Icariin
Appearance
(Redirected from C33H40O15)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
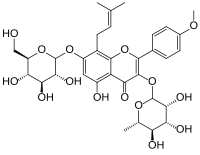
7-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-5-hydroxy-4′-methoxy-8-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-3-(α-L-rhamnopyranosyloxy)flavone
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
5-Hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-8-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-7-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3-{[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.107.649 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C33H40O15 | |
| Molar mass | 676.668 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Icariin is a chemical compound classified as a prenylated flavonol glycoside, a type of flavonoid. It is the 8-prenyl derivative of kaempferol 3,7-O-diglucoside. The compound has been isolated from several species of plant belonging to the genus Epimedium which are commonly known as horny goat weed, Yin Yang Huo,[1] and Herba epimedii.[2] Extracts from these plants produce aphrodisiac effects, and are used in traditional Chinese medicine to enhance erectile function.[3] However, clinical trial data are lacking to support these claims.[4][5]
References
[edit]- ^ Liu JJ, Li SP, Wang YT (2006). "Optimization for quantitative determination of four flavonoids in Epimedium by capillary zone electrophoresis coupled with diode array detection using central composite design". J Chromatogr A. 1103 (2): 344–349. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.11.036. PMID 16337210.
- ^ Cai WJ, Huang JH, Zhang SQ, Wu B, Kapahi P, Zhang XM, Shen ZY (2011). Blagosklonny MV (ed.). "Icariin and its derivative icariside II extend healthspan via insulin/IGF-1 pathway in C. elegans". PLOS ONE. 6 (12): e28835. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...628835C. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028835. PMC 3244416. PMID 22216122.
- ^ Makarova MN, Pozharitskaya ON, Shikov AN, Tesakova SV, Makarov VG, Tikhonov VP (2007). "Effect of lipid-based suspension of Epimedium koreanum Nakai extract on sexual behavior in rats". J Ethnopharmacol. 114 (3): 412–416. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2007.08.021. PMID 17890032.
- ^ "Horny Goat Weed". Drugs.com. August 5, 2019. Retrieved November 7, 2019.
- ^ Fang, Jian; Zhang, Yongjun (2017-10-12). "Icariin, an Anti-atherosclerotic Drug from Chinese Medicinal Herb Horny Goat Weed". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 8: 734. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00734. ISSN 1663-9812. PMC 5644024. PMID 29075193.
