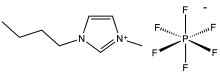
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-butyl-3-methylimidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate
| |
| Other names
BMIM-PF6
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.203.179 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C8H15F6N2P | |
| Molar mass | 284.186 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Light yellow liquid |
| Density | 1.38 g/mL (20 °C) |
| Melting point | −8 °C (18 °F; 265 K) |
| insoluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, also known as BMIM-PF6, is a viscous, colourless, hydrophobic and non-water-soluble ionic liquid with a melting point[1] of -8 °C. Together with 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, BMIM-BF4, it is one of the most widely studied ionic liquids. It is known to very slowly decompose in the presence of water.[2]
Preparation and uses
[edit]BMIM-PF6 is commercially available. It may be obtained in two steps: BMIM-Cl is synthesized by alkylating 1-methylimidazole with 1-chlorobutane. A metathesis reaction with potassium hexafluorophosphate gives the desired compound; the tetrafluoroborate may be prepared by analogously using potassium tetrafluoroborate.[3]
BMIM-PF6 has been investigated in electrochemistry where it serves both as solvent and electrolyte.[4] and electrochemical CO2 reduction.[5]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Mihkel Koel (2008). Ionic Liquids in Chemical Analysis. CRC Press. p. xxvii. ISBN 978-1-4200-4646-5.
- ^ R.P. Swatloski; J.D. Holbrey & R.D. Rogers (2003). "Ionic liquids are not always green: hydrolysis of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate". Green Chem. 5 (4): 361–363. doi:10.1039/b304400a.
- ^ Dupont J, Consorti C, Suarez P, de Souza R (2004). "Preparation of 1-Butyl-3-methyl imidazolium-based Room Temperature Ionic Liquids". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 10, p. 184.
- ^ Álvaro Pérez-Salado Kamps, Dirk Tuma, Jianzhong Xia, Gerd Maurer (2003), Solubility of CO2 in the Ionic Liquid [bmim] [PF6], vol. 48, pp. 746–749, doi:10.1021/je034023f
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Yeonji Oh, Xile Hu (2015), Ionic liquids enhance the electrochemical CO2 reduction catalyzed by MoO2, vol. 51, pp. 13698–13701, doi:10.1039/C5CC05263G
Further reading
[edit]- S. Carda-Broch; A. Berthod; D.W. Armstrong (2003). "Solvent properties of the 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid". Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 375 (2): 191–199. doi:10.1007/s00216-002-1684-1. PMID 12560962. S2CID 32506513.

