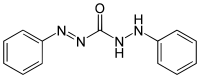
Diphenylcarbazone
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-anilino-3-phenyliminourea
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.909 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H12N4O | |
| Molar mass | 240.26 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow to red odorless solid[1] |
| Melting point | 157 °C[2] |
| poor[1] | |
| Hazards[4] | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H315, H319, H335[3] | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501[3] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
1,5-Diphenylcarbazone (or simply Diphenylcarbazone) is a chemical compound from the group of the carbazones (nitrogen compounds with the basic structure HN=N-CO-NH-NH2).
Properties
[edit]Diphenylcarbazone is an orange solid that dissolves well in Ethanol, Chloroform and Benzene and is almost insoluble in water.[1][2] It forms a purple complex compound with Hg(II) ions. Likewise, other metal ions, such as Cr(III) ions form colored complexes with Diphenylcarbazone. Diphenylcarbazone can be produced from Diphenylcarbazide via oxidation. Certain commercial products of diphenylcarbazone are a mixture with Diphenylcarbazide, which also forms colored complex compounds with certain metal ions.
Uses
[edit]Diphenylcarbazone is used as an indicator for endpoint determination in mercurimetry: If a Sodium chloride solution is titrated with Mercury(II) nitrate solution, undissociated Mercury(II) chloride is formed. If the end point is exceeded, then the color complex forms with diphenylcarbazone. This method is used in water analysis to determine chloride. If you add a certain amount of mercury(II) nitrate solution in excess to a chloride solution, you can determine the color intensity of the complex photometrically and thus deduce the chloride content.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c "Diphenylcarbazone 538-62-5 | TCI EUROPE N.V." www.tcichemicals.com.
- ^ a b Entry on 1,5-Diphenylcarbazon. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on 1. August 2014
- ^ a b "1,5-Diphenylcarbazone". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 7 June 2020.
 This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Institutes of Health.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Institutes of Health. - ^ SDS on 1,5-Diphenylcarbonohydrazone by TCI Europe, accessed on May 27, 2020
