Chenzhou
Chenzhou
郴州市 | |
|---|---|
 Chen River and the residential on the river bank in Chenzhou City | |
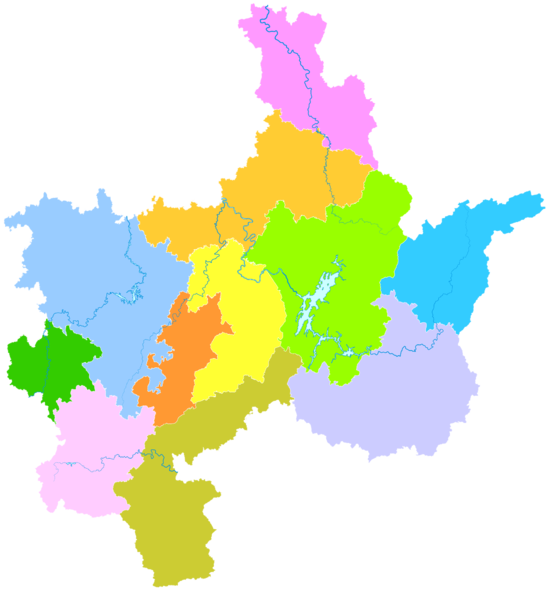
 Chenzhou's administrative area in Hunan | |
| Coordinates (Chenzhou municipal government): 25°46′12″N 113°00′58″E / 25.770°N 113.016°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Hunan |
| Municipal seat | Beihu District |
| Area | |
| 19,317 km2 (7,458 sq mi) | |
| • Urban (2017)[1] | 580.00 km2 (223.94 sq mi) |
| Population (2010 census) | |
| 4,581,778 | |
| • Density | 240/km2 (610/sq mi) |
| • Urban (2020)[1] | 960,000 |
| GDP[2] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | CN¥ 298.1 billion US$ 44.2 billion |
| • Per capita | CN¥ 64,279 US$ 9,558 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 423000 |
| Area code | 0735 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-HN-10 |
| License plate prefixes | 湘L |
| Website | en |
Chenzhou (Chinese: 郴州; pinyin: Chēnzhōu) is a prefecture-level city located in the south of Hunan province, China, bordering the provinces of Jiangxi to the east and Guangdong to the south. Its administrative area covers 19,317 square kilometres (7,458 sq mi), 9.2% of the provincial area, and its total population reached 4,581,779 in the 2010 census, 26% of them living in urban areas, 74% of them live in rural areas.[3]
History
[edit]Chenzhou is a historical city dating back from the Qin dynasty. The area was historically named Guiyang (simplified Chinese: 桂阳; traditional Chinese: 桂陽; pinyin: Guìyáng) Commandery before being renamed to the current name in the year 735 during the Tang dynasty. The Chinese character 郴, meaning "City in the Forest", uniquely refers to only the area. Known to be popular among the literacy circle of the Tang courts, poets such as Wang Changling, Du Fu, Han Yu, Liu Yuxi and Qin Guan have visited and wrote poems to the natural beauty of the area.
According to unsourced claims from Jung Chang and Jon Halliday in their book Mao: The Unknown Story, Chenzhou, along with neighboring Leiyang city was razed in 1928 by troops (Chinese Red Army) under the command of Zhu De, who was following directives which originated in Moscow and passed on by higher officials of the Chinese Communist Party. The strategy was to leave large numbers of peasants from the cities with no option but to join communist uprisings. [citation needed]
Chenzhou was the site of a large investigation when its municipal government and party committee, led by Secretary Li Dalun, was charged on multiple counts of corruption in June 2006. [4]
Food
[edit]Chenzhou is a thousand-year-old city, known as the "land of the Nine Immortals and Two Buddhas". It is a blessed place for the development of Taoism and Buddhist culture, leaving many legends of gods and Buddhas. Among them, Su Dan, Shoufo Zhou Quanzhen, Liu Zhan, Liu Yi and other legends have also spread overseas, becoming the most valuable intangible cultural heritage in China. In addition to visiting the local treasures of nature, you can also taste the folk flavors of Chenzhou.
Zilong County Tanzi Pork
[edit]Zilong County Tanzi Pork is a famous traditional dish in Chenzhou, Hunan Province, which belongs to Hunan cuisine. It is said that General Zhao Zilong, a famous general of the Three Kingdoms, planned to take Guiyang County. During the period when he was stationed in Guiyang County, he was good at governing the army and the people. The army did not disturb the people and was supported by the people. The people called Guiyang County Zilong County. In order to express their love for General Zhao Zilong, the local people used pork skin and pork belly into the five-clawed chili sauce jar in Fangyuan. After marinating with traditional folk techniques for several months, they gave them wine and rice to General Zilong. The taste was fragrant and spicy, and the aftertaste was long. General Zilong did not want to enjoy it alone, so he gave it to the lord Liu Bei to enjoy. After eating, Liu Bei had a great appetite and was full of praise, and then gave him the name "Zilong County jar meat". Zilong County's jar meat got its name from this, and it has been passed down.
Yongxing Roast Chicken
[edit]"Yongxing Roast Chicken" is quite strict with the ingredients. The main material is a native rooster for more than two years. The ginger is ginger, and the oil must be made of native tea oil. For each step of stewing, stir-frying and slightly simmering, you must master the heat and time. Dry rice pepper, three-color pepper, soybean oil, chicken essence and other ingredients and seasonings are available to make a spicy and delicious roast chicken. There is an endless stream of people around the country who come to taste it, and they are full of praise after enjoying it.
Anren Dou pepper
[edit]Anren Dou pepper is the most classic famous dish in Anren County, Hunan Province. As long as Anren people hear this dish, they will be full of praise and clap their hands. When outsiders eat this dish, they all have an endless aftertaste. This dish is spicy and fragrant. It is classic but not flamboyant. It is low-key and willing to be lonely to accompany generations of Anren people, and can be deeply rooted in the hearts of the hearts of the symbol of disease prevention and health.
Linwu duck
[edit]A specialty of Linwu County, Chenzhou City, Hunan Province, is a Chinese geographical indication product. It is one of the eight famous ducks in China. It is a food owned by Shunhua Duck Industry. It has a long breeding history and is mainly produced in the Wushui River Basin of Linwu County, one of the sources of the Pearl River. The growth cycle of Linwu duck is very long. It weighs only two and a half catties in 70 or 80 days. It has the characteristics of tender meat and delicious taste. It is famous for nourishing yin and reducing fire, beauty and fitness. Its taste ranks first among local hemp ducks in China. As a tribute to the imperial court, it is well-known in southern Hunan and Guangdong. It was included in the Records of Livestock and Poultry Breeds in Hunan Province and won the Gold Award for High-quality Agricultural Products in Hunan Province.
Guiyang rice noodle meat
[edit]Guiyang rice noodle meat is a traditional famous dish in Guiyang County, Chenzhou City, Hunan Province. It has always been well-known among the people in Guiyang. It is a must-have dish for banquets such as festivals, weddings and parties in Guiyang.
Taro lotus duck
[edit]Taro lotus duck is a famous dish of Yizhang. The tender green taro lotus and a little spicy taste are combined with delicious duck meat. The taste is rich, fresh and spicy, delicious, the taste is mellow, the oily color is thick, and there is no greasy feeling, which is mouth-watering. At the 3rd Chenzhou Folk Cuisine Cooking Competition, Yizhang taro lotus duck was rated as a famous folk dish in Chenzhou.
Geography
[edit]Chenzhou is situated at the juncture of Hunan and Guangdong provinces at the foot of small Qitian Mountains of the Nanling Mountain Range. Places of interest, natural scenic spots, ancient relics and buildings make for over 100 tourism spots in the city. The major ones are the Suxian Hill, the Wanhuayan, the Dongjiang Lake, and the Wugai Mountain Hunting Field.[5] Suxian Hill is located 2 kilometers east of Chenzhou, and covers 15 square kilometers.[6][7]
Climate
[edit]Chenzhou has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification: Cfa), with four distinct seasons. Spring is subject to heavy rainfall, while the summers are long, hot, and humid with lesser rainfall, and autumn is comfortable and rather dry. Winter is rather brief, but cold snaps occur with temperatures occasionally dropping below freezing, and while not heavy, rain can be frequent.[5]
| Climate data for Chenzhou, elevation 185 m (607 ft), (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 27.0 (80.6) |
32.0 (89.6) |
33.7 (92.7) |
35.6 (96.1) |
36.2 (97.2) |
38.0 (100.4) |
40.3 (104.5) |
40.5 (104.9) |
38.6 (101.5) |
36.4 (97.5) |
33.5 (92.3) |
27.4 (81.3) |
40.5 (104.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
13.4 (56.1) |
17.3 (63.1) |
23.9 (75.0) |
28.0 (82.4) |
31.2 (88.2) |
34.2 (93.6) |
33.0 (91.4) |
29.2 (84.6) |
24.6 (76.3) |
19.0 (66.2) |
13.1 (55.6) |
23.1 (73.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.6 (43.9) |
9.3 (48.7) |
13.1 (55.6) |
19.2 (66.6) |
23.6 (74.5) |
27.0 (80.6) |
29.6 (85.3) |
28.3 (82.9) |
24.7 (76.5) |
19.8 (67.6) |
14.2 (57.6) |
8.6 (47.5) |
18.7 (65.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 4.1 (39.4) |
6.6 (43.9) |
10.1 (50.2) |
15.9 (60.6) |
20.2 (68.4) |
23.9 (75.0) |
26.1 (79.0) |
25.0 (77.0) |
21.4 (70.5) |
16.3 (61.3) |
10.8 (51.4) |
5.5 (41.9) |
15.5 (59.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −5.9 (21.4) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
2.9 (37.2) |
10.0 (50.0) |
13.4 (56.1) |
18.6 (65.5) |
18.3 (64.9) |
13.2 (55.8) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 80.0 (3.15) |
97.8 (3.85) |
156.1 (6.15) |
169.3 (6.67) |
188.2 (7.41) |
195.7 (7.70) |
126.3 (4.97) |
191.3 (7.53) |
86.8 (3.42) |
72.0 (2.83) |
78.4 (3.09) |
68.2 (2.69) |
1,510.1 (59.46) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 16.4 | 16.1 | 19.4 | 16.5 | 17.4 | 15.8 | 10.3 | 14.6 | 11.7 | 10.7 | 11.7 | 12.0 | 172.6 |
| Average snowy days | 3.5 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 6.3 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 80 | 80 | 80 | 76 | 75 | 74 | 66 | 72 | 76 | 75 | 76 | 76 | 76 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 53.5 | 53.4 | 59.5 | 91.2 | 111.9 | 127.7 | 219.0 | 162.3 | 121.1 | 118.0 | 100.0 | 84.4 | 1,302 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 16 | 17 | 16 | 24 | 27 | 31 | 52 | 40 | 33 | 33 | 31 | 26 | 29 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration[8][9] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[10] | |||||||||||||
Administrative divisions
[edit]
- Beihu District (北湖区), 815 km2 (315 sq mi). Population: 300,000 (2003).
- Suxian District (苏仙区), 1,342 km2 (518 sq mi). Population: 249,900
- Zixing City (资兴市) 2,716 km2 (1,049 sq mi). Population: 360,000
- Guiyang County (桂阳县), 2,954 km2 (1,141 sq mi). Population: 790,000
- Yongxing County (永兴县), 1,979 km2 (764 sq mi). Population: 630,000
- Yizhang County (宜章县), 2,086 km2 (805 sq mi). Population: 560,000
- Jiahe County (嘉禾县), 696 km2 (269 sq mi). Population: 340,000
- Linwu County (临武县), 1,375 km2 (531 sq mi). Population: 310,000
- Rucheng County (汝城县), 2,424 km2 (936 sq mi). Population: 360,000
- Guidong County (桂东县), 1,453 km2 (561 sq mi). Population: 170,000
- Anren County (安仁县), 1,461 km2 (564 sq mi). Population: 390,000
| Map |
|---|
Economy
[edit]Major deposits of tungsten, bismuth and molybdenum make Chenzhou a production base for non-ferrous metals.
Colleges and universities
[edit]- Xiangnan University(湘南学院)
- Chenzhou Vocational Technical College(郴州职业技术学院)
Notable people
[edit]- Duan Yixuan, a singer and actress
- Long Yang, a hostess in CCTV
- Ouyang Jingling, a paralympic athlete
- Xue Yiwei, Chinese writer living in Montreal[11]
- Li Xingxue (李星学), Chinese botanist and member of Chinese Academy of Sciences
Government
[edit]The current CPC Party Secretary of Chenzhou is Wu Ju Pei[12] and the current mayor is Kan Bao Yong.[13]
Tourism
[edit]The areas of interest in Chenzhou include: Wanhua Rock (万华岩), Wugai Mountain Hunting Field, Suxian Hill and Dongjiang Lake.
Suxian Hill, also known as the "18th blessed land in china," is a natural and historical tourism site.[6] The hill is the site of many cultural legends, and boasts a scenic temple and Taoist relics.[14] It also features an observation building designed by architect Yang Ying (杨瑛).[15]
The city is served by Chenzhou Beihu Airport.
References
[edit]- ^ a b Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, ed. (2019). China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2017. Beijing: China Statistics Press. p. 68. Archived from the original on 18 June 2019. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ^ "2022年湖南省各市州地区生产总值(三季度".
- ^ (in Chinese) Demographics of Chenzhou Archived May 11, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, Official website of Chenzhou Government, August 28, 2007.
- ^ "zh:湖南郴州市委书记落马背后:治下发生连串丑闻" [Behind the fall of Hunan's Chenzhou city party secretary: a string of scandals under his rule]. THE STATE COUNCIL THE PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF CHINA (in Chinese). 2006-06-09. Retrieved 2024-06-07.
- ^ a b "zh:郴州自然地理" [Physical Geography of Chenzhou]. The People's Government of ChenZhou City (in Chinese). 2013-06-15. Retrieved 2024-06-06.
- ^ a b "Chenzhou | Half the Sky". Archived from the original on 2014-04-25.
- ^ "苏仙岭". Archived from the original on 2016-03-20. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 11 June 2023.
- ^ "Experience Template" 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- ^ 郴州 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 (in Chinese). Weather China. Retrieved 21 November 2022.
- ^ "The Fate of a Novel Amid China's Reform". University of California Los Angeles. Retrieved 2022-07-29.
- ^ Wang, Jianliang (2022-03-03). "zh:吴巨培任湖南郴州市委书记" [Wu Jupei appointed Secretary of Chenzhou Municipal Committee, Hunan Province]. 澎湃 (in Chinese). Retrieved 2024-06-08.
- ^ Tang, Sisi (2022-03-11). "zh:阚保勇同志任中共郴州市委委员、常委、副书记" [Comrade Kan Bao-yong is a member, member of the Standing Committee and deputy secretary of the CPC Chenzhou Municipal Committee.]. www.czxww.cn (in Chinese). Retrieved 2024-06-08.
- ^ "Chenzhou Hunan: A Blessed Land Known as South Gate of Hunan".
- ^ "好屋列传·苏仙岭景观瞭望台:本身也是风景". 2018-04-19. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
External links
[edit]- Chenzhou News Website, run by Chenzhou Government
- Official website of Chenzhou Government