contaminated (i.e. handled in an unsterile manner, or allowed to touch an unsterile surface). Operating room staff must wear sterile attire (scrubs, a scrub cap, a sterile surgical gown, sterile latex or non-latex polymer gloves and a surgical mask), and they must scrub hands and arms with an approved disinfectant agent before each procedure.
Preoperative care
[edit]Prior to surgery, the person is given a medical examination, receives certain pre-operative tests, and their physical status is rated according to the ASA physical status classification system. If these results are satisfactory, the person requiring surgery signs a consent form and is given a surgical clearance. If the procedure is expected to result in significant blood loss, an autologous blood donation may be made some weeks prior to surgery. If the surgery involves the digestive system, the person requiring surgery may be instructed to perform a bowel prep by drinking a solution of polyethylene glycol the night before the procedure. People preparing for surgery are also instructed to abstain from food or drink (an NPO order after midnight on the night before the procedure), to minimize the effect of stomach contents on pre-operative medications and reduce the risk of aspiration if the person vomits during or after the procedure.[12]
Some medical systems have a practice of routinely performing chest x-rays before surgery. The premise behind this practice is that the physician might discover some unknown medical condition which would complicate the surgery, and that upon discovering this with the chest x-ray, the physician would adapt the surgery practice accordingly.[13] However, medical specialty professional organizations recommend against routine pre-operative chest x-rays for people who have an unremarkable medical history and presented with a physical exam which did not indicate a chest x-ray.[13] Routine x-ray examination is more likely to result in problems like misdiagnosis, overtreatment, or other negative outcomes than it is to result in a benefit to the person.[13] Likewise, other tests including complete blood count, prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, basic metabolic panel, and urinalysis should not be done unless the results of these tests can help evaluate surgical risk.[14]
Preparing for surgery
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (January 2019) |
A surgical team may include a surgeon, anesthetist, a circulating nurse, and a "scrub tech", or surgical technician, as well as other assistants who provide equipment and supplies as required. While informed consent discussions may be performed in a clinic or acute care setting, the pre-operative holding area is where documentation is reviewed and where family members can also meet the surgical team. Nurses in the preoperative holding area confirm orders and answer additional questions of the family members of the patient prior to surgery. In the pre-operative holding area, the person preparing for surgery changes out of their street clothes and are asked to confirm the details of his or her surgery as previously discussed during the process of informed consent. A set of vital signs are recorded, a peripheral IV line is placed, and pre-operative medications (antibiotics, sedatives, etc.) are given.[15]
When the patient enters the operating room and is appropriately anesthetized, the team will then position the patient in an appropriate surgical position. If hair is present at the surgical site, it is clipped (instead of shaving). The skin surface within the operating field is cleansed and prepared by applying an antiseptic (typically chlorhexidine gluconate in alcohol, as this is twice as effective as povidone-iodine at reducing the risk of infection).[16] Sterile drapes are then used to cover the borders of the operating field. Depending on the type of procedure, the cephalad drapes are secured to a pair of poles near the head of the bed to form an "ether screen", which separate the anesthetist/anesthesiologist's working area (unsterile) from the surgical site (sterile).[17]
Anesthesia is administered to prevent pain from the trauma of cutting, tissue manipulation, application of thermal energy, and suturing. Depending on the type of operation, anesthesia may be provided locally, regionally, or as general anesthesia. Spinal anesthesia may be used when the surgical site is too large or deep for a local block, but general anesthesia may not be desirable. With local and spinal anesthesia, the surgical site is anesthetized, but the person can remain conscious or minimally sedated. In contrast, general anesthesia may render the person unconscious and paralyzed during surgery. The person is typically intubated to protect their airway and placed on a mechanical ventilator, and anesthesia is produced by a combination of injected and inhaled agents. The choice of surgical method and anesthetic technique aims to solve the indicated problem, minimize the risk of complications, optimize the time needed for recovery, and limit the surgical stress response.
Intraoperative phase
[edit]The intraoperative phase begins when the surgery subject is received in the surgical area (such as the operating theater or surgical department), and lasts until the subject is transferred to a recovery area (such as a post-anesthesia care unit).[18]
An incision is made to access the surgical site. Blood vessels may be clamped or cauterized to prevent bleeding, and retractors may be used to expose the site or keep the incision open. The approach to the surgical site may involve several layers of incision and dissection, as in abdominal surgery, where the incision must traverse skin, subcutaneous tissue, three layers of muscle and then the peritoneum. In certain cases, bone may be cut to further access the interior of the body; for example, cutting the skull for brain surgery or cutting the sternum for thoracic (chest) surgery to open up the rib cage. Whilst in surgery aseptic technique is used to prevent infection or further spreading of the disease. The surgeons' and assistants' hands, wrists and forearms are washed thoroughly for at least 4 minutes to prevent germs getting into the operative field, then sterile gloves are placed onto their hands. An antiseptic solution is applied to the area of the person's body that will be operated on. Sterile drapes are placed around the operative site. Surgical masks are worn by the surgical team to avoid germs on droplets of liquid from their mouths and noses from contaminating the operative site.[citation needed]
Work to correct the problem in body then proceeds. This work may involve:
- excision – cutting out an organ, tumor,[19] or other tissue.
- resection – partial removal of an organ or other bodily structure.[20]
- reconnection of organs, tissues, etc., particularly if severed. Resection of organs such as intestines involves reconnection. Internal suturing or stapling may be used. Surgical connection between blood vessels or other tubular or hollow structures such as loops of intestine is called anastomosis.[21]
- reduction – the movement or realignment of a body part to its normal position. e.g. Reduction of a broken nose involves the physical manipulation of the bone or cartilage from their displaced state back to their original position to restore normal airflow and aesthetics.[22]
- ligation – tying off blood vessels, ducts, or "tubes".[23]
- grafts – may be severed pieces of tissue cut from the same (or different) body or flaps of tissue still partly connected to the body but resewn for rearranging or restructuring of the area of the body in question. Although grafting is often used in cosmetic surgery, it is also used in other surgery. Grafts may be taken from one area of the person's body and inserted to another area of the body. An example is bypass surgery, where clogged blood vessels are bypassed with a graft from another part of the body. Alternatively, grafts may be from other persons, cadavers, or animals.[24]
- insertion of prosthetic parts when needed. Pins or screws to set and hold bones may be used. Sections of bone may be replaced with prosthetic rods or other parts. Sometimes a plate is inserted to replace a damaged area of skull. Artificial hip replacement has become more common.[25] Heart pacemakers or valves may be inserted. Many other types of prostheses are used.
- creation of a stoma, a permanent or semi-permanent opening in the body[26]
- in transplant surgery, the donor organ (taken out of the donor's body) is inserted into the recipient's body and reconnected to the recipient in all necessary ways (blood vessels, ducts, etc.).[27]
- arthrodesis – surgical connection of adjacent bones so the bones can grow together into one. Spinal fusion is an example of adjacent vertebrae connected allowing them to grow together into one piece.[28]
- modifying the digestive tract in bariatric surgery for weight loss.
- repair of a fistula, hernia, or prolapse.
- repair according to the ICD-10-PCS, in the Medical and Surgical Section 0, root operation Q, means restoring, to the extent possible, a body part to its normal anatomic structure and function. This definition, repair, is used only when the method used to accomplish the repair is not one of the other root operations. Examples would be colostomy takedown, herniorrhaphy of a hernia, and the surgical suture of a laceration.[29]
- other procedures, including:
- clearing clogged ducts, blood or other vessels
- removal of calculi (stones)
- draining of accumulated fluids
- debridement – removal of dead, damaged, or diseased tissue
Blood or blood expanders may be administered to compensate for blood lost during surgery. Once the procedure is complete, sutures or staples are used to close the incision. Once the incision is closed, the anesthetic agents are stopped or reversed, and the person is taken off ventilation and extubated (if general anesthesia was administered).[30]
Postoperative care
[edit]After completion of surgery, the person is transferred to the post anesthesia care unit and closely monitored. When the person is judged to have recovered from the anesthesia, he/she is either transferred to a surgical ward elsewhere in the hospital or discharged home. During the post-operative period, the person's general function is assessed, the outcome of the procedure is assessed, and the surgical site is checked for signs of infection. There are several risk factors associated with postoperative complications, such as immune deficiency and obesity. Obesity has long been considered a risk factor for adverse post-surgical outcomes. It has been linked to many disorders such as obesity hypoventilation syndrome, atelectasis and pulmonary embolism, adverse cardiovascular effects, and wound healing complications.[31] If removable skin closures are used, they are removed after 7 to 10 days post-operatively, or after healing of the incision is well under way.[citation needed]
It is not uncommon for surgical drains to be required to remove blood or fluid from the surgical wound during recovery. Mostly these drains stay in until the volume tapers off, then they are removed. These drains can become clogged, leading to abscess.[32]
Postoperative therapy may include adjuvant treatment such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or administration of medication such as anti-rejection medication for transplants. For postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV), solutions like saline, water, controlled breathing placebo and aromatherapy can be used in addition to medication.[33] Other follow-up studies or rehabilitation may be prescribed during and after the recovery period. A recent post-operative care philosophy has been early ambulation. Ambulation is getting the patient moving around. This can be as simple as sitting up or even walking around. The goal is to get the patient moving as early as possible. It has been found to shorten the patient's length of stay. Length of stay is the amount of time a patient spends in the hospital after surgery before they are discharged. In a recent study[34] done with lumbar decompressions, the patient's length of stay was decreased by 1–3 days.
The use of topical antibiotics on surgical wounds to reduce infection rates has been questioned.[35] Antibiotic ointments are likely to irritate the skin, slow healing, and could increase risk of developing contact dermatitis and antibiotic resistance.[35] It has also been suggested that topical antibiotics should only be used when a person shows signs of infection and not as a preventative.[35] A systematic review published by Cochrane (organisation) in 2016, though, concluded that topical antibiotics applied over certain types of surgical wounds reduce the risk of surgical site infections, when compared to no treatment or use of antiseptics.[36] The review also did not find conclusive evidence to suggest that topical antibiotics increased the risk of local skin reactions or antibiotic resistance.[citation needed]
Through a retrospective analysis of national administrative data, the association between mortality and day of elective surgical procedure suggests a higher risk in procedures carried out later in the working week and on weekends. The odds of death were 44% and 82% higher respectively when comparing procedures on a Friday to a weekend procedure. This "weekday effect" has been postulated to be from several factors including poorer availability of services on a weekend, and also, decrease number and level of experience over a weekend.[37]
Postoperative pain affects an estimated 80% of people who underwent surgery.[38] While pain is expected after surgery, there is growing evidence that pain may be inadequately treated in many people in the acute period immediately after surgery. It has been reported that incidence of inadequately controlled pain after surgery ranged from 25.1% to 78.4% across all surgical disciplines.[39] There is insufficient evidence to determine if giving opioid pain medication pre-emptively (before surgery) reduces postoperative pain the amount of medication needed after surgery.[38]
Postoperative recovery has been defined as an energy‐requiring process to decrease physical symptoms, reach a level of emotional well‐being, regain functions, and re‐establish activities.[40] Moreover, it has been identified that patients who have undergone surgery are often not fully recovered on discharge.[citation needed]
Epidemiology
[edit]United States
[edit]This section needs to be updated. (February 2025) |
In 2011, of the 38.6 million hospital stays in U.S. hospitals, 29% included at least one operating room procedure. These stays accounted for 48% of the total $387 billion in hospital costs.[41]
The overall number of procedures remained stable from 2001 to 2011. In 2011, over 15 million operating room procedures were performed in U.S. hospitals.[42]
Data from 2003 to 2011 showed that U.S. hospital costs were highest for the surgical service line; the surgical service line costs were $17,600 in 2003 and projected to be $22,500 in 2013.[43] For hospital stays in 2012 in the United States, private insurance had the highest percentage of surgical expenditure.[44] in 2012, mean hospital costs in the United States were highest for surgical stays.[44]
Special populations
[edit]Elderly people
[edit]Older adults have widely varying physical health. Frail elderly people are at significant risk of post-surgical complications and the need for extended care. Assessment of older people before elective surgery can accurately predict the person's recovery trajectories.[45] One frailty scale uses five items: unintentional weight loss, muscle weakness, exhaustion, low physical activity, and slowed walking speed. A healthy person scores 0; a very frail person scores 5. Compared to non-frail elderly people, people with intermediate frailty scores (2 or 3) are twice as likely to have post-surgical complications, spend 50% more time in the hospital, and are three times as likely to be discharged to a skilled nursing facility instead of to their own homes.[45] People who are frail and elderly (score of 4 or 5) have even worse outcomes, with the risk of being discharged to a nursing home rising to twenty times the rate for non-frail elderly people.[citation needed]
Children
[edit]Surgery on children requires considerations that are not common in adult surgery. Children and adolescents are still developing physically and mentally making it difficult for them to make informed decisions and give consent for surgical treatments. Bariatric surgery in youth is among the controversial topics related to surgery in children.[citation needed]
Vulnerable populations
[edit]Doctors perform surgery with the consent of the person undergoing surgery. Some people are able to give better informed consent than others. Populations such as incarcerated persons, people living with dementia, the mentally incompetent, persons subject to coercion, and other people who are not able to make decisions with the same authority as others, have special needs when making decisions about their personal healthcare, including surgery.
Global surgery
[edit]Global surgery has been defined as 'the multidisciplinary enterprise of providing improved and equitable surgical care to the world's population, with its core belief as the issues of need, access and quality".[46] Halfdan T. Mahler, the 3rd Director-General of the World Health Organization (WHO), first brought attention to the disparities in surgery and surgical care in 1980 when he stated in his address to the World Congress of the International College of Surgeons, "'the vast majority of the world's population has no access whatsoever to skilled surgical care and little is being done to find a solution.As such, surgical care globally has been described as the 'neglected stepchild of global health,' a term coined by Paul Farmer to highlight the urgent need for further work in this area.[47] Furthermore, Jim Young Kim, the former President of the World Bank, proclaimed in 2014 that "surgery is an indivisible, indispensable part of health care and of progress towards universal health coverage."[48]
In 2015, the Lancet Commission on Global Surgery (LCoGS) published the landmark report titled "Global Surgery 2030: evidence and solutions for achieving health, welfare, and economic development", describing the large, pre-existing burden of surgical diseases in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) and future directions for increasing universal access to safe surgery by the year 2030.[49] The Commission highlighted that about 5 billion people lack access to safe and affordable surgical and anesthesia care and 143 million additional procedures were needed every year to prevent further morbidity and mortality from treatable surgical conditions as well as a $12.3 trillion loss in economic productivity by the year 2030.[49] This was especially true in the poorest countries, which account for over one-third of the population but only 3.5% of all surgeries that occur worldwide.[50] It emphasized the need to significantly improve the capacity for Bellwether procedures – laparotomy, caesarean section, open fracture care – which are considered a minimum level of care that first-level hospitals should be able to provide in order to capture the most basic emergency surgical care.[49][51] In terms of the financial impact on the patients, the lack of adequate surgical and anesthesia care has resulted in 33 million individuals every year facing catastrophic health expenditure – the out-of-pocket healthcare cost exceeding 40% of a given household's income.[49][52]
In alignment with the LCoGS call for action, the World Health Assembly adopted the resolution WHA68.15 in 2015 that stated, "Strengthening emergency and essential surgical care and anesthesia as a component of universal health coverage."[53] This not only mandated the WHO to prioritize strengthening the surgical and anesthesia care globally, but also led to governments of the member states recognizing the urgent need for increasing capacity in surgery and anesthesia. Additionally, the third edition of Disease Control Priorities (DCP3), published in 2015 by the World Bank, declared surgery as essential and featured an entire volume dedicated to building surgical capacity.[54]
Data from WHO and the World Bank indicate that scaling up infrastructure to enable access to surgical care in regions where it is currently limited or is non-existent is a low-cost measure relative to the significant morbidity and mortality caused by lack of surgical treatment.[55] In fact, a systematic review found that the cost-effectiveness ratio – dollars spent per DALYs averted – for surgical interventions is on par or exceeds those of major public health interventions such as oral rehydration therapy, breastfeeding promotion, and even HIV/AIDS antiretroviral therapy.[56] This finding challenged the common misconception that surgical care is financially prohibitive endeavor not worth pursuing in LMICs.
A key policy framework that arose from this renewed global commitment towards surgical care worldwide is the National Surgical Obstetric and Anesthesia Plan (NSOAP).[57] NSOAP focuses on policy-to-action capacity building for surgical care with tangible steps as follows: (1) analysis of baseline indicators, (2) partnership with local champions, (3) broad stakeholder engagement, (4) consensus building and synthesis of ideas, (5) language refinement, (6) costing, (7) dissemination, and (8) implementation. This approach has been widely adopted and has served as guiding principles between international collaborators and local institutions and governments. Successful implementations have allowed for sustainability in terms of longterm monitoring, quality improvement, and continued political and financial support.[57]
Human rights
[edit]Access to surgical care is increasingly recognized as an integral aspect of healthcare and therefore is evolving into a normative derivation of human right to health.[58] The ICESCR Article 12.1 and 12.2 define the human right to health as "the right of everyone to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health"[59] In the August 2000, the UN Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (CESCR) interpreted this to mean "right to the enjoyment of a variety of facilities, goods, services, and conditions necessary for the realization of the highest attainable health".[60] Surgical care can be thereby viewed as a positive right – an entitlement to protective healthcare.[60]
Woven through the International Human and Health Rights literature is the right to be free from surgical disease. The 1966 ICESCR Article 12.2a described the need for "provision for the reduction of the stillbirth-rate and of infant mortality and for the healthy development of the child"[61] which was subsequently interpreted to mean "requiring measures to improve… emergency obstetric services".[60] Article 12.2d of the ICESCR stipulates the need for "the creation of conditions which would assure to all medical service and medical attention in the event of sickness",[62] and is interpreted in the 2000 comment to include timely access to "basic preventative, curative services… for appropriate treatment of injury and disability.".[63] Obstetric care shares close ties with reproductive rights, which includes access to reproductive health.[63]
Surgeons and public health advocates, such as Kelly McQueen, have described surgery as "Integral to the right to health".[64] This is reflected in the establishment of the WHO Global Initiative for Emergency and Essential Surgical Care in 2005,[65] the 2013 formation of the Lancet Commission for Global Surgery,[66] the 2015 World Bank Publication of Volume 1 of its Disease Control Priorities Project "Essential Surgery",[12] and the 2015 World Health Assembly 68.15 passing of the Resolution for Strengthening Emergency and Essential Surgical Care and Anesthesia as a Component of Universal Health Coverage.[53] The Lancet Commission for Global Surgery outlined the need for access to "available, affordable, timely and safe" surgical and anesthesia care;[66] dimensions paralleled in ICESCR General Comment No. 14, which similarly outlines need for available, accessible, affordable and timely healthcare.[60]
History
[edit]
Trepanation
[edit]Surgical treatments date back to the prehistoric era. The oldest for which there is evidence is trepanation,[67] in which a hole is drilled or scraped into the skull, thus exposing the dura mater in order to treat health problems related to intracranial pressure.
Ancient Egypt
[edit]Prehistoric surgical techniques are seen in Ancient Egypt, where a mandible dated to approximately 2650 BC shows two perforations just below the root of the first molar, indicating the draining of an abscessed tooth. Surgical texts from ancient Egypt date back about 3500 years ago. Surgical operations were performed by priests, specialized in medical treatments similar to today,[68] and used sutures to close wounds.[69] Infections were treated with honey.[70]
India
[edit]9,000-year-old skeletal remains of a prehistoric individual from the Indus River valley show evidence of teeth having been drilled.[71] Sushruta Samhita is one of the oldest known surgical texts and its period is usually placed in the first millennium BCE.[72] It describes in detail the examination, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of numerous ailments, as well as procedures for various forms of cosmetic surgery, plastic surgery and rhinoplasty.[73]
Sri Lanka
[edit]In 1982 archaeologists were able to find significant evidence when the ancient land, called 'Alahana Pirivena' situated in Polonnaruwa, with ruins, was excavated. In that place ruins of an ancient hospital emerged. The hospital building was 147.5 feet in width and 109.2 feet in length. The instruments which were used for complex surgeries were there among the things discovered from the place, including forceps, scissors, probes, lancets, and scalpels. The instruments discovered may be dated to 11th century AD.[74][75][76][77]
Ancient and Medieval Greece
[edit]
In ancient Greece, temples dedicated to the healer-god Asclepius, known as Asclepieia (Greek: Ασκληπιεία, sing. Asclepieion Ασκληπιείον), functioned as centers of medical advice, prognosis, and healing.[78] In the Asclepieion of Epidaurus, some of the surgical cures listed, such as the opening of an abdominal abscess or the removal of traumatic foreign material, are realistic enough to have taken place.[30] The Greek Galen was one of the greatest surgeons of the ancient world and performed many audacious operations – including brain and eye surgery – that were not tried again for almost two millennia. Hippocrates stated in the oath (c. 400 BCE) "I will not use the knife, even upon those suffering from stones, but I will leave this to those who are trained in this craft."[79]
Researchers from the Adelphi University discovered in the Paliokastro on Thasos ten skeletal remains, four women and six men, who were buried between the fourth and seventh centuries A.D. Their bones illuminated their physical activities, traumas, and even a complex form of brain surgery. According to the researchers: "The very serious trauma cases sustained by both males and females had been treated surgically or orthopedically by a very experienced physician/surgeon with great training in trauma care. We believe it to have been a military physician". The researchers were impressed by the complexity of the brain surgical operation.[80]
In 1991 at the Polystylon fort in Greece, researchers discovered the head of a Byzantine warrior of the 14th century. Analysis of the lower jaw revealed that a surgery has been performed, when the warrior was alive, to the jaw which had been badly fractured and it tied back together until it healed.[81]
Islamic world
[edit]During the Islamic Golden Age, largely based upon Paul of Aegina's Pragmateia, the writings of Albucasis (Abu al-Qasim Khalaf ibn al-Abbas Al-Zahrawi), an Andalusian-Arab physician and scientist who practiced in the Zahra suburb of Córdoba, were influential.[82][83] Al-Zahrawi specialized in curing disease by cauterization. He invented several surgical instruments for purposes such as inspection of the interior of the urethra and for removing foreign bodies from the throat, the ear, and other body organs. He was also the first to illustrate the various cannulae and to treat warts with an iron tube and caustic metal[clarification needed] as a boring instrument. He describes what is thought to be the first attempt at reduction mammaplasty for the management of gynaecomastia[84] and the first mastectomy to treat breast cancer.[85] He is credited with the performance of the first thyroidectomy.[86] Al-Zahrawi pioneered techniques of neurosurgery and neurological diagnosis, treating head injuries, skull fractures, spinal injuries, hydrocephalus, subdural effusions and headache. The first clinical description of an operative procedure for hydrocephalus was given by Al-Zahrawi, who clearly describes the evacuation of superficial intracranial fluid in hydrocephalic children.[87]
Early modern Europe
[edit]

In Europe, the demand grew for surgeons to formally study for many years before practicing; universities such as Montpellier, Padua and Bologna were particularly renowned. In the 12th century, Rogerius Salernitanus composed his Chirurgia, laying the foundation for modern Western surgical manuals. Barber-surgeons generally had a bad reputation that was not to improve until the development of academic surgery as a specialty of medicine, rather than an accessory field.[88] Basic surgical principles for asepsis etc., are known as Halsteads principles.
There were some important advances to the art of surgery during this period. The professor of anatomy at the University of Padua, Andreas Vesalius, was a pivotal figure in the Renaissance transition from classical medicine and anatomy based on the works of Galen, to an empirical approach of 'hands-on' dissection. In his anatomic treaties De humani corporis fabrica, he exposed the many anatomical errors in Galen and advocated that all surgeons should train by engaging in practical dissections themselves.[citation needed]
The second figure of importance in this era was Ambroise Paré (sometimes spelled "Ambrose"[89]), a French army surgeon from the 1530s until his death in 1590. The practice for cauterizing gunshot wounds on the battlefield had been to use boiling oil; an extremely dangerous and painful procedure. Paré began to employ a less irritating emollient, made of egg yolk, rose oil and turpentine. He also described more efficient techniques for the effective ligation of the blood vessels during an amputation.[citation needed]
Modern surgery
[edit]The discipline of surgery was put on a sound, scientific footing during the Age of Enlightenment in Europe. An important figure in this regard was the Scottish surgical scientist, John Hunter, generally regarded as the father of modern scientific surgery.[90] He brought an empirical and experimental approach to the science and was renowned around Europe for the quality of his research and his written works. Hunter reconstructed surgical knowledge from scratch; refusing to rely on the testimonies of others, he conducted his own surgical experiments to determine the truth of the matter. To aid comparative analysis, he built up a collection of over 13,000 specimens of separate organ systems, from the simplest plants and animals to humans.[citation needed]
He greatly advanced knowledge of venereal disease and introduced many new techniques of surgery, including new methods for repairing damage to the Achilles tendon and a more effective method for applying ligature of the arteries in case of an aneurysm.[91] He was also one of the first to understand the importance of pathology, the danger of the spread of infection and how the problem of inflammation of the wound, bone lesions and even tuberculosis often undid any benefit that was gained from the intervention. He consequently adopted the position that all surgical procedures should be used only as a last resort.[92]
Other important 18th- and early 19th-century surgeons included Percival Pott (1713–1788) who described tuberculosis on the spine and first demonstrated that a cancer may be caused by an environmental carcinogen (he noticed a connection between chimney sweep's exposure to soot and their high incidence of scrotal cancer). Astley Paston Cooper (1768–1841) first performed a successful ligation of the abdominal aorta, and James Syme (1799–1870) pioneered the Symes Amputation for the ankle joint and successfully carried out the first hip disarticulation.
Modern pain control through anesthesia was discovered in the mid-19th century. Before the advent of anesthesia, surgery was a traumatically painful procedure and surgeons were encouraged to be as swift as possible to minimize patient suffering. This also meant that operations were largely restricted to amputations and external growth removals. Beginning in the 1840s, surgery began to change dramatically in character with the discovery of effective and practical anaesthetic chemicals such as ether, first used by the American surgeon Crawford Long, and chloroform, discovered by Scottish obstetrician James Young Simpson and later pioneered by John Snow, physician to Queen Victoria.[93] In addition to relieving patient suffering, anaesthesia allowed more intricate operations in the internal regions of the human body. In addition, the discovery of muscle relaxants such as curare allowed for safer applications.[citation needed]
Infection and antisepsis
[edit]The introduction of anesthetics encouraged more surgery, which inadvertently caused more dangerous patient post-operative infections. The concept of infection was unknown until relatively modern times. The first progress in combating infection was made in 1847 by the Hungarian doctor Ignaz Semmelweis who noticed that medical students fresh from the dissecting room were causing excess maternal death compared to midwives. Semmelweis, despite ridicule and opposition, introduced compulsory handwashing for everyone entering the maternal wards and was rewarded with a plunge in maternal and fetal deaths; however, the Royal Society dismissed his advice.[citation needed]

Until the pioneering work of British surgeon Joseph Lister in the 1860s, most medical men believed that chemical damage from exposures to bad air (see "miasma") was responsible for infections in wounds, and facilities for washing hands or a patient's wounds were not available.[94] Lister became aware of the work of French chemist Louis Pasteur, who showed that rotting and fermentation could occur under anaerobic conditions if micro-organisms were present. Pasteur suggested three methods to eliminate the micro-organisms responsible for gangrene: filtration, exposure to heat, or exposure to chemical solutions. Lister confirmed Pasteur's conclusions with his own experiments and decided to use his findings to develop antiseptic techniques for wounds. As the first two methods suggested by Pasteur were inappropriate for the treatment of human tissue, Lister experimented with the third, spraying carbolic acid on his instruments. He found that this remarkably reduced the incidence of gangrene and he published his results in The Lancet.[95] Later, on 9 August 1867, he read a paper before the British Medical Association in Dublin, on the Antiseptic Principle of the Practice of Surgery, which was reprinted in the British Medical Journal.[96][97][98] His work was groundbreaking and laid the foundations for a rapid advance in infection control that saw modern antiseptic operating theatres widely used within 50 years.[citation needed]
Lister continued to develop improved methods of antisepsis and asepsis when he realised that infection could be better avoided by preventing bacteria from getting into wounds in the first place. This led to the rise of sterile surgery. Lister introduced the Steam Steriliser to sterilize equipment, instituted rigorous hand washing and later implemented the wearing of rubber gloves. These three crucial advances – the adoption of a scientific methodology toward surgical operations, the use of anaesthetic and the introduction of sterilised equipment – laid the groundwork for the modern invasive surgical techniques of today.
The use of X-rays as an important medical diagnostic tool began with their discovery in 1895 by German physicist Wilhelm Röntgen. He noticed that these rays could penetrate the skin, allowing the skeletal structure to be captured on a specially treated photographic plate.
-
Hieronymus Fabricius, Operationes chirurgicae, 1685
-
John Syng Dorsey wrote the first American textbook on surgery
-
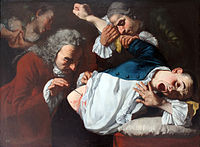
An operation in 1753, painted by Gaspare Traversi.
Surgical specialties
[edit]- General surgery
- Breast
- Cardiothoracic
- Colorectal
- Craniofacial surgery
- Dental surgery
- Endocrine
- Gynaecology
- Neurosurgery
- Ophthalmology
- Oncological
- Oral and maxillofacial surgery
- Transplant
- Orthopaedic surgery
- Hand surgery
- Otolaryngology
- Paediatric (Pediatric)
- Periodontal surgery
- Plastic
- Podiatric surgery
- Skin
- Trauma
- Urology
- Vascular
Learned societies
[edit]- World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies
- American College of Surgeons
- American College of Osteopathic Surgeons
- American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons
- American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons
- Royal Australasian College of Surgeons
- Royal Australasian College of Dental Surgeons
- Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada
- Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland
- Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh
- Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Glasgow
- Royal College of Surgeons of England
See also
[edit]- Anesthesia – State of medically-controlled temporary loss of sensation or awareness
- ASA physical status classification system – System for assessing the fitness of patients before surgery
- Biomaterial – Any substance that has been engineered to interact with biological systems for a medical purpose
- Cardiac surgery – Type of surgery performed on the heart
- Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) – Procedural classification used in the United States – for outpatient surgical procedures medical coding
- Surgical drain – Tube used to remove pus, blood or other fluids from a wound
- Endoscopy – Procedure used in medicine to look inside the body
- Fluorescence image-guided surgery – medical imaging technique
- Hypnosurgery – Practice of using hypnosis for sedation during surgery
- Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) – a family of health care databases etc. from the US
- ICD-10 Procedure Coding System – Medical classification system used for procedural coding (International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition, Procedural Coding System; inpatient surgical procedures medical coding)
- Jet ventilation – Methods of inspiratory support
- List of surgical procedures
- Minimally invasive procedure – Surgical technique that limits size of surgical incisions needed
- Operative report
- Perioperative mortality – Any death occurring within 30 days after surgery
- Physician Assistant – Mid-level health care provider
- Remote surgery – ability for a doctor to perform surgery on a patient even though they are not physically in the same location
- Robot-assisted surgery – Surgical procedure
- Surgeon's assistant – Healthcare professional
- Surgical Outcomes Analysis and Research – Medical research program
- Surgical sieve
- Trauma surgery – Surgical specialty
- Reconstructive surgery – Surgery to restore form and function
- Rheumasurgery – Medical speciality of inflammatory diseases
- WHO Surgical Safety Checklist
- Women in medicine
List of Surgery-related fields
[edit]- Bariatric surgery
- Cardiac surgery
- Cardiothoracic surgery
- Colorectal surgery
- Endocrine surgery
- Ophthalmology
- General surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Oral and maxillofacial surgery
- Orthopedic surgery
- Hand surgery
- Otolaryngology
- Pediatric surgery
- Plastic surgery
- Reproductive surgery
- Surgical oncology
- Transplant surgery
- Trauma surgery
- Urology
- Vascular surgery
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Doctor's surgery". Collins English Dictionary. Archived from the original on 10 February 2018. Retrieved 10 February 2018.
- ^ The Medical times: a journal of medical science, literature, criticism, and news. 1845/46, Sept. - Apr. 1846.
- ^ "Reconstructive Procedures". American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Cosmetic Procedures". American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "UCLA Non-survival Surgical Procedures". UCLA Research Policy & Compliance. 9 May 2005.
- ^ "IACUC Policy on Surgery". 16 July 2008.
- ^ "segmental resection". National Cancer Institute Dictionary of Cancer Terms. Retrieved 31 July 2020.
- ^ "extirpation". Merriam-Webster dictionary. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ^ Lemos P, Jarrett P, Philip B, eds. (2006). Day surgery: development and practice (PDF). London: International Association for Ambulatory Surgery. ISBN 978-989-20-0234-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 November 2020. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- ^ Twersky RS, Philip BK, eds. (2008). Handbook of ambulatory anesthesia (2nd ed.). New York: Springer. p. 284. ISBN 978-0-387-73328-9.
- ^ Fingar KR, Stocks C, Weiss AJ, Steiner CA (December 2014). "Most Frequent Operating Room Procedures Performed in U.S. Hospitals, 2003–2012". HCUP Statistical Brief No. 186. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Archived from the original on 3 May 2015.
- ^ a b Debas HT, Donker P, Gawande A, Jamison DT, Kruk ME, Mock CN, editors. Essential Surgery. Disease Control Priorities. 3rd ed. Washington, DC: International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / World Bank Group; 2015
- ^ a b c American College of Radiology. "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question". Choosing Wisely: An Initiative of the ABIM Foundation. Archived from the original on 10 February 2013. Retrieved 17 August 2012., citing
- "American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria". American College of Radiology. 2000. Archived from the original on 10 February 2013. Retrieved 4 September 2012. Last reviewed 2011.
- Gómez-Gil E, Trilla A, Corbella B, Fernández-Egea E, Luburich P, de Pablo J, et al. (2002). "Lack of clinical relevance of routine chest radiography in acute psychiatric admissions". General Hospital Psychiatry. 24 (2): 110–113. doi:10.1016/s0163-8343(01)00179-7. PMID 11869746.
- Archer C, Levy AR, McGregor M (November 1993). "Value of routine preoperative chest x-rays: a meta-analysis". Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia. 40 (11): 1022–1027. doi:10.1007/BF03009471. PMID 8269561.
- Munro J, Booth A, Nicholl J (1997). "Routine preoperative testing: a systematic review of the evidence". Health Technology Assessment. 1 (12): i–iv, 1–62. doi:10.3310/hta1120. PMID 9483155.
- Grier DJ, Watson LJ, Hartnell GG, Wilde P (August 1993). "Are routine chest radiographs prior to angiography of any value?". Clinical Radiology. 48 (2): 131–133. doi:10.1016/S0009-9260(05)81088-8. PMID 8004892.
- Gupta SD, Gibbins FJ, Sen I (January 1985). "Routine chest radiography in the elderly". Age and Ageing. 14 (1): 11–14. doi:10.1093/ageing/14.1.11. PMID 4003172.
- Amorosa JK, Bramwit MP, Mohammed TL, Reddy GP, Brown K, Dyer DS, et al. (March 2013). "ACR appropriateness criteria routine chest radiographs in intensive care unit patients". Journal of the American College of Radiology. 10 (3). National Guideline Clearinghouse: 170–174. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2012.11.013. PMID 23571057. Archived from the original on 15 September 2012. Retrieved 4 September 2012.
- ^ American Society for Clinical Pathology, "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Society for Clinical Pathology, archived from the original on 1 September 2013, retrieved 1 August 2013, which cites
- Keay L, Lindsley K, Tielsch J, Katz J, Schein O (January 2019). "Routine preoperative medical testing for cataract surgery". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD007293. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007293.pub4. PMC 6353242. PMID 30616299.
- Katz RI, Dexter F, Rosenfeld K, Wolfe L, Redmond V, Agarwal D, et al. (January 2011). "Survey study of anesthesiologists' and surgeons' ordering of unnecessary preoperative laboratory tests". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 112 (1): 207–212. doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e31820034f0. PMID 21081771. S2CID 8480050.
- Munro J, Booth A, Nicholl J (1997). "Routine preoperative testing: a systematic review of the evidence". Health Technology Assessment. 1 (12): i–iv, 1–62. doi:10.3310/hta1120. PMID 9483155.
- Reynolds TM (January 2006). "National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence guidelines on preoperative tests: the use of routine preoperative tests for elective surgery". Annals of Clinical Biochemistry. 43 (Pt 1): 13–16. doi:10.1258/000456306775141623. PMID 16390604.
- Capdenat Saint-Martin E, Michel P, Raymond JM, Iskandar H, Chevalier C, Petitpierre MN, et al. (March 1998). "Description of local adaptation of national guidelines and of active feedback for rationalising preoperative screening in patients at low risk from anaesthetics in a French university hospital". Quality in Health Care. 7 (1): 5–11. doi:10.1136/qshc.7.1.5. PMC 2483578. PMID 10178152.
- ^ "The day of your surgery – adult: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 24 January 2019.
- ^ Wade RG, Burr NE, McCauley G, Bourke G, Efthimiou O (December 2021). "The Comparative Efficacy of Chlorhexidine Gluconate and Povidone-iodine Antiseptics for the Prevention of Infection in Clean Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis". Annals of Surgery. 274 (6): e481 – e488. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000004076. PMID 32773627.
- ^ Martin S (2007). Minor Surgical Procedures for Nurses and Allied Healthcare Professionals. England: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. p. 122. ISBN 978-0-470-01990-0.
- ^ Page 2 in: Spry C (2009). Essentials of perioperative nursing. Sudbury, Mass: Jones and Bartlett Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7637-5881-3. OCLC 227920274.
- ^ Wagman LD. "Principles of Surgical Oncology" Archived 15 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (Eds) Cancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach Archived 4 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine. 11 ed. 2008.
- ^ Küçükkartallar T, Gündeş E, Yılmaz H, Aksoy F (1 March 2013). "A case of multiorgan resection for locally advanced stomach cancer". Turkish Journal of Surgery/Ulusal Cerrahi Dergisi. 29 (1): 31–32. doi:10.5152/UCD.2013.07. ISSN 1300-0705. PMC 4379777. PMID 25931839.
- ^ "magnetic compression anastomosis: Topics by Science.gov". www.science.gov. Retrieved 30 October 2022.
- ^ Alvi S, Patel BC (2022), "Nasal Fracture Reduction", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30855883, retrieved 30 October 2022
- ^ Sung S, Abramovitz A (2022), "Tubal Ligation", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 31751063, retrieved 30 October 2022
- ^ Prohaska J, Cook C (2022), "Skin Grafting", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30422469, retrieved 30 October 2022
- ^ Bori E, Galbusera F, Innocenti B (2022), "Hip prosthesis: biomechanics and design", Human Orthopaedic Biomechanics, Elsevier, pp. 361–376, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-824481-4.00032-9, ISBN 978-0-12-824481-4, retrieved 30 October 2022
- ^ Whitehead A, Cataldo P (22 May 2017). "Technical Considerations in Stoma Creation". Clinics in Colon and Rectal Surgery. 30 (3): 162–171. doi:10.1055/s-0037-1598156. ISSN 1531-0043. PMC 5498162. PMID 28684933.
- ^ Zalewska K. "National Standards for Organ Retrieval from Deceased Donors" (PDF). NHS Blood and Transplant. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 October 2022. Retrieved 30 October 2022.
- ^ Nouh MR (2012). "Spinal fusion-hardware construct: Basic concepts and imaging review". World Journal of Radiology. 4 (5): 193–207. doi:10.4329/wjr.v4.i5.193. ISSN 1949-8470. PMC 3386531. PMID 22761979.
- ^ Gillern S, Bleier JI (2014). "Parastomal Hernia Repair and Reinforcement: The Role of Biologic and Synthetic Materials". Clinics in Colon and Rectal Surgery. 27 (4): 162–171. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1394090. ISSN 1531-0043. PMC 4226750. PMID 25435825.
- ^ a b Askitopoulou, H., Konsolaki, E., Ramoutsaki, I., Anastassaki, E. Surgical cures by sleep induction as the Asclepieion of Epidaurus. The history of anesthesia: proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium, by José Carlos Diz, Avelino Franco, Douglas R. Bacon, J. Rupreht, Julián Alvarez. Elsevier Science B.V., International Congress Series 1242(2002), pp. 11–17. [1][permanent dead link]
- ^ Doyle SL, Lysaght J, Reynolds JV (December 2010). "Obesity and post-operative complications in patients undergoing non-bariatric surgery". Obesity Reviews. 11 (12): 875–886. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2009.00700.x. PMID 20025695. S2CID 7712323.
- ^ Pastorino A, Tavarez MM (24 July 2023). "Incision and drainage". StatPearls Publishing. PMID 32310532. Retrieved 11 March 2024.
- ^ Hines S, Steels E, Chang A, Gibbons K (March 2018). "Aromatherapy for treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (3): CD007598. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007598.pub3. PMC 6494172. PMID 29523018.
- ^ Huang J, Shi Z, Duan FF, Fan MX, Yan S, Wei Y, et al. (June 2021). "Benefits of Early Ambulation in Elderly Patients Undergoing Lumbar Decompression and Fusion Surgery: A Prospective Cohort Study". Orthopaedic Surgery. 13 (4): 1319–1326. doi:10.1111/os.12953. PMC 8274205. PMID 33960687.
- ^ a b c American Academy of Dermatology (February 2013), "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Academy of Dermatology, archived from the original on 1 December 2013, retrieved 5 December 2013, which cites
- Sheth VM, Weitzul S (2008). "Postoperative topical antimicrobial use". Dermatitis. 19 (4): 181–189. doi:10.2310/6620.2008.07094. PMID 18674453.
- ^ Heal CF, Banks JL, Lepper PD, Kontopantelis E, van Driel ML (November 2016). "Topical antibiotics for preventing surgical site infection in wounds healing by primary intention" (PDF). The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016 (11): CD011426. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd011426.pub2. PMC 6465080. PMID 27819748. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 July 2018. Alt URL
- ^ Aylin P, Alexandrescu R, Jen MH, Mayer EK, Bottle A (May 2013). "Day of week of procedure and 30 day mortality for elective surgery: retrospective analysis of hospital episode statistics". BMJ. 346: f2424. doi:10.1136/bmj.f2424. PMC 3665889. PMID 23716356.
- ^ a b Doleman B, Leonardi-Bee J, Heinink TP, Bhattacharjee D, Lund JN, Williams JP (December 2018). "Pre-emptive and preventive opioids for postoperative pain in adults undergoing all types of surgery". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018 (12): CD012624. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012624.pub2. PMC 6517298. PMID 30521692.
- ^ Yang MM, Hartley RL, Leung AA, Ronksley PE, Jetté N, Casha S, et al. (April 2019). "Preoperative predictors of poor acute postoperative pain control: a systematic review and meta-analysis". BMJ Open. 9 (4): e025091. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025091. PMC 6500309. PMID 30940757.
- ^ Allvin R, Berg K, Idvall E, Nilsson U (March 2007). "Postoperative recovery: a concept analysis". Journal of Advanced Nursing. 57 (5): 552–558. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2006.04156.x. PMID 17284272.
- ^ Weiss AJ, Elixhauser A, Andrews RM (February 2014). "Characteristics of Operating Room Procedures in U.S. Hospitals, 2011". HCUP Statistical Brief No. 170. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. PMID 24716251. Archived from the original on 28 March 2014.
- ^ Weiss AJ, Elixhauser A (March 2014). "Trends in Operating Room Procedures in U.S. Hospitals, 2001–2011". HCUP Statistical Brief No. 171. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. PMID 24851286. Archived from the original on 28 March 2014.
- ^ Weiss AJ, Barrett ML, Steiner CA (July 2014). "Trends and Projections in Inpatient Hospital Costs and Utilization, 2003–2013". HCUP Statistical Brief No. 175. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. PMID 25165806. Archived from the original on 3 August 2014.
- ^ a b Moore B, Levit K, Elixhauser A (October 2014). "Costs for Hospital Stays in the United States, 2012". HCUP Statistical Brief No. 181. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. PMID 25521003. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014.
- ^ a b Makary MA, Segev DL, Pronovost PJ, Syin D, Bandeen-Roche K, Patel P, et al. (June 2010). "Frailty as a predictor of surgical outcomes in older patients". Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 210 (6): 901–908. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.01.028. PMID 20510798.
- ^ Bath M, Bashford T, Fitzgerald JE (2019). "What is 'global surgery'? Defining the multidisciplinary interface between surgery, anaesthesia and public health". BMJ Global Health. 4 (5): e001808. doi:10.1136/bmjgh-2019-001808. PMC 6830053. PMID 31749997.
- ^ Farmer PE, Kim JY (April 2008). "Surgery and global health: a view from beyond the OR". World Journal of Surgery. 32 (4): 533–536. doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9525-9. PMC 2267857. PMID 18311574.
- ^ Dare AJ, Grimes CE, Gillies R, Greenberg SL, Hagander L, Meara JG, et al. (December 2014). "Global surgery: defining an emerging global health field". Lancet. 384 (9961): 2245–2247. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60237-3. PMID 24853601. S2CID 37349469.
- ^ a b c d Meara JG, Leather AJ, Hagander L, Alkire BC, Alonso N, Ameh EA, et al. (August 2015). "Global Surgery 2030: evidence and solutions for achieving health, welfare, and economic development". Lancet. 386 (9993): 569–624. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60160-X. PMID 25924834. S2CID 2048403.
- ^ Weiser TG, Regenbogen SE, Thompson KD, Haynes AB, Lipsitz SR, Berry WR, et al. (July 2008). "An estimation of the global volume of surgery: a modelling strategy based on available data". Lancet. 372 (9633): 139–144. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60878-8. PMID 18582931. S2CID 17918156.
- ^ O'Neill KM, Greenberg SL, Cherian M, Gillies RD, Daniels KM, Roy N, et al. (November 2016). "Bellwether Procedures for Monitoring and Planning Essential Surgical Care in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Caesarean Delivery, Laparotomy, and Treatment of Open Fractures". World Journal of Surgery. 40 (11). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 2611–2619. doi:10.1007/s00268-016-3614-y. PMID 27351714. S2CID 12830913.
- ^ Xu K, Evans DB, Kawabata K, Zeramdini R, Klavus J, Murray CJ (July 2003). "Household catastrophic health expenditure: a multicountry analysis". Lancet. 362 (9378): 111–117. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13861-5. PMID 12867110. S2CID 2052830.
- ^ a b Price R, Makasa E, Hollands M (September 2015). "World Health Assembly Resolution WHA68.15: "Strengthening Emergency and Essential Surgical Care and Anesthesia as a Component of Universal Health Coverage"—Addressing the Public Health Gaps Arising from Lack of Safe, Affordable and Accessible Surgical and Anesthetic Services". World Journal of Surgery. 39 (9): 2115–2125. doi:10.1007/s00268-015-3153-y. PMID 26239773. S2CID 13027859.
- ^ Debas HT, Donkor P, Gawande A, Jamison DT, Kruk ME, Mock CN (24 March 2015). Debas HT, Donkor P, Gawande A, Jamison DT, Kruk ME, Mock CN (eds.). Disease Control Priorities. Vol. 1 Essential Surgery (Third ed.). doi:10.1596/978-1-4648-0346-8. hdl:10986/21568. ISBN 978-1-4648-0346-8. PMID 26740991.
- ^ McQueen KA, Ozgediz D, Riviello R, Hsia RY, Jayaraman S, Sullivan SR, et al. (June 2010). "Essential surgery: Integral to the right to health". Health and Human Rights. 12 (1): 137–152. PMID 20930260.
- ^ Chao TE, Sharma K, Mandigo M, Hagander L, Resch SC, Weiser TG, et al. (June 2014). "Cost-effectiveness of surgery and its policy implications for global health: a systematic review and analysis". The Lancet. Global Health. 2 (6): e334 – e345. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(14)70213-X. PMID 25103302.
- ^ a b Truché P, Shoman H, Reddy CL, Jumbam DT, Ashby J, Mazhiqi A, et al. (January 2020). "Globalization of national surgical, obstetric and anesthesia plans: the critical link between health policy and action in global surgery". Globalization and Health. 16 (1): 1. doi:10.1186/s12992-019-0531-5. PMC 6941290. PMID 31898532.
- ^ Marks S (2016). "Normative Expansion of the Right to Health and the Proliferation of Human Rights". George Washington International Law Review: 101–44.
- ^ UN General Assembly. International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights – United Nations Treaty Series. In: Nations U, editor. 1966
- ^ a b c d UN Committee on Economic Social and Cultural Rights. CESCR General Comment No. 14: The Right to the Highest Attainable Standard of Health (Art. 12) 2000
- ^ UN General Assembly. International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights – United Nations Treaty Series. In: Nations U, editor. 1966.
- ^ 2. UN General Assembly. International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights – United Nations Treaty Series. In: Nations U, editor. 1966.
- ^ a b UN Committee on Economic Social and Cultural Rights. CESCR General Comment No. 14: The Right to the Highest Attainable Standard of Health (Art. 12) 2000.
- ^ McQueen KA, Ozgediz D, Riviello R, Hsia RY, Jayaraman S, Sullivan SR, et al. (June 2010). "Essential surgery: Integral to the right to health". Health and Human Rights. 12 (1): 137–152. PMID 20930260.
- ^ World Health Organization. Global Initiative for Emergency and Essential Surgical Care 2017 [cited 2017 October 23rd]. Available from: "WHO Global Initiative for Emergency and Essential Surgical Care". Archived from the original on 25 March 2012. Retrieved 9 February 2012.
- ^ a b Meara JG, Leather AJ, Hagander L, Alkire BC, Alonso N, Ameh EA, et al. (February 2016). "Global Surgery 2030: evidence and solutions for achieving health, welfare, and economic development". International Journal of Obstetric Anesthesia. 25: 75–78. doi:10.1016/j.ijoa.2015.09.006. PMID 26597405.
- ^ Capasso, Luigi (2002). Principi di storia della patologia umana: corso di storia della medicina per gli studenti della Facoltà di medicina e chirurgia e della Facoltà di scienze infermieristiche (in Italian). Rome: SEU. ISBN 978-88-87753-65-3. OCLC 50485765.
- ^ Shiffman M (2012). Cosmetic Surgery: Art and Techniques. Springer. p. 20. ISBN 978-3-642-21837-8.
- ^ Sullivan R (August 1996). "The identity and work of the ancient Egyptian surgeon". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 89 (8): 467–473. doi:10.1177/014107689608900813. PMC 1295891. PMID 8795503.
- ^ James P. Allen, The Art of Medicine in Ancient Egypt. (New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2005) 72.
- ^ "Stone age man used dentist drill". BBC News. 6 April 2006. Archived from the original on 22 April 2009. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ^ Singh PB, Rana PS (2002). Banaras Region: A Spiritual and Cultural Guide. Varanasi: Indica Books. p. 31. ISBN 978-81-86569-24-5.
- ^ Rana RE, Arora BS (1 January 2002). "History of plastic surgery in India". Journal of Postgraduate Medicine. 48 (1): 76–78. PMID 12082339. Archived from the original on 1 March 2009 – via www.jpgmonline.com.
- ^ Somadewa, Raj; Rev. Deerananda, Hanguranketha; Kannangara, Padmasiri; Senadhiraja, Anusha; Gunawardhana, W. S. Shiromala (2014). History - Grade 10 (PDF). Translated by Bandara, A.B.S. Aloka. Educational Publications Department. ISBN 978-955-25-0663-5.
- ^ "Surgery in an ancient kingdom". www.sundaytimes.lk. Retrieved 5 September 2023.
- ^ Aluwihare AP (3 August 2021). "Surgical Instruments at the Alahana Parivena Hospital in Polonnaruwa" (PDF). Clinics in Surgery. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 October 2022. Retrieved 5 September 2023.
- ^ Uragoda CG. "Medicine and Surgery" (PDF). National Science Foundation. Retrieved 5 September 2023.
- ^ Risse, G.B. Mending bodies, saving souls: a history of hospitals. Oxford University Press, 1990. p. 56 [2]
- ^ "Greek Medicine". www.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 13 January 2025.
- ^ "Adelphi researcher discovers early, complex brain surgery in ancient Greece". Archived from the original on 10 April 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- ^ Laura Geggel (29 September 2021). "Byzantine warrior with gold-threaded jaw unearthed in Greece". livescience.com.
- ^ Zimmerman LM, Veith I (1993). Great Ideas in the History of Surgery. Norman Publishing. pp. 82–83. ISBN 978-0-930405-53-3. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ^ Pormann PE (2004). The Oriental Tradition of Paul of Aegina's Pragmateia. Brill. pp. 300–04. ISBN 978-90-04-13757-8. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- ^ Ahmad Z (2007), "Al-Zahrawi – The Father of Surgery", ANZ Journal of Surgery, 77 (Suppl. 1): A83, doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.2007.04130_8.x, S2CID 57308997
- ^ "Pioneer Muslim Physicians". IslamiCity. aramcoworld.com. 9 December 2012. Archived from the original on 21 March 2017. Retrieved 20 March 2017.[better source needed]
- ^ Ignjatovic M: Overview of the history of thyroid surgery. Acta Chir Iugosl 2003; 50: 9–36.
- ^ Aschoff A, Kremer P, Hashemi B, Kunze S (October 1999). "The scientific history of hydrocephalus and its treatment". Neurosurgical Review. 22 (2–3): 67–93, discussion 94–95. doi:10.1007/s101430050035. PMID 10547004. S2CID 10077885.
- ^ Himmelmann L (2007). "[From barber to surgeon- the process of professionalization]". Svensk Medicinhistorisk Tidskrift. 11 (1): 69–87. PMID 18548946.
- ^ Levine JM (March 1992). "Historical notes on pressure ulcers: the cure of Ambrose Paré". Decubitus. 5 (2): 23–4, 26. PMID 1558689.
- ^ Moore W (2005). The Knife Man: The Extraordinary Life and Times of John Hunter, Father of Modern Surgery. Crown Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-7679-1652-3. Retrieved 7 February 2013.
- ^ "John Hunter: "the father of scientific surgery": Resources from the collection of the P.I. Nixon Library". Archived from the original on 26 October 2013. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ "John Hunter: 'Founder of Scientific Surgery'". Archived from the original on 14 December 2013. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ^ Gordon ML (2002). Sir James Young Simpson and Chloroform (1811–1870). The Minerva Group, Inc. p. 108. ISBN 978-1-4102-0291-8. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ Robinson V (2005). The Story of Medicine. Kessinger Publishing. p. 420. ISBN 978-1-4191-5431-7.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Lister J (March 1867). "On a new method of treating compound fracture, abscess, etc.: with observations on the conditions of suppuration". The Lancet. 89 (2272): 326–329. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)51192-2.
Five articles running from:
Volume 89, Issue 2272, 16 March 1867, pp. 326–29 (Originally published as Volume 1, Issue 2272)
to:
Volume 90, Issue 2291, 27 July 1867, pp. 95–96 Originally published as Volume 2, Issue 2291 - ^ Lister J (September 1867). "On the Antiseptic Principle in the Practice of Surgery". British Medical Journal. 2 (351): 246–248. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.351.246. PMC 2310614. PMID 20744875.. Reprinted in Lister BJ (August 2010). "The classic: On the antiseptic principle in the practice of surgery. 1867". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 468 (8): 2012–2016. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1320-x. PMC 2895849. PMID 20361283.
- ^ Lister J. "Modern History Sourcebook: Joseph Lister (1827–1912): Antiseptic Principle Of The Practice Of Surgery, 1867". Fordham University. Archived from the original on 7 November 2011. Retrieved 2 September 2011.Modernized version of text
- ^ Lister J (December 2007). On the Antiseptic Principle of the Practice of Surgery by Baron Joseph Lister. Project Gutenberg. Archived from the original on 9 October 2011. Retrieved 2 September 2011. E-text, audio at Project Gutenberg.
Further reading
[edit]- Bartolo, M., Bargellesi, S., Castioni, C. A., Intiso, D., Fontana, A., Copetti, M., Scarponi, F., Bonaiuti, D., & Intensive Care and Neurorehabilitation Italian Study Group (2017). Mobilization in early rehabilitation in intensive care unit patients with severe acquired brain injury: An observational study. Journal of rehabilitation medicine, 49(9), 715–722.
- Ni, C.-yan, Wang, Z.-hong, Huang, Z.-ping, Zhou, H., Fu, L.-juan, Cai, H., Huang, X.-xuan, Yang, Y., Li, H.-fen, & Zhou, W.-ping. (2018). Early enforced mobilization after liver resection: A prospective randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Surgery, 54, 254–258.
- Lei, Y. T., Xie, J. W., Huang, Q., Huang, W., & Pei, F. X. (2021). Benefits of early ambulation within 24 h after total knee arthroplasty: a multicenter retrospective cohort study in China. Military Medical Research, 8(1), 17.
- Stethen, T. W., Ghazi, Y. A., Heidel, R. E., Daley, B. J., Barnes, L., Patterson, D., & McLoughlin, J. M. (2018). Walking to recovery: the effects of missed ambulation events on postsurgical recovery after bowel resection. Journal of gastrointestinal oncology, 9(5), 953–961.
- Yakkanti, R. R., Miller, A. J., Smith, L. S., Feher, A. W., Mont, M. A., & Malkani, A. L. (2019). Impact of early mobilization on length of stay after primary total knee arthroplasty. Annals of translational medicine, 7(4), 69.