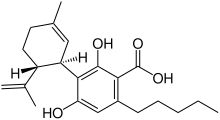
Cannabidiolic acid
Appearance
(Redirected from CBDA)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1′R,2′R)-2,6-Dihydroxy-5′-methyl-4-pentyl-2′-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1′,2′,3′,4′-tetrahydro[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H30O4 | |
| Molar mass | 358.478 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), is a cannabinoid produced in cannabis plants.[1] It is the precursor to cannabidiol (CBD). It is most abundant in the glandular trichomes on the female seedless flowers or more accurately infructescence often colloquially referred to as buds or flowers.[2]
Biosynthesis
[edit]Cannabidiolic acid is a natural product sesquiterpene biosynthesized in cannabis via Cannabidiolic acid synthase from the conjugation of olivetolic acid and cannabigerolic acid.[3]
Decarboxylation
[edit]CBDA is the chemical precursor to cannabidiol (CBD). Through the process of decarboxylation cannabidiol is derived through a loss of one carbon and two oxygen atoms acetyl from the 1 position of the benzoic acid ring.
References
[edit]- ^ Takeda, Shuso (2013). "[Medicinal chemistry and pharmacology focused on cannabidiol, a major component of the fiber-type cannabis]". Yakugaku Zasshi: Journal of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan. 133 (10): 1093–1101. doi:10.1248/yakushi.13-00196. ISSN 1347-5231. PMID 24088353.
- ^ Livingston, Samuel J.; Quilichini, Teagen D.; Booth, Judith K.; Wong, Darren C. J.; Rensing, Kim H.; Laflamme‐Yonkman, Jessica; Castellarin, Simone D.; Bohlmann, Joerg; Page, Jonathan E.; Samuels, A. Lacey (2020). "Cannabis glandular trichomes alter morphology and metabolite content during flower maturation". The Plant Journal. 101 (1): 37–56. doi:10.1111/tpj.14516. ISSN 1365-313X. PMID 31469934.
- ^ PubChem. "Cannabidiolic acid". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2019-12-23.
