Buffalo Creek Reservation
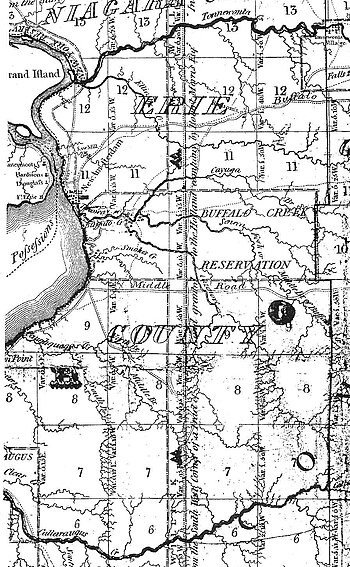
The Buffalo Creek Reservation was a tract of land surrounding Buffalo Creek in the central portion of Erie County, New York.[1][2] It contained approximately 49,920 acres (202.0 km2) of land and was set aside for the Seneca Nation following negotiations with the United States after the American Revolutionary War.
History
[edit]The territory around Buffalo Creek was conquered by the Seneca in the 1600s from the Wenrohronon, also called Wenro. Sometime between 1660 and 1690 the Seneca began to occupy the area.[2]: p.44 This was during the period of the Beaver Wars, when the Iroquois nations worked to expand their territory and hunting grounds.
During the American Revolution, the Sullivan Expedition of 1779 destroyed many towns of the Seneca, as they were allies of the British. The homeless people fled to the protection of the British at Fort Niagara. At one point the British were reported to be feeding and housing over 5000 refugees. Following a terrible winter of 1779–80 at Niagara, the Iroquois began to disperse. Joseph Brant took a group of mixed tribal members to the Grand River in Canada, where the Crown promised them a large grant of land.
The Tuscarora went to Lewiston. The remaining Seneca, Cayugas, and Onondaga peoples, led by Sayenqueraghta (Old King) and his son-in-law Roland Montour, chose to settle at Buffalo Creek.[2]: pp.61–62
Because the Seneca had been allies of the defeated British, the US forced them to cede most of their territory. By the Treaty of Big Tree in 1797, the Seneca relinquished all of Western New York except for twelve reservations, including Buffalo Creek. This reservation encompassed much of the present site of the city of Buffalo, New York, as well as its southern and western suburbs. By 1817 an estimate placed the population on the reservation at around 700 Seneca, plus small numbers of other displaced people.[2]: p.113
In 1804, Joseph Ellicott laid out the village of Buffalo, and his office in Batavia was making sales for the Holland Land Company. The purchase of Seneca reservations at Caneadea, Big Tree, Squawky Hill, and Gardeau, along the Genesee river, together with parcels from the Buffalo Creek and Cattaraugus Reservations in 1826 by Thomas Ogden, Benjamin W. Rodgers, and Robert Troup incentivized further efforts to dispossess the Haudenosaunee nations. Beginning in 1837, four agents of the Ogden Land Company, Heman Potter a Buffalo attorney, Orlando Allen, James Stryker, and Henry P. Wilcox bribed, intimidated and deceived 43 of the more than 80 Seneca chiefs to agree to the Treaty of Buffalo Creek, which was part of the Indian Removal policy initiated by President Andrew Jackson's administration. It required the Seneca of western New York to cede all of their reservation lands and move west of the Mississippi River, specifically to Wisconsin and Indian Territory (present-day Oklahoma), within five years. After the land sale that required the treaty fell through, the US negotiated a new treaty, which the Senate ratified in 1842. At the same time late in 1842, the land company established by David A. Ogden found buyers for a 5,000 acre portion of the Buffalo Creek Reservation; these were members of the Ebenezer Society, and their leader Christian Metz soon occupied the house of Chief John Seneca.
The Buffalo Creek reservation was the only reservation to be dissolved: the Seneca were allowed to keep their Cattaraugus, Oil Springs, Allegany and Tonawanda reservations after legal battles in the 1850s fought by Onondaga chief Samuel George and other leaders.[3]
Current status
[edit]This section needs to be updated. (November 2024) |
The modern Buffalo Creek Reservation consists of a nine-acre plot of land, which was part of the original reservation. In 2010, the Seneca bought the land from Carl Paladino, whose Ellicott Development Company continues to own much of the surrounding land.[4] The Seneca developed the Seneca Buffalo Creek Casino on this property, the revenues of which are used for economic development. A branch of its "Seneca One Stop" convenience store chain is being erected on the plot in 2020, with plans to open it in 2021.[5]
The Seneca Nation hosts an annual event opened to the public that commemorates the signing of the Buffalo Creek Treaty of 1842.[6][7]
42°51′45″N 78°39′45″W / 42.86250°N 78.66250°W
References
[edit]- ^ Holland Land Company map - circa. 1821
- ^ a b c d Houghton, Frederick (1920). "The History of the Buffalo Creek Reservation". Publications of the Buffalo Historical Society. Vol. 24. Buffalo Historical Society. pp. 109–116.
- ^ Hauptman, Laurence (2008). Seven Generations of Iroquois Leadership: The Six Nations Since 1800. Syracuse University Press. ISBN 978-0-8156-3165-1.
- ^ "Carl Paladino: The accidental candidate". Crain's New York Business. Sep 26, 2010. Retrieved Feb 23, 2021.
- ^ "Seneca Nation bringing tax free gas, cigarettes to downtown Buffalo". wgrz.com. 11 November 2020. Retrieved Feb 23, 2021.
- ^ "Buffalo Creek Commemoration". SNI. Retrieved 2024-11-25.
- ^ "State & Union: Seneca Nation reflects on Treaty of 1842". Olean Times Herald. 2024-05-18. Retrieved 2024-11-25.
