Isepamicin
Appearance
(Redirected from C22H43N5O12)
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
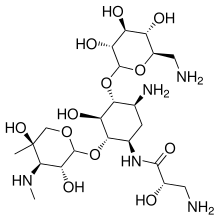
| Other names | Isepamycin (2S)-3-Amino-N-[(1R,2S,3S,4R,5S)-5-amino-4-[(3R,4S,5S,6R)-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-2-[(3R,4R,5R)-3,5-dihydroxy-5-methyl-4-methylaminooxan-2-yl]oxy-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]-2-hydroxypropanamide |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.055.567 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H43N5O12 |
| Molar mass | 569.609 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Isepamicin (isepamycin) is an aminoglycoside antibiotic.
It was patented in 1973 and approved for medical use in 1988.[1] It has been identified by the World Health Organization as a Critically Important Antimicrobial for human use.[2]
Synthesis
[edit]Isepamicin can be synthesized by derivatization of gentamicin B (1) with benzyl N-[(2S)-3-(2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)-2-hydroxy-3-oxopropyl]carbamate (2), followed by deprotection.[3][4][5][6]

References
[edit]- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 508. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ "Critically important antimicrobials for human medicine" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2012.
- ^ Serradell, MN; Blancafort, P.; Roberts, PJ; Castaer, J.; SCH-21420. Drugs Fut 1979, 4, 7, 525.
- ^ John J. Wright, U.S. patent 4,029,882 (1977 to Merck Sharp and Dohme Corp).
- ^ Thieme
- ^ ChemDrug
