Mazapertine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
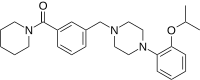
(Piperidin-1-yl){3-[(4-{2-[(propan-2-yl)oxy]phenyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}methanone | |
| Other names
RWJ-37796
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H35N3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 421.585 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Mazapertine (RWJ-37796) is an antipsychotic agent that was developed by Johnson & Johnson but never marketed. It exerts its pharmacological effect through affinity for dopamine D2, serotonin 5-HT1A, and α1-adrenergic receptors.[1]
Mazapertine is safe and well tolerated when administered orally.[2]
Analogs of mazapertine with conformational restriction have been prepared and have greater affinity for the 5-HT1A receptor.[3]
Synthesis
[edit]The laboratory synthesis of mazapertine has been reported.[4][5][6] It begins with alkylation of 2-nitrophenol (1) with isopropyl bromide to give 2-isopropoxynitrobenzene (2). Catalytic hydrogenation of nitro group gives 2-isopropoxyaniline (3). Intermolecular ring formation of this aniline with bis(2-chloroethyl)amine yields 1-(2-isopropoxyphenyl)piperazine (4). Separately, amide formation of 3-(chloromethyl)benzoyl chloride (5) with piperidine gives 1-[3-(chloromethyl)benzoyl]piperidine (6). The last step is the convergent synthesis between the above two arms of the synthesis to afford the alkylation product mazapertine (7).
References
[edit]- ^ Reitz, A. B.; Baxter, E. W.; Codd, E. E.; Davis, C. B.; Jordan, A. D.; Maryanoff, B. E.; Maryanoff, C. A.; McDonnell, M. E.; Powell, E. T.; Renzi, M. J.; Schott, M. R.; Scott, M. K.; Shank, R. P.; Vaught, J. L. (1998). "Orally Active Benzamide Antipsychotic Agents with Affinity for Dopamine D2, Serotonin 5-HT1A, and Adrenergic α1Receptors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 41 (12): 1997–2009. doi:10.1021/jm970164z. PMID 9622541.
- ^ Kleinbloesem, C. H.; Jaquet-Müller, F. O.; Al-Hamdan, Y.; Baldauf, C.; Gisclon, L.; Wesnes, K.; Curtin, C. R.; John Stubbs, R.; Walker, S. A.; Brunner-Ferber, F. O. (1996). "Incremental dosage of the new antipsychotic mazapertine induces tolerance to cardiovascular and cognitive effects in healthy men". Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 59 (6): 675–685. doi:10.1016/S0009-9236(96)90008-9. PMID 8681493. S2CID 45947831.
- ^ Baxter, Ellen W.; Reitz, Allen B. (1997). "Hindered rotation congeners of mazapertine: High affinity ligands for the 5-HT1A receptor". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 7 (7): 763. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(97)00074-7.
- ^ Reitz, Allen B.; Bennett, Debra J.; Blum, Paul S.; Codd, Ellen E.; Maryanoff, Cynthia A.; Ortegon, Marta E.; Renzi, Michael J.; Scott, Malcolm K.; Shank, Richard P.; Vaught, Jeffry L. (1994). "A New Arylpiperazine Antipsychotic with High D2/D3/5-HT1A/.alpha.1A-Adrenergic Affinity and a Low Potential for Extrapyramidal Effects". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 37 (8): 1060–1062. doi:10.1021/jm00034a003. PMID 7909336.
- ^ Reitz, Allen B.; Baxter, Ellen W.; Codd, Ellen E.; Davis, Coralie B.; Jordan, Alfonzo D.; Maryanoff, Bruce E.; Maryanoff, Cynthia A.; McDonnell, Mark E.; Powell, Eugene T.; Renzi, Michael J.; Schott, Mary R.; Scott, Malcolm K.; Shank, Richard P.; Vaught, Jeffry L. (1998). "Orally Active Benzamide Antipsychotic Agents with Affinity for Dopamine D2, Serotonin 5-HT1A, and Adrenergic α1 Receptors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 41 (12): 1997–2009. doi:10.1021/jm970164z. PMID 9622541.
- ^ Allen B. Reitz, U.S. patent 5,569,659 (1996 to Ortho McNeil Pharmaceutical Inc)

