Baddeley's model of working memory
Baddeley's model of working memory is a model of human memory proposed by Alan Baddeley and Graham Hitch in 1974, in an attempt to present a more accurate model of primary memory (often referred to as short-term memory). Working memory splits primary memory into multiple components, rather than considering it to be a single, unified construct.[1]
Baddeley and Hitch proposed their three-part working memory model as an alternative to the short-term store in Atkinson and Shiffrin's 'multi-store' memory model (1968). This model is later expanded upon by Baddeley and other co-workers to add a fourth component, and has become the dominant view in the field of working memory. However, alternative models are developing, providing a different perspective on the working memory system.
The original model of Baddeley & Hitch was composed of three main components: the central executive which acts as a supervisory system and controls the flow of information from and to its slave systems: the phonological loop and the visuo-spatial sketchpad. The phonological loop stores verbal content, whereas the visuo-spatial sketchpad caters to visuo-spatial data. Both the slave systems only function as short-term storage centers.
Baddeley and Hitch's argument for the distinction of two domain-specific slave systems in the older model was derived from experimental findings with dual-task paradigms. Performance of two simultaneous tasks requiring the use of two separate perceptual domains (i.e. a visual and a verbal task) is nearly as efficient as performance of the tasks individually. In contrast, when a person tries to carry out two tasks simultaneously that use the same perceptual domain, performance is less efficient than when performing the tasks individually.[2]
A fourth component of Baddeley's model was added 25 years later to complement the central executive system. It was designated as episodic buffer. It is considered a limited-capacity system that provides temporary storage of information by conjoining information from the subsidiary systems, and long-term memory, into a single episodic representation.[3]

Components
[edit]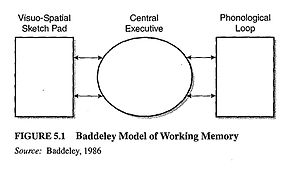
Central executive
[edit]The central executive is a flexible system responsible for the control and regulation of cognitive processes. It directs focus and targets information, making working memory and long-term memory work together. It can be thought of as a supervisory system that controls cognitive processes, making sure the short-term store is actively working, and intervenes when they go astray and prevents distractions.[4]
It has the following functions:
- Updating and coding incoming information and replacing old information
- Binding information from a number of sources into coherent episodes
- Coordination of the slave systems
- Shifting between tasks or retrieval strategies
- Inhibition, suppressing dominant or automatic responses[4]
- Selective attention
The central executive has two main systems: the visuo-spatial sketchpad, for visual information, and the phonological loop, for verbal information.[5]
Using the dual-task paradigm, Baddeley and Della Salla have found, for instance, that patients with Alzheimer's dementia are impaired when performing multiple tasks simultaneously, even when the difficulty of the individual tasks is adapted to their abilities.[6] Two tasks include a memory tasks and a tracking task. Individual actions are completed well, but as the Alzheimer's becomes more prominent in a patient, performing two or more actions becomes more and more difficult. This research has shown the deteriorating of the central executive in individuals with Alzheimer's.[7]
Recent research on executive functions suggests that the 'central' executive is not as central as conceived in the Baddeley & Hitch model. Rather, there seem to be separate executive functions that can vary largely independently between individuals and can be selectively impaired or spared by brain damage.[8]
Phonological loop
[edit]
The phonological loop (or articulatory loop) as a whole deals with sound or phonological information. It consists of two parts: a short-term phonological store with auditory memory traces that are subject to rapid decay and an articulatory rehearsal component (sometimes called the articulatory loop) that can revive the memory traces.
Any auditory verbal information is assumed to enter automatically into the phonological store. Visually presented language can be transformed into phonological code by silent articulation and thereby be encoded into the phonological store. This transformation is facilitated by the articulatory control process. The phonological store acts as an "inner ear", remembering speech sounds in their temporal order, whilst the articulatory process acts as an "inner voice" and repeats the series of words (or other speech elements) on a loop to prevent them from decaying. The phonological loop may play a key role in the acquisition of vocabulary, particularly in the early childhood years.[9] It may also be vital for learning a second language.

Five main findings provide evidence for the phonological loop:
- The effect of phonological similarity:
Lists of words that sound similar are more difficult to remember than words that sound different. Semantic similarity (similarity of meaning) has comparatively little effect, supporting the assumption that verbal information is coded largely phonologically in working memory.[10] - The effect of articulatory suppression:
Memory for verbal material is impaired when people are asked to say something irrelevant aloud. This is assumed to block the articulatory rehearsal process, leading memory traces in the phonological loop to decay.[11] - Transfer of information between codes:
With visually presented items, adults usually name and sub-vocally rehearse them, so the information is transferred from a visual to an auditory encoding. Articulatory suppression prevents this transfer, and in that case the above-mentioned effect of phonological similarity is erased for visually presented items.[12] - Neuropsychological evidence:
A defective phonological store explains the behavior of patients with a specific deficit in phonological short-term memory. Aphasic patients with developmental verbal dyspraxia are unable to set up the speech motor codes necessary for articulation, caused by a deficiency of the articulatory rehearsal process.[13] - On the other hand, patients with dysarthria, whose speech problems are secondary, show a normal capacity for rehearsal. This suggests that it is the subvocal rehearsing that is crucial.[14]
Evidence in support of a phonological short-term store
[edit]An accumulation of literature across decades has lent strong support to the theory of phonological STS. In a 1971 study, Stephen Madigan demonstrated that a larger recency effect is seen during forward serial recall when people are presented a list auditorally as opposed to visually. (A smaller effect is seen in backwards serial recall.)[15] In his study, auditory presentation led to greater recall of the most recently studied items. Catherine Penney expanded on this discovery to observe that modality effects can also be found in the case of free recall tasks.[16] In 1965, Dallett had discovered that this observed modality effect is greatly reduced by the addition of a "suffix" item to the presented list; this suffix is a distractor item that is not to be recalled.[17] Robert Greene utilized this observation in 1987 to discover that this suffix effect has a larger impact on lists learned auditorally as opposed to visually.[18] The culmination of all of these findings results in strong support of the theory that there is a short-term store that phonologically stores recently learned items. In addition, Bloom and Watkins found that the suffix effect is greatly diminished when the suffix is not interpreted as linguistic sound, which agrees with the phonological short term store theory as it would be largely unaffected by non-linguistic distractors.[19]
Visuo-spatial working memory
[edit]Alan Baddeley's theory of working memory has yet another aspect to which memory can be stored short term. The visuo-spatial sketchpad is the store that holds visual information for manipulation.[20] The visuo-spatial sketchpad is thought to be its own storage of working memory in that it does not interfere with the short term processes of the phonological loop. In research, it has been found that the visuo-spatial sketchpad can work simultaneously with the phonological loop to process both auditory and visual stimuli without either of the processes affecting the efficacy of the other.[21] Baddeley re-defined the theory of short-term memory as a working memory to explain this phenomenon. In the original theory of short-term memory, it is understood that a person only has one store of immediate information processing which could only hold a total of 7 items plus or minus two items to be stored in a very short period of time, sometimes a matter of seconds. The digit-span test is a perfect example of a measurement for classically defined short-term memory. Essentially, if one is not able to encode the 7 plus or minus two items within a few minutes by finding an existing association for the information to be transferred into long-term memory, then the information is lost and never encoded.[22]
However, visuo-spatial short-term memory can retain visual and/or spatial information over brief periods of time.[22] When this memory is in use, individuals are able to momentarily create and revisit a mental image that can be manipulated in complex or difficult tasks of spatial orientation. There are some who have disparities in the areas of the brain that allow for this to happen from different types of brain damage.[21] There can also be a misunderstanding here in the differences between transient memories such as the visual sensory memory. A transient memory is merely a fleeting type of sensory memory; therefore, as the visual sensory memory is a type of sensory memory, there is a store for the information, but the store lasts for only a second or so. A common effect of the visual sensory memory is that individuals may remember seeing things that weren't really there or not remembering particular things that were in their line of sight. The memory is only momentary, and if it isn't attended to within a matter of seconds, it is gone.[20]
There are two different pathways in the brain that control different functions of what is known inclusively as the visuo-spatial sketchpad. The sketchpad consists of the spatial short-term memory and the object memory. The spatial short-term memory is how one is able to learn and thus remember "where" they are in comparative representation to other objects. The object memory of the visuo-spatial sketchpad is essential in learning and remembering "what" an object is.[22] The differences between these two differing visual abilities is due in large part because of different pathways of each of the abilities in the brain. The visual pathway in the brain that detects spatial representation of a person to and within their environment is the dorsal stream. The visual pathway that determines objects shapes, sizes, colors and other definitive characteristics is called the ventral stream.[21] Each of these two streams runs independent of one another so that the visual system may process one without the other (like in brain damage for instance) or both simultaneously. The two streams do not depend on one another, so if one is functioning manipulatively, the other can still send its information through.
Logie's elaboration of the visuospatial sketchpad
[edit]Logie has proposed that the visuo-spatial sketchpad can be further subdivided into two components:
- The visual cache, which stores information about form and color.
- The inner scribe, which deals with spatial and movement information. It also rehearses information in the visual cache and transfers information to the central executive.[23]
Three main findings provide evidence for the distinction between visual and spatial parts of the visuospatial sketchpad:
- There is less interference between visual and spatial tasks than between two visual tasks or two spatial tasks.[24]
- Brain damage can influence one of the components without influencing the other.[25]
- Results from brain-imaging show that working memory tasks with visual objects activate mostly areas in the left hemisphere, whereas tasks with spatial information activate more areas in the right hemisphere.[26]
Episodic buffer
[edit]In 2000 Baddeley added a fourth component to the model, the episodic buffer. This component is a limited capacity passive system,[27] dedicated to linking information across domains to form integrated units of visual, spatial, and verbal information with time sequencing (or episodic chronological ordering[27]), such as the memory of a story or a movie scene. The episodic buffer is also assumed to have links to long-term memory and semantic meaning.[3]
The episodic buffer "acts as a buffer store, not only between the components of Working Memory, but also linking Working Memory to perception and Long-Term Memory".[27] Baddeley assumes that "retrieval from the buffer occurred through conscious awareness".[27] It allows individuals to use integrated units of information they already have to imagine new concepts. Since this is likely "an attention-demanding process...the buffer would depend heavily on the Central Executive".[27]
The main motivation for introducing this component was the observation that some (in particular, highly intelligent) patients with amnesia, who presumably have no ability to encode new information in long-term memory, nevertheless have good short-term recall of stories, recalling much more information than could be held in the phonological loop.[28] "The episodic buffer appears...capable of storing bound features and making them available to conscious awareness but not itself responsible for the process of binding".[29]
It is assumed that "conscious access to the phonological loop or sketchpad may operate via the buffer".[30] This is based on the assumption that both the visuo-spatial sketchpad and phonological loop act as minor buffers, combining information within their sensory area. The episodic buffer may also interact with smell and taste.[30]
Biology/neuroscience
[edit]There is much evidence for a brief memory buffer, as distinct from the long term store. The phonological loop seems to be connected to activation in the left hemisphere, more specifically the temporal lobe. The visuo-spatial sketchpad activates different areas depending on task difficulty; less intense tasks seem to activate in the occipital lobe, whereas more complex tasks appear in the parietal lobe. The central executive is still a mystery, although it would seem to be more or less located in the frontal lobes of the brain. The episodic buffer seems to be in both hemispheres (bilateral) with activations in both the frontal and temporal lobes, and even the left portion of the hippocampus.[31] In terms of genetics, the gene ROBO1 has been associated with phonological buffer integrity or length.[32][33]
Validity of the model
[edit]The strength of Baddeley's model is its ability to integrate a large number of findings from work on short-term and working memory. Additionally, the mechanisms of the slave systems, especially the phonological loop, has inspired a wealth of research in experimental psychology, neuropsychology, and cognitive neuroscience.
However, criticisms have been raised, for instance of the phonological-loop component, because some details of the findings are not easily explained by the original Baddeley and Hitch model, including the controversy regarding the 7±2 rule.[34][35]
The episodic buffer is seen as a helpful addition to the model of working memory, but it has not been investigated extensively and its functions remain unclear.[36]
See also
[edit]- Echoic memory
- Prefrontal cortex § Attention and memory
- The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two
- Working memory
References
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Baddeley, Alan D.; Hitch, Graham (1974-01-01), Bower, Gordon H. (ed.), "Working Memory", Psychology of Learning and Motivation, vol. 8, Academic Press, pp. 47–89, retrieved 2025-03-17
- ^ "Working Memory - Outline and Discussion - Psychology Unlocked". 7 January 2017. Archived from the original on 15 August 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ^ a b Baddeley, Alan (1 November 2000). "The episodic buffer: a new component of working memory?". Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 4 (11): 417–423. doi:10.1016/S1364-6613(00)01538-2. PMID 11058819. S2CID 14333234.
- ^ a b Wongupparaj, P.; Kumari, V. & Morris, R.G. (2015). "The relation between a multicomponent working memory and intelligence: The roles of central executive and short-term storage functions". Intelligence. 53: 166–180. doi:10.1016/j.intell.2015.10.007. S2CID 146523621.
- ^ Baddeley, A. (2010). "Working memory". Current Biology. 20 (4): R136 – R140. Bibcode:2010CBio...20.R136B. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.12.014. PMID 20178752.
- ^ Baddeley A, Della Sala S (October 1996). "Working memory and executive control" (PDF). Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 351 (1346): 1397–403. doi:10.1098/rstb.1996.0123. JSTOR 3069185. PMID 8941951. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-20.
- ^ Baddeley, A (1992-01-31). "Working memory" (PDF). Science. 255 (5044). American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS): 556–559. Bibcode:1992Sci...255..556B. doi:10.1126/science.1736359. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 1736359.
- ^ Miyake, A.; Friedman, N. P.; Emerson, M. J.; Witzki, A. H.; Howerter, A.; Wager, T. D. (2000). "The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contributions to complex "frontal lobe" tasks: A latent variable analysis". Cognitive Psychology. 41 (1): 49–100. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.485.1953. doi:10.1006/cogp.1999.0734. PMID 10945922. S2CID 10096387.
- ^ Baddeley A, Gathercole S, Papagno C (January 1998). "The phonological loop as a language learning device". Psychol Rev. 105 (1): 158–73. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.464.9511. doi:10.1037/0033-295X.105.1.158. PMID 9450375. S2CID 15650449.
- ^ a) Conrad. R. & Hull, A.J. (November 1964). "Information, acoustic confusion and memory span" (PDF). British Journal of Psychology. 55 (4): 429–32. doi:10.1111/j.2044-8295.1964.tb00928.x. PMID 14237884. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-10-20. Retrieved 2011-02-22.
b) Baddeley AD (November 1966). "Short-term memory for word sequences as a function of acoustic, semantic and formal similarity" (PDF). Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology. 18 (4): 362–5. doi:10.1080/14640746608400055. PMID 5956080. S2CID 32498516. - ^ Baddeley, A.D.; Thomson, N; Buchanan, M (1975). "Word length and the structure of short-term memory". Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior. 14 (6): 575–589. doi:10.1016/S0022-5371(75)80045-4.
- ^ Murray, D.J. (1968). "Articulation and acoustic confusability in short term memory". Journal of Experimental Psychology. 78 (4, Pt.1): 679–684. doi:10.1037/h0026641.
- ^ Waters, G.F.; et al. (1992). "The role of high-level speech planning in rehearsal: Evidence from patients with apraxia of speech". Journal of Memory and Language. 31: 54–73. doi:10.1016/0749-596X(92)90005-I.
- ^ Baddeley, A.D.; Wilson, B.A. (1985). "Phonological coding and shortterm memory in patients without speech". Journal of Memory and Language. 24 (4): 490–502. doi:10.1016/0749-596X(85)90041-5.
- ^ Stephen Madigan (1971). "Modality and Recall Order Interactions in Short-Term Memory for Serial Order". Journal of Experimental Psychology. 87 (2): 294–296. doi:10.1037/h0030549.
- ^ Catherine Penney (1975). "Modality Effects in Short-Term Verbal Memory". Psychological Bulletin. 82 (1): 68–84. doi:10.1037/h0076166.
- ^ Kent M. Dallett (1965). "Primary Memory: The effects of redundancy upon digit repetition". Psychonomic Science. 3 (6): 237–238. doi:10.3758/bf03343114.
- ^ Robert Green (1987). "Stimulus suffixes and visual presentation". Memory and Cognition. 15 (6): 497–503. doi:10.3758/bf03198383. PMID 3695943.
- ^ Lance C. Bloom; Michael J. Watkins (1999). "Two-Component Theory of the Suffix Effect: Contrary Findings". Journal of Experimental Psychology. 25 (6): 1452–1474. doi:10.1037/0278-7393.25.6.1452. PMID 10605831.
- ^ a b Gluck, Mark A.; Mercado, Eduardo; Myers, Catherine E. (2008). Leaning and Memory: From Brain to Behavior. New York, NY: Worth Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7167-8654-2.
- ^ a b c Denis, Michel; Logie, Robert; Cornoldo, Cesare (2012). "The processing of visuo-spatial information: Neuropsychological and neuroimaging investigations". Imagery, Language and Visuo-Spatial Thinking. Hove, US: Psychology Press. pp. 81–102.
- ^ a b c Baddeley, Alan; Eysenck, Michael W.; Anderson, Michael C. (2009). Memory. New York, NY: Psychology Press. ISBN 978-1-84872-000-8.
- ^ Logie, R.H. (1995). Visuo-spatial working memory, Hove, UK: Lawrence Eribaum Associates.
- ^ Klauer, K. C.; Zhao, Z. (2004). "Double dissociations in visual and spatial short-term memory". Journal of Experimental Psychology: General. 133 (3): 355–381. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.133.3.355. PMID 15355144.
- ^ mentioned in: http://www.psypress.com/ek5/resources/demo_ch06-sc-02.asp Archived 2007-09-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Smith EE, Jonides J (June 1997). "Working memory: a view from neuroimaging". Cogn Psychol. 33 (1): 5–42. doi:10.1006/cogp.1997.0658. PMID 9212720. S2CID 1051679.
- ^ a b c d e Baddeley, Alan (2011-11-30). "Working Memory: Theories, Models, and Controversies". Annual Review of Psychology. 63 (1): 1–29. doi:10.1146/annurev-psych-120710-100422. ISSN 0066-4308. PMID 21961947.
- ^ Baddeley A, Wilson BA (2002). "Prose recall and amnesia: implications for the structure of working memory". Neuropsychologia. 40 (10): 1737–43. doi:10.1016/S0028-3932(01)00146-4. PMID 11992661. S2CID 22404837.
- ^ Baddeley, Alan; Allen, Richard J; Hitch, Graham J (2010-10-01). "Investigating the episodic buffer". Psychologica Belgica. 50 (3–4): 223. doi:10.5334/pb-50-3-4-223. ISSN 2054-670X.
- ^ a b Baddeley, Alan D.; Allen, Richard J.; Hitch, Graham J. (2011). "Binding in visual working memory: The role of the episodic buffer". Neuropsychologia. 49 (6): 1393–1400. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.12.042. PMID 21256143. S2CID 28063175.
- ^ Rudner, Mary; Fransson, Peter; Ingvar, Martin; Nyberg, Lars; Rönnberg, Jerker (2007-01-01). "Neural representation of binding lexical signs and words in the episodic buffer of working memory". Neuropsychologia. 45 (10): 2258–2276. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.02.017. PMID 17403529. S2CID 6090818.
- ^ Sternberg, Robert J. (2007). Cognitive Psychology. WADSWORTH. pp. 205–206.
- ^ Bates, Timothy C.; Luciano, Michelle; Medland, Sarah E.; Montgomery, Grant W.; Wright, Margaret J.; Martin, Nicholas G. (January 2011). "Genetic Variance in a Component of the Language Acquisition Device: ROBO1 Polymorphisms Associated with Phonological Buffer Deficits" (PDF). Behav. Genet. 41 (1): 50–7. doi:10.1007/s10519-010-9402-9. PMID 20949370. S2CID 13129473.
- ^ Jones, D. M.; Macken, W. J.; Nicholls, A. P. (2004). "The phonological store of working memory: is it phonological and is it a store?". Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. 30 (3): 656–674. doi:10.1037/0278-7393.30.3.656. PMID 15099134. S2CID 17454765.
- ^ Nairne, J. S. (2002). "Remembering over the short-term: The case against the standard model". Annual Review of Psychology. 53: 53–81. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135131. PMID 11752479.
- ^ "Cognitive Psychology: A Student's Handbook :: 5th Edition: Chapter Topic". Archived from the original on 2007-09-28. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
Bibliography
[edit]- Baddeley, A.D.; Wilson, B. A. (2002). "Prose recall and amnesia: implications for the structure of working memory". Neuropsychologia. 40 (10): 1737–1743. doi:10.1016/S0028-3932(01)00146-4. PMID 11992661. S2CID 22404837.
- Baddeley, A.D. (2000). "The episodic buffer: a new component of working memory?". Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 4 (11): 417–423. doi:10.1016/S1364-6613(00)01538-2. PMID 11058819. S2CID 14333234.
- Baddeley, A.D. (2007). Working memory, thought and action. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Baddeley, A.D.; Della Sala, S.; Robbins, T. W.; Baddeley, A. (1996). "Working memory and executive control". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society. 351 (1346): 1397–1404. doi:10.1098/rstb.1996.0123. PMID 8941951.
- Baddeley, A.D., & Hitch, G. (1974). Working memory. In G.H. Bower (Ed.), The psychology of learning and motivation: Advances in research and theory (Vol. 8, pp. 47–89). New York: Academic Press.
